一、IO流概述
- 简介
文件通常是由一连串的字节或字符构成,组成文件的字节序列称为字节流,组成文件的字符序列称为字符流。Java 中根据流的方向可以分为输入流和输出流。输入流是将文件或其它输入设备的数据加载到内存的过程;输出流恰恰相反,是将内存中的数据保存到文件或其他输出设备。
- 分类
文件是由字符或字节构成,那么将文件加载到内存或再将文件输出到文件,需要有输入和输出流的支持,那么在 Java 语言中又把输入和输出流分为了两个,字节输入和输出流,字符输入和输出流。

- IO流四大家族
1. java.io.InputStream;//字节输入流
2. java.io.OutputStream;//字节输出流
3. java.io.Reader;//字符输入流
4. java.io.Writer;//字符输出流
- java.io包下需要掌握的流
文件专属:
1. java.io.FileInputStream;
2. java.io.FileOutputStream;
3. java.io.FileReader;
4. java.io.FileWriter;
转换流:
5. java.io.InputStreamReader;
6. java.io.OutputStreamWriter;
缓冲流:
7. java.io.BufferedReader;
8. java.io.BufferedWriter;
9. java.io.BufferedInputStream;
10. java.io.BufferedOutputStream;
数据流专属:
11. java.io.DataInputStream;
12. java.io.DataOutputStream;
标准输入输出流:
13.java.io.PrintWriter;
14.java.io.PrintStream;
对象专属流:
15.java.io.ObjectInputStream;
16.java.io.ObjectOutputStream;
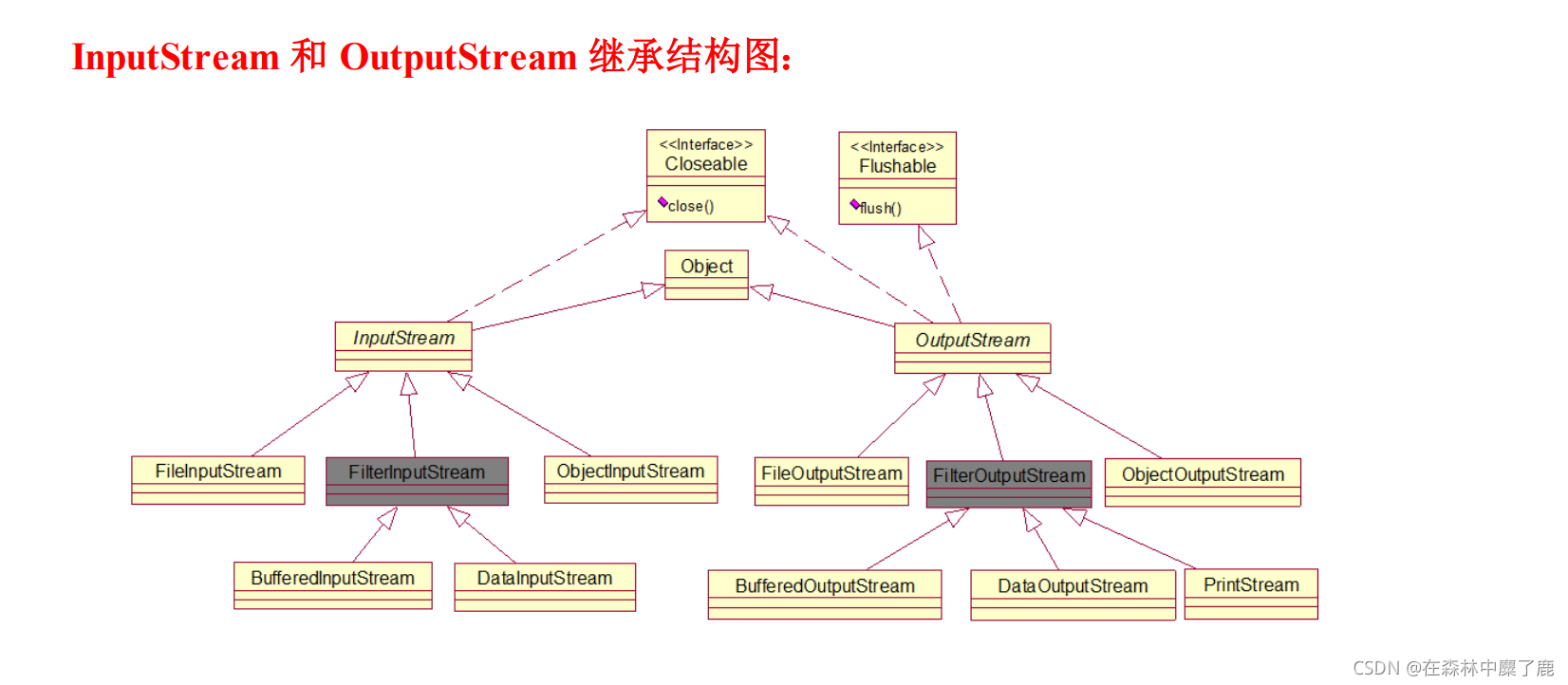
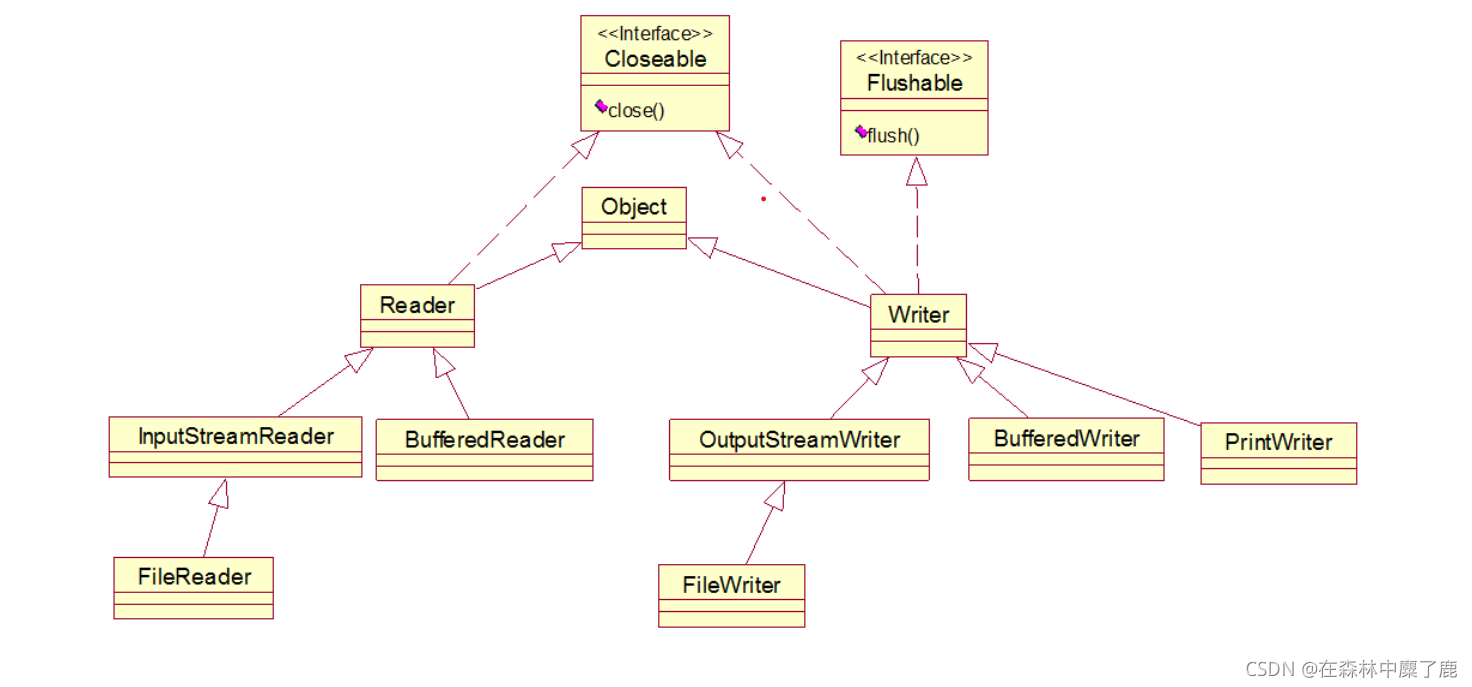
- 字节流与字符流的继承结构示意图
字节流:
字符流 :
1. InputStream 字节输入流
- 概述
InputStream 是字节输入流,InputStream 是一个抽象类,所有继承了 InputStream 的类都是字节输入流,其子类如下。

- 主要方法
1.close();//关闭此输入流并释放与该流关联的所有系统资源.
