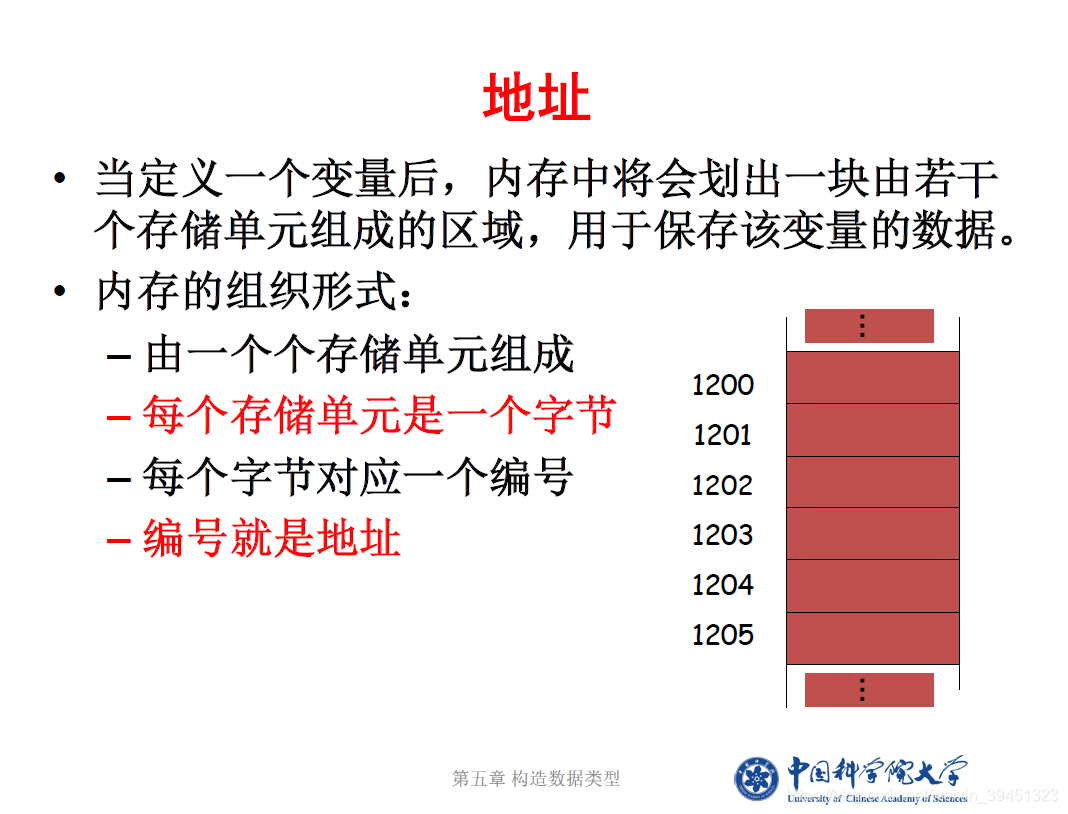
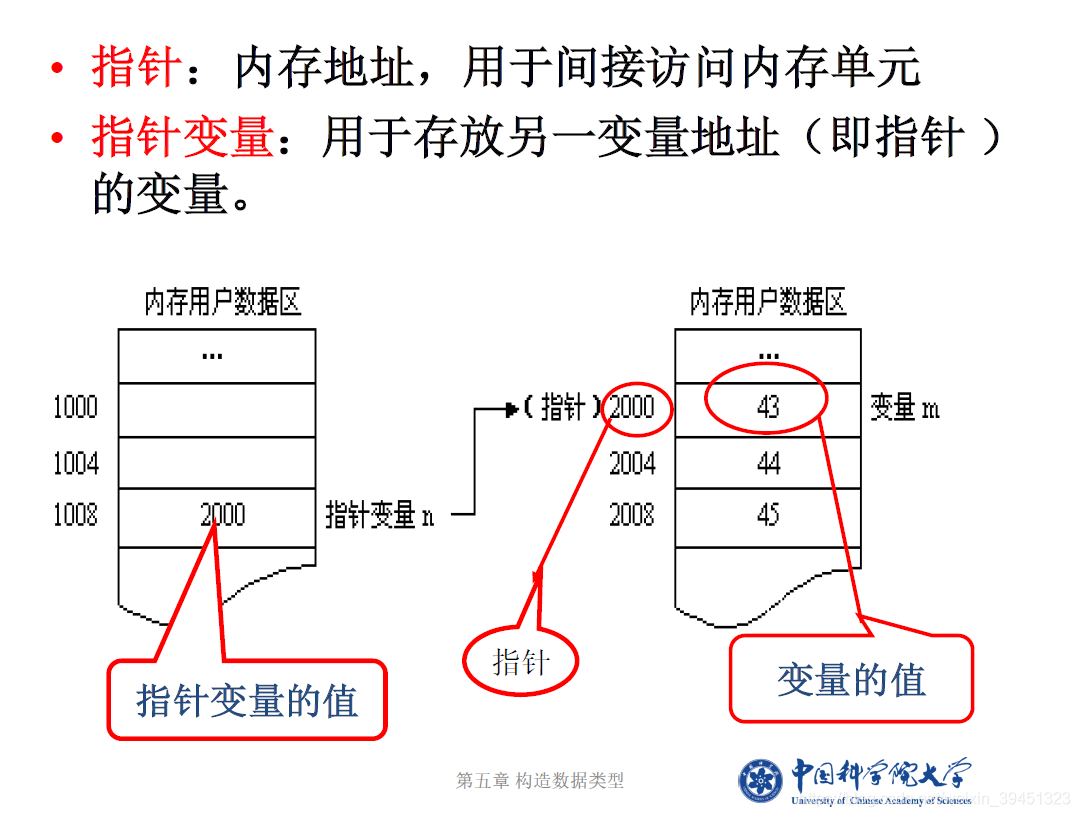
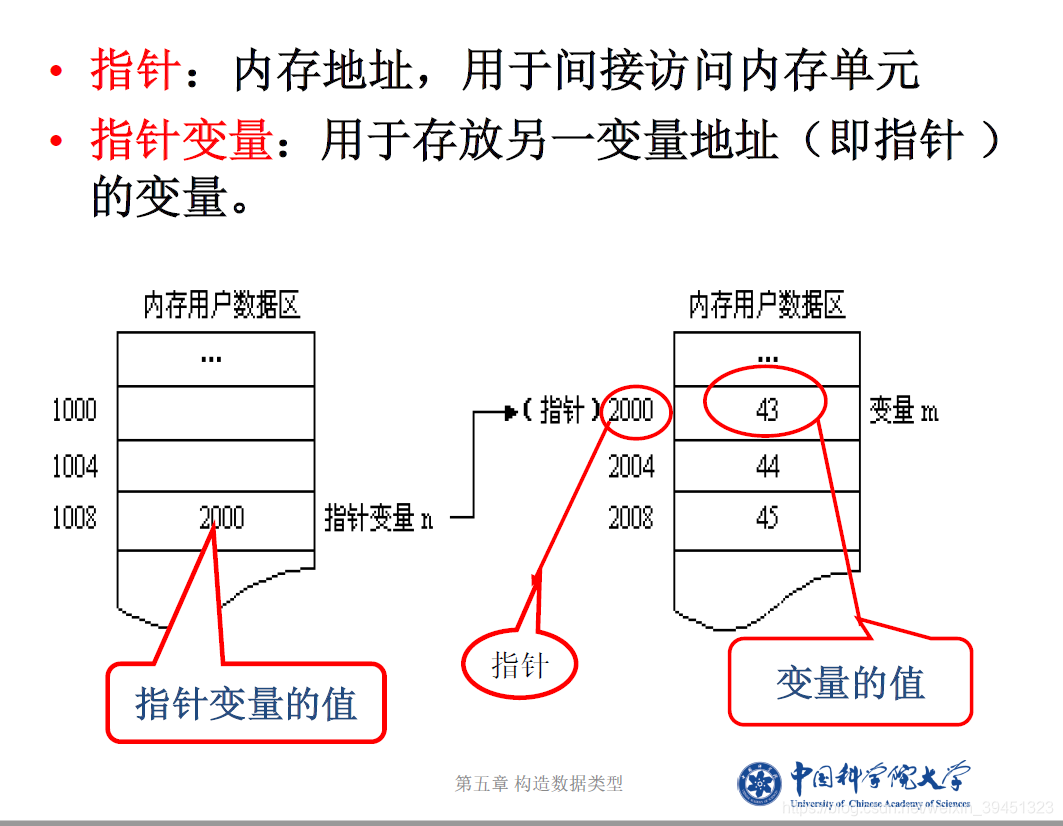
C++学习之 指针与引用

1. 指针

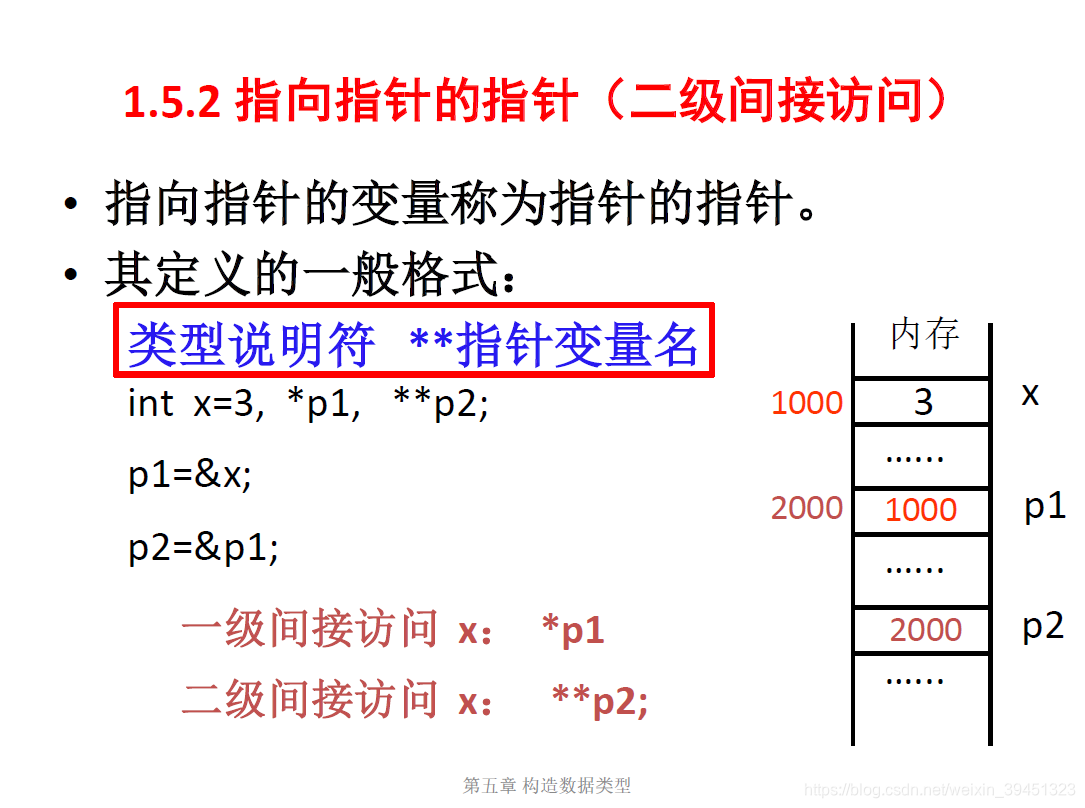
1.1 指针的定义




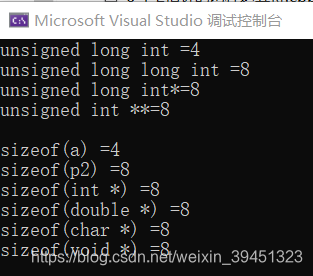
//指针定义.cpp
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
//指针变量数据值的数据类型以及指针变量的存储大小
cout << "unsigned long int =" << sizeof(unsigned long) << endl;
cout << "unsigned long long int =" << sizeof(unsigned long long) << endl;
cout << "unsigned long int*=" << sizeof(unsigned long*) << endl;
cout << "unsigned int **=" << sizeof(int**) << endl;
cout << endl;
int a;
char* p2;
cout << "sizeof(a) =" << sizeof(a) << endl;
cout << "sizeof(p2) =" << sizeof(p2) << endl;
cout << "sizeof(int *) =" << sizeof(int*) << endl;
cout << "sizeof(double *) =" << sizeof(double*) << endl;
cout << "sizeof(char *) =" << sizeof(char*) << endl;
cout << "sizeof(void *) =" << sizeof(void*) << endl;
return 0;
}





