在接触了C一段时间后,我开始接触C++,C++更关注的是结构化,所以也第一次有了多文件编译的概念,而这次在重温C的过程中,我也第一次尝试和使用了多文件编译。
在C primer plus 关于这个介绍中,我自己的心得为以下三点:
- 函数声明与常量的定义言放在同一个头文件中,后缀名是.h,直接修改后缀名;
- 函数的原型(在以后更多是常用函数的原型)要放在一个源代码文件中,后缀名是.c
- 主程序放在一个文件中;
在我看来这样的设置很合适,结构分明,条理清晰;
下面是书上的代码实现:
头文件:
#define QUIT 5
#define HOTEL1 180.0
#define HOTEL2 225.0
#define HOTEL3 255.0
#define HOTEL4 355.0
#define DISCOUNT 0.95
#define STARS "****************"
int menu(void);
int getnights(void);
void showprice(double rate,int nights);
函数源代码:
#include<stdio.h>
#include"hotel.h"
int menu(void){
int code,status;
printf("\n%s%s\n",STARS,STARS);
printf("Enter the number of the hotel\n");
printf("1) the first 2) the second\n"
"3) the third 4) the forth\n");
printf("5) to quit");
printf("\n%s%s\n",STARS,STARS);
while((status=scanf("%d",&code))!=1||code<1&&code>5){
if(status!=1)
scanf("%*s");//处理非整数输入 原来的那个输入其实是在缓存区
printf("please enter an integer from 1 to 5.\n");
}
return code;
}
int getnights(void) {
int nights;
printf("how many nights are needed?\n");
while(scanf("%d",&nights)!=1){
scanf("%*s");
printf("enter an integer,please.\n");
}
return nights;
}
void showprice(double rate,int nights){
int n;
double total=0.0;
double factor=1.0;
for(n=1;n<=nights;n++,factor*=DISCOUNT)
total+=rate*factor;
printf("the total cost is:%.2lf\n",total);
}
主程序
#include<stdio.h>
#include"hotel.h"
int main(){
int nights;
double hotel_rate;
int code;
while((code=menu())!=QUIT){
switch(code){
case 1:hotel_rate=HOTEL1;
break;
case 2:hotel_rate=HOTEL2;
break;
case 3:hotel_rate=HOTEL3;
break;
case 4:hotel_rate=HOTEL4;
break;
default:hotel_rate=0.0;
printf("Oops!\n");
break;
}
nights=getnights();
showprice(hotel_rate,nights);
}
printf("thank you and goodbye.");
return 0;
}
注意:在.c的文件中,要包含头文件,头文件才可以正常在其他文件中使用
具体格式
#include "头文件名称"
下面想说的是如何在DEV—C++中实现多文件编译。
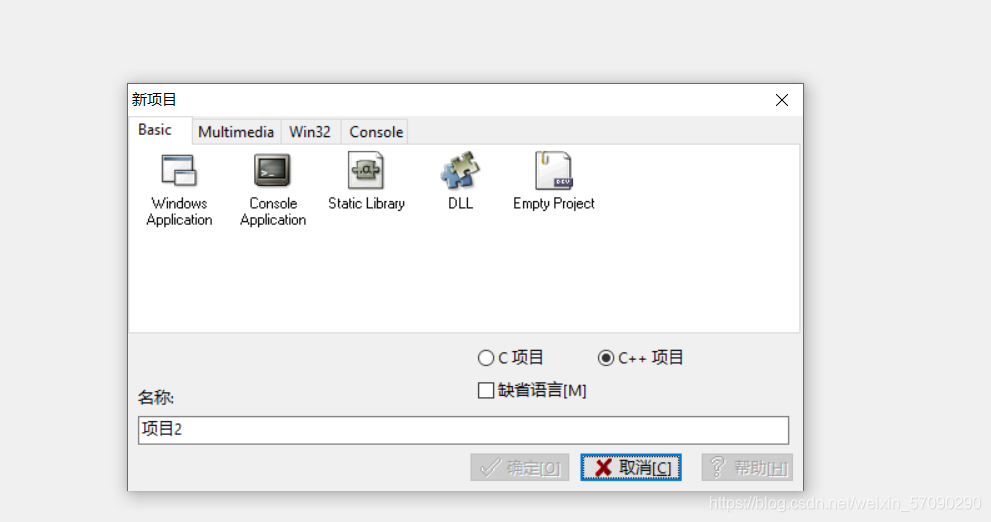
首先先新建一个项目,勾选空项目,选择C语言
然后在项目中添加相应需要的源代码文件