目录
1 对象的初始化和清理

1.1 构造函数和析构函数



#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
#include<string>
//对象的初始化和清理
//1、构造函数 进行初始化操作
class Person
{
//1.1 、构造函数
//没有返回值 不用写void
//函数名 与类名相同
//构造函数可以有参数,可以发生重载
//创建对象的时候,构造函数会自动调用,而且只调用一次
Person()
{
cout << "Person构造函数的调用" << endl;
}
//2、析构函数 进行清理的操作
//没有返回值 不写void
//函数名和类名相同 在名称前加~
//析构函数不可以有参数的,不可以发生重载
//对象在销毁前 会自动调用析构函数,而且只会调用一次
~Person()
{
cout << "Person的析构函数调用" << endl;
}
};
//构造和析构都是必须有的实现,如果我们自己不提供,编译器会提供一个空实现的构造和析构
void test01()
{
Person p;//在栈上的数据,test01执行完毕后,释放这个对象
}
int main()
{
test01();
system("pause");
return 0;
}
1.2 构造函数的分类以及调用

#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
#include<string>
//1 构造函数的分类及调用
//分类
// 按照参数分类 无惨构造(默认构造)和有参构造
// 按照类型分类 普通构造和拷贝构造
class Person
{
public:
//构造函数
Person()
{
cout << "Person的无参构造函数调用" << endl;
}
Person(int a)
{
age = a;
cout << "Person的有参构造函数调用" << endl;
}
//拷贝构造函数
Person(const Person& p)
{
//将传入的人身上的所有属性,拷贝到我身上
age = p.age;
cout << "Person的拷贝构造函数调用" << endl;
}
~Person()
{
cout << "Person的析构函数调用" << endl;
}
int age;
};
//调用
void test01()
{
//1、括号法
Person p1;//默认构造函数
Person p2(10);//有参构造函数
Person p3(p2);//拷贝构造函数
//注意事项
//调用默认构造函数时候,不要加()
//因为下面这行代码,编译器胡认为是一个函数的声明,不会认为在创建对象
//Person p1();
//2、显示法
Person p1;
Person p2 = Person(10);//有参构造
Person p3 = Person(p2);//拷贝构造
Person(10);//匿名对象 特点:当前行执行结束后,系统会立即回收掉匿名对象
//注意事项2
//不要利用拷贝构造函数 初始化匿名对象 编译器会认为Person(p3) == Person p3;对象声明
//Person(p3);
//3、隐视转换法
Person p4 = 10; //相当于 写了 Person p4 =Person(10); 有参构造
Person p5 = p4;//拷贝构造
}
int main()
{
system("pause");
return 0;
}
1.3 拷贝构造函数调用时机

#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
#include<string>
// 拷贝构造函数调用时机
// 1、使用一个已经创建完毕的对象来初始化一个新对象
//2、值传递的方式给函数参数传值
//3、值方式返回局部对象
class Person
{
public:
Person()
{
cout << "Person默认构造函数调用" << endl;
}
Person(int age)
{
cout << "Person有参构造函数调用" << endl;
m_Age = age;
}
Person(const Person &p)
{
cout << "Person拷贝构造函数调用" << endl;
m_Age = p.m_Age;
}
~Person()
{
cout << "Person析构函数调用" << endl;
}
int m_Age;
};
// 1、使用一个已经创建完毕的对象来初始化一个新对象
void test0111()
{
Person p1(20);
Person p2(p1);
}
//2、值传递的方式给函数参数传值
void dowork(Person p)
{
}
void test02()
{
Person p;
dowork(p);
}
//3、值方式返回局部对象
Person doWork2()
{
Person p1;
return p1;
}
void test03()
{
Person p = doWork2();
}
int main()
{
//test0111();
//test02();
test03();
system("pause");
return 0;
}
1.4 构造函数调用规则