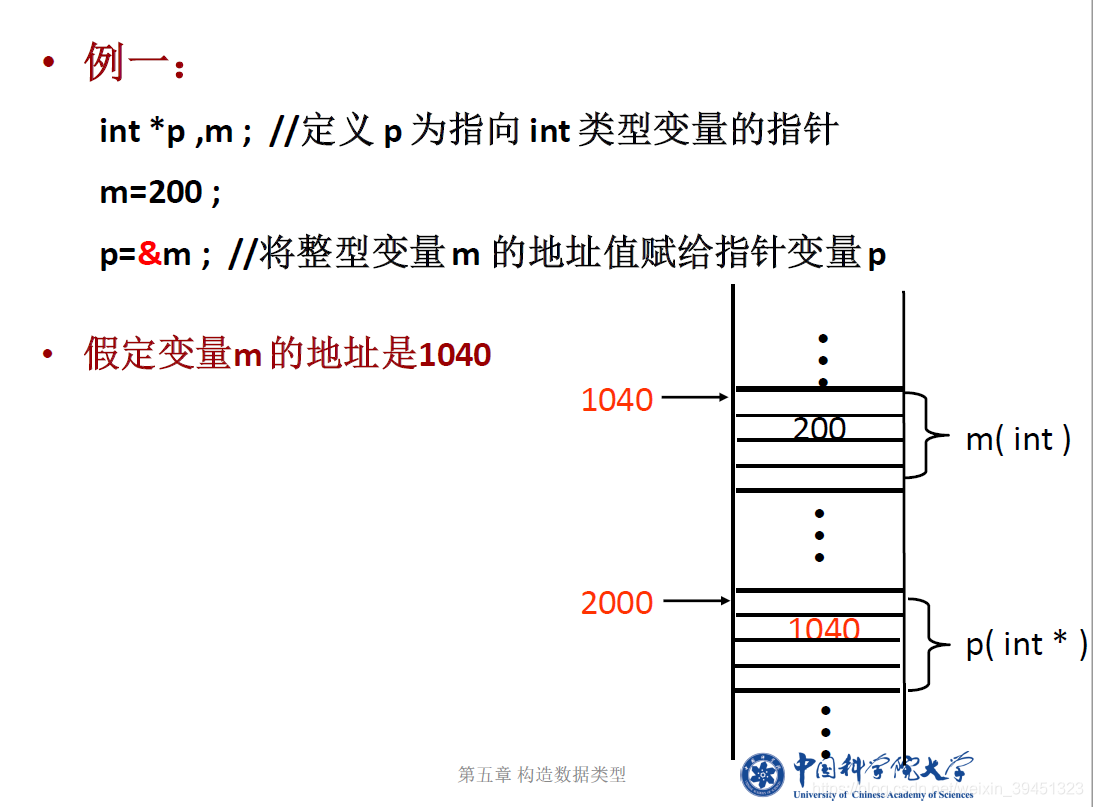
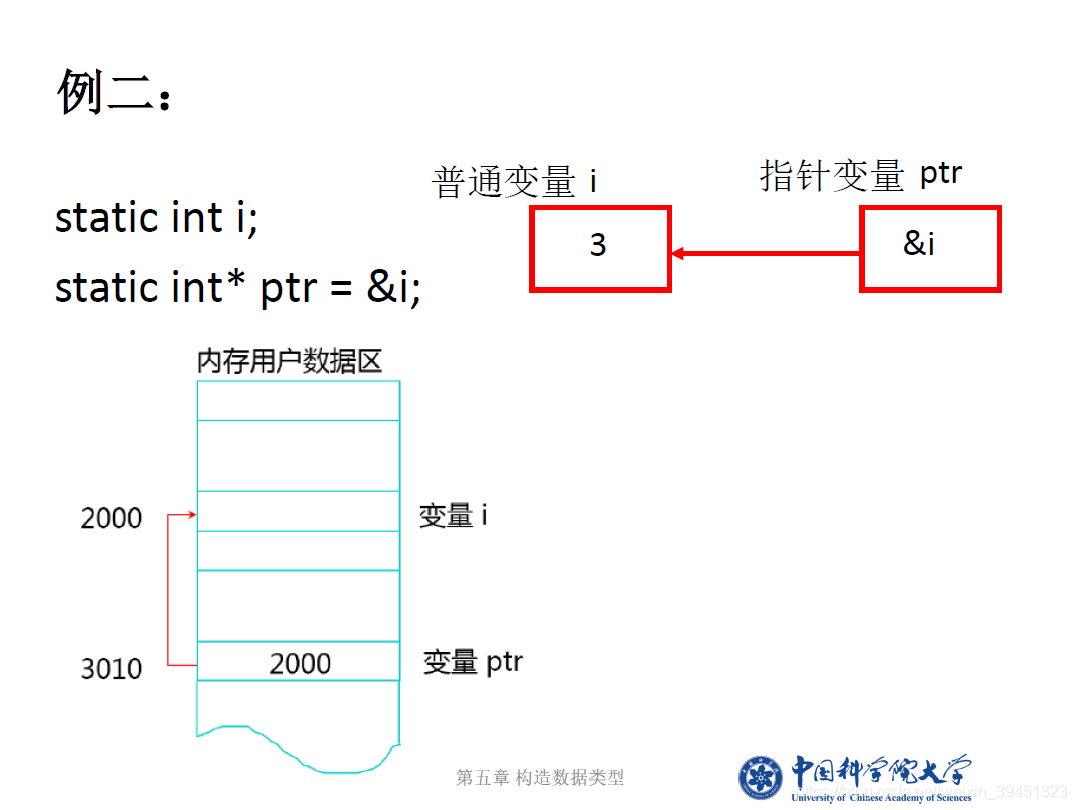
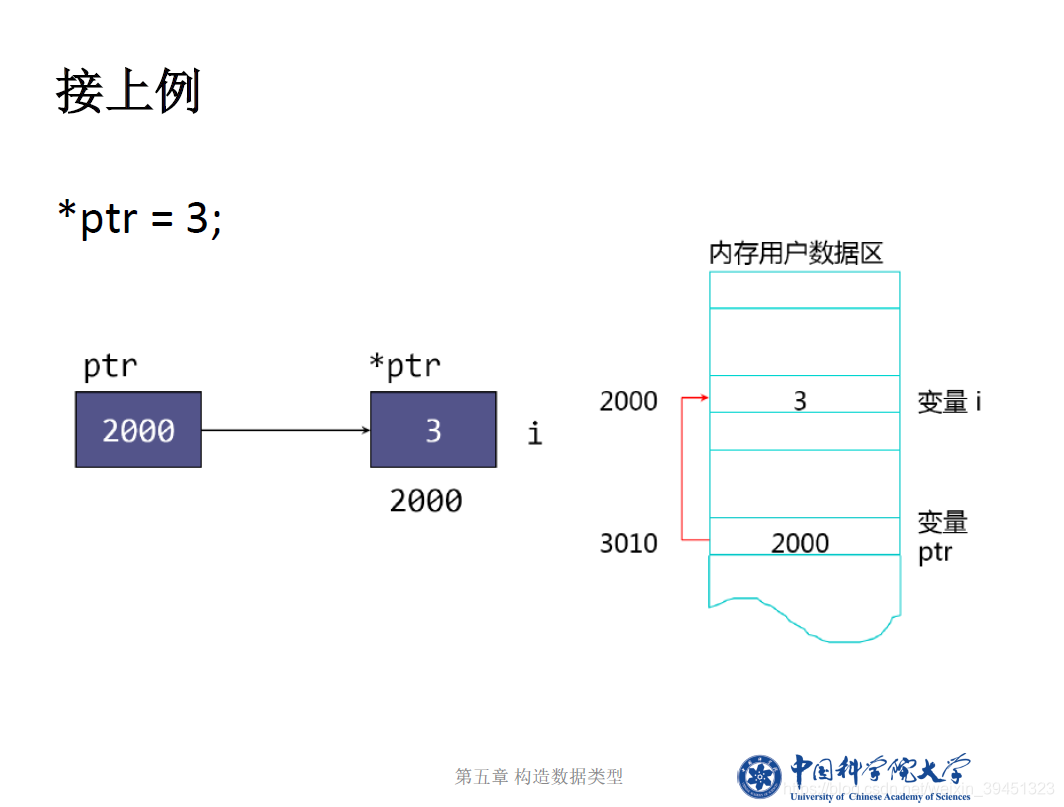

