??图的生成树是图的最小连通子图,包含了图里所有顶点,但仅含有比顶点数小1 的边数。边数再小将不连通,边数再多一条,则顶点间将有多条路径。生成树里的边的权值之和最小的树叫做最小生成树。最小生成树有着实际应用与意义。比如权值对应路程,则对应路程最短,施工造价最小。
??如何找到一个最小生成树呢?
??至此,为了纪念这位伟大的科学家,Prim,我们将他提出的查找最小生成树的算法叫做prim算法,也叫普里姆算法。
??该算法依据的核心定理是:将图里顶点分成两个集合,则连接这两个顶点集合的边中,边的权值最小的边,一定出现在最小生成树里。
??依据这条定理,我们就可以从无到有,把最小生成树的边一条一条建立起来。两个顶点集分别是已建立MST里的顶点,和未进入MST的顶点。MST : mininmal spanning tree最小生成树。
??感谢bilibi懒猫老师的精彩讲解。
??要不然这个算法的核心真不好懂。课本里所有每一行代码都认识,连接起来就一团乱麻了。知其所以然后,很容易知其然了。
??图由邻接矩阵存储,给出图的所有信息。MST则用边集数组存储,所谓边集数组,就是给边建立对应的结构体变量,包含边的两个顶点和权值。所有边组成边的数组,给出图里所有边的信息。MST可以直接输出所有的边的信息。
??函数primSolutionMST:prim算法解决方案建立最小生成树。
??main函数所在源文件代码:
#include<iostream>
#include<stdio.h>
using namespace std;
#define MAXVERTEX 15
#define INFINI 65555
struct GraphAdjaMatrix {
char vertexes[MAXVERTEX];
int edges[MAXVERTEX][MAXVERTEX];
int numVertexes;
int numEdges;
};
struct Edge {
int indexA;
int indexB;
int weightAB;
};
struct GraphEdgeSetArray {
int vertexNum;
int edgeNum;
char vertexes[MAXVERTEX];
Edge edges[MAXVERTEX];
};
extern void createGraphAdjMatrix(GraphAdjaMatrix &graphAdjMatrix,
int numVertexes,int numEdges,int edges[][6],char vertexes[]);
extern void dispalyGraphAdjMatrix(GraphAdjaMatrix &graphAdjMatrix);
extern void primSolutionMST(GraphAdjaMatrix& graphAdjMatrix,
GraphEdgeSetArray & graphMST,int indexStart);
int main() {
GraphAdjaMatrix graphAdjMatrix ;
int numVertexes = 6, numEdges = 10;
int edges[][6] = { {0,34,46,INFINI,INFINI,19},
{34,0,INFINI,INFINI,12,INFINI},
{46,INFINI,0,17,INFINI,25},
{INFINI,INFINI,17,0,38,25},
{INFINI,12,INFINI,38,0,26},
{19,INFINI,25,25,26,0} };
char vertexes[] = {'a','b','c','d','e','f'};
createGraphAdjMatrix(graphAdjMatrix,numVertexes,numEdges,edges,vertexes);
dispalyGraphAdjMatrix(graphAdjMatrix);
