一、处理数字?
求和
1. a+b 未知组数,每行给出a b

#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main(){
int a,b;
while(cin>>a>>b){
cout<<a+b<<endl;
}
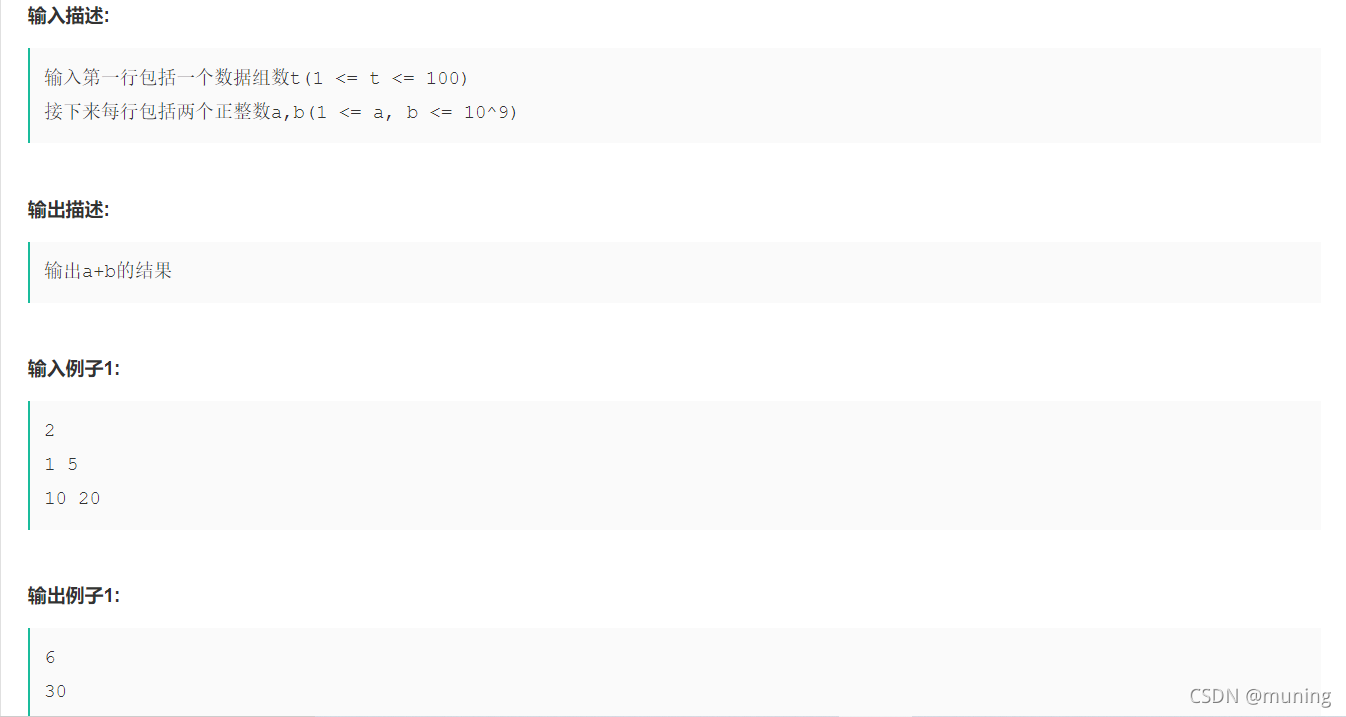
}2.a+b? t 组数,每行给出a b
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main(){
int t;
cin>>t;
int a,b;
while(t--){
cin>>a>>b;
cout<<a+b<<endl;
}
}?3.a+b? 未知组数,每行给出a b,以0 0结束输入

