@TOCC++三种继承方式:
先看一张继承关系表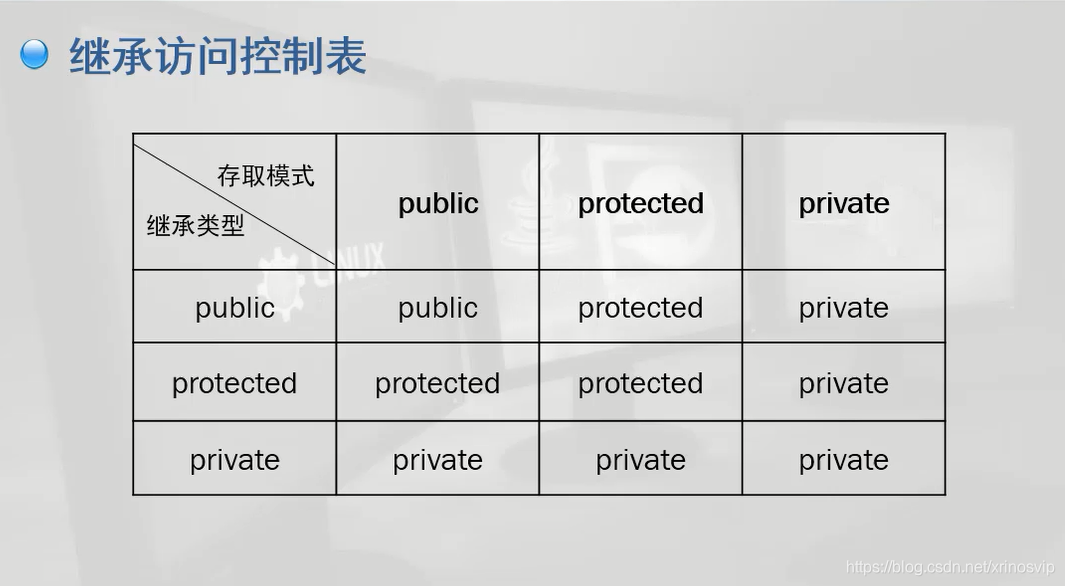
三种继承方式:
1.首先说明一点:类实例(即类对象)不能直接访问类的 private成员和protected成员,但是能直接访问类的public成员。
2.另外无论哪种继承方式,子类都不能直接访问父类的 private成员;但是能直接访问父类的 protected成员和public成员(注意:是子类,而不是类实例),并且能通过父类的protected成员函数和public成员函数间接访问父类的private成员;这句话强调了类与类之间通过继承方式的访问规则,而非类与实例之间的访问规则。
3.子类通过public方式继承父类,则父类中的public、protected和private属性的成员在 子类 中 依次 是 public、protected和private属性,即通过public继承并不会改变父类原来的数据属性。
4.子类通过protected方式继承父类,则父类中的public、protected和private属性的成员在 子类 中 依次 是 protected、protected和private属性,即通过protected继承原来父类中public属性降级为子类中的protected属性,其余父类属性在子类中不变。
5.子类通过private方式继承父类,则父类中的public、protected和private属性的成员在 子类 中 依次 是 private、private和private属性,即通过private继承原来父类中public属性降级为子类中的private属性,protected属性降级为子类中的private属性,其余父类属性在子类中不变。
注意: 其实父类的原属性并未改变,只是通过 继承关系被继承到子类中的父类成员的个别属性有所变化 ,即只是在子类中父类的个别成员属性降级了,原来父类的成员属性并未变。
code如下:
类声明的头文件 heritage.h
//
// Created by ZP on 2021/7/28.
//
#ifndef HERITAGE_HERITAGE_H
#define HERITAGE_HERITAGE_H
class A{
private:
int a;
protected:
int b;
public:
int c;
A(int A, int B, int C);
~A();
void set(int val_a, int val_b, int val_c);
int get_a() const;
int get_b() const;
int get_c() const;
};
class B{
private:
int x;
protected:
int y;
public:
int z;
B();
~B();
void set(int &val_x, int &val_y, int &val_z);
int get_x() const;
int get_y() const;
int get_z() const;
};
class C{
private:
int u;
protected:
int v;
public:
explicit C(int U = 10, int V = 18);
~C();
void set(int val_u, int val_v);
void set(int &val_u);
int get_uv() const;
};
// public heritage
class D: public A{
private:
int m_total;
public:
D(int v1, int v2, int v3): A(v1, v2, v3){
m_total= 0;
}
~D()= default;
inline int add() {
// m_total = c + b + A::get_a(); // a is class A's private value.
m_total = c + b + get_a();
return m_total;
}
};
// protected heritage
class E: protected B{
private:
int m_tesult;
public:
E(): B(){
m_tesult = 0;
}
~E() = default;
void get_xyz() const;
// 要修改 B 的私有变量 x ,则要调用 B 类 的set方法或者声明一个类E的成员函数为类B的友元函数, 从而访问 private value.
void set_xyz(int X, int Y, int Z);
inline int mul(){
m_tesult = y * z * get_x(); // x is private value
return m_tesult;
}
};
// private heritage
class F: private C{
private:
int m_result;
public:
F(int v1, int v2): C(v1, v2){
m_result = 0;
}
~F() = default;
void set_uv(int U, int V);
inline int product(){
return get_uv();
}
};
#endif //HERITAGE_HERITAGE_H
头文件heritage.h的实现代码 heritage.cpp
//
// Created by ZP on 2021/7/28.