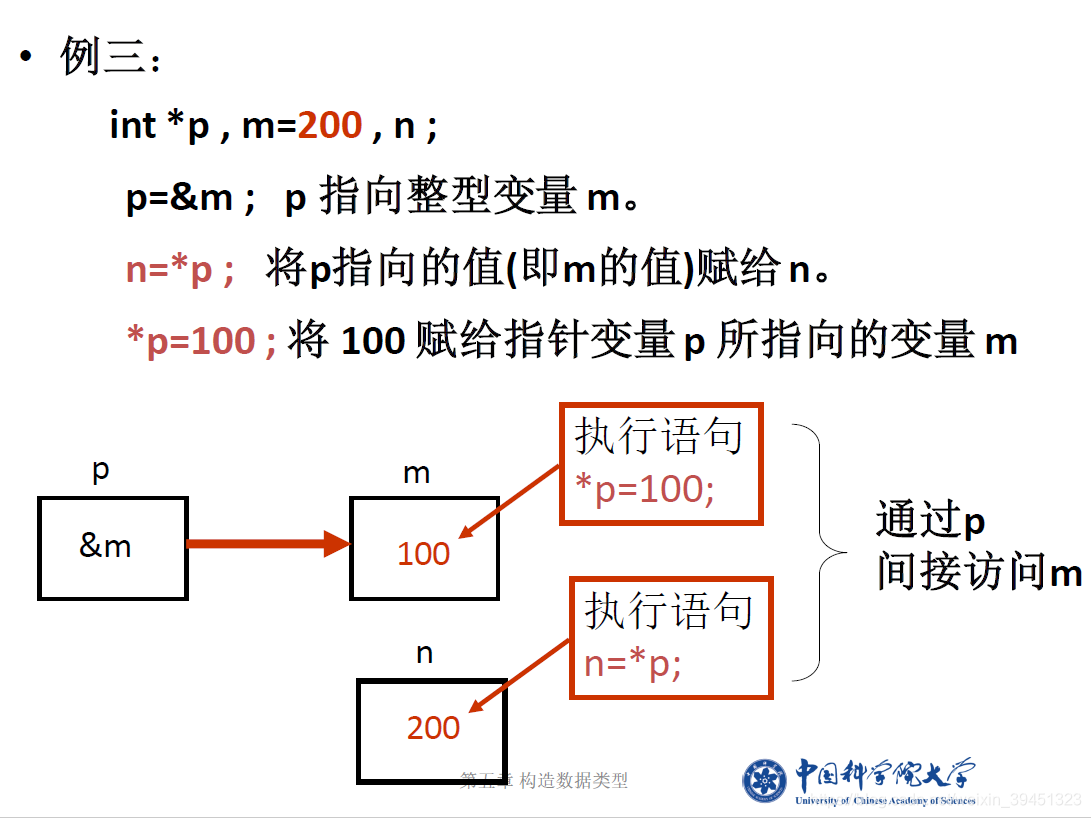
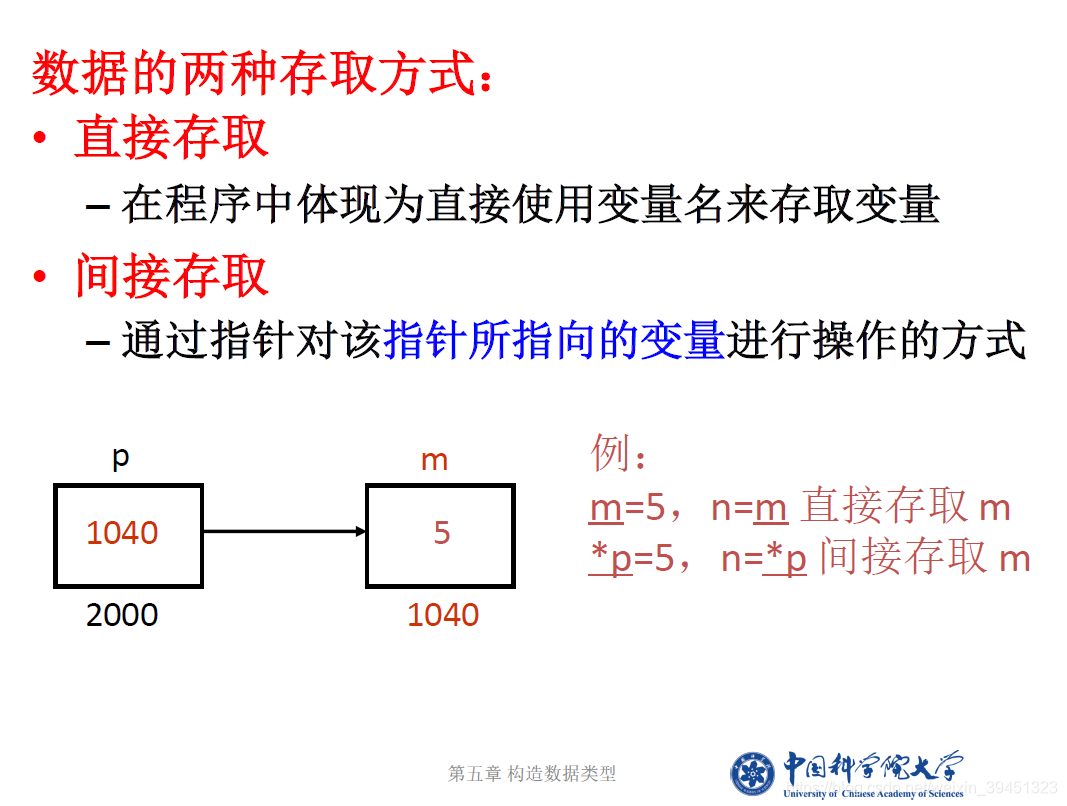
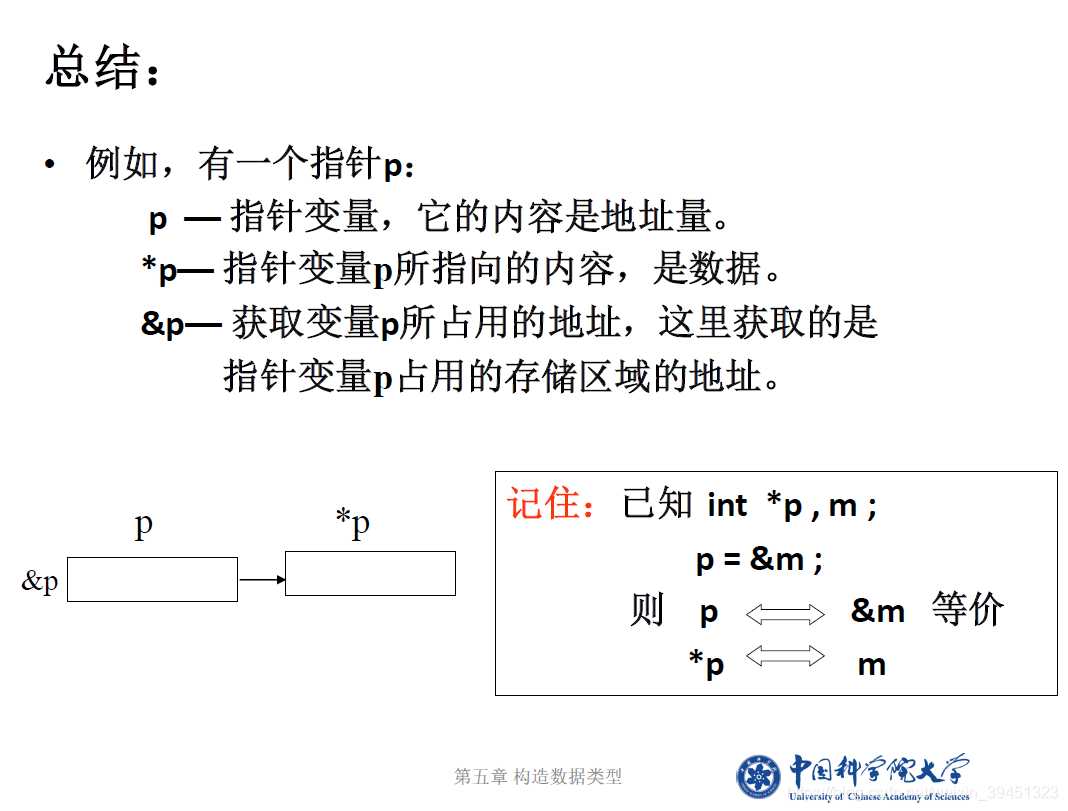


//指针的定义、赋值与使用,取地址等
#include <iostream>
#include <iomanip> //输出进制设置
using namespace std;
int main()
{
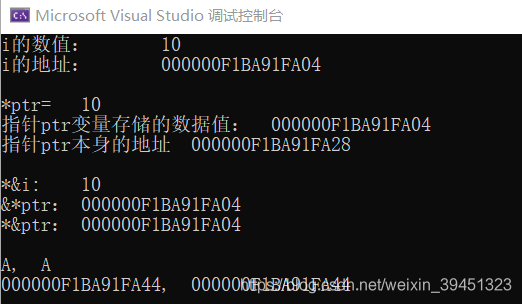
int i; //定义整型变量i
int* ptr = &i; //取i的地址赋给ptr
i = 10;
cout << "i的数值:\t" << i << endl; //输出整型变量i的值
cout << "i的地址:\t" << &i << endl;
cout << endl;
cout << "*ptr= \t" << *ptr << endl; //输出int型指针所指地址的内容
cout << "指针ptr变量存储的数据值: " << ptr << endl; //变量i的地址
cout << "指针ptr本身的地址 " << &ptr << endl << endl;
cout << "*&i: \t" << *&i << endl; // &*i错误:*操作数必须是指针,或者地址
cout << "&*ptr:\t" << &*ptr << endl;
cout << "*&ptr:\t" << *&ptr << endl;
cout << endl;
char c = 'A';
char* cp = &c;
cout << c << ", " << *cp << endl;
cout << (void*)&c << ", " << (void*)cp << endl;
return 0;
}
1.2 指针的初始化



//void指针.cpp
//空指针赋值测试
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int a = 10, b;
int* p1 = &a;
int* p2 = p1; //正确
//double *p3=p1; //错误
void* p3 = p1; //正确
int* p4 = (int*)p3;
}









/1三种const用法总结
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
int a = 3;
int b;
/*定义指向const的指针(指针指向的内容不能被修改)*/
const int* p1;
int const* p2;
p1 = p2 = &a; //正确
//*p1=9; //不正确
//*p2=8; //不正确(指针指向的内容不能被修改)
/*定义const指针(由于指针本身的值不能改变所以必须得初始化)*/
int* const p3 = &a;
*p3 = 5; //正确
//p3=p1; //不正确(指针本身的值不能改变)
/*指针本身和它指向的内容都是不能被改变的所以也得初始化*/
const int* const p4 = &a;
int const* const p5 = &b;
//p4=p5;//不正确 (指针本身和它指向的内容都是不能被改变)
//*p4=*p5=4; //不正确(指针本身和它指向的内容都是不能被改变)
return 0;
}
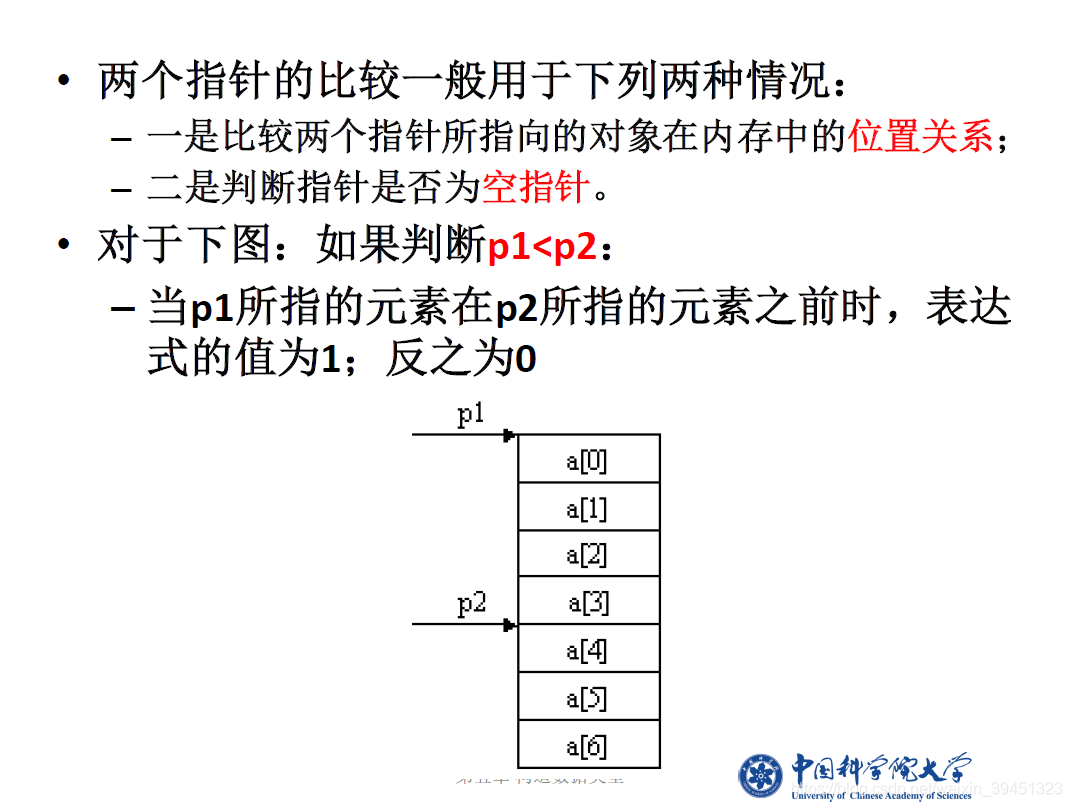
1.3 指针运算