#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
#include<string>
//构造函数的调用规则
//1、创建一个类,c++编译器会给每个类都添加至少3个函数
//默认构造(空实现)
//析构函数(空实现)
//拷贝构造(值拷贝)
//2、如果我们写了有参构造函数,编译器就不再提供默认构造,依然提供拷贝构造
//如果我们写了拷贝构造函数,编译器就不再提供其他普通构造函数了
class Person
{
public:
Person()
{
cout << "Person的默认构造函数调用" << endl;
}
Person(int age)
{
cout << "Person的有参构造函数调用" << endl;
m_Age = age;
}
/*Person(const Person& p)
{
cout << "Person的拷贝构造函数调用" << endl;
m_Age = p.m_Age;
}*/
~Person()
{
cout << "Person的析构函数调用" << endl;
}
int m_Age;
};
void test01()
{
Person p;
p.m_Age = 18;
Person p2(p);
cout << "p2的年龄为:" << p2.m_Age << endl;
}
void test02()
{
}
int main()
{
//test01();
system("pause");
return 0;
}
1.5 深拷贝与浅拷贝

#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
#include<string>
//深拷贝与浅拷贝
class Person
{
public:
Person()
{
cout << "Person的默认构造函数调用" << endl;
}
Person(int age,int height)
{
m_Height = new int(height);
m_Age = age;
cout << "Person的有参构造函数调用" << endl;
}
//自己实现拷贝构造函数 解决拷贝带来的问题
Person(const Person& p)
{
cout << "Person拷贝构造函数调用" << endl;
m_Age = p.m_Age;
//m_Height=p.m_Height;编译器默认实现就是这行代码
//深拷贝操作
m_Height = new int(*p.m_Height);
}
~Person()
{
//析构代码,将堆区开辟数据做释放操作;
if (m_Height != NULL)
{
delete m_Height;
m_Height = NULL;
}
cout << "Person的析构构造函数调用" << endl;
}
int m_Age;
int* m_Height;
};
void test001()
{
Person p1(18,160);
cout << "p1的年龄为:" << p1.m_Age<<"身高为"<<*p1.m_Height << endl;
Person p2(p1);
cout << "p2的年龄为:" << p2.m_Age << "身高为" << *p2.m_Height << endl;
}
int main()
{
test001();
system("pause");
return 0;
}

1.6 初始化列表

#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
#include<string>
//初始化列表
class Person
{
public:
//传统初始化操作
//Person(int a, int b, int c)
//{
// m_A = a;
// m_B = b;
// m_C = c;
//}
//初始化列表初始化属性
Person(int a,int b,int c) :m_A(a), m_B(b), m_C(c)
{
}
void test01()
{
Person p(30,20,10);
}
int m_A;
int m_B;
int m_C;
};
int main()
{
system("pause");
return 0;
}
1.7 类对象作为类成员

#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
#include<string>
//类对象作为类成员
//手机类
class Phone
{
public:
Phone(string pName)
{
m_PName = pName;
cout << "Phone 构造函数" << endl;
}
~Phone()
{
cout << "Phone 析构函数" << endl;
}
string m_PName;
};
class Person
{
public:
//Phoen m_Phone =pName 隐式转换法
Person(string name, string pName) :m_Name(name), m_Phone(pName)
{
cout << "Person构造函数" << endl;
}
~Person()
{
cout << "Person析构函数" << endl;
}
//姓名
string m_Name;
//手机
Phone m_Phone;
};
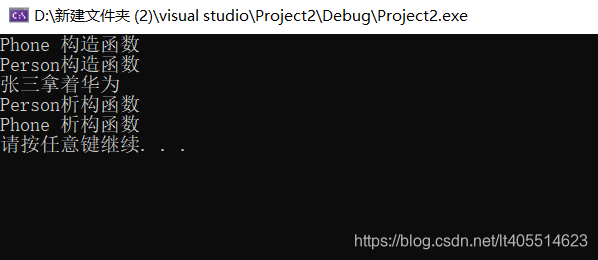
//当其他类对象作为本类成员,构造时候先构造类对象,再构造自身,析构的顺序与构造相反
void test011()
{
Person p ("张三", "华为");
cout << p.m_Name << "拿着" << p.m_Phone.m_PName << endl;
}
int main()
{
test011();
system("pause");
return 0;
}
1.8 静态成员