2.read();//从输入流读取下一个数据.
3.read(byte[] b);//从输入流中读取一定数量的字节并将其存储在缓冲区数组 b 中。
4.read(byte[] b, int off, int len);//将输入流中最多 len 个数据字节读入字节数组
2. OutputStream 字节输出流
- 继承子类

- 主要方法
1.close();//关闭此输出流并释放放与此流有关的所有系统资源.
2.flush();// 刷新此输出流并强制写出所有缓冲的输出字节.
3.write(byte[] b);//将 b.length 个字节从指定的字节数组写入此输出流.
4.write(byte[] b, int off, int len);//将指定字节数组中从偏移量 off 开始的 len个字节写入此输出流.
5.write(int b);//将指定的字节写入此输出流.
3. Reader 字符输入流
- 继承子类
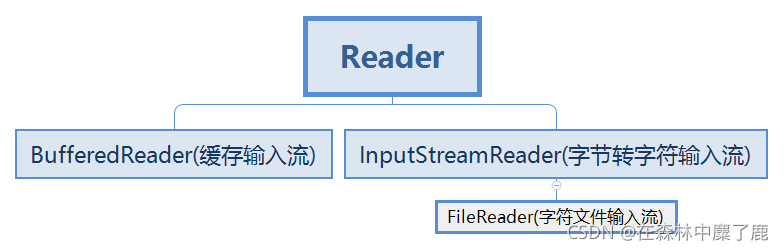
- 常用方法
1.close();//关闭该流
2.read();//读取单个字符
3.read(char[] c);//将字符读入数组
4.read(char[] c, int off, int len);//将字符读入数组的某一部分
4. Writer 字符输出流
- 继承子类
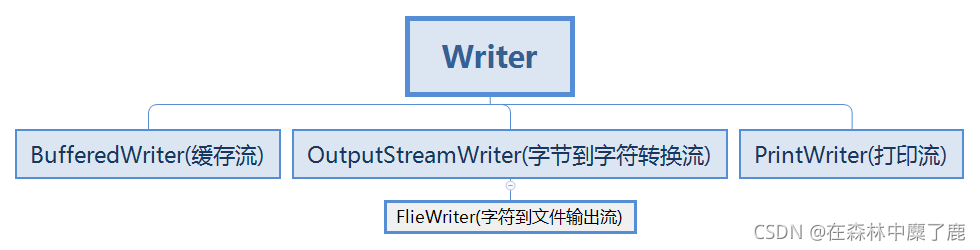
2. 常用方法
1.append(char c); //指定字符追加到此writer
2.close();//关闭此流, 但要先刷新.
3.flush();//刷新此流.
4.write(char[] c);//写入字符数组.
5.write(char[] cbuf, int off, int len);//写入字符数组的某一部分.
6.write(int c);//写入单个字符.
7.write(String str);//写入字符串.
8.write(String str, int off, int len);//写入字符串的某一部分.
二、文件流
1. 分类
文件字节输入流、文件字节输出流、文件字符输入流、文件字符输出流.