#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main(){
int a,b;
while(cin>>a>>b){
if(a==0 && b==0) break;
cout<<a+b<<endl;
}
return 0;
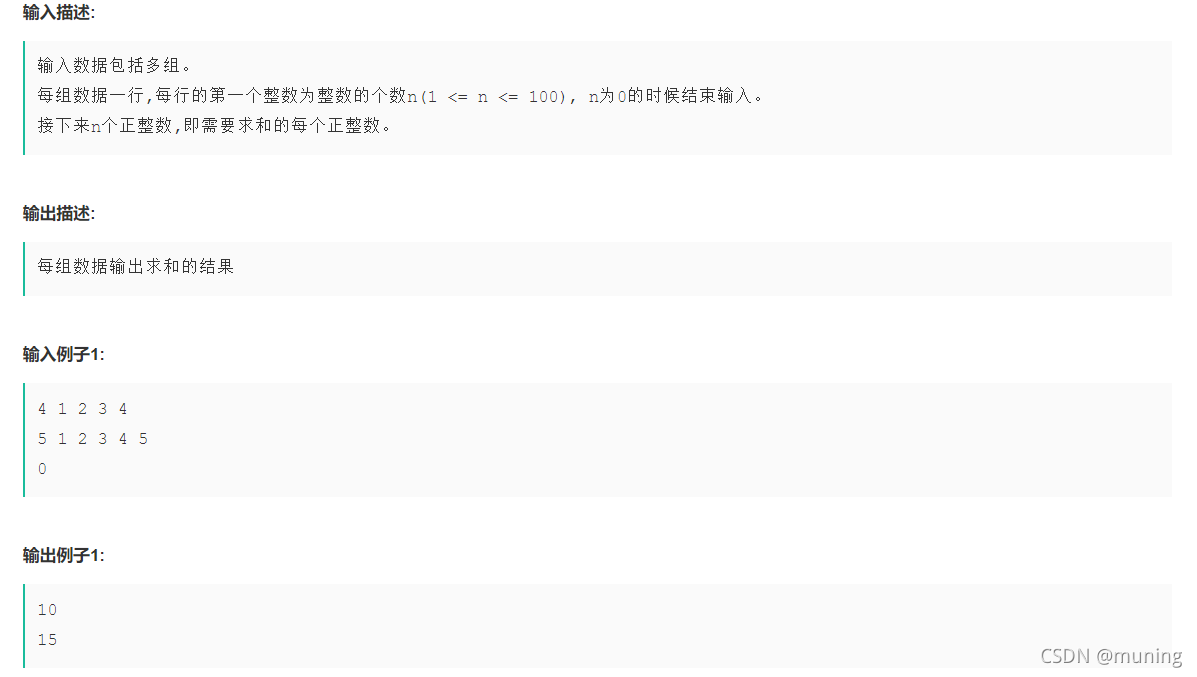
}?4.sum? 未知组数,每行第一个整数n是该组数据的元素个数,剩下的数是元素;当n为0结束输入
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main(){
int n;
while(cin>>n){
if(n==0) break;