#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
#include<string>
//静态成员函数
//所有对象共享同一个函数
//静态成员函数只能访问静态成员变量
class Person
{
public:
//静态成员函数
static void func()
{
m_A = 100;//静态成员函数可以访问 静态成员变量
//m_B = 200;//静态成员函数 不可以访问 费静态成员变量,无法区分到底是那个对象的m_B属性
cout << "static void func 调用" << endl;
}
static int m_A;//静态成员变量
int m_B;//非静态成员变量
private:
//静态成员函数也是有访问权限的
static void func2()
{
cout << "func2调用" << endl;
}
};
void test011()
{
//1、通过对象访问
Person p;
p.func();
//2、通过类名访问
Person::func();
//Person::func2();//私有权限访问不到
}
int main()
{
test011();
system("pause");
return 0;
}
2 C++对象模型和this指针
2.1 成员变量和成员函数分开存储

#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
#include<string>
// 成员变量和 成员函数 分开存储的
class Person
{
int m_A;//非静态成员变量 属于类的对象上
static int m_B;//静态成员变量 不属于类对象上
void func(){}//非静态成员函数 不属于类对象上
static void func2(){}//静态成员函数 不属于类的对象上
};
int Person::m_B = 0;
void test011() {
Person p;
//空对象占用内存空间: 1
//C++编译器会给每一个空对象也分配一个字节空间,是为了区分空对象占用内存的位置
//每一个空对象也应该有一个独一无二的内存地址
cout << "size of p=" << sizeof(p) << endl;
}
void test02() {
Person p;
cout << "size of p=" << sizeof(p) << endl;
}
int main()
{
system("pause");
return 0;
}
2.2 this指针概念

#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
#include<string>
class Person
{
public:
Person(int age)
{
//this指针指向被调用的成员函数所属的对象
this->age = age;
}
int age;
Person& PersonAddAge(Person& p)
{
this->age += p.age;
//this指向p2的指针,而*this指向的就是P2这个对象本体
return *this;
}
};
//1、 解决名称冲突
void test001()
{
Person p1(18);
cout << "p1的年龄为:" << p1.age << endl;
}
//2 返回对象本身用 *this
void test02()
{
Person p1(10);
Person p2(10);
//链式编程思想
p2.PersonAddAge(p1).PersonAddAge(p1).PersonAddAge(p1);
cout << "p2的年龄为:" << p2.age << endl;
}
int main()
{
test02();
system("pause");
return 0;
}
2.3 空指针访问成员函数

#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
#include<string>
// 空指针调用成员函数
class Person {
public:
void showClassName() {
cout << "this is Person class" << endl;
}
void showPersonAge()
{
//报错原因是因为传入的指针是为NULL
if (this == NULL)
{
return;
}
cout << "agw=" << m_Age << endl;
}
int m_Age;
};
void test011()
{
Person* p = NULL;
p->showClassName();
p->showPersonAge();
}
int main()
{
system("pause");
return 0;
}
2.4 const修饰成员函数

#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
#include<string>
//常函数
class Person
{
public:
//this指针的本质 是指针常量 指针的指向是不可以修改的
//const Person * const this;
//在成员函数后面加const,修饰的是this指向,让指针指向的值也不可以修改
void showPerson() const
{
this->m_B = 100;
//this->m_A=100;
//this=NULL;//this指针不可以修改指针的指向的
}
void func()
{
}
int m_A;
mutable int m_B;//特殊变量,即使在常函数中,也可以修改这个值,加关键字mutable
};
//常对象
void test02()
{
const Person p;//在对象前加const,变为常对象
//p.m_A=100;
p.m_B = 100;//m_B是特殊值,在常对象下也可以修改
//常对象只能调用常函数
p.showPerson();
//p.func();//常对象 不可以调用普通成员函数,因为普通成员函数可以修改属性
}
int main()
{
system("pause");
return 0;
}
2.5 友元