2. FileInputStream 文件字节输入流
语法格式:
InputStream is = null;
try {
is = new FileInputStream("c:\\test.txt");
int b = 0;
while ((b = is.read()) != -1) {
//直接打印
//System.out.print(b);
//输出字符
System.out.print((char)b);
}
}catch(FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}catch(IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
try {
if (is != null){
is.close();
}
}catch(IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
3. FileOutputStream 文件字节输出流
语法格式 :
InputStream is = null;
OutputStream os = null;
try {
is = new FileInputStream("c:\\test.txt");
os = new FileOutputStream("d:\\test.txt.bak");
int b = 0;
while ((b = is.read()) != -1) {
os.write(b);
}
System.out.println("文件复制完毕!");
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
try {
if (is != null){
is.close();
}
if (os != null) {
os.close();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
4. FileReader 文件字符输入流
语法格式 :
Reader r = null;
try {
r = new FileReader("c:\\test.txt");
int b = 0;
while ((b = r.read()) != -1) {
//输出字符
System.out.print((char)b);
}
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
try {
if (r != null) {
r.close();
}
} catch (IOException e) {}
}
5. FileWriter 文件字符输出流
语法格式 :
try {
//以下方式会将文件的内容进行覆盖
//w = new FileWriter("c:\\test.txt");
//w = new FileWriter("c:\\test.txt", false);
//以下为 true 表示,在文件后面追加
w = new FileWriter("c:\\test.txt", true);
w.write("你好你好!!!!");
//换行
w.write("\n");
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
try {
if (w != null){
w.close();
}
} catch (IOException e) {}
}
三、缓冲流
1. 概述
缓冲流主要是为了提高效率而存在的,减少物理读取次数,缓冲流主要有:BufferedInputStream、BufferedOutputStream、BufferedReader、BufferedWriter,并且 BufferedReader 提供了实用方法readLine(),可以直接读取一行,BufferWriter 提供了 newLine()可以写换行符。
2. BufferedOutputStream与BufferedInputStream示例
InputStream is = null;
OutputStream os = null;
try {
is = new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream("c:\\test.txt"));
os = new BufferedOutputStream(newFileOutputStream("d:\\test.txt.bak"));
int b = 0;
while ((b = is.read()) != -1) {
os.write(b);
}
//手动调用 flush,将缓冲区中的内容写入到磁盘
//也可以不用手动调用,缓存区满了自动回清楚了
//而当输出流关闭的时候也会先调用flush
os.flush();
System.out.println("文件复制完毕!");
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
try {
if (is != null){
is.close();
}
if (os != null) {
//在 close 前会先调用 flush
os.close();
}
} catch (IOException e) {}
}
3. BuffedReader与BufferedWriter示例
BufferedReader r = null;
BufferedWriter w = null;
try {
r = new BufferedReader(
new FileReader("c:\\test.txt"));
w = new BufferedWriter(
new FileWriter("d:\\test.txt.bak"));
String s = null;
while ((s = r.readLine()) != null) {
w.write(s);
//w.write("\n");
//可以采用如下方法换行
w.newLine();
}
System.out.println("文件复制完毕!");
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
try {
if (r != null) {
r.close();
}
if (w != null) {
//在 close 前会先调用 flush
w.close();
}
}catch(IOException e) {}
}
四、 转换流
1. 概述
转换流主要有两个 InputStreamReader 和 OutputStreamWriter。InputStreamReader 主要是将字节流输入流转换成字符输入流 OutputStreamWriter 主要是将字节流输出流转换成字符输出流
2. InputStreamReader
BufferedReader br = null;
try {
br = new BufferedReader(
new InputStreamReader(
new FileInputStream("c:\\test.txt")));
String s = null;
while ((s = br.readLine()) != null) {
System.out.println(s);
}
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
try {
if (br != null) {
br.close();
}
}catch(IOException e) {}
}
3. OutputStreamWriter
BufferedWriter bw = null;
try {
bw = new BufferedWriter(
new OutputStreamWriter(
new FileOutputStream("c:\\603.txt")));
bw.write("asdfsdfdsf");
bw.newLine();
bw.write("风光风光风光好");
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
try {
if (bw != null) {
bw.close();
}
} catch (IOException e) {}
}
五、打印流
1. 概述
打印流主要包含两个:PrintStream 和 PrintWriter,分别对应字节流和字符流
2. PrintStream重定向输出
OutputStream os = null;
try {
os = new FileOutputStream("c:/console.txt");
System.setOut(new PrintStream(os));
System.out.println("asdfkjfd;lldffdfdrerere");
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
try {
if (os != null) {
os.close();
}
}catch(IOException e) {}
}
3. System.in接受屏幕输入
BufferedReader br = null;
try {
br = new BufferedReader(
new InputStreamReader(System.in));
String s = null;
while ((s=br.readLine()) != null) {
System.out.println(s);
//为 q 退出循环
if ("q".equals(s)) {
break;
}
}
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
try {
if (br != null) {
br.close();
}
} catch (IOException e) {}
}
六、对象流
1. 概述
对象流可以将 Java 对象转换成二进制写入磁盘,这个过程通常叫做序列化,并且还可以从盘读出完整的 Java 对象,而这个过程叫做反序列化。对象流主要包括:ObjectInputStream 和 ObjectOutputStream.