//
#include <iostream>
#include "heritage.h"
using namespace std;
// class A implement
A::A(int A, int B, int C):a(A), b(B), c(C){
}
A::~A() {
}
void A::set(int val_a, int val_b, int val_c) {
this->a = val_a;
this->b = val_b;
this->c = val_c;
}
int A::get_a() const {
return a;
}
int A::get_b() const {
return b;
}
int A::get_c() const {
return c;
}
// class B
B::B() {
x = 0;
y = 1;
z = 2;
}
B::~B() = default;
void B::set(int &val_x, int &val_y, int &val_z) {
this->x = val_x;
this->y = val_y;
this->z = val_z;
}
int B::get_x() const {
return x;
}
int B::get_y() const {
return y;
}
int B::get_z() const {
return z;
}
// class C
C::C(int U, int V): u(U), v(V) {
}
C::~C() = default;
void C::set(int val_u, int val_v) {
this->u = val_u;
this->v = val_v;
}
void C::set(int &val_u) {
this->u = val_u;
}
int C::get_uv() const {
return u * v;
}
// class E
void E::get_xyz() const {
cout << "x: " << get_x() << "\ty: " << y << "\tz: " << z << endl;
}
void E::set_xyz(int X, int Y, int Z){
set(X, Y, Z);
}
// class F
void F::set_uv(int U, int V) {
v = V; // private heritage, 但是还是能在子类内部 直接使用 父类的 protected value
set(U); // private heritage, 但是还是能在子类内部 直接使用 父类的 public function
}
主函数代码 main.cpp
//
// Created by ZP on 2021/7/28.
//
#include <iostream>
#include "heritage.h"
using std::cout;
using std::endl;
int main(){
A a(100, 200, 300);
cout << "a: " << a.get_a() << "\tb: " << a.get_b() << "\tc: " << a.get_c() << endl;
// 实例a 能直接访问 类A 的 public value, 但是不能直接访问 protected and private 变量,要想访问,需通过成员函数访问
cout << "public c: \t" << a.c << endl;
cout << endl;
B b;
cout << "x: " << b.get_x() << "\ty: " << b.get_y() << "\tc: " << b.get_z() << endl;
cout << "public z: \t" << b.z << endl; // public value 破坏了 类的数据隐藏封装特性。
cout << endl;
C c;
cout << "u*v: " << c.get_uv()<< endl;
cout << endl;
// class D public heritage
D d(10, 20, 30);
cout << "d: " << d.get_a() << "\t" << d.get_b() << "\t" << d.get_c() << endl;
cout << "d_total: " << d.add() << endl;
d.set(12, 13, 14);
cout << "d-set: " << d.get_a() << "\t" << d.get_b() << "\t" << d.get_c() << endl;
cout << "d_total: " << d.add() << endl;
cout << "d heritage class A's public c: \t" << d.c << endl;
cout << endl;
// class E protected heritage
E e;
e.get_xyz();
cout << "e_product: " << e.mul() << endl;
e.set_xyz(1, 2, 3);
e.get_xyz();
cout << "e_product: " << e.mul() << endl;
// 实例 不能直接访问 heritage class 的 public value, 因为被继承的 public value 变成了 protected value。
// e.z
cout << endl;
F f(50, 100);
// private u, protected v;public set函数 通过 private heritage 后,全部为 private, 类实例 不能 直接访问
// f.set(10, 10);
// f.u;
// f.v;
cout << "f_product: " << f.product() << endl;
f.set_uv(50, 50);
cout << "f_product set_uv: " << f.product() << endl;
return 0;
}
运行结果:
E:\programme\C_C++\CLion\C++\Exercise\heritage\cmake-build-debug\heritage.exe
a: 100 b: 200 c: 300
public c: 300
x: 0 y: 1 c: 2
public z: 2
u*v: 180
d: 10 20 30
d_total: 60
d-set: 12 13 14
d_total: 39
d heritage class A's public c: 14
x: 0 y: 1 z: 2
e_product: 0
x: 1 y: 2 z: 3
e_product: 6
f_product: 5000
f_product set_uv: 2500
Process finished with exit code 0