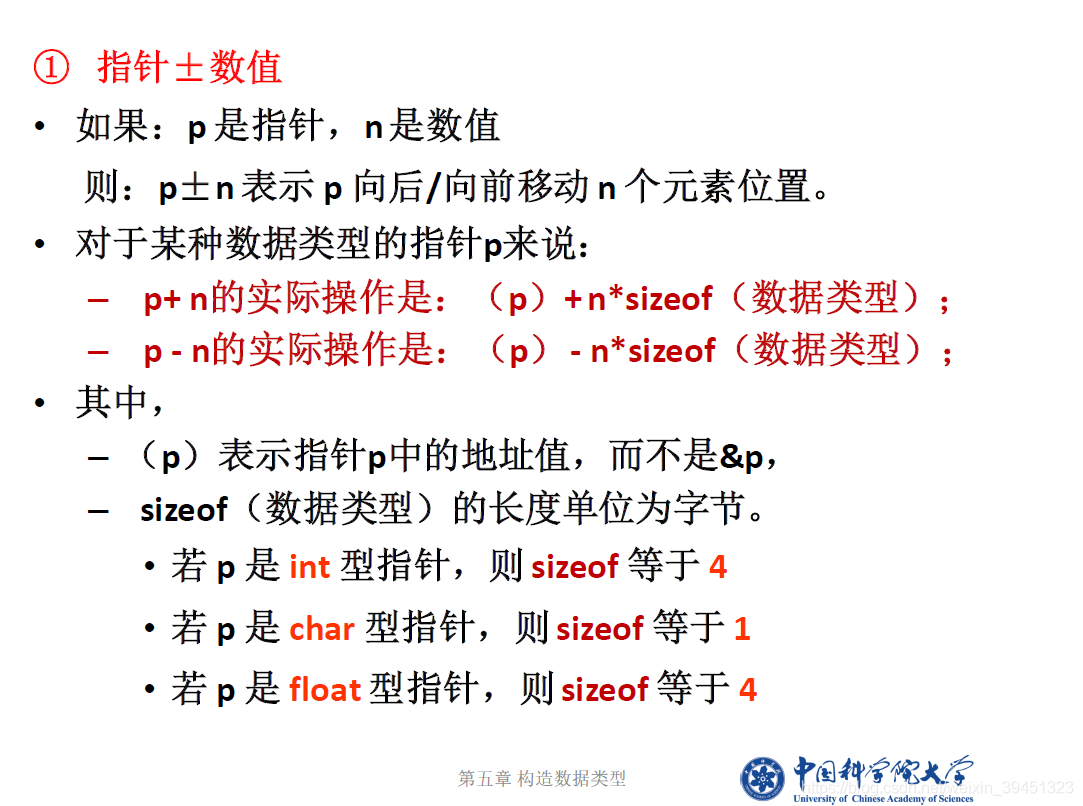
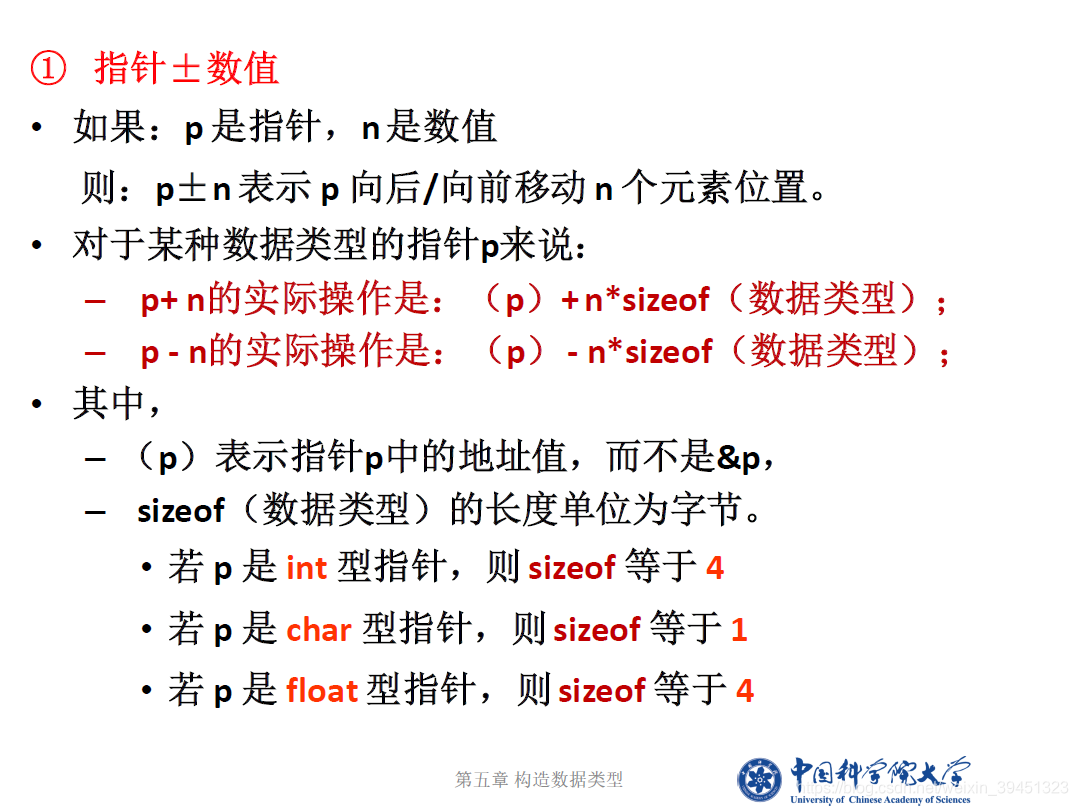
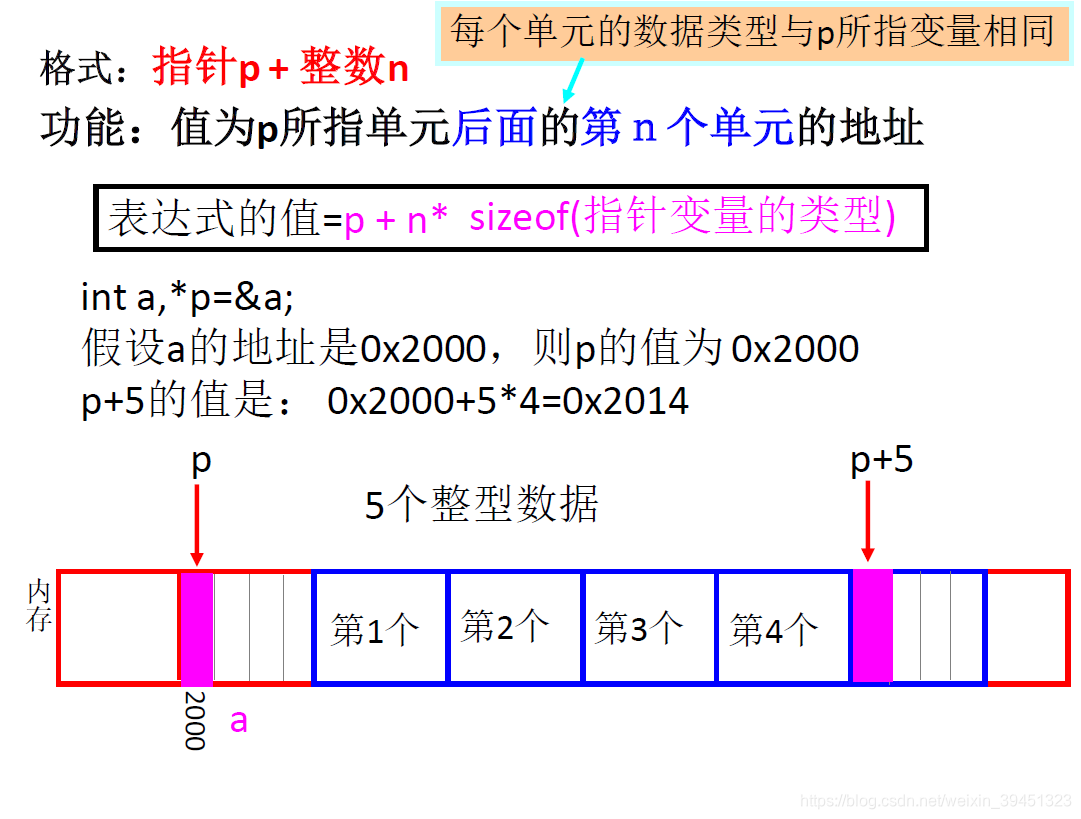


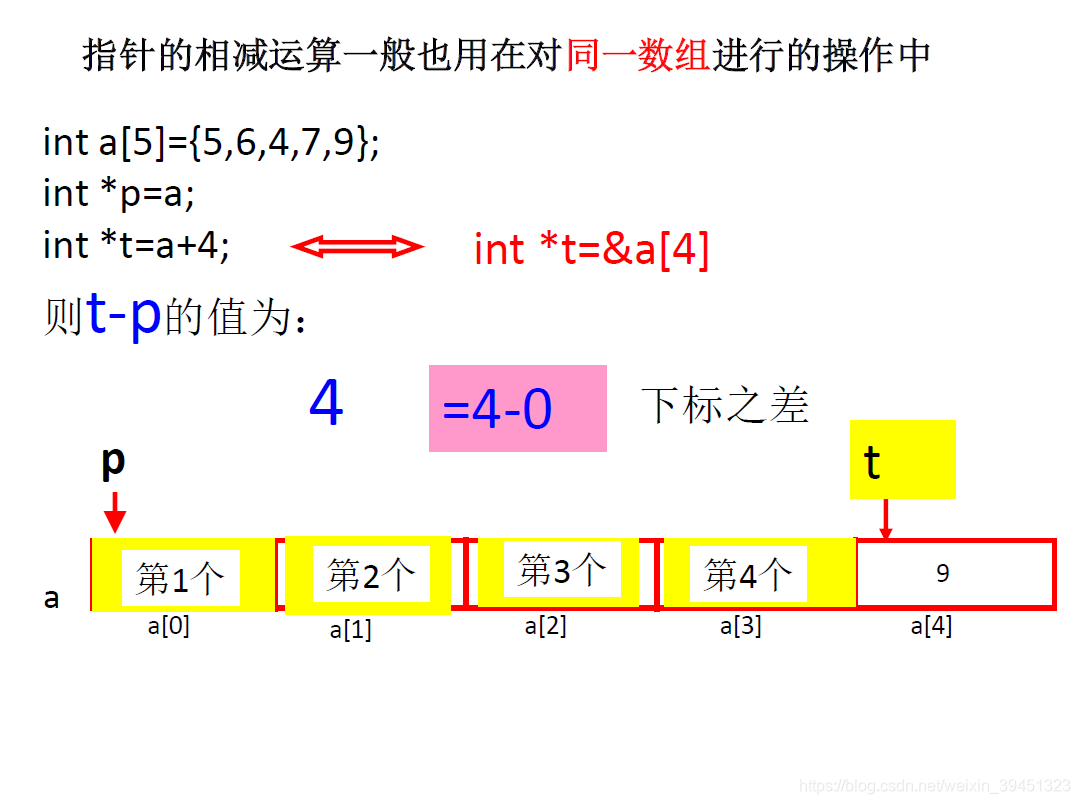
//6-1-5-1指针算术运算.cpp
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int a[5] = { 5,6,4,7,9 };
int* p = &a[3];
cout << "*p =" << *p << endl;
p = p - 3;
cout << "*p =" << *p << endl;
int* t = a + 4;
cout << "*t =" << *t << endl;
/*
cout<<t-p<<endl; //表示t和p之间差几个元素
cout<<p<<endl;
cout<<t<<endl;
*/
return 0;
}