2. 如何实现序列化与反序列化
- 序列化
如果实现序列化该类必须实现序列化接口 java.io.Serializable,该接口没有任何方法,该接口只是一种标记接口,标记这个类是可以序列化的。
ObjectOutputStream oos = null;
try {
oos = new ObjectOutputStream(
new FileOutputStream("c:/Person.dat"));
Person person = new Person();
person.name = "张三";
oos.writeObject(person);
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}catch(IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
try {
if (oos != null) {
oos.close();
}
}catch(IOException e) {}
}
class Personn implements Serializable {
String name;
}
- 反序列化
ObjectInputStream ois = null;
try {
ois = new ObjectInputStream(
new FileInputStream("c:/Person.dat"));
//反序列化
Person person = (Person)ois.readObject();
System.out.println(person.name);
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}catch(IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
try {
if (ois != null) {
ois.close();
}
} catch (IOException e) {}
}
class Person implements Serializable {
String name;
//采用 transient 关键字修饰此属性,序列化时会忽略
transient int age;
}
3. 定义序列化版本号解决版本冲突问题
//在类中加入下列代码
private static final long serialVersionUID = -111111111111111111L;
上述代码可用于解决以下问题,如当前一个Peson类只有有String name属性,在序列化Peson时会生成一个版本号serialVersionUID,先加入一个sex属性后,在使用时版本号会重新生成,此时JVM认为这是不兼容的两个类。用自定义序列化版本号可以解决。其中serialVersionUID 只与序列化有关。
七、File类
1. Java中新建一个文件、文件夹
//createNewFile(),delete(),mkdir(),mkdirs()
File file = new File("test.txt");
File dir = new Flie("D:\\course\\Java");
dir.mkdir();
dir.mkdirs();
file.createNewFile();
2. 判断文件的函数
1.exists();//判断文件是否存在
2.isFile();//测试当前 File 对象表示的文件是否为一个“普通”文件
3.isAbsolute();//测试当前 File 对象表示的文件是否为一个绝对路径名
4.isDirectory();//测试当前 File 对象表示的文件是否为一个路径
5.canRead();//测试应用程序是否能从指定的文件中进行读取
6.canWrite();//测试应用程序是否能写当前文件
7.isHidden();
3. 文件属性的函数
1.lastModified();//返回当前 File 对象表示的文件最后修改的时间
2.length();//返回当前 File 对象表示的文件长度
3.list();//返回当前 File 对象指定的路径文件列表
4.listFiles();
5.renameTo();
6.getName();//返回表示当前对象的文件名或路径名(如果是路径,则返回最后一级子路径名)
7.getParent();//f返回回当前 File 对象所对应目录(最后一级子目录)的父目录名
8.getPath();//返回的是定义时的路径,可能是相对路径,也可能是绝对路径,这个取决于定义时用的是相对路径还是绝对路
9.getAbsolutePath();//返回由该对象表示的文件的绝对路径名
10.delete();//删除当前对象指定的文件
八、数据流
1. 概述
DataOutputStream数据输出流允许应用程序将基本Java数据类型写到基础输出流中,DataInputStream数据输入流允许应用程序以机器无关的方式从底层输入流中读取基本的Java类型.
