建立结构体声明
结构声明描述了一个结构的组织布局。
类似这样:
struct Student
{
char id[8];
char name[8];
char sex[4];
int age;
};
用一对花括号括起来的是结构成员列表,成员可以是任意一种C的数据类型,甚至可以是其他结构。右花括号后面的声明必不可少
该声明并未创建实际的数据对象,只描述了该对象由什么组成。也可以把结构声明称为模板,它现在并不占用存储空间。
定义结构变量
上面说的结构的声明只相当于图纸,下一步是创建结构变量:
struct Student Stud1;
这里Student的作用相当于一般声明中的int , float等。
内存示意图如下(先不考虑内存对齐问题):
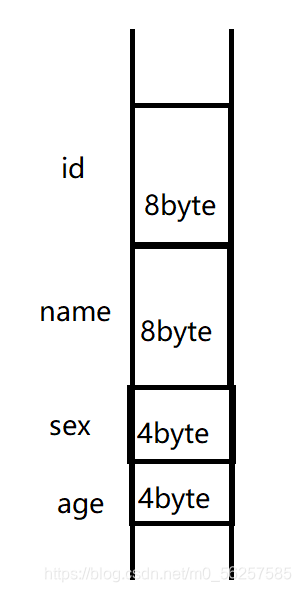
初始化结构
先来看初始化变量和数组:
int x = 0;
int ar[5] = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5};
结构体也可以这样初始化:
struct Student Stud1 =
{
"11001",
"Sauron",
"man",
18
};
访问结构体成员
使用结构成员运算符——点(.)访问结构中的成员。
例如:
scanf_s("%s", &Stud1.id);
本质来说, .id, .name , .sex这些的作用就相当于Stud1的下标。
结构的初始化器
结构的指定初始化器使用点运算符和成员名表示特定的元素。例如只初始化Stud1的name成员:
struct Student Stud1 =
{
.name = "Sauron"
};
结构数组
一般情况下不可能只处理一个学生的信息, 在处理多个学生时,每个学生都用Student类型的结构变量来表示。比如要处理学生的成绩,先设计一个结构体:
struct Student
{
char id[10];
char name[10];
double score[3];
};
然后声明Student类型结构的数组:
const int SIZE = 10;
struct Student Stud[SIZE];
内存示意图类似于此:
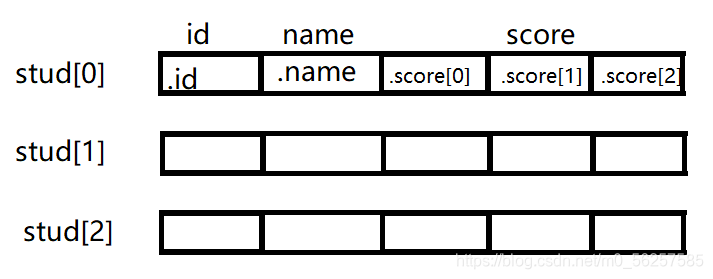
这样可以处理多个变量的信息
比如随便写一个查询学生成绩的代码:
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<string.h>
#include<assert.h>
#define SIZE 10
typedef struct Student
{
char id[10];
char name[10];
double score[3];
}Student;
void Init_Student(struct Student* pstud, int n); //初始化结构数组
void Search_Student(struct Student* pstud, int n); //查找学生
char* s_gets(char* st, int n);
int main()
{
struct Student Stud[SIZE];
int num = 0;
Init_Student(Stud, SIZE);
printf("Please enter students' number that you wanna search\n");
printf(" or enter q to quit: ");
while (scanf_s("%d", &num) == 1)
{
if (num > 10 || num < 0)
{
printf("Input error, please try again: ");
continue;
}
Search_Student(Stud, num - 1);
printf("Please enter next Students' number that you wanna search\n");
printf(" or enter q to quit: ");
}
printf("Program Exit!\n Bye.\n");
return 0;
}
void Init_Student(struct Student* pstud, int n)
{
assert(pstud != nullptr);
int i = 0, j = 0;
for (i = 0; i < n; ++i)
{
printf("Please input NO. %d student's info:\n", i + 1);
s_gets((pstud + i)->id, 10);
s_gets((pstud + i)->name, 10);
scanf_s("%lf %lf %lf", &pstud[i].score[0], &pstud[i].score[1], &pstud[i].score[2]);
}
}
void Search_Student(struct Student* pstud, int n)
{
assert(pstud != nullptr);
printf("NO. %d student's info:\n", n);
printf("ID: %-10s\n", (pstud + n)->id);
printf("Name: %-10s\n", (pstud + n)->name);
printf("Chinese: %lf\n", pstud[n].score[0]);
printf("Math: %lf\n", pstud[n].score[1]);
printf("English: %lf\n", pstud[n].score[2]);
}
char* s_gets(char* st, int n)
{
assert(st != nullptr);
char* ret_val = fgets(st, n, stdin);
char* find;
if (ret_val)
{
find = strchr(st, '\n');
if (find)
*find = '\0';
else
while (getchar() != '\n')
continue;
}
return ret_val;
}
指向结构的指针
声明结构指针:
struct Student* pstud;
声明的语法和其他类型指针声明一样
现在pstud可以指向现有的Student类型的结构,若stud1是一个Student类型的结构,则可以这样:
pstud = &stud1;
若指向一个结构数组,则:
pstud = stud;
或指向数组的第一个成员:
pstud = &stud[0];
用指针访问成员
最常用的方法:
使用->运算符。
有这样的关系:
若 pstud == & stud1;
则有 pstud->id 等价于 stud1.id
若 pstud == &stud[0];
则有 pstud->id 等价于 stud[0].id
向函数传递结构的信息
在以前的函数学习中,函数的参数可能是int, float这些类型的数字,也可能是一个地址。
ANSI C允许把结构作为参数传递给函数。
传递结构成员
例如:
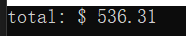
#include<stdio.h>
struct Money
{
double x;
double y;
};
double sum(double a, double b);
int main(void)
{
struct Money m = { 235.55, 300.76 };
printf("total: $ %5.2lf\n", sum(m.x, m.y));
return 0;
}
double sum(double a, double b)
{
return (a + b);
}
运行结果:
传递结构的地址
#include<stdio.h>
struct Money
{
double x;
double y;
};
double sum(struct Money* ptr);
int main(void)
{
struct Money m = { 235.55, 300.76 };
printf("total: $ %5.2lf\n", sum(&m));
return 0;
}
double sum(struct Money* ptr)
{
return (ptr->x + ptr->y);
}
这样输出的结果也肯定是和上面一样的。
传递结构
#include<stdio.h>
struct Money
{
double x;
double y;
};
double sum(struct Money n);
int main(void)
{
struct Money m = { 235.55, 300.76 };
printf("total: $ %5.2lf\n", sum(m));
return 0;
}
double sum(struct Money n)
{
return (n.x + n.y);
}
结构和结构指针的选择
编写一个与结构相关的函数, 若以结构作为参数和返回值,函数处理的是原始数据的副本,这样可以保护原始数据,代码风格也更加清楚。
若以结构指针为参数,程序执行起来会很快,因为传递的是地址。
缺点是若函数本意不是修改结构的数据,这样传递地址可能会导致影响原来结构中的数据。
所以如何选择, 要看函数的作用。