【C/C++基础进阶系列】C/C++ 基础知识 -- 内存模型简介与内存问题
【1】C/C++ 内存模型
C/C++ 内存模型图示
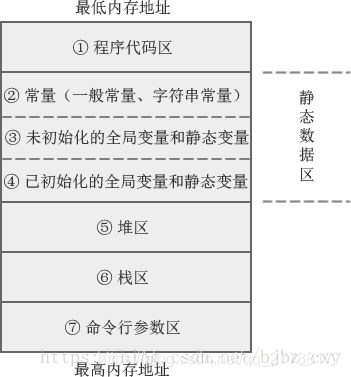
C/C++ 编译的程序占用的内存分为以下几个部分
- 1、栈区 (stack),由编译器自动分配释放,存放函数的参数值,局部变量的值等,其操作方式先入先出 (FILO)
- 2、堆区 (heap),由程序员分配释放,若程序员不释放,程序结束时可能由 OS 回收
- 3、数据区,主要包括静态全局区和常量区
- 全局区(静态区)(static),全局变量和静态变量的存储是放在一块的,程序结束后由系统释放
- 初始化的全局变量和静态变量在一块区域
- 未初始化的全局变量和未初始化的静态变量在相邻的另一块区域
- 常量区,常量字符串就是放在这里的,程序结束后由系统释放
- 全局区(静态区)(static),全局变量和静态变量的存储是放在一块的,程序结束后由系统释放
- 4、代码区,存放函数体的二进制代码
【2】内存相关问题的概念
内存泄漏
向系统申请分配内存进行使用 (new),但使用完了以后却未归还 (delete),结果该申请到的那块内存无法再访问,而系统也不能再次将该块内存分配给其他需要的程序;
- 1. 常发性内存泄漏,发生内存泄漏的代码会被多次执行到,每次被执行的时候都会导致一块内存泄漏
- 2. 偶发性内存泄漏,发生内存泄漏的代码只有在某些特定环境或操作过程下才会发生
- 3. 一次性内存泄漏,发生内存泄漏的代码只会被执行一次,或者由于算法上的缺陷,导致总会有一块仅且一块内存发生泄漏
- 4. 隐式内存泄漏,程序在运行过程中不停的分配内存,但是直到结束的时候才释放内存;
- 严格的说这里并没有发生内存泄漏,因为最终程序释放了所有申请的内存,但是对于一个服务器程序,需要运行几天,几周甚至几个月,不及时释放内存也可能导致最终耗尽系统的所有内存,因此称这类内存泄漏为隐式内存泄漏
内存溢出
要求分配的内存超出了系统能够提供的空间,系统不能满足需求,产生的溢出;
内存越界
向系统申请了一块内存,但在使用这块内存的时候,超出了所申请的范围
- 产生的后果
- 1. 破坏堆中的内存分配信息数据,特别是动态分配的内存块的内存信息数据
- 2. 破坏程序自己的其他对象的内存空间,这种破坏会影响程序执行的不正确性
- 3. 破坏了空闲内存块
缓冲区溢出
程序在运行过程中,为了临时存取数据的需要,一般都要分配一些内存空间,通常称这些空间为缓冲区;如果向缓冲区中写入超过其本身长度的数据,以致于缓冲区无法容纳,就会造成缓冲区以外的存储单元被改写,这种现象就称为缓冲区溢出;
栈溢出
栈溢出是缓冲区溢出的一种;
- 上溢,栈满时再做进栈操作必定产生空间溢出;
- 下溢,栈空时再做退栈操作也产生空间溢出;
产生原因
- 1. 局部数组过大
- 2. 递归调用层次太多,递归函数在运行时会执行压栈操作,当压栈次数太多时,也会导致栈溢出
- 3. 指针或数组越界
【3】Valgrind 的使用
【3.1】Valgrind 的消息输出格式
# valgrind du –x –s
.
.
// 在这个 12 字节的数组后面没有存储空间
==29404== Address 0x1189AD84 is 0 bytes after a block of size 12 alloc'd
// 内存是在 130 行 (vg_replace_malloc.c) 的 strdup() 程序中进行分配的
==29404== at 0xFFB9964: malloc (vg_replace_malloc.c:130)
// strdup() 是在 libc.so.6 库的 setlocale() 中调用的
==29404== by 0xFEE1AD0: strdup (in /lib/tls/libc.so.6)
// main() 调用了 setlocale()
==29404== by 0xFE94D30: setlocale (in /lib/tls/libc.so.6)
==29404== by 0x10001414: main (in /usr/bin/du)【3.2】使用未初始化的内存
{
int i[5];
if (i[0] == 0)
{
i[1] = 1;
}
return 0;
}
# gcc –g –o test1 test1.c
# valgrind ./test1
.