2. DataInputStream
内部方法详解
1.read(byte b[])---从数据输入流读取数据存储到字节数组b中.
2.read(byte b[],int off,in len)---从数据输入流中读取数据存储到数组b里面,位置从off开始,长度为len个字节.
3.readFully(byte b[])---从数据输入流中循环读取b.length个字节到数组b中.
4.readFully(byte b[],int off,in len )---从数据输入流中循环读取len个字节到字节数组b中.从b的off位置开始
5.skipBytes(int b)---跳过n个字节.
6.readBoolean()---从数据输入流读取布尔类型的值.
7.readByte()---从数据输入流中读取一个字节.
8.readUnsignedByte()---从数据输入流中读取一个无符号的字节,返回值转换成int类型.
9.readShort()---从数据输入流读取一个short类型数据.
10.readUnsignedShort()---从数据输入流读取一个无符号的short类型数据.
11.readChar()---从数据输入流中读取一个字符数据
12.readInt()---从数据输入流中读取一个int类型数据.
13.readLong()---从数据输入流中读取一个long类型的数据.
14.readFloat()---从数据输入流中读取一个float类型的数据.
15.readDouble()---从数据输入流中读取一个double类型的数据.
16.readUTF()---从数据输入流中读取用UTF-8格式编码的UniCode字符格式的字符串.
3. DataOutputStream
内部方法详解
1.intCount(int value)---数据输出流增加的字节数.
2.write(int b)---将int类型的b写到数据输出流中.
3.write(byte b[],int off, int len)---将字节数组b中off位置开始,len个长度写到数据输出流中.
4.flush()---刷新数据输出流.
5.writeBoolean()---将布尔类型的数据写到数据输出流中,底层是转化成一个字节写到基础输出流中.
6.writeByte(int v)---将一个字节写到数据输出流中(实际是基础输出流).
7.writeShort(int v)---将一个short类型的数据写到数据输出流中,底层将v转换2个字节写到基础输出流中.
8.writeChar(int v)---将一个charl类型的数据写到数据输出流中,底层是将v转换成2个字节写到基础输出流中.
9.writeInt(int v)---将一个int类型的数据写到数据输出流中,底层将4个字节写到基础输出流中.
10.writeLong(long v)---将一个long类型的数据写到数据输出流中,底层将8个字节写到基础输出流中.
11.writeFloat(flloat v)---将一个float类型的数据写到数据输出流中,底层会将float转换成int类型,写到基础输出流中.
12.writeDouble(double v)---将一个double类型的数据写到数据输出流中,底层会将double转换成long类型,写到基础输出流中.
13.writeBytes(String s)---将字符串按照字节顺序写到基础输出流中.
14.writeChars(String s)---将字符串按照字符顺序写到基础输出流中.
15.writeUTF(String str)---以机器无关的方式使用utf-8编码方式将字符串写到基础输出流中.
16.size()---写到数据输出流中的字节数.
九、IO + Propertities存取配置文件
Properties类是hashtable的子类,它具备map集合的特点,而且它里面存储的键值对都是字符。Properties 可保存在流中或从流中加载。其load()方法可从配置文件中获取键值对。
Properties properties = new Properties();
FileReader fr = null;
try {
//fr = new FileReader("C:\\Users\\ASDS\\Desktop\\class1.txt");
fr = new FileReader("src\\demo1\\class2.txt");
properties.load(fr); //从class.txt文件中获取键值对
fr.close();
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
String username = properties.getProperty("username");//get class.text className value
String password = properties.getProperty("password");//get class.text methodName value
System.out.println(username);
System.out.println(password);