//全局函数做友元
//建筑类
class Building
{
//goodGay全局函数是Building好朋友,可以访问Building中私有函数
friend void goodGay(Building* building);
public:
Building()
{
m_SittingRoom = "客厅";
m_BedRoom = "卧室";
}
public:
string m_SittingRoom;//客厅
private:
string m_BedRoom;//卧室
};
//全局函数
void goodGay(Building* building)
{
cout << "好基友全局函数 正在访问:"<< building->m_SittingRoom << endl;
cout << "好基友全局函数 正在访问:" << building->m_BedRoom << endl;
}
void test01()
{
Building building;
goodGay(&building);
}
//类做友元
class Building;
class GoodGay {
public:
GoodGay();
void visit();//参观函数 访问Building中的属性
Building* building;
};
class Building {
//GoodGay类是本类的好朋友,可以访问本类中私有成员
friend class GoodGay;
public:
Building();
public:
string m_SittingRoom;
private:
string m_BedRoom;
};
//类外写成员函数
Building::Building()
{
m_SittingRoom = "客厅";
m_BedRoom = "卧室";
}
GoodGay::GoodGay()
{
//创建建筑物对象
building = new Building;
}
void GoodGay::visit()
{
cout << "好基友类正在访问:" << building->m_SittingRoom << endl;
cout << "好基友类正在访问:" << building->m_BedRoom << endl;
}
void test()
{
GoodGay gg;
gg.visit();
}
//成员函数做友元
class Building;
class GoodGay
{
public:
GoodGay();
void visit();//让visit函数可以访问Building中私有成员
void visit2();//让visit2函数不可以访问Building中私有成员
Building* building;
};
class Building
{
//告诉编译器 GoodGay类下的visit成员函数作为本类的好朋友,可以访问私有成员
friend void GoodGay::visit();
public:
Building();
public:
string m_SittingRoom;//客厅
private:
string m_BedRoom;//卧室
};
//类外实现成员函数
Building::Building()
{
m_SittingRoom = "客厅";
m_BedRoom = "卧室";
}
GoodGay::GoodGay()
{
building = new Building;
}
void GoodGay::visit()
{
cout << "visit 函数正在访问:" << building->m_SittingRoom << endl;
cout << "visit 函数正在访问:" << building->m_BedRoom << endl;
}
void GoodGay::visit2()
{
cout << "visit 函数正在访问:" << building->m_SittingRoom << endl;
}
int main()
{
}
2.6 运算符重载

2.6.1 加号运算符重载

//加号运算符重载
class Person
{
public:
//1、成员函数重载+号
Person operator+(Person& p)
{
Person temp;
temp.m_A = this->m_A + p.m_A;
temp.m_B = this->m_B + p.m_B;
return temp;
}
int m_A;
int m_B;
};
void test01()
{
Person p1;
p1.m_A = 10;
p1.m_B = 10;
Person p2;
p2.m_A = 10;
p2.m_B = 10;
Person p3 = p1 + p2;
cout << "p3.m_A=" << p3.m_A << endl;
cout << "p3.m_B=" << p3.m_B << endl;
}
int main()
{
test01();
}
//加号运算符重载
class Person
{
public:
int m_A;
int m_B;
};
//2、全局函数重载+号
Person operator+(Person& p1, Person& p2)
{
Person temp;
temp.m_A = p1.m_A + p2.m_A;
temp.m_B = p1.m_B + p2.m_B;
return temp;
}
void test01()
{
Person p1;
p1.m_A = 10;
p1.m_B = 10;
Person p2;
p2.m_A = 10;
p2.m_B = 10;
Person p3 = p1 + p2;
cout << "p3.m_A=" << p3.m_A << endl;
cout << "p3.m_B=" << p3.m_B << endl;
}
int main()
{
test01();
}
//成员函数重载本质调用
//Person p3=p1.operator+(p2);
//全局函数重载本质调用
//Person p3=operator+(p1,p2);
2.6.2 左移运算符重载
作用:可以输出自定义数据类型
class Person
{
public:
//利用成员函数重载 左移运算符 p.operator<<(cout) 简化版本 p<<cout
//不会利用成员函数重载 <<运算符,因为无法实现 cout在左侧
//void operator<<(cout )
int m_A;
int m_B;
};
//只能利用全局函数重载左移运算符
ostream& operator<<(ostream & cout, Person& p) //本质 operator<<(cout,p) 简化 cout<<p
{
cout << "m_A=" << p.m_A << " m_B=" << p.m_B;
return cout;
}
void test01()
{
Person p;
p.m_A = 10;
p.m_B = 10;
cout << p << endl;;
}
int main()
{
test01();
}
//总结 :重载左移运算符配合友元可以实现输出自定义数据型
2.6.3 递增运算符重载
作用:通过重载递增运算符,实现自己的整型数据。
//重载递增运算符
//自定义整型
class MyInteger
{
friend ostream& operator<<(ostream& cout, MyInteger myint);
public:
MyInteger()
{
m_Num = 0;
}
//重载前置++运算符 返回引用是为了一直对一个数据进行递增操作
MyInteger& operator++()
{
//先进行++
m_Num++;
return *this;
}
//重载后置++运算符
//void operator++(int) int 代表占位参数,可以用于区分前置和后置递增
MyInteger operator++(int) // 局部对象 在函数执行完就释放掉了,所以返回的是值
{
//先 记录当时结果
MyInteger temp = *this;
//后 递增
m_Num++;
//最后将记录结果做返回
return temp;
}
private:
int m_Num;
};
//重载<<运算符
ostream& operator<<(ostream& cout, MyInteger myint)
{
cout << myint.m_Num;
return cout;
}
void test01()
{
MyInteger myint;
cout << ++myint << endl;
}
void test02()
{
MyInteger myint2;
cout << myint2++ << endl;
cout << myint2 << endl;
}
int main()
{
test01();
}
//总结: 前置递增返回的是引用,后置递增返回的是值
2.6.4 赋值运算符重载