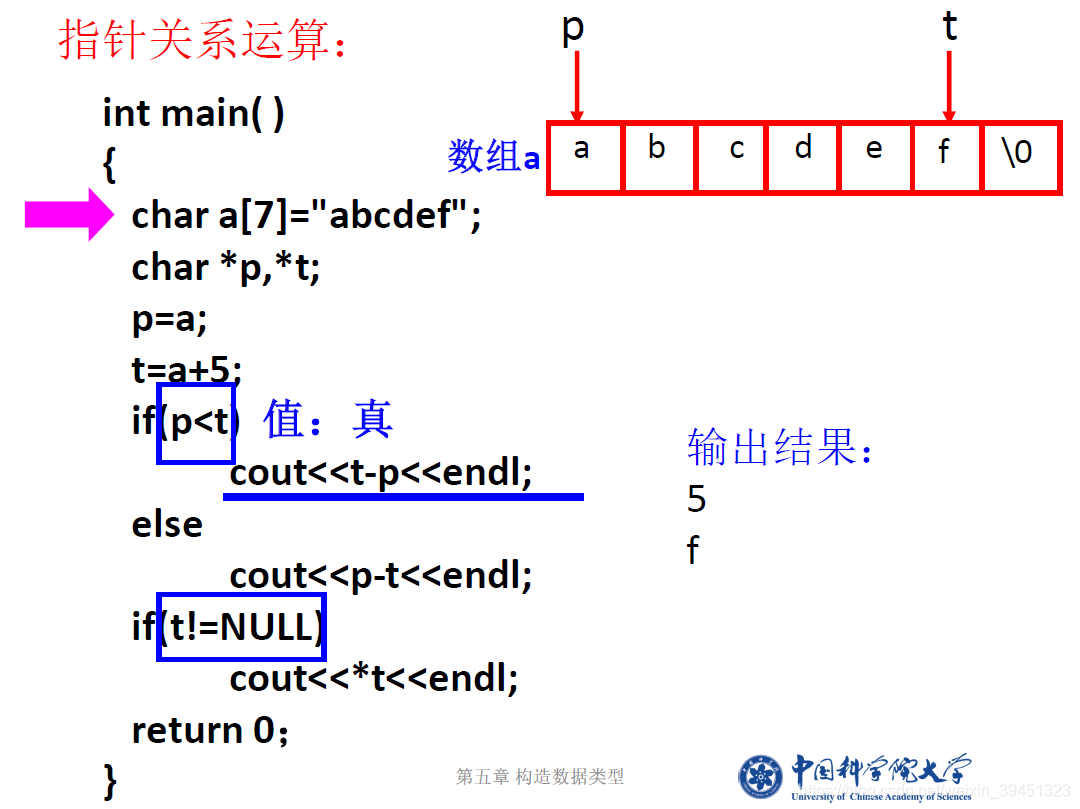
1.4 用指针访问数组元素





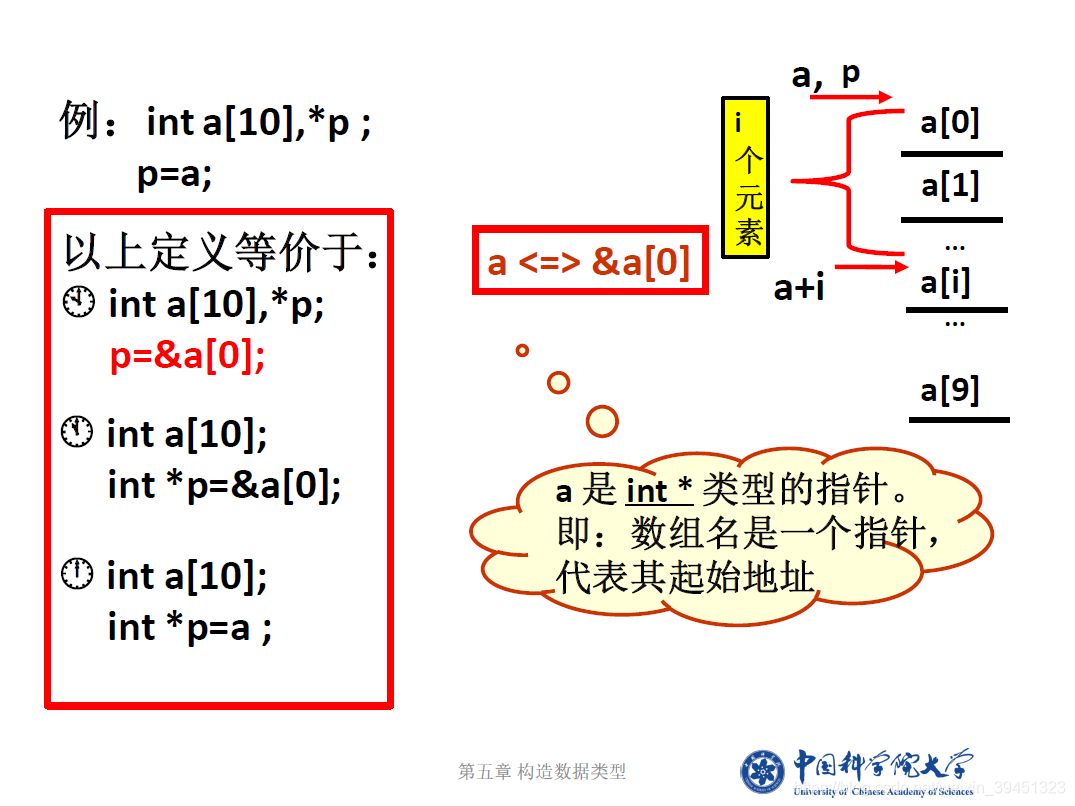
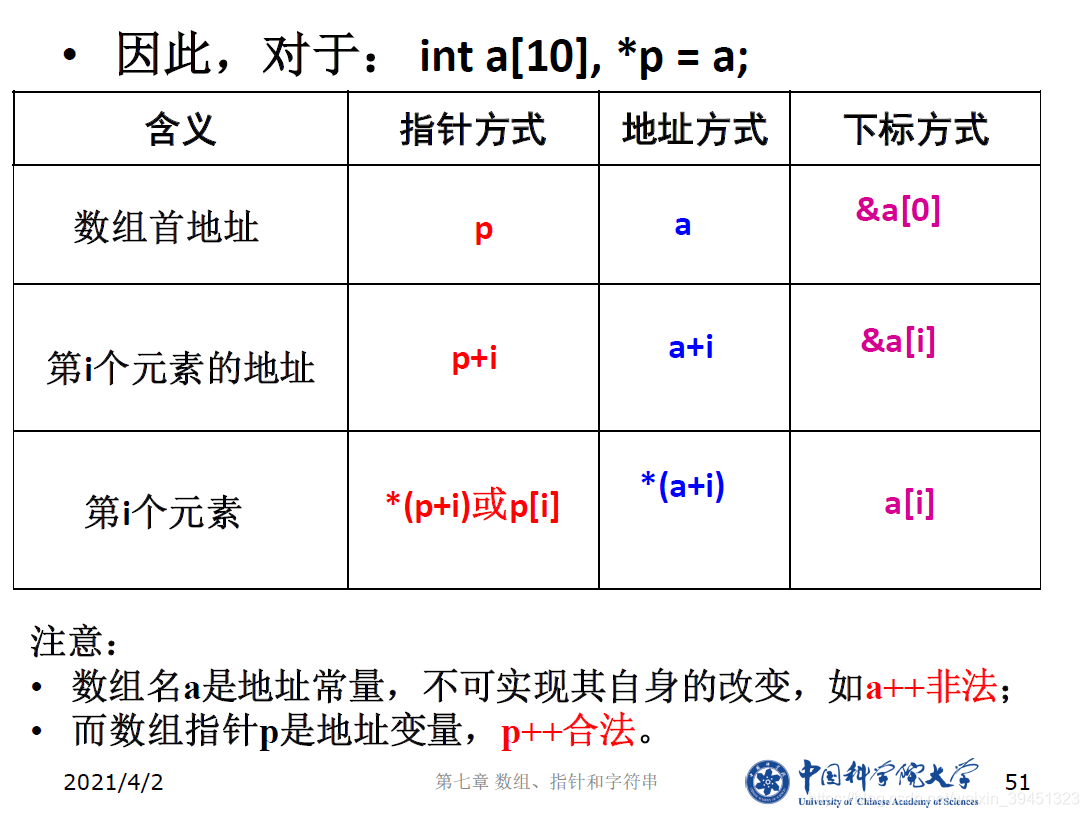

//访问数组元素的三种方法.cpp
//比较通过数组名和指向数组的指针访问数组元素
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int x[5] = { 10,12,14,16,18 };
//下标法
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) //利用下标法输出数组元素
cout << x[i] << '\t';
cout << endl;
//地址法
for (int j = 0; j < 5; j++)
cout << *(x + j) << '\t'; //利用数组名输出数组元素
cout << endl;
//指针法
int* p = x;
for (int k = 0; k < 5; k++)
cout << *p++ << '\t'; //利用指向数组的指针访问数组中的每个元素
cout << endl;
return 0;
}