int sum=0;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
int num;
cin>>num;
sum += num;
}
cout<<sum<<endl;
}
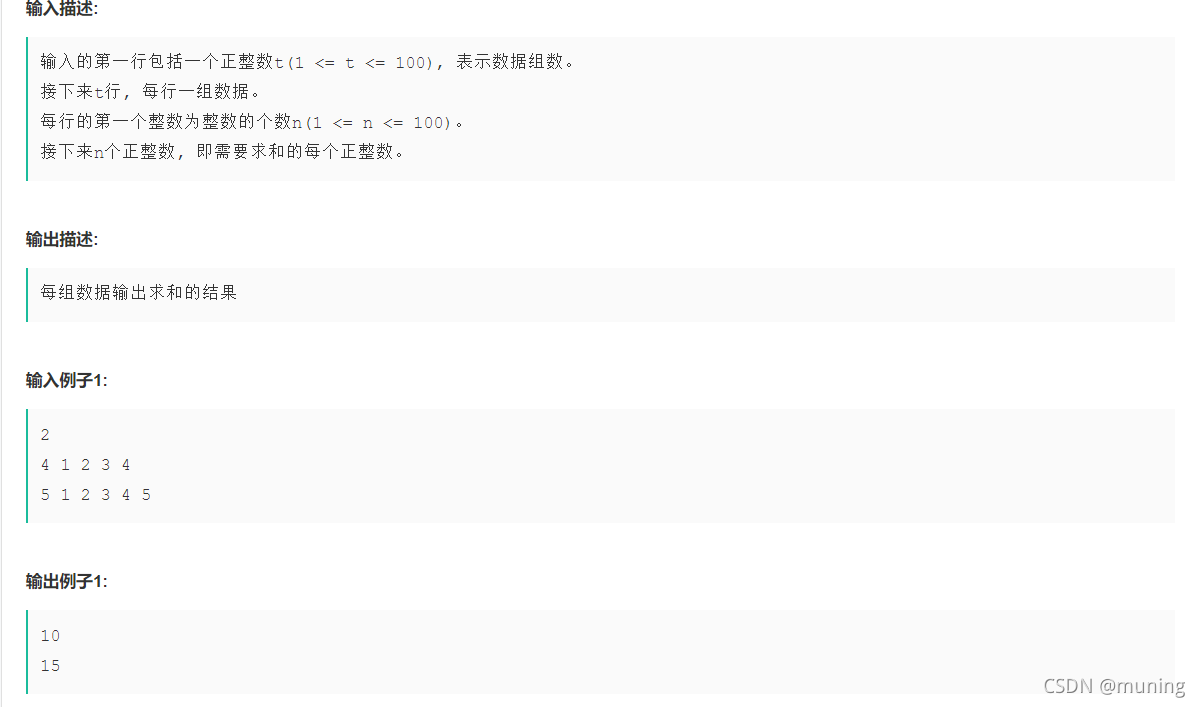
}?5.sum? t 组数,每行第一个整数n是该组数据的元素个数,剩下的数是元素
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main(){
int t;
cin>>t;
int n;
while(t--){
int a,sum=0;
cin>>n;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
