依赖注入和控制反转
在框架的底层设计中,需要很多类的协同工作,如果这些类之间依赖性很强,会出现许多的副作用。软件工程提倡的是高内聚,低耦合,为了降低类的耦合性,控制反转(IoC)是一种有效的设计原则,而依赖注入是控制反转的一种实现方式。
依赖注入例子:
<?php
/**
* Created by PhpStorm.
* User: 10475
* Date: 2018/8/27
* Time: 22:59
*/
namespace app\demo\controller;
use think\Request;
class Demo3
{
public function test(Request $request)
{
dump($request->get());
}
}
控制反转和依赖注入详解
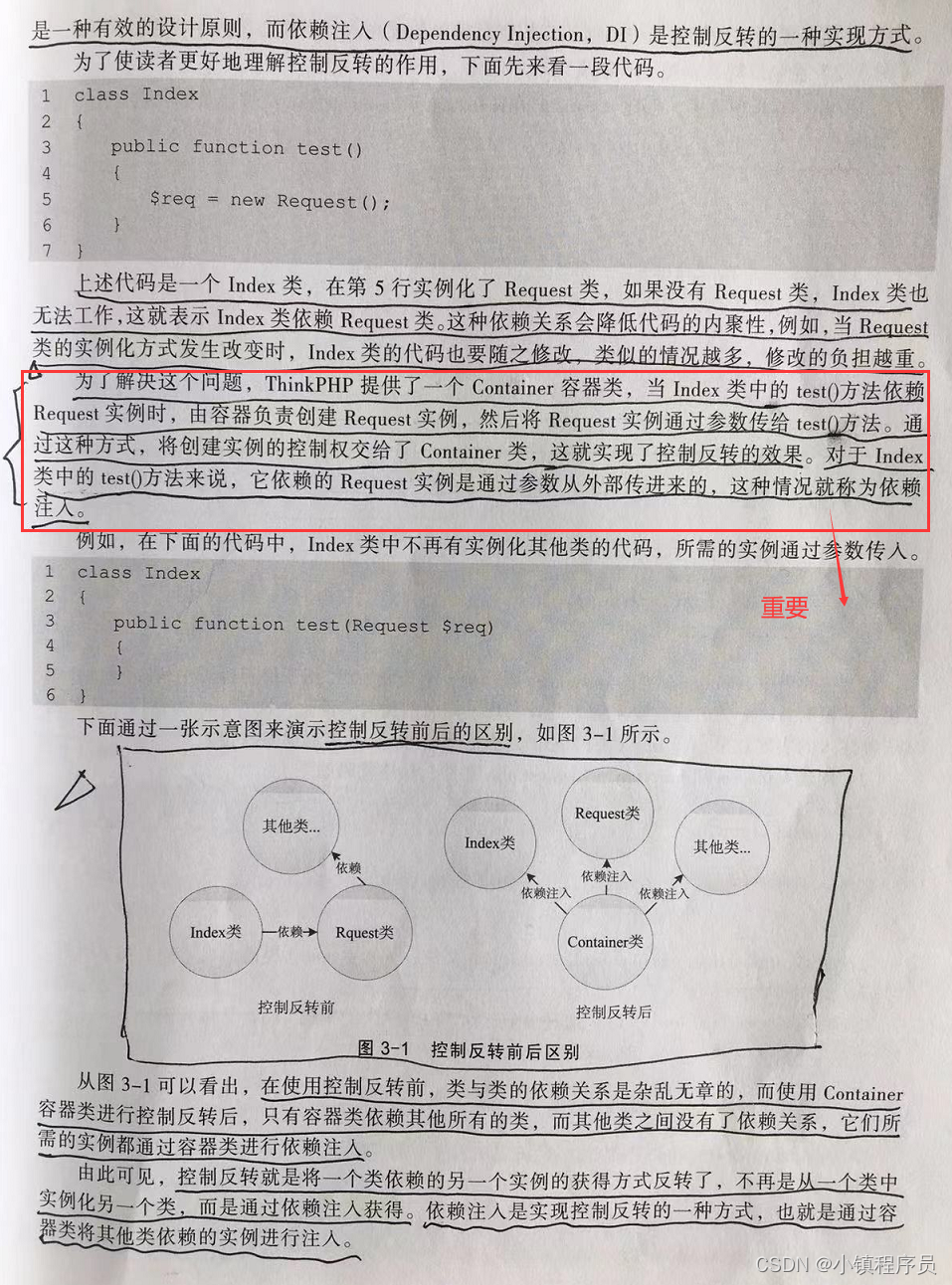
Container类(也叫Container容器类)很重要,在使用控制反转前,类与类的依赖关系是杂乱无章的,而使用了Container容器类进行控制反转后,只有容器类依赖其他所有的类,而其他类之间没有了依赖关系,他们所需的实例都通过容器类进行依赖注入。
Container类的源码(看一部分就行):
```php
<?php
// +----------------------------------------------------------------------
// | ThinkPHP [ WE CAN DO IT JUST THINK ]
// +----------------------------------------------------------------------
// | Copyright (c) 2006~2018 http://thinkphp.cn All rights reserved.
// +----------------------------------------------------------------------
// | Licensed ( http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0 )
// +----------------------------------------------------------------------
// | Author: liu21st <liu21st@gmail.com>
// +----------------------------------------------------------------------
namespace think;
use Closure;
use InvalidArgumentException;
use ReflectionClass;
use ReflectionFunction;
use ReflectionMethod;
class Container
{
/**
* 容器对象实例
* @var Container
*/
protected static $instance;
/**
* 容器中的对象实例
* @var array
*/
protected $instances = [];
/**
* 容器绑定标识
* @var array
*/
protected $bind = [];
/**
* 获取当前容器的实例(单例)
* @access public
* @return static
*/
public static function getInstance()
{
if (is_null(static::$instance)) {
static::$instance = new static;
}
return static::$instance;
}
/**
* 获取容器中的对象实例
* @access public
* @param string $abstract 类名或者标识
* @param array|true $vars 变量
* @param bool $newInstance 是否每次创建新的实例
* @return object
*/
public static function get($abstract, $vars = [], $newInstance = false)
{
return static::getInstance()->make($abstract, $vars, $newInstance);
}
/**
* 绑定一个类、闭包、实例、接口实现到容器
* @access public
* @param string $abstract 类标识、接口
* @param mixed $concrete 要绑定的类、闭包或者实例
* @return Container
*/
public static function set($abstract, $concrete = null)