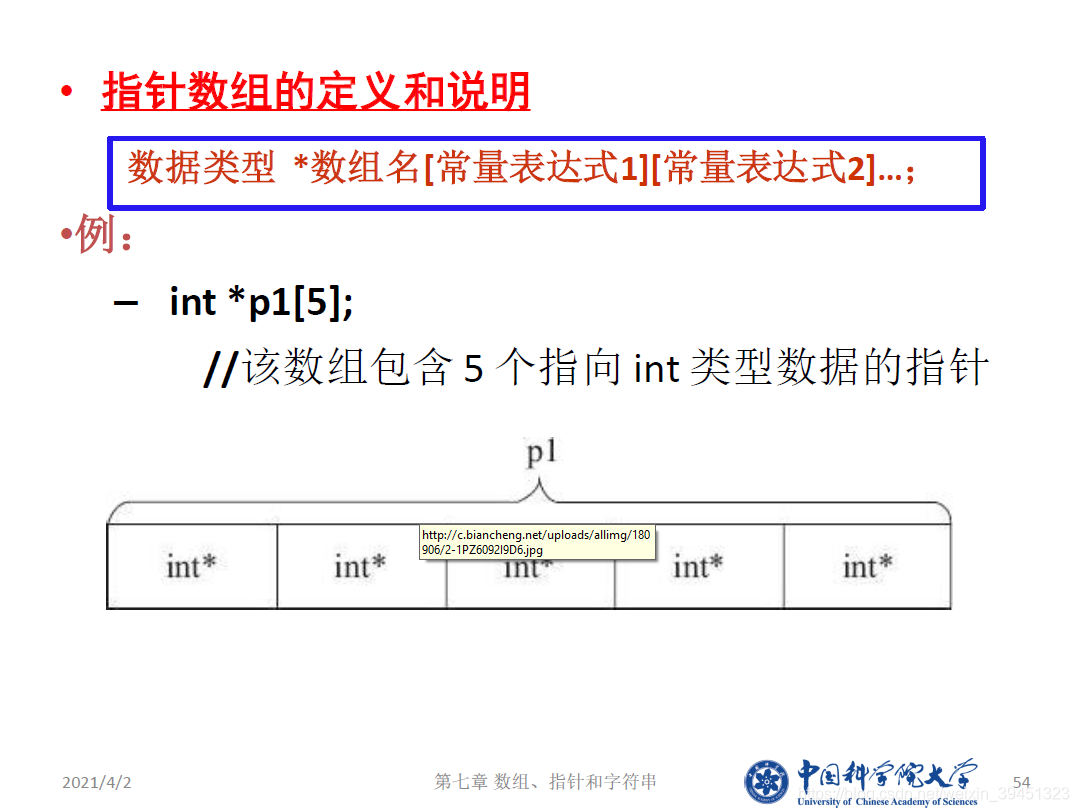
//指针数组.cpp
//利用指针数组输出另一个数组中各元素的值
#include <iostream>
#include<cstring>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
/*****指针数组**********/
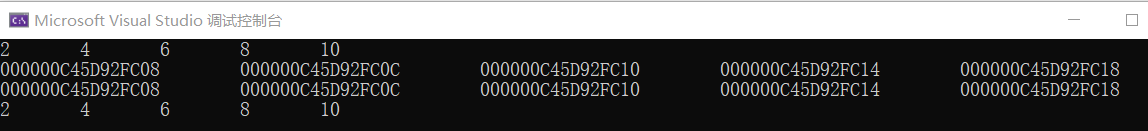
float a[5] = { 2, 4, 6, 8, 10 };
float* p[5] = { &a[0], &a[1], &a[2], &a[3], &a[4] };
int i;
for (i = 0; i < 5; i++) cout << *p[i] << '\t';
cout << endl;
for (i = 0; i < 5; i++) cout << p[i] << '\t';
cout << endl;
for (i = 0; i < 5; i++) cout << &a[i] << '\t';
cout << endl;
for (i = 0; i < 5; i++) cout << a[i] << '\t';
cout << '\n';
return 0;
}
//指针数组
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int x[2][3] = { {1,2,3},{14,15,26} };
int i, j;
int* p[2] = { x[0],x[1] }; //声明指针数组并初始化
for (i = 0; i < 2; i++)
{
for (j = 0; j < 3; j++)
cout << *(p[i] + j) << '\t'; //利用指针数组输出元素值
cout << endl;
}
return 0;
}


//数组指针.cpp
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int x[2][3] = { {1,2,3},{4,5,6} };
int i, j;
int(*p)[3] = x; //指针p被声明为数组指针
//每个指针指向一个一维数组
for (i = 0; i < 2; i++)
{
for (j = 0; j < 3; j++)
cout << *(*(p + i) + j) << '\t';
/* cout << *(*(x + i) + j) << '\t';*/ //此语句和上面的语句有同样的输出
cout << endl;
}
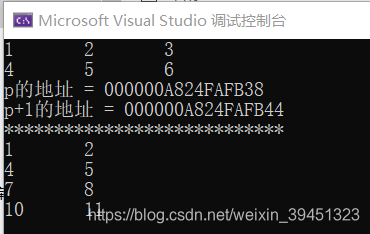
cout << "p的地址 = " << p << endl;
cout << "p+1的地址 = " << p + 1 << endl;
cout << "****************************" << endl;
int y[4][2] = { {1,2},{4,5},{7,8},{10,11} };
int(*q)[2] = y;
for (i = 0; i < 4; i++)
{
for (j = 0; j < 2; j++)
cout << *(*(q + i) + j) << '\t';
cout << endl;
}
return 0;
}
1.5 指针和字符串







//指针与字符串
#include <iostream>
#include<cstring>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
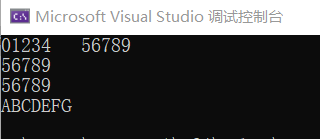
char a[] = "01234"; //字符数组形式表示字符串
char* b = (char *)"56789"; //字符指针形式表示字符串
char c[10];
char* pa = a, * pb = b;
cout << a << '\t' << b << endl;
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++)
*pa++ = *pb++; //逐个字符引用字符串
cout << a << endl; //整体引用字符串
cout << b << endl;
strcpy_s(c, "ABCDEFG");
cout << c << endl;
return 0;
}
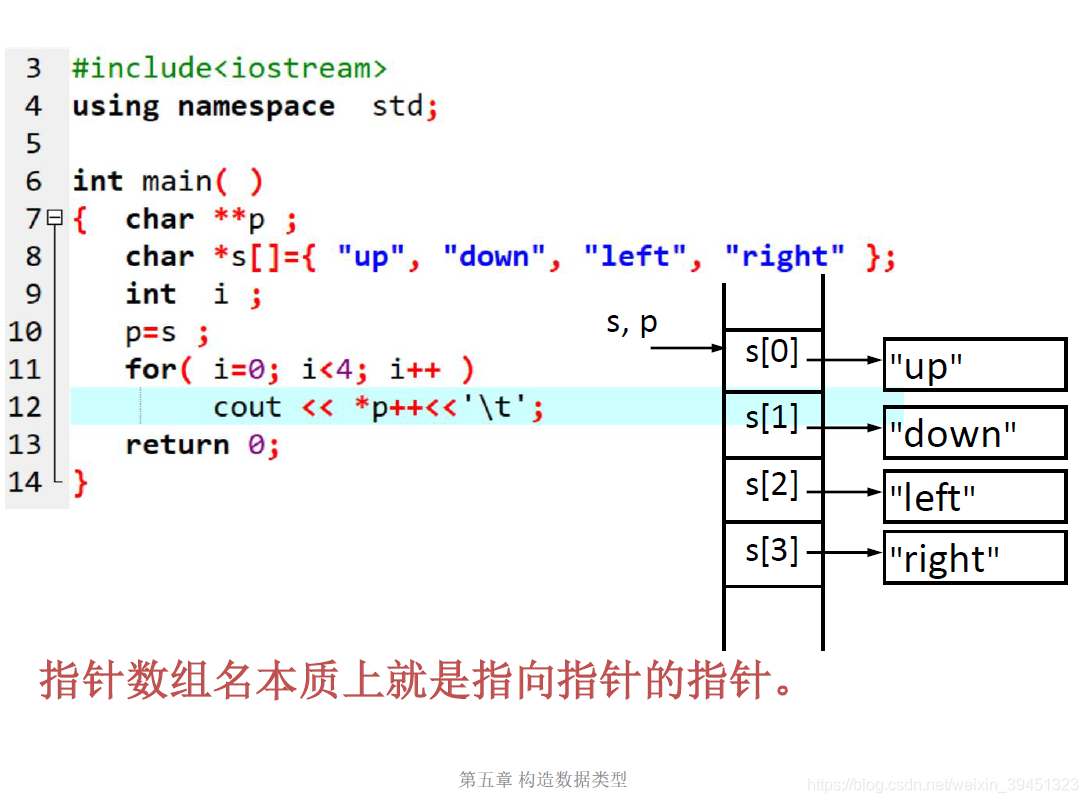
//指针的指针.cpp
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
const char ** p;
const char* s[] = { "up", "down", "left", "right" };
int i;
p = s;
for (i = 0; i < 4; i++)
cout << *p++ << '\t';
//cout << *(p++)<<'\t';
return 0;
}

1.6 指针与函数




//指针型函数的正确应用1
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
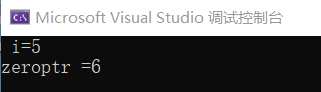
int main() {
int array[10] = { 1,0,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10 }; //主函数中定义的数组
int* search(int* a, int num);
int* zeroptr = search(array, 10); //将主函数中数组的首地址传给子函数
cout << "zeroptr =" << *zeroptr << endl;
return 0;
}
int* search(int* a, int num) { //指针a指向主函数中定义的数组
for (int i = 0; i < num; i++)
if (a[i] == 6)
{
cout << " i=" << i << endl;
return &a[i]; //返回的地址指向的元素是在主函数中定义的
}
}//函数运行结束时,a[i]的地址仍有效
//指针型函数的错误应用
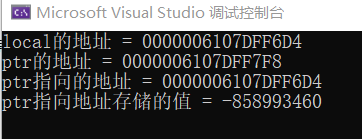
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
int* function();
int* ptr = function();
cout << "ptr的地址 = " << &ptr << endl;
cout << "ptr指向的地址 = " << ptr << endl;
cout << "ptr指向地址存储的值 = " << *ptr << endl;
cout << endl;
*ptr = 5;
return 0;
}
int* function() {
int local = 100; //非静态局部变量作用域和寿命都仅限于本函数体内
cout << "local的地址 = " << &local << endl;
return &local;
}//函数运行结束时,变量local被释放



