thinkphp框架视图层、逻辑层、模型层详解
说明
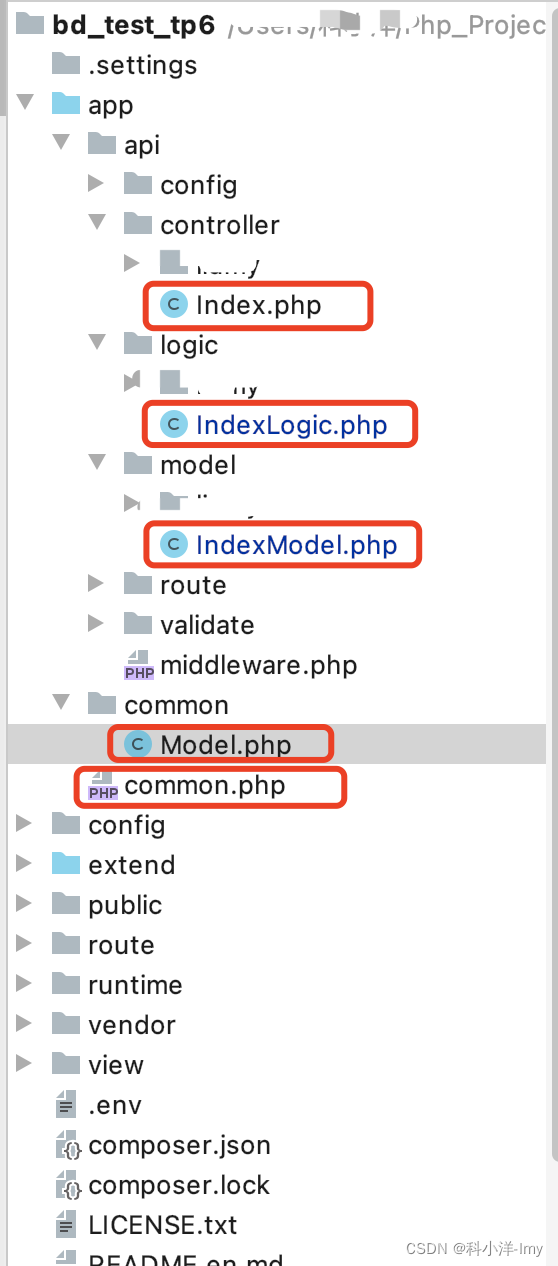
| 为了开发方便、规范我们可以分为三层开发 我们以tp框架的多应用模式开发为例 例如在api下面我们创建视图层(controller) 、逻辑层(logic)、模型层/数据层(model) 这三种层次的创建大家也可以自定义创建也可以不叫视图层等 |
|---|
视图层 api/controller/liumy/Index.php
<?php
namespace app\api\controller;
use app\api\logic\IndexLogic;
/**
* TODO 视图层
* ==============================================
* XXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXX。
* ==============================================
* @date: 2022/2/23 10:30
* @author: XXXXX
* @version: 1.1
*/
class Index
{
public static $userinfo;
public static $indexLogic;
public function __construct()
{
self::$indexLogic = new IndexLogic($_POST);
}
/**
* 举例获取订单列表数据
*/
public function order_list(){
//去调用逻辑层
self::$indexLogic->orderList();
}
}
逻辑层 api/logic/liumy/IndexLogic.php
<?php
namespace app\api\logic;
use app\api\model\IndexModel;
/**
* TODO 逻辑层
* ==============================================
* XXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXX。
* ==============================================
* @date: 2022/2/23 10:30
* @author: XXXXX
* @version: 1.1
*/
class IndexLogic
{
public static $indexModel;
public static $postdata;
public function __construct($params)
{
self::$postdata = $params;
self::$indexModel = new IndexModel();
}
/**
* 举例获取订单列表数据
* @throws \think\db\exception\DataNotFoundException
* @throws \think\db\exception\DbException
* @throws \think\db\exception\ModelNotFoundException
*/
public function orderList()
{
//去调用模型层 去获取数据库数据
$res = self::$indexModel->orderList(1, 20);
//根据结果 进行需要的逻辑处理
exit(json_encode(['code' => 200, 'msg' => '操作成功', 'data' => $res]));
}
}
模型层/数据层 api/model/liumy/IndexModel.php
- 该方法中主要是对要获取的数据的条件、字段、排序、分页、表连接、分组等处理好 再去调用Model 根据不同的需求调用Model中不同的方法
- 调用方式 mode(‘表名’)->方法(参数)
<?php
namespace app\api\model;
/**
* TODO 模型层/数据层
* ==============================================
* XXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXX。
* ==============================================
* @date: 2022/2/23 10:30
* @author: XXXXX
* @version: 1.1
*/
class IndexModel
{
/**
* 举例获取订单列表数据
* @return array|\think\Collection|\think\facade\Db[]
* @throws \think\db\exception\DataNotFoundException
* @throws \think\db\exception\DbException
* @throws \think\db\exception\ModelNotFoundException
*/
public function orderList($page=1,$size=10)
{
$where = [['goods.status', '=', 4],];
$field = 'sum(update_weight) as weight,sum(update_number) as number,
goods.first_type,goods.second_type,goods.valuation,
valuation.name,goods.id,goods.actual_num,goods.actual_weight,
type.name as first_type,type_two.name as second_type
';
$join = [
['fun_banshou_valuation valuation', 'goods.valuation = valuation.id', 'inner'],
['fun_banshou_code code', 'goods.id = code.goodsid', 'left'],
['fun_banshou_receiving_type type', 'goods.first_type = type.id', 'inner'],
['fun_banshou_receiving_type type_two', 'goods.second_type = type_two.id', 'inner'],
];
$res = model('banshou_goods')->pageList($where, $page, $size, $field, 'goods', $join, '', 'goodsid');
foreach ($res as $item => $value) {