cout << endl;
GraphEdgeSetArray graphMST;
primSolutionMST(graphAdjMatrix,graphMST,3);
cout << "its minimal spanning tree is as following :" << endl;
for (int i = 0; i < graphMST.edgeNum; i++) {
cout << '(' << graphMST.vertexes[graphMST.edges[i].indexA] << ',';
cout << graphMST.vertexes[graphMST.edges[i].indexB] << ')';
cout << graphMST.edges[i].weightAB;
cout << " ";
cout << '(' <<graphMST.edges[i].indexA << ',';
cout << graphMST.edges[i].indexB << ')';
cout << graphMST.edges[i].weightAB << endl;;
}
return 0;
}
各函数所在源文件代码:
#include<iostream>
#include<stdio.h>
using namespace std;
#define MAXVERTEX 15
#define INFINI 65555
struct GraphAdjaMatrix {
char vertexes[MAXVERTEX];
int edges[MAXVERTEX][MAXVERTEX];
int numVertexes;
int numEdges;
};
struct Edge {
int indexA;
int indexB;
int weightAB;
};
struct GraphEdgeSetArray {
int vertexNum;
int edgeNum;
char vertexes[MAXVERTEX];
Edge edges[MAXVERTEX];
};
void createGraphAdjMatrix(GraphAdjaMatrix &graphAdjMatrix,
int numVertexes, int numEdges, int edges[][6], char vertexes[]) {
graphAdjMatrix.numVertexes = numVertexes;
graphAdjMatrix.numEdges = numEdges;
for (int i = 0; i < numVertexes; i++)
graphAdjMatrix.vertexes[i] = vertexes[i];
for (int row = 0; row < numVertexes; row++)
for (int column = 0; column < numVertexes; column++)
graphAdjMatrix.edges[row][column] = edges[row][column];
}
void dispalyGraphAdjMatrix(GraphAdjaMatrix &graphAdjMatrix) {
cout << "adjacensy matrix :" << endl;
int row,column;
printf("%3c",' ');
for (row = 0; row < graphAdjMatrix.numVertexes; row++)
printf("%3c",graphAdjMatrix.vertexes[row]);
printf("\n");
for (row = 0; row < graphAdjMatrix.numVertexes; row++) {
printf("%-3c", graphAdjMatrix.vertexes[row]);