cin>>a;
sum += a;
}
cout<<sum<<endl;
}
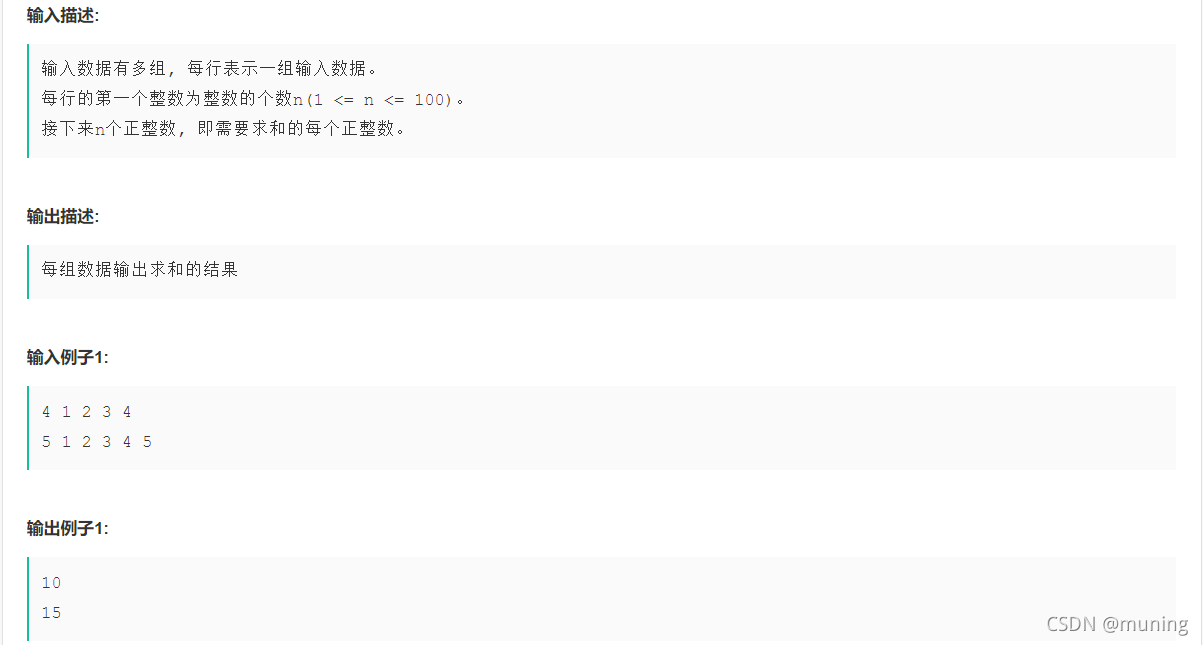
}6.sum? 未知组数,每行第一个整数n是该组数据的元素个数,剩下的数是元素
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main(){
int t;
while(cin>>t){
int a,sum=0;
for(int i=0;i<t;i++){
cin>>a;
sum += a;
}
cout<<sum<<endl;
}
}7. sum? ?未知组数,每行元素个数不确定
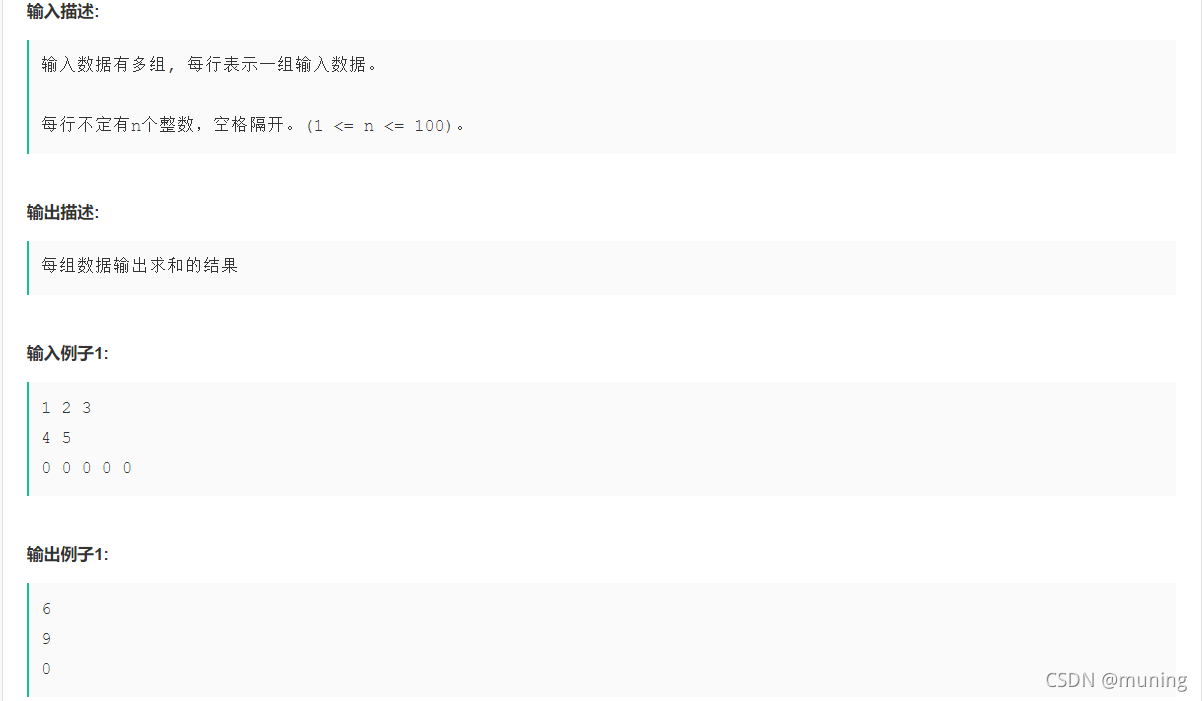
?