$field = 'update_number,update_weight,bar_code';
$where = [['goodsid', '=', $value['id']], ['status', '=', '30'],];
$res[$item]['code'] = model('banshou_code')->getList($where, '', $field);
}
return $res;
}
}
模型层/数据层中对应的model方法
路径:app/common.php
<?php
/**
* 数据库模型对象
* @param $table
* @return object
*/
if(!function_exists('model')) {
function model($table = ''): \app\common\Model
{
return new \app\common\Model($table);
}
}
model方法中对应的\app\common\Model
- 该方法中主要封装了数据库的数据的CURD等数据操作 可根据model自行传值调用 当然这里面的方法 可以根据项目的实际情况进行修改或者添加新的方法
路径:app/common/Model.php
<?php
namespace app\common;
use think\db\exception\DataNotFoundException;
use think\db\exception\DbException;
use think\db\exception\ModelNotFoundException;
use think\facade\Db;
/**
* TODO 数据处理Model
* ==============================================
* XXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXX。
* ==============================================
* @date: 2022/2/23 10:30
* @author: XXXXX
* @version: 1.1
*/
class Model
{
private static $query_obj = null;
public $table;
public function __construct($table = '')
{
$this->table = $table;
}
/**
* 获取单条数据
* @param array $where
* @param bool $field
* @param string $alias
* @param null $join
* @param string $order
* @param null $data
* @return array|mixed|Db|\think\Model|null
* @throws DataNotFoundException
* @throws DbException
* @throws ModelNotFoundException
*/
final public function getInfo($where = [], $field = true, $alias = 'a', $join = null, $order = '', $data = null)
{
if (empty($join)) {
$result = Db::name($this->table)->where($where)->order($order)->field($field)->find($data);
} else {
$db_obj = Db::name($this->table)->alias($alias);
$db_obj = $this->parseJoin($db_obj, $join);
$result = $db_obj->where($where)->order($order)->field($field)->find($data);
}
return $result;
}
/**
* 获取列表数据
* @param array $where
* @param null $limit
* @param bool $field
* @param string $alias
* @param null $join
* @param string $order
* @param string $group
* @return array
* @throws DataNotFoundException
* @throws DbException
* @throws ModelNotFoundException
*/
final public function getList($where = [], $limit = null, $field = true, $alias = 'a', $join = null, $order = '', $group = '')
{
self::$query_obj = Db::name($this->table)->where($where)->order($order);
if (!empty($join)) {
self::$query_obj = self::$query_obj->alias($alias);
self::$query_obj = $this->parseJoin(self::$query_obj, $join);
}
if (!empty($group)) {
self::$query_obj = self::$query_obj->group($group);
}
if (!empty($limit)) {
self::$query_obj = self::$query_obj->limit($limit);
}
return self::$query_obj->field($field)->select()->toArray();
}
/**
* 获取分页列表数据
* @param array $where
* @param int $page
* @param int $limit
* @param bool $field
* @param string $alias
* @param null $join
* @param string $order
* @param string $group
* @return array
* @throws DataNotFoundException
* @throws DbException
* @throws ModelNotFoundException
*/
final public function pageList($where = [], $page = 1, $limit = 10, $field = true, $alias = 'a', $join = null, $order = '', $group = '')
{