.
==31363==
// 依赖于文件 test1.c 中第 5 行中的一个未初始化的变量
==31363== Conditional jump or move depends on uninitialised value(s)
==31363== at 0x1000041C: main (test1.c:5)
==31363==
==31363== ERROR SUMMARY: 1 errors from 1 contexts (suppressed: 7 from 1)
==31363== malloc/free: in use at exit: 0 bytes in 0 blocks.
==31363== malloc/free: 0 allocs, 0 frees, 0 bytes allocated.
==31363== For counts of detected errors, rerun with: -v
==31363== No malloc'd blocks -- no leaks are possible.【3.3】内存泄漏
int main(void)
{
char *p1;
char *p2;
p1 = (char *) malloc(512);
p2 = (char *) malloc(512);
p1 = p2;
free(p1);
free(p2);
}
# gcc –g –o test2 test2.c
# valgrind ./test2
.
.
==31468== Invalid free() / delete / delete[]
==31468== at 0xFFB9FF0: free (vg_replace_malloc.c:152)
==31468== by 0x100004B0: main (test2.c:12)
// 报告了 512 字节的内存泄漏,可能出现的位置在 test2.c:11,test2.c:12 处
==31468== Address 0x11899258 is 0 bytes inside a block of size 512 free'd
==31468== at 0xFFB9FF0: free (vg_replace_malloc.c:152)
==31468== by 0x100004A4: main (test2.c:11)
==31468==
==31468== ERROR SUMMARY: 1 errors from 1 contexts (suppressed: 7 from 1)
==31468== malloc/free: in use at exit: 512 bytes in 1 blocks.
==31468== malloc/free: 2 allocs, 2 frees, 1024 bytes allocated.
==31468== For counts of detected errors, rerun with: -v
==31468== searching for pointers to 1 not-freed blocks.
==31468== checked 167936 bytes.
==31468==
==31468== LEAK SUMMARY:
==31468== definitely lost: 512 bytes in 1 blocks.
==31468== possibly lost: 0 bytes in 0 blocks.
==31468== still reachable: 0 bytes in 0 blocks.
==31468== suppressed: 0 bytes in 0 blocks.
==31468== Use --leak-check=full to see details of leaked memory.【3.4】内存的非法读写
int main() {
int i, *iw, *ir;
iw = (int *)malloc(10 * sizeof(int));
ir = (int *)malloc(10 * sizeof(int));
for ( i = 0; i < 11; i++)
{
// i = 10 处会产生非法写操作
iw[i] = i;
}
for (i = 0; i < 11; i++)
{
// i = 10 处会产生非法读操作
ir[i] = iw[i];
}
free(iw);
free(ir);
}
# gcc –g –o test3 test3.c
# valgrind ./test3
.
.
==31522== Invalid write of size 4
==31522== at 0x100004C0: main (test3.c:9)
// test3.c 的第 9 行发现一个非法的 4 字节写操作
==31522== Address 0x11899050 is 0 bytes after a block of size 40 alloc'd
==31522== at 0xFFB9964: malloc (vg_replace_malloc.c:130)
==31522== by 0x10000474: main (test10.c:4)
==31522==
==31522== Invalid read of size 4
==31522== at 0x1000050C: main (test3.c:12)
// test3.c 的在第 12 行发现一个非法的 4 字节读操作
==31522== Address 0x11899050 is 0 bytes after a block of size 40 alloc'd
==31522== at 0xFFB9964: malloc (vg_replace_malloc.c:130)
==31522== by 0x10000474: main (test10.c:4)
==31522==
==31522== ERROR SUMMARY: 2 errors from 2 contexts (suppressed: 7 from 1)
==31522== malloc/free: in use at exit: 0 bytes in 0 blocks.
==31522== malloc/free: 2 allocs, 2 frees, 84 bytes allocated.
==31522== For counts of detected errors, rerun with: -v
==31522== No malloc'd blocks -- no leaks are possible.【附录】C/C++ 避免内存泄漏的代码技巧简介
【附录 A-1】C/C++ 智能指针,参见博客,【C/C++基础进阶系列】C/C++ STL -- 智能指针
【附录 A-2】C/C++ 模板封装,参见 SRS 服务器 SrsAutoFree,博客?【网络通信 -- 直播】SRS 源码分析 -- 代码编写技巧总结
参考致谢
本博客为博主学习笔记,同时参考了网上众博主的博文以及相关专业书籍,在此表示感谢,本文若存在不足之处,请批评指正。
【1】C++ 新经典
【3】C语言内存模型