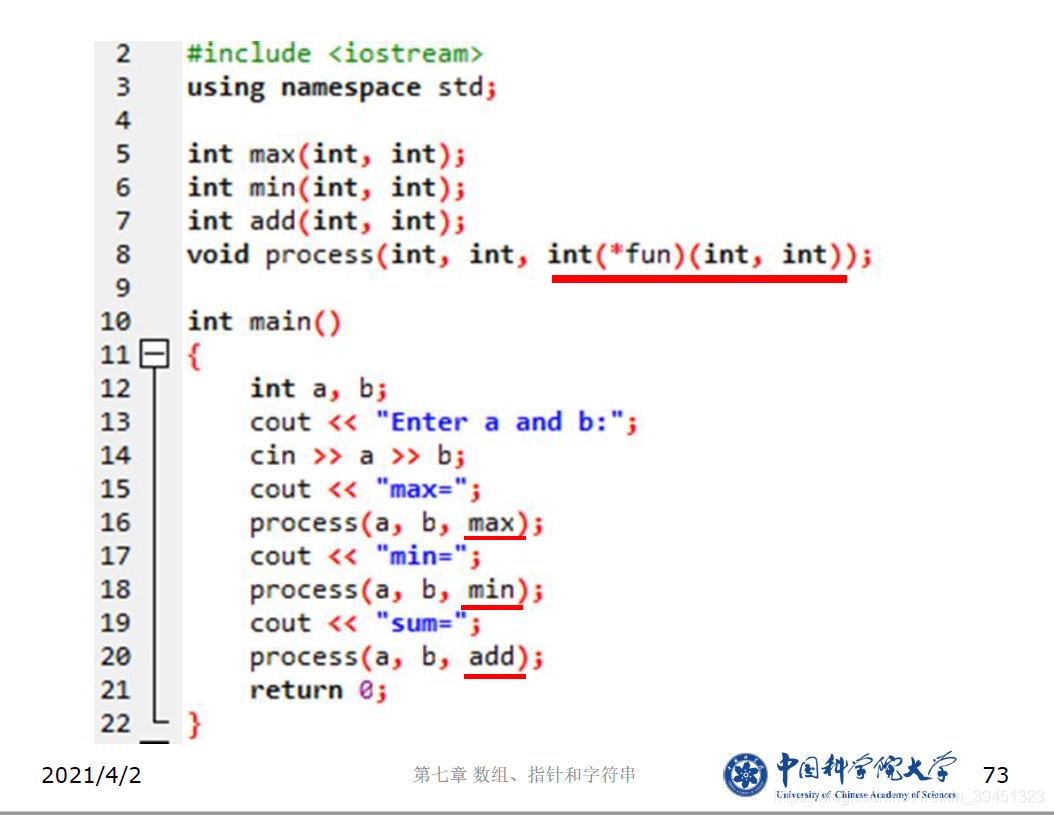
//函数指针应用
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int max(int, int);
int min(int, int);
int add(int, int);
void process(int, int, int(*fun)(int, int));
int main()
{
int a, b;
cout << "Enter a and b:";
cin >> a >> b;
cout << "max=";
process(a, b, max);
cout << "min=";
process(a, b, min);
cout << "sum=";
process(a, b, add);
return 0;
}
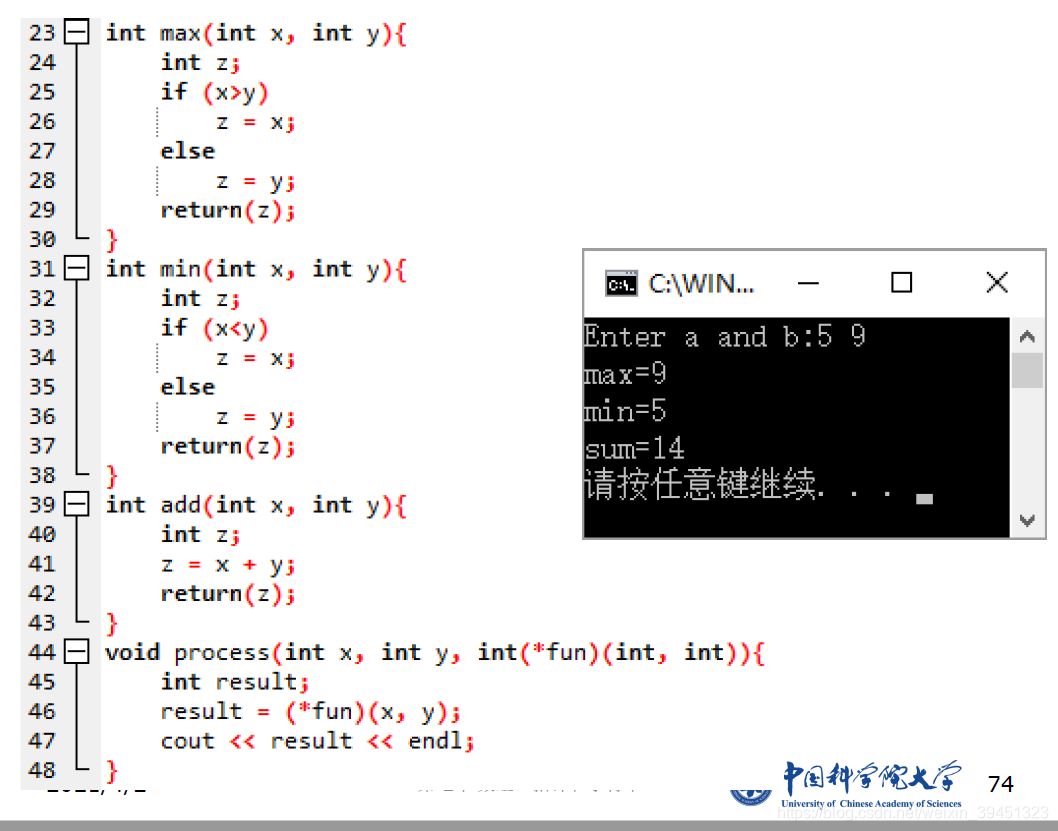
int max(int x, int y) {
int z;
if (x > y)
z = x;
else
z = y;
return(z);
}
int min(int x, int y) {
int z;
if (x < y)
z = x;
else
z = y;
return(z);
}
int add(int x, int y) {
int z;
z = x + y;
return(z);
}
void process(int x, int y, int(*fun)(int, int)) {
int result;
result = (*fun)(x, y);
cout << result << endl;
}

// 数组名作为函数参数.cpp
// 定义一个数组元素逆置的函数,在主函数中调用该函数测试。
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
void transpose(char[], int n); //逆置函数原型声明
int main()
{
char a[5] = { 'A','B','C','D','E' };
int i;
cout << "原数组:";
for (i = 0; i < 5; i++) cout << '\t' << a[i]; cout << endl;
transpose(a, 5);
cout << "逆置后:";
for (i = 0; i < 5; i++) cout << '\t' << a[i]; cout << endl;
return 0;
}
void transpose(char x[], int n) {
char temp;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++, n--) {
temp = x[i];
x[i] = x[n - 1];
x[n - 1] = temp;
}
}
2.引用

2.1 引用的概念




//引用的概念
//引用的声明和使用。
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
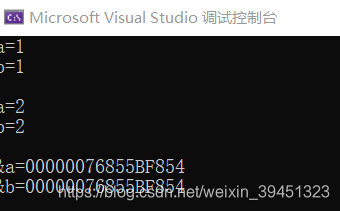
{
int a=1;
int &b=a; //b是变量a的引用
cout<<"a="<<a<<endl;
cout<<"b="<<b<<endl<<endl;
b=2;
cout<<"a="<<a<<endl;
cout<<"b="<<b<<endl<<endl;
cout<<"&a="<<&a<<endl;
cout<<"&b="<<&b<<endl;
return 0;
}
2.2 引用的操作

// 交换两个变量的值(按值传递)
//第5章例子:5-2-3.cpp
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
void swap(int, int); //函数声明
int main()
{
int a = 3, b = 4;
cout << "a的地址 =" << &a << " , b的地址 =" << &b << endl;
cout << "主程序,初始值:a=" << a << "\t b=" << b << endl << endl;
swap(a, b);
cout << "主程序,返回后:a=" << a << "\t b=" << b << endl;
return 0;
}
void swap(int x, int y)
{
cout << "x的地址 =" << &x << " , y的地址 =" << &y << endl;
cout << "交换之前 a=" << x << "\t b=" << y << "\n";
int t = x;
x = y;
y = t;
cout << "交换之后 a=" << x << "\t b=" << y << "\n\n";
}



// 交换两个变量的值(按地址传递)
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
void swap(int*, int*); //函数声明
int main()
{
int a = 3, b = 4;
cout << "a=" << a << ",b="
<< b << endl;
cout << "a的地址 =" << &a << " , b的地址 =" << &b << endl;
swap(&a, &b);
cout << "a=" << a << ",b="
<< b << endl;
return 0;
}
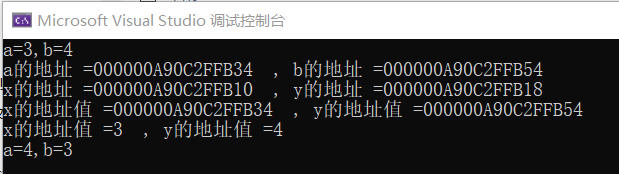
void swap(int* x, int* y)
{
int t = *x;
cout << "x的地址 =" << &x << " , y的地址 =" << &y << endl;
cout << "x的地址值 =" << x << " , y的地址值 =" << y << endl;
cout << "x的地址值 =" << *x << " , y的地址值 =" << *y << endl;
*x = *y;
*y = t;
}
2.3 引用传递


// 交换两个变量的值(引用传递)
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
void swap(int&, int&); //函数声明
int main()
{
int a = 3, b = 4;
cout << "a的地址值 =" << &a << " , b的地址值 =" << &b << endl;
cout << "a=" << a << ",b="
<< b << endl;
swap(a, b);
cout << "a=" << a << ",b="
<< b << endl;
return 0;
}
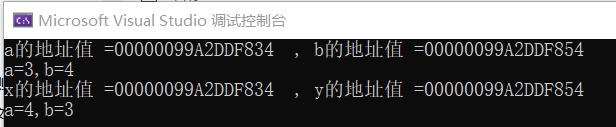
void swap(int& x, int& y)
{
int t = x;
cout << "x的地址值 =" << &x << " , y的地址值 =" << &y << endl;
x = y;
y = t;
}
- 三种传递方式的比较
//三种传递方式的比较
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
//值传递
void change1(int n)
{
cout << "\n" << "值传递--函数操作地址" << &n; //显示的是拷贝的地址而不是源地址
n++;
}
//引用传递
void change2(int& n)
{
cout << "\n" << "引用传递--函数操作地址" << &n;
n++;
}
//指针传递
void change3(int* n)
{
cout << "\n" << "指针传递--函数操作地址" << &*n;
*n = *n + 1;
}
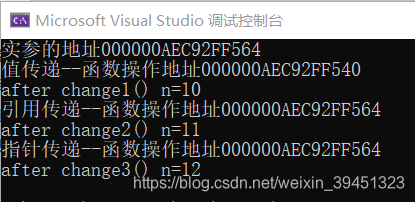
int main() {
int n = 10;
cout << "实参的地址" << &n;
change1(n);
cout << "\n" << "after change1() n=" << n;
change2(n);
cout << "\n" << "after change2() n=" << n;
change3(&n);
cout << "\n" << "after change3() n=" << n << "\n";
return 0;
}
2.4 引用返回

//返回引用的函数
//定义一个函数,返回两个数较大值的引用
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int maxab;
int& maxRef(int x, int y) //函数的返回类型是引用
{
//int maxab; //这样会返回非静态局部变量
if (x > y) maxab = x;
else maxab = y;
return maxab;
}
int main()
{
int a, b;
cout << "Input a and b:";
cin >> a >> b;
cout << maxRef(a, b) << endl;
return 0;
}
//返回引用的函数
//引用返回函数:函数作为左值的时候,需要定义为引用返回形式
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int a[] = { 1,6,11,12 };
// 下面部分是正确的
int &index(int i); //a是全局变量,&表示返回的是a[i]的引用,就是a[i]本身
int main()
{
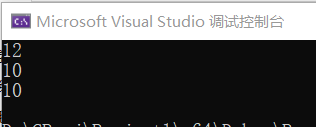
cout<<index(3)<<endl; // 输出12
index(3)=10; //将a[3]改为10
cout<<index(3)<<endl; // 输出10
cout << a[3] << endl; // 输出10
return 0;
}
int& index(int i)
{
return a[i];
}
//
//下面是测试部分,不用返回引用函数 ,产生错误
/*
int index(int i);
int main()
{
cout<<index(3)<<endl; // 输出12
index(3)=10; //将a[3]改为10
cout<<index(3)<<endl; // 输出10
return 0;
}
int index(int i)
{
return a[i];
}
*/
2.5 利用引用返回多个值

