学习资料及工具:bilibili视频网站黑马程序员匠心之作,BV1et411b73Z,共大概300+集https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1et411b73Z?p=2
工具:Visual 2015
虽然不是0基础,但是之前感觉之前学过的和没学过一样,所以用0基础视频进行学习,此系列帖子作为笔记使用(主要是字丑)。
目录
正文
8 结构体
8.1 结构体的基本概念
构体属于用户自定义的数据类型,类似int、float等,用法也和他们相似
8.2 结构体的定义和使用
语法:struct 结构体名 {结构体成员列表};
通过结构体变量创建有三种方式:
- struct 结构体名 变量名
- struct 结构体名 变量名 = {成员1值,成员2值……}(建议第二种)
- 定义结构体时顺便创建
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
#include<string>
//创建学生数据类型
struct student
{
//成员列表
string name;//引入姓名、年龄和分数三个数据
int age;
float score;
}s3;//第三种定义方式,但不推荐
int main()
{
//通过学生类型创建具体的学生
struct student s1;//其中struct关键字可以省略,没有影响
//给s1赋值,与C++中定义好的数据类型不同,自定义数据类型需用.赋值而不是=
s1.age = 15;
s1.name = "张三";
s1.score = 80;
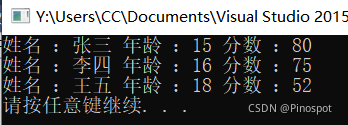
cout << "姓名 :" << s1.name << " 年龄 :" << s1.age << " 分数 :" << s1.score << endl;
//第二种方式创建学生
struct student s2 = { "李四",16,75 };//按照自己定义的顺序来输入变量
cout << "姓名 :" << s2.name << " 年龄 :" << s2.age << " 分数 :" << s2.score << endl;
//第三种的创建方式在定义之后
s3.age = 18;
s3.name = "王五";
s3.score = 52;
cout << "姓名 :" << s3.name << " 年龄 :" << s3.age << " 分数 :" << s3.score << endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
}结果如下:
总结:struct关键字其实不难,可以类比为int a = 10;其中struct 结构体名 类比为?int,变量名类比为a,最后你所赋的值可以类比为10。
其中struct还可以省略?,所以命名规则其实差不多。
8.3 结构体数组
作用:将自定义的结构体放入数组中方便维护
语法:struct 结构体名 数组名[元素个数]=?{{},{},{}……};
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
//定义结构体
struct student
{
string name;
int age;
float score;
};
int main()
{
struct student stuArray[3] = {
{ "张三",18,52 },
{ "李四",17,75 },
{ "王五",15,86 },
};//创建结构体数组
//后期可以给数组中的值单独进行修改,比如把数组第一个元素改成赵六
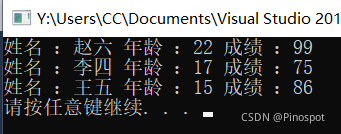
stuArray[0].name = "赵六";//把张三的值修改成赵六
stuArray[0].age = 22;
stuArray[0].score = 99;
//遍历结构体
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++)
{
cout << "姓名 :"<< stuArray[i].name
<<" 年龄 :"<< stuArray[i].age
<<" 成绩 :"<< stuArray[i].score<< endl;
}
system("pause");
return 0;
}结果如下:
8.4 结构体指针
作用:通过指针访问结构体成员
利用操作符->可通过指针访问结构体成员
注:加*解引用是将指针指向了变量,而不能访问,等于你用*告诉电脑变量在哪。结构体中访问得用->符号?
?
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
#include<string>
struct student
{
string name;
int age;
float score;
};
int main()
{
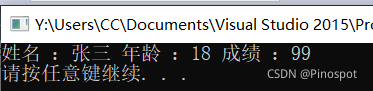
student s = { "张三",18,99 };
student *p = &s;//指向结构体变量
cout << "姓名 :" << p->name//使用指针访问数据
<< " 年龄 :" << p->age//唯独这一步和之前的指针不同,需要额外记忆
<< " 成绩 :" << p->score << endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
}结果如下:
8.5 结构体中嵌套结构体
作用:结构体的成员是另一个结构体
比如:定义了老师这个结构体,老师还带不同的学生。?
?
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
#include<string>
struct student//学生结构体
{
string name;
int age;
float score;
};
struct teacher//老师结构体
{
string name;
int num;//职工编号
struct student stu;//struct studen可以理解为int,后面那部分为自己设定的变量
};
int main()
{
teacher t;//分别设定数值
t.name = "老王 ";
t.num = 22054;
t.stu.age = 18;//每一层嵌套,都要加.
t.stu.name = "小王";
t.stu.score = 89;
//输出并打印
cout << "老师姓名 :" << t.name << " 职工编号 :" << t.num
<< " 学生姓名 :"<<t.stu.name<<" 学生年龄 :"<<t.stu.age<<" 学生成绩 :"<<t.stu.score
<<endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
}结果如下:
 ?8.6 结构体做函数参数
?8.6 结构体做函数参数
作用:将结构体作为参数向函数中传递
传递方式有两种:
- 值传递(不会改变实参)
- 地址传递(会改变实参)
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
#include<string>
struct student
{
string name;
int age;
float score;
};
void printstu1(struct student s)//创建一个打印数据的函数,值传递
{
s.age = 200;
cout << "子函数1中打印 :" << s.name << " 年龄 :" << s.age << " 成绩 :" << s.score << endl;
}
void printstu2(struct student *s)//创建一个打印数据的函数,地址传递
{
s->age = 100;
cout << "子函数2中打印 :" << s->name << " 年龄 :" << s->age << " 成绩 :" << s->score << endl;
}
int main()
{
//将学生传入到一个参数并打印信息
//创建结构体变量
struct student s = { "张三",18,86};
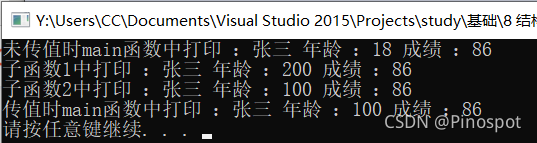
cout << "未传值时main函数中打印 :" << s.name << " 年龄 :" << s.age << " 成绩 :" << s.score << endl;
printstu1(s);
printstu2(&s);
cout << "传值时main函数中打印 :" << s.name << " 年龄 :" << s.age << " 成绩 :" << s.score << endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
}?结果如下:
8.7 const使用场景
作用:防止误操作
?
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
#include<string>
struct student
{
string name;
int age;
float score;
};
//使用指针传递,一次只传递四个字节(如果用值传递,一次会传输所有的数据)
void printstu(const student *s)
{
//s->age =100;这行代码取消注释后会报错,是因为const限定了形参不允许修改
cout << "姓名 :" << s->name << " 年龄 :" << s->age << " 成绩 :" << s->score << endl;
}
int main()
{
//创建结构体变量
struct student s = { "张三",18,86 };
printstu(&s);//用地址传递有个问题,在子函数中修改数据会导致实参发生变化
system("pause");
return 0;
}?