//赋值运算符重载
class Person
{
public:
Person(int age)
{
m_Age = new int(age);
}
~Person()
{
if (m_Age != NULL)
{
delete m_Age;
m_Age = NULL;
}
}
//重载 赋值运算符
Person& operator=(Person& p)
{
//编译器是提供浅拷贝
//m_Age=p.m_Age;
//应该先判断是否有属性在堆区,如果有先释放干净,然后在深拷贝
if (m_Age != NULL)
{
delete m_Age;
m_Age = NULL;
}
//深拷贝
m_Age = new int(*p.m_Age);
//返回对象本身
return *this;
}
int* m_Age;
};
void test01()
{
Person p1(18);
Person p2(20);
Person p3(30);
p3=p2 = p1;//赋值运算
cout << "P1的年龄为:" << *p1.m_Age << endl;
cout << "P2的年龄为:" << *p2.m_Age << endl;
}
2.6.5 关系运算符

// 重载关系运算符
class Person
{
public:
Person(string name, int age)
{
m_Name = name;
m_Age = age;
}
//重载 == 号
bool operator==(Person& p)
{
if (this->m_Name == p.m_Name && this->m_Age == p.m_Age)
{
return true;
}
return false;
}
bool operator !=(Person& p)
{
if (this->m_Name == p.m_Name && this->m_Age == p.m_Age)
{
return false;
}
return true;
}
string m_Name;
int m_Age;
};
void test01()
{
Person p1("Tom", 18);
Person p2("Tom", 18);
if (p1 == p2)
{
cout << "p1和p2是相等的!" << endl;
}
else
{
cout << "p1和p2是不相等的!" << endl;
}
if (p1 != p2)
{
cout << "p1和p2不是相等的!" << endl;
}
else
{
cout << "p1和p2是相等的" << endl;
}
}
int main()
{
test01();
return 0;
}
2.6.6 函数调用运算符重载

// 函数调用运算符重载
//打印输出类
class MyPrint
{
public:
//重载函数调用运算符
void operator()(string test)
{
cout << test << endl;
}
};
void MyPrint02(string test)
{
cout << test << endl;
}
void test01()
{
MyPrint myprint;
myprint("hello world");//由于使用起来非常类似于函数调用,因此称为仿函数
MyPrint02("hello world");
}
//仿函数非常灵活 ,没有固定写法
//加法类
class MyAdd
{
public:
int operator()(int num1, int num2)
{
return num1 + num2;
}
};
void test02()
{
MyAdd myadd;
int ret = myadd(100, 100);
cout << "ret=" << ret << endl;
//匿名函数对象
cout << MyAdd()(100, 100) << endl;
}
int main()
{
test01();
test02();
return 0;
}