{
return static::getInstance()->bind($abstract, $concrete);
}
/**
* 绑定一个类、闭包、实例、接口实现到容器
* @access public
* @param string|array $abstract 类标识、接口
* @param mixed $concrete 要绑定的类、闭包或者实例
* @return $this
*/
public function bind($abstract, $concrete = null)
{
if (is_array($abstract)) {
$this->bind = array_merge($this->bind, $abstract);
} elseif ($concrete instanceof Closure) {
$this->bind[$abstract] = $concrete;
} elseif (is_object($concrete)) {
$this->instances[$abstract] = $concrete;
} else {
$this->bind[$abstract] = $concrete;
}
return $this;
}
/**
* 绑定一个类实例当容器
* @access public
* @param string $abstract 类名或者标识
* @param object $instance 类的实例
* @return $this
*/
public function instance($abstract, $instance)
{
if (isset($this->bind[$abstract])) {
$abstract = $this->bind[$abstract];
}
$this->instances[$abstract] = $instance;
return $this;
}
/**
* 判断容器中是否存在类及标识
* @access public
* @param string $abstract 类名或者标识
* @return bool
*/
public function bound($abstract)
{
return isset($this->bind[$abstract]) || isset($this->instances[$abstract]);
}
/**
* 判断容器中是否存在类及标识
* @access public
* @param string $name 类名或者标识
* @return bool
*/
public function has($name)
{
return $this->bound($name);
}
/**
* 创建类的实例
* @access public
* @param string $abstract 类名或者标识
* @param array|true $args 变量
* @param bool $newInstance 是否每次创建新的实例
* @return object
*/
public function make($abstract, $vars = [], $newInstance = false)
{
if (true === $vars) {
// 总是创建新的实例化对象
$newInstance = true;
$vars = [];
}
if (isset($this->instances[$abstract]) && !$newInstance) {
$object = $this->instances[$abstract];
} else {
if (isset($this->bind[$abstract])) {
$concrete = $this->bind[$abstract];
if ($concrete instanceof Closure) {
$object = $this->invokeFunction($concrete, $vars);
} else {
$object = $this->make($concrete, $vars, $newInstance);
}
} else {
$object = $this->invokeClass($abstract, $vars);
}
if (!$newInstance) {
$this->instances[$abstract] = $object;
}
}
return $object;
}
/**
* 执行函数或者闭包方法 支持参数调用
* @access public
* @param string|array|\Closure $function 函数或者闭包
* @param array $vars 变量
* @return mixed
*/
public function invokeFunction($function, $vars = [])
{