self::$query_obj = Db::name($this->table)->where($where)->order($order);
if (!empty($join)) {
self::$query_obj = self::$query_obj->alias($alias);
self::$query_obj = $this->parseJoin(self::$query_obj, $join);
}
if (!empty($group)) {
self::$query_obj = self::$query_obj->group($group);
}
return self::$query_obj->field($field)->page($page, $limit)->select()->toArray();
}
/**
* 获取表所有数据
* @return array|\think\Collection|Db[]
* @throws DataNotFoundException
* @throws DbException
* @throws ModelNotFoundException
*/
final public function selectAll()
{
return Db::name($this->table)->select();
}
/**
* join分析
* @param $db_obj
* @param array $join
* @return mixed
*/
protected function parseJoin($db_obj, array $join)
{
foreach ($join as $item) {
list($table, $on, $type) = $item;
$type = strtolower($type);
switch ($type) {
case "left":
$db_obj = $db_obj->leftJoin($table, $on);
break;
case "inner":
$db_obj = $db_obj->join($table, $on);
break;
case "right":
$db_obj = $db_obj->rightjoin($table, $on);
break;
case "full":
$db_obj = $db_obj->fulljoin($table, $on);
break;
default:
break;
}
}
return $db_obj;
}
/**
* 删除单条数据
* @param $id
* @param $destroy
* @return int
* @throws DbException
*/
final protected function deleteOne($id, $destroy)
{
if (empty($id)) {
return Db::name($this->table)->delete($id);
} else {
return Db::name($this->table)->destroy($destroy);
}
}
/**
* 修改数据
* @param $where
* @param $data
* @return int
* @throws DbException
*/
final public function update($where, $data): int
{
return Db::name($this->table)->where($where)->update($data);
}
/**
* 自定义的方法
* @param $data
* @return mixed
* @throws DataNotFoundException
* @throws DbException
* @throws ModelNotFoundException
*/
final public function schedulingCycle($data)
{
foreach ($data as $item => $value) {
//转化时间
$data[$item]['s_data'] = date("Y-m-d", $value['s_data']);
// $data[$item]['s_data']=date("Y-m-d H:i",$value['s_data']);
$data[$item]['num'] = Db::table('fun_banshou_goods')->field('num')->where('id', 'in', $value['goods_id'])->sum('num');
$data[$item]['weight'] = Db::table('fun_banshou_goods')->field('weight')->where('id', 'in', $value['goods_id'])->sum('weight');
$data[$item]['name'] = Db::table('fun_banshou_goods')->alias('goods')->field('name')
->where('goods.id', 'in', $value['goods_id'])
->join('fun_test_cate cate', 'goods.first_type = cate.id')
->select();
$name = '';
foreach ($data[$item]['name'] as $value) {
$name .= $value['name'] . '/';
}
$data[$item]['name'] = substr($name, 0, strlen($name) - 1);
}
return $data;
}
/**
* 添加数据
* @param $data
* @return int|string
*/
final public function insert($data)
{
return Db::name($this->table)->insertGetId($data);
}
/**
* 删除数据
* @param $where
* @param null $data
* @return int
* @throws DbException
*/
final public function delete($where, $data = null)
{
return Db::name($this->table)->where($where)->delete($data);
}
/**
* 事物开启
*/
final public function startTrans()
{
Db::startTrans();
}
/**
* 事物提交
*/
final public function commit()
{
Db::commit();
}
/**
* 事物回滚
*/
final public function rollback()
{
Db::rollback();
}
}
目录结构