//5-21:利用引用返回多个值
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int factor(int, int&, int&);
int main()
{
int number, squared=0, cubed=0, error;
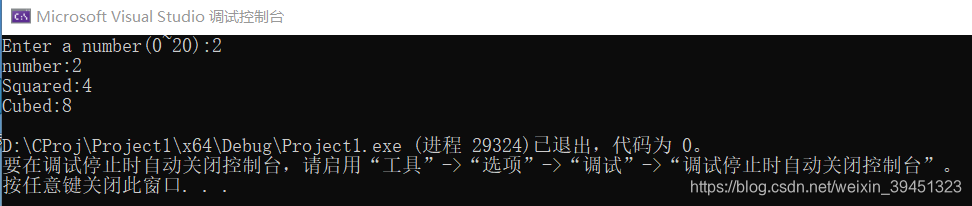
cout << "Enter a number(0~20):";
cin >> number;
error = factor(number, squared, cubed);
if (error) //error =1
cout << "Error encountexd!\n";
else
{
cout << "number:" << number << endl;
cout << "Squared:" << squared << endl;
cout << "Cubed:" << cubed << endl;
}
return 0;
}
int factor(int n, int &rsquared, int &rcubed)
{
if (n > 20 || n < 0) //n的值在0~20之间,否则返回1
return 1;
rsquared = n * n;
rcubed = n * n * n;
return 0;
}
3.动态内存分配


// 6-3-1-1动态内存分配.cpp
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
int n, i;
cin >> n;
int a[n]; //正常情况下,这是错误的。n在编译时就应该确定下来。
//n应该是常数
for (i = 0; i < n; i++)
cout << "a[" << i << "] = " << a[i] << endl;
return 0;
}



//动态空间分配--一维数组.cpp
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int n, * p, i;
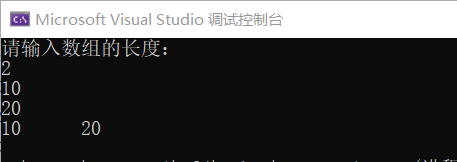
cout << "请输入数组的长度:" << endl;
cin >> n;
p = new int[n]; // 申请空间
//判断申请空间是否成功
if (p == NULL) //或 p==0
{
cout << "动态分配不成功,终止执行!\n";
exit(3); //在整个程序中,只要调用 exit ,就结束
}
for (i = 0; i < n; i++) // 使用空间
//cout << "请输入第"<<"个数:" << endl; // 问“为啥在中见加个cout会引发程序终止
cin >> p[i]; // 或 cin >> *(p+i);
for (i = 0; i < n; i++)
cout << p[i] << '\t'; // 或 cout << *(p+i);
cout << '\n';
delete[] p; // 释放空间
return 0;
}

// 动态空间分配--二维数组.cpp
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int m;
cin >> m;
int(*p1)[4] = new int[m][4];
for (int i1 = 0; i1 < m; i1++)
{
for (int i2 = 0; i2 < 4; i2++)
{
cin >> p1[i1][i2];
}
}
for (int i1 = 0; i1 < m; i1++)
{
for (int i2 = 0; i2 < 4; i2++)
{
cout << p1[i1][i2] << '\t';
}
}
delete[]p1;
return 0;
}
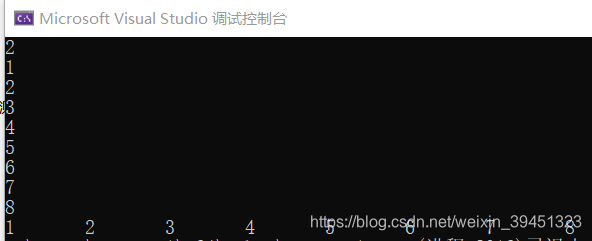
// 动态空间分配--二维数组.cpp
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int i, j, height, width;
cin >> height >> width;
cout << endl;
int** array2D = new int* [height];
for (i = 0; i < height; ++i)
{
array2D[i] = new int[width];
}
// 设置值
for (i = 0; i < height; ++i)
{
for (j = 0; j < width; ++j)
{
// 内存非连续,注意防止越界.
array2D[i][j] = i * width + j;
}
}
// 访问:输出数组
for (i = 0; i < height; ++i)
{
for (j = 0; j < width; ++j)
{
cout << array2D[i][j] << " , ";
}
cout << endl;
}
// 首先回收低一级的动态数组.
for (i = 0; i < height; ++i)
{
delete[] array2D[i];
}
// 然后回收高一级的动态数组.
delete[] array2D;
return 0;
}
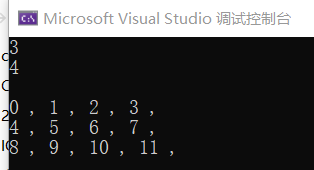




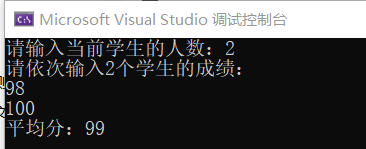
//动态空间分配--简单例子.cpp
//编程学生人数未知前提下,求多名学生某门课程的平均分功能。
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int count, i; int* score;
double total = 0;
cout << "请输入当前学生的人数:";
cin >> count;
score = new int[count]; //根据人数,动态申请存储空间
if (!score)
{
cout << "分配空间失败!" << endl; exit(0);
}
cout << "请依次输入" << count << "个学生的成绩:" << endl;
for (i = 0; i < count; i++)
{
cin >> score[i]; total += score[i];
}
cout << "平均分:" << total / count << endl;
delete[]score; //释放score分配的存储空间
return 0;
}
4. 实战


/*本版V3完成的功能与V2版相同。
(1)订单信息中为了操作方便,只保留了订单编号和商品编号。
(2)将订单编号数组、商品编号数组和当前订单个数作为参数在各个函数中传递。
(3)添加、删除订单时,除了传递表示订单编号和商品编号的数组外,将表示订单个数的整型变量以引
用形式传递。
(4)查询、修改、浏览订单时,传递表示订单编号、商品编号的数组和值传递表示订单个数的整型变量。
*/
#include <iostream>
#include <iomanip>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
#define MaxNum 100 //定义数组大小
#define N 14 //控制输出格式中长度
#define M 12 //订单编号、商品编号的长度
//所有函数声明
int password(); //口令函数
void menu(string* order_num, string* goods_num, int count); //主菜单函数
void Append(string* order_num, string* goods_num, int& count); //添加订单函数
int effective(string* order_num, string* goods_num, int count, string ch); //判断订单编号唯一性函数
int Search_order_num(string* order_num, string* goods_num, int count, string ch);//查询函数 //按订单编号查询函数
void Delete_menu(string* order_num, string* goods_num, int& count);//删除函数
void Modify(string* order_num, string* goods_num, int count);//修改订单函数
void Print_goods(string* order_num, string* goods_num, int count, int i);//浏览订单信息函数
//主函数
int main()
{
int count = 0; //用来记录当前订单的个数
string order_num[MaxNum]; //订单编号
string goods_num[MaxNum]; //商品编号
if (password())
menu(order_num, goods_num, count); //前两个参数都是数组,使用的是地址
return 0;
}
void menu(string* order_num, string* goods_num, int count)//主菜单函数
{
cout << endl;
while (1)
{
cout << "*****************************************************" << endl;
cout << "* 根据所做操作选择以下数字序号: *" << endl;
cout << "* 1:添加订单 2:查找订单 *" << endl;
cout << "* 3:修改订单 4:删除订单 *" << endl;
cout << "* 5:浏览订单 0:退出 *" << endl;
cout << "*****************************************************" << endl;
int n, i;
cin >> n;
switch (n)
{
case 1:
{
Append(order_num, goods_num, count);
break;
}
case 2:
{
char ch[20];
cout << "请输入查询的订单编号:" << endl;
cin >> ch;
i = Search_order_num(order_num, goods_num, count, ch);
if (i != -1)
{
cout << "查找成功!" << endl;
cout << setw(N) << "订单编号" << setw(N) << "商品编号" << endl;
cout << setw(N) << order_num[i] << setw(N) << goods_num[i] << endl;
}
else
cout << "查找失败!" << endl;
break;
}
case 3:
{
Modify(order_num, goods_num, count);
break;
}
case 4:
{
Delete_menu(order_num, goods_num, count);
break;
}
case 5:
{
if (count == 0)
{
cout << "表中无订单信息!" << endl;
}
else
{
cout << setw(N) << "订单编号" << setw(N) << "商品编号" << endl;
for (i = 0; i < count; i++)
Print_goods(order_num, goods_num, count, i);
}
break;
}
case 0:
return;
default:
cout << "输入有误,请重新输入!" << endl;
}
}
}
int effective(string* order_num, string* goods_num, int count, string ch)
{
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++)
if (order_num[count] == order_num[i])
return 0;
return 1;
}
void Append(string* order_num, string* goods_num, int& count)//添加订单函数
{
string ch;
cout << "请输入订单信息:" << endl;
cout << "订单编号:";
cin >> ch;
while (1)
{
if (effective(order_num, goods_num, count, ch) == 0)
{
cout << "订单编号重复,请重新输入!" << endl;
cin >> ch;
}
else
break;
}
order_num[count] = ch;
cout << "商品编号:"; cin >> goods_num[count];
cout << "添加完毕!" << endl;
count++;
}
int Search_order_num(string* order_num, string* goods_num, int count, string ch)//查找函数
{
int i;
for (i = 0; i < count; i++)
if (order_num[i] == ch)
return i;
return -1;
}
void Print_goods(string* order_num, string* goods_num, int count, int i)//显示指定订单的信息
{
cout << setw(N) << order_num[i] << setw(N) << goods_num[i] << endl;
}
void Modify(string* order_num, string* goods_num, int count)//修改函数,先按订单编号查找,后修改
{
string num;
int m;
cout << "请输入所要修改的订单编号:";
cin >> num;
m = Search_order_num(order_num, goods_num, count, num);
if (m == -1)
{
cout << "所输入订单编号有误,库中不存在该订单信息!" << endl;
return;
}
cout << "当前订单信息如下:" << endl;
cout << setw(N) << "订单编号" << setw(N) << "商品编号" << endl;
Print_goods(order_num, goods_num, count, m);
cout << "请输入新的商品编号:" << endl;
cin >> goods_num[m];
cout << "修改完毕!" << endl;
}
void Delete_menu(string* order_num, string* goods_num, int& count)//删除函数
{
string ch;
char xx;
cout << "请输入删除的订单编号:" << endl;
cin >> ch;
int i = 0, j;
while (i < count)
{
if (order_num[i] == ch)
break;
i++;
}
if (i >= count)
cout << "该订单不存在!" << endl;
else
{
cout << "已查询到,订单信息:" << endl;
cout << setw(N) << "订单编号" << setw(N) << "商品编号" << endl;
Print_goods(order_num, goods_num, count, i);
cout << "请选择(删除Y,放弃N):";
cin >> xx;
if (xx == 'y' || xx == 'Y')
{
for (j = i + 1; j < count; j++)
{
order_num[j - 1] = order_num[j];
goods_num[j - 1] = goods_num[j];
}
count--;
cout << "删除完毕!" << endl;
}
else
cout << "放弃本次删除操作!" << endl;
}
}
int password()//口令函数
{
string p;
int n = 0;
cout << "请输入登录口令:" << endl;
while (1)
{
cin >> p;
if (p == "abcd")
{
cout << "输入口令正确!" << endl;
return 1;
}
else
{
cout << "输入口令错误,请重新输入!" << endl;
n++;
if (n == 3)
{
cout << "已输入3次,您无权进行操作!" << endl;
return 0;
}
}
}
}