$reflect = new ReflectionFunction($function);
$args = $this->bindParams($reflect, $vars);
return $reflect->invokeArgs($args);
}
/**
* 调用反射执行类的方法 支持参数绑定
* @access public
* @param string|array $method 方法
* @param array $vars 变量
* @return mixed
*/
public function invokeMethod($method, $vars = [])
{
if (is_array($method)) {
$class = is_object($method[0]) ? $method[0] : $this->invokeClass($method[0]);
$reflect = new ReflectionMethod($class, $method[1]);
} else {
// 静态方法
$reflect = new ReflectionMethod($method);
}
$args = $this->bindParams($reflect, $vars);
return $reflect->invokeArgs(isset($class) ? $class : null, $args);
}
/**
* 调用反射执行callable 支持参数绑定
* @access public
* @param mixed $callable
* @param array $vars 变量
* @return mixed
*/
public function invoke($callable, $vars = [])
{
if ($callable instanceof Closure) {
$result = $this->invokeFunction($callable, $vars);
} else {
$result = $this->invokeMethod($callable, $vars);
}
return $result;
}
/**
* 调用反射执行类的实例化 支持依赖注入
* @access public
* @param string $class 类名
* @param array $vars 变量
* @return mixed
*/
public function invokeClass($class, $vars = [])
{
$reflect = new ReflectionClass($class);
$constructor = $reflect->getConstructor();
if ($constructor) {
$args = $this->bindParams($constructor, $vars);
} else {
$args = [];
}
return $reflect->newInstanceArgs($args);
}
/**
* 绑定参数
* @access protected
* @param \ReflectionMethod|\ReflectionFunction $reflect 反射类
* @param array $vars 变量
* @return array
*/
protected function bindParams($reflect, $vars = [])
{
$args = [];
if ($reflect->getNumberOfParameters() > 0) {
// 判断数组类型 数字数组时按顺序绑定参数
reset($vars);
$type = key($vars) === 0 ? 1 : 0;
$params = $reflect->getParameters();
foreach ($params as $param) {
$name = $param->getName();
$class = $param->getClass();
if ($class) {
$className = $class->getName();
$args[] = $this->make($className);
} elseif (1 == $type && !empty($vars)) {
$args[] = array_shift($vars);
} elseif (0 == $type && isset($vars[$name])) {
$args[] = $vars[$name];
} elseif ($param->isDefaultValueAvailable()) {
$args[] = $param->getDefaultValue();
} else {
throw new InvalidArgumentException('method param miss:' . $name);
}
}
}
return $args;
}
}