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main(){
int a,sum=0;
while(cin>>a){
sum += a;
if(cin.get()=='\n'){
cout<<sum<<endl;
sum=0;
}
}
}补充一个:
7.1 sum? 未知组数,每行元素个数不确定,元素之间以逗号分隔
输入:
1,2,3,4,8
45,2,8,-3
输出:
1,2,3,4,8
-3,2,8,45
【当元素是int】和下面处理字符串用的 10 类似,增加一个处理:利用函数atoi将字符串转换为int,注意要加上c_str。
#include<vector>
#include<algorithm>
#include <iostream>
#include<string>
#include<sstream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string s;
vector<int> data;
while (getline(cin, s)) {
string b;
stringstream a(s); //a(s) 表示a是s的一个拷贝
while (getline(a, b, ','))
data.push_back(atoi(b.c_str()));
sort(data.begin(), data.end());
cout << data[0];
int n = data.size();
for (int i = 1; i < n; ++i) {
cout << ',' <<data[i];
}
cout << endl;
data.clear();
}
return 0;
}【当元素是float】
例如输入:1.3,-3.9,2.02,-2234。改成atof函数即可。
#include<vector>
#include<algorithm>
#include <iostream>
#include<string>
#include<sstream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string s;
vector<float> data;
while (getline(cin, s)) {
string b;
stringstream a(s); //a(s) 表示a是s的一个拷贝
while (getline(a, b, ','))
data.push_back(atof(b.c_str()));
sort(data.begin(), data.end());
cout << data[0];
int n = data.size();
for (int i = 1; i < n; ++i) {
cout << ',' << data[i];
}
cout << endl;
data.clear();
}
return 0;
}如果int不够存,也可以用atol将其转换为long。