for (column = 0; column < graphAdjMatrix.numVertexes; column++)
if (graphAdjMatrix.edges[row][column] == INFINI)
printf("%3s", "∞");
else
printf("%3d",graphAdjMatrix.edges[row][column]);
cout << endl;
}
}
void primSolutionMST(GraphAdjaMatrix& graphAdjMatrix,
GraphEdgeSetArray& graphMST, int indexStart) {
Edge edgeShortest;
bool inMST[MAXVERTEX], outOfMST[MAXVERTEX];
for (int i = 0; i < graphAdjMatrix.numVertexes; i++) {
inMST[i] = false;
outOfMST[i] = true;
}
inMST[indexStart] = true;
outOfMST[indexStart] = false;
graphMST.vertexNum = graphAdjMatrix.numVertexes;
for (int i = 0; i < graphAdjMatrix.numVertexes; i++)
graphMST.vertexes[i] = graphAdjMatrix.vertexes[i];
graphMST.edgeNum = 0;
int indexInMST, indexOutOfMST;
while (graphMST.edgeNum <= graphMST.vertexNum - 1) {
edgeShortest.weightAB = INFINI;
edgeShortest.indexA = -1;
edgeShortest.indexB = 0;
for (indexInMST = 0; indexInMST < graphAdjMatrix.numVertexes; indexInMST++)
for (indexOutOfMST = 0; indexOutOfMST < graphAdjMatrix.numVertexes; indexOutOfMST++)
if ((indexInMST != indexOutOfMST)
&& (inMST[indexInMST] && outOfMST[indexOutOfMST]) &&
graphAdjMatrix.edges[indexInMST][indexOutOfMST] < edgeShortest.weightAB) {
edgeShortest.indexA = indexInMST;
edgeShortest.indexB = indexOutOfMST;
edgeShortest.weightAB = graphAdjMatrix.edges[indexInMST][indexOutOfMST];
}
graphMST.edges[graphMST.edgeNum] = edgeShortest;
graphMST.edgeNum++;
inMST[edgeShortest.indexB] = true;
outOfMST[edgeShortest.indexB] = false;
}
graphMST.edgeNum--;
}
对应的图及最小生成树如下:

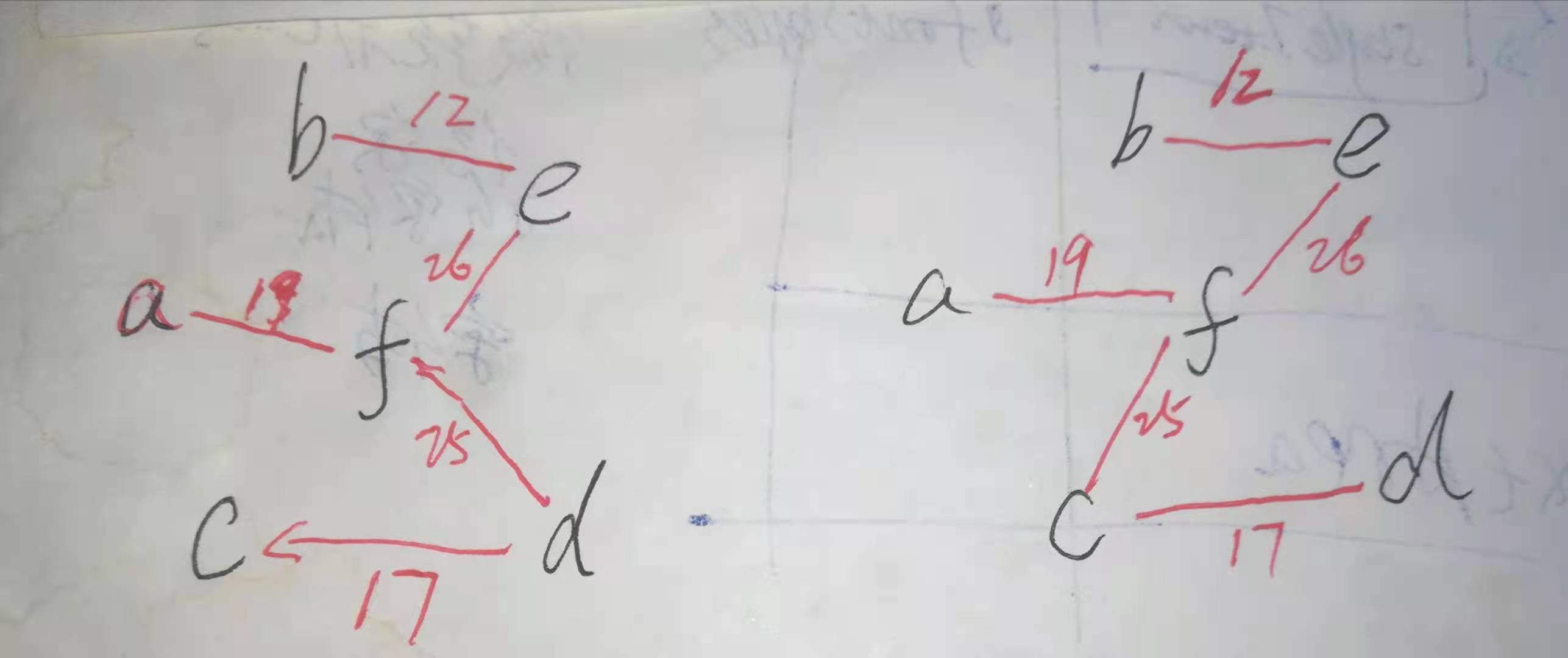
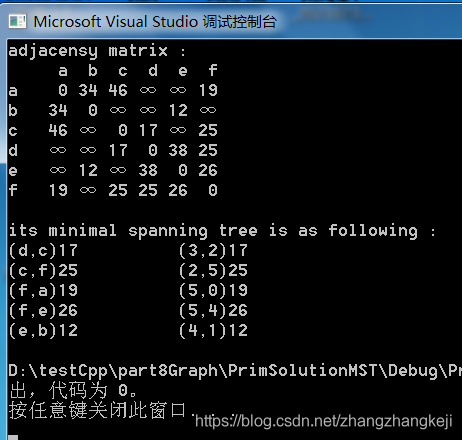
bilibnili懒猫老师的给出的结果如截图:
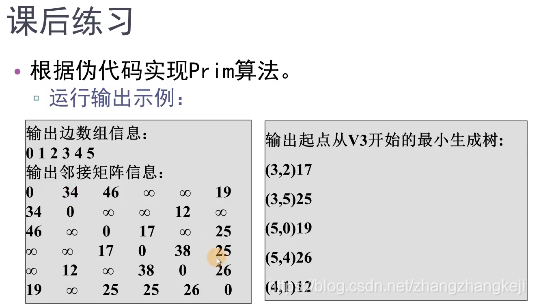
??可见得到的最小生成树并不一样,这是因为有权值相同的边造成的。但都是正确的,所以,最小生成树也不是唯一的。
谢谢阅读。