图像处理基本方法-将BMP图片二值化-c语言实现
c语言实现图片二值化,主要使用函数bmpBinarizationProccess实现。
函数定义
int bmpBinarizationProccess(char u8PicNameiIn[], char u8PicNameOut[], unsigned char thresholdLow, unsigned char thresholdHigh, int mode)
其中
u8PicNameiIn为原始图像数据。
u8PicNameOut为输出图像数据。
thresholdLow为转换阈值。
thresholdHigh为最大值。
mode为转换类型。
具体函数调用
bmpBinarizationProccess(u8PicNameRead,u8PicNameOut,thresholdLow,thresholdHigh,mode);
代码实现
/*******************************************************
* file:testGray.c
* date:2021-07-10
* version:1.0.0.1
* author:jack8126
* description: bmp file, change to gray picture
*******************************************************/
#include <stdio.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <math.h>
#include <time.h>
#include <string.h>
#define PRINT_CTRL 1
typedef unsigned char WORD8; /* 8位无符号整型 */
typedef unsigned short WORD16; /* 16位无符号整型 */
typedef unsigned int WORD32; /* 32位无符号整型 */
typedef unsigned char BYTE; /* 8位无符号整型 */
typedef signed int INT; /* 32位有符号整型 */
typedef signed char CHAR; /* 8位有符号字符型 */
typedef signed long LONG; /* 32位有符号长整型 */
typedef unsigned long uLONG; /* 32位无符号长整型 */
typedef signed short SHORT; /* 16位有符号整型 */
typedef void *LPVOID; /* 空类型 */
typedef unsigned char BOOLEAN; /* 布尔类型 */
#pragma pack(push)
#pragma pack(1)
typedef struct INFOHEADER
{
WORD32 biSize;
WORD32 biWidth;
WORD32 biHeight;
WORD16 biPlanes;
WORD16 biBitCount;
WORD32 biCompression;
WORD32 biSizeImage;
WORD32 biXPelsPerMeter;
WORD32 biYPelsPerMeter;
WORD32 biClrUsed;
WORD32 biClrImportant;
}BITMAPINFOHEADER;
typedef struct tagBITMAPFILEHEADER
{
WORD16 bfType;
WORD32 bfSize;
WORD16 bfReserved1;
WORD16 bfReserved2;
WORD32 bfOffBits;
} BITMAPFILEHEADER;
#pragma pack(pop)
int bmpBinarizationProccess(char u8PicNameiIn[], char u8PicNameOut[], unsigned char thresholdLow, unsigned char thresholdHigh, int mode)
{
INT ptn1Fd;
INT fileLong = 0;
BITMAPFILEHEADER bmp_file_header_save = {0};
BITMAPINFOHEADER bmp_info_header_save = {0};
//FILE* fdRead = NULL;
FILE* fdWrite = NULL;
int bmpSize = 0;
INT nWriteLen = 0;
BYTE *ptnBufRead = NULL;
INT readLen = 0;
INT i = 0;
INT j = 0;
INT iWidth = 0;
INT iHeight = 0;
INT iBmpBit = 3;
int iBmpSize = 0;
BYTE u8R = 0;
BYTE u8G = 0;
BYTE u8B = 0;
BYTE u8Tmp = 0;
int ntmp = 0;
if ((access(u8PicNameiIn, F_OK))!= 0)
{
printf("%s not found\n", u8PicNameiIn);
return -1;
}
// read bmp input file
ptn1Fd = open(u8PicNameiIn, O_RDONLY);
printf("open file name %s ptn1Fd %d \n",u8PicNameiIn,ptn1Fd);
if (ptn1Fd < 0)
{
printf("open %s error\n", u8PicNameiIn);
return 1;
}
fileLong = lseek(ptn1Fd, 0, SEEK_END);
printf("the pic size fileLong is %d.\r\n",fileLong);
bmpSize = fileLong - 54;
iBmpSize = bmpSize;
lseek(ptn1Fd, 0, SEEK_SET);
readLen = read(ptn1Fd, &bmp_file_header_save, 14);
lseek(ptn1Fd, 14, SEEK_SET);
readLen = read(ptn1Fd, &bmp_info_header_save, 40);
lseek(ptn1Fd, 54, SEEK_SET);
printf("read bmp_header.biHeight=%d,biWidth=%d\r\n",
bmp_info_header_save.biHeight,bmp_info_header_save.biWidth);
nWriteLen = bmp_info_header_save.biHeight*bmp_info_header_save.biWidth*3;
printf("nWriteLen = %d\n\r",nWriteLen);
iWidth = bmp_info_header_save.biWidth;
iHeight = bmp_info_header_save.biHeight;
printf("bmpSize=%d\r\n",bmpSize);
ptnBufRead = (BYTE *)malloc(bmpSize);
if (ptnBufRead == NULL)
{
printf("malloc ptnBuf failed.\r\n");
close(ptn1Fd);
return -1;
}
memset(ptnBufRead, 0, bmpSize);
// read bmp file
readLen = read(ptn1Fd, ptnBufRead, bmpSize);
printf("readLen=%d\r\n",readLen);
// draw a rectangle
#if 1
for (i = 0; i < iHeight; i++)
{
for (j = 0; j< iWidth; j++)
{
ntmp = (iHeight -1 - i)*3*iWidth + (j )*3;
u8B = ptnBufRead[ntmp + 0];
u8G = ptnBufRead[ntmp + 1];
u8R = ptnBufRead[ntmp + 2];
u8Tmp = u8R * 0.299 + u8G * 0.587 + u8B * 0.114;
if(mode == 0)
{
if(u8Tmp < thresholdLow)
{
ptnBufRead[ntmp + 0] = 0;
ptnBufRead[ntmp + 1] = 0;
ptnBufRead[ntmp + 2] = 0;
}
else
{
ptnBufRead[ntmp + 0] = thresholdHigh;
ptnBufRead[ntmp + 1] = thresholdHigh;
ptnBufRead[ntmp + 2] = thresholdHigh;
}
}
else
{
}
}
}
#endif
printf(" for out ntmp=%d\r\n",ntmp);
// save output file
fdWrite = fopen(u8PicNameOut, "w+");
// write bmp file header
fwrite(&bmp_file_header_save, 1, 14, fdWrite);
fseek(fdWrite,0,SEEK_END);
// write bmp info header
fwrite(&bmp_info_header_save, 1, 40, fdWrite);
//lseek(ptn1Fd, 54, SEEK_SET);
fseek(fdWrite,0,SEEK_END);
// write bmp data
fwrite(ptnBufRead, 1, nWriteLen, fdWrite);
// release
if(NULL != ptnBufRead)
{
free(ptnBufRead);
ptnBufRead = NULL;
}
if(ptn1Fd)
{
close(ptn1Fd);
}
//fclose(fdRead);
if(fdWrite)
{
fclose(fdWrite);
fdWrite = NULL;
}
}
//主函数
int main(int argc, char * * argv)
{
BYTE u8PicNameRead[64] = {0};
BYTE u8PicNameOut[64] = {0};
int iBmpBit = 3;
int iBmpBitTmp = 0;
struct timeval tStartTime;
struct timeval tEndTime;
int isecond = 0;
int iusecond = 0;
unsigned char thresholdLow = 0;
unsigned char thresholdHigh = 0;
int mode = 0;
if(argc < 5)
{
printf("please input like this:\r\n");
printf("./testBinarization.bin test.bmp test-out.bmp 120 255\r\n");
printf("test.bmp ---------- input file \r\n");
printf("test-out.bmp ----------output file \r\n");
printf("128 --------------------- threshold low \r\n");
printf("255 --------------------- threshold high \r\n");
return -1;
}
printf("argv[1]=%s\r\n",argv[1]);
printf("argv[2]=%s,\r\n",argv[2]);
sprintf(u8PicNameRead,"%s",argv[1]);
sprintf(u8PicNameOut,"%s",argv[2]);
thresholdLow = atoi(argv[3]);
thresholdHigh = atoi(argv[4]);
printf("u8PicNameRead=%s\r\n",u8PicNameRead);
printf("thresholdLow =%d\r\n",thresholdLow);
printf("thresholdHigh =%d\r\n",thresholdHigh);
gettimeofday(&tStartTime, NULL);
//printf("tStartTime time.tv_sec = %d, time.tv_usec = %d.\r\n", tStartTime.tv_sec, tStartTime.tv_usec);
bmpBinarizationProccess(u8PicNameRead,u8PicNameOut,thresholdLow,thresholdHigh,mode);
gettimeofday(&tEndTime, NULL);
if(tEndTime.tv_sec >= tStartTime.tv_sec)
{
isecond = tEndTime.tv_sec-tStartTime.tv_sec;
}
if(tEndTime.tv_usec >= tStartTime.tv_usec)
{
iusecond = tEndTime.tv_usec-tStartTime.tv_usec;
}
else
{
isecond--;
iusecond = tEndTime.tv_usec-tStartTime.tv_usec + 1000000;
}
//printf("tEndTime time.tv_sec = %d, time.tv_usec = %d.\r\n", tEndTime.tv_sec, tEndTime.tv_usec);
printf("make Binarization use time tv_sec=%ds, ms=%d, tv_usec=%dus\r\n",isecond,iusecond/1000,iusecond);
printf("u8PicNameOut=%s\r\n",u8PicNameOut);
return 0;
}
编译程序
编译命令如下
gcc testBinarization.c -o testBinarization.bin
执行完上述命令之后,会生成testBinarization.bin文件,后面执行程序时需要该文件。