二、字符串
给每组的字符串排序
8.字符串排序? 字符串个数n,每个字符串以空格隔开
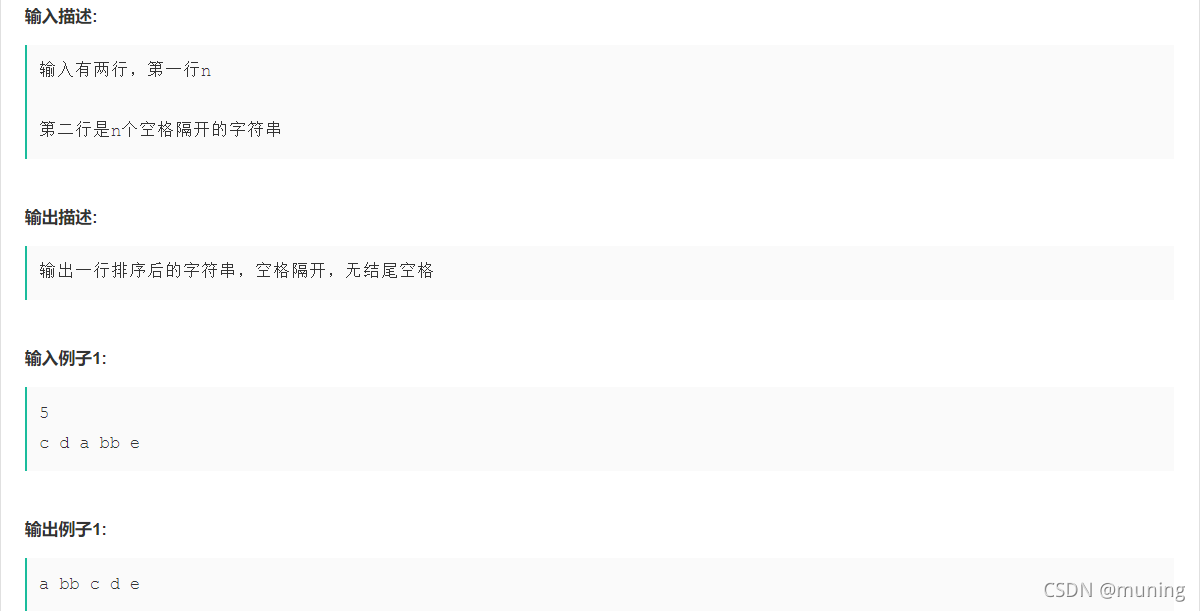
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
#include<algorithm>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;
int main(){
int n;
cin>>n;
vector<string> strs;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
string str;
cin>>str;
strs.push_back(str);
}
sort(strs.begin(),strs.end());
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
cout<<strs[i]<<" ";
}
return 0;
}9. 字符串排序 未知组数,每行给出多个字符串,以空格分开
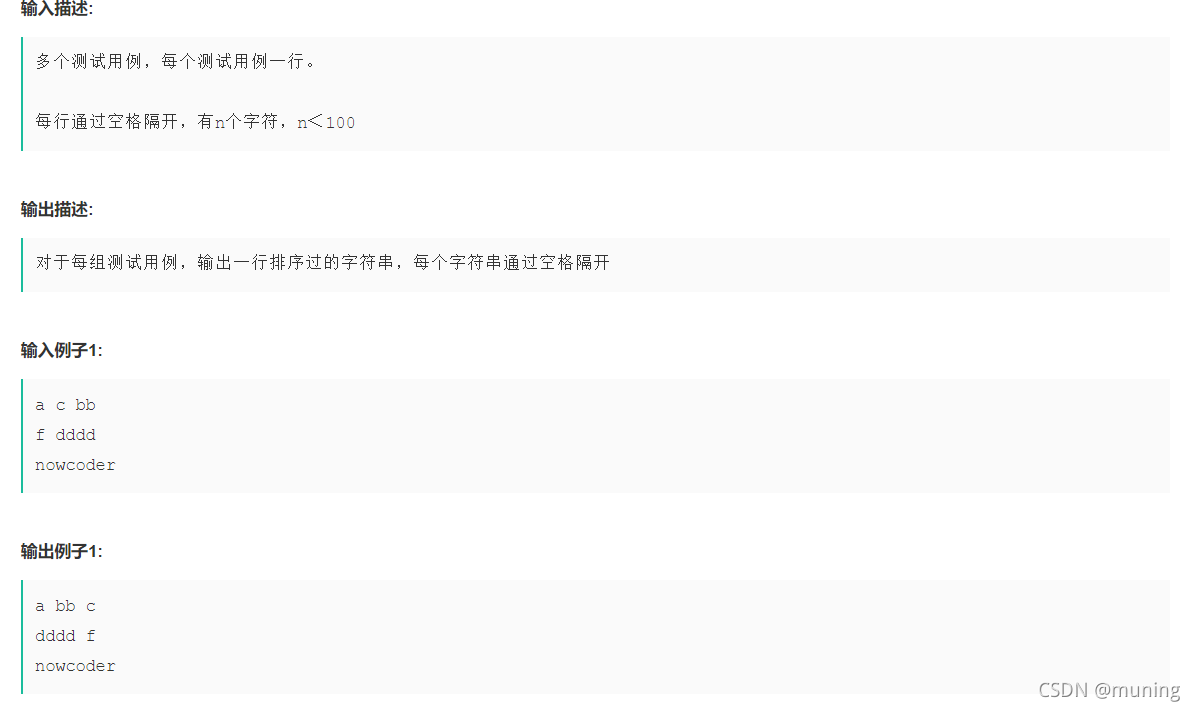
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
#include<string>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;
int main(){
vector<string> strs;
string s;
while(cin>>s){
strs.push_back(s);
if(cin.get()=='\n'){
sort(strs.begin(),strs.end());
for(string& tmp:strs){
cout<<tmp<<" ";
}
cout<<endl;
strs.clear();
}
}
return 0;
}10.字符串排序 未知组数,每行给出多个字符串,以逗号分开

#include<vector>
#include<algorithm>
#include <iostream>
#include<string>
#include<sstream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string s;
vector<string> str;
while (getline(cin, s)) {
string b;
stringstream a(s); //a(s) 表示a是s的一个拷贝
while (getline(a, b, ','))
str.push_back(b);
sort(str.begin(), str.end());
cout << str[0];
int n = str.size();
for (int i = 1; i < n; ++i) {
cout << ',' << str[i];
}