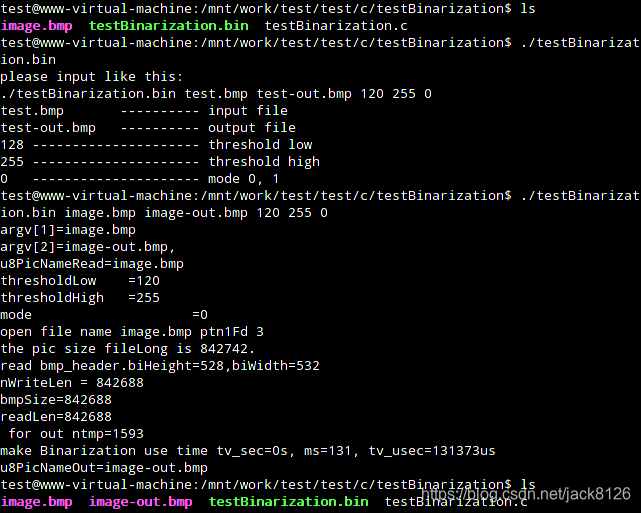
执行程序
使用如下命令执行程序,可将bmp图片转换为灰度图片。
./testBinarization.bin image.bmp image-out.bmp 120 255 0
./testBinarization.bin image.bmp image-out-2.bmp 120 255 1
执行完上述命令后,生成image-out.bmp和image-out-2.bmp文件。

原图

二值化图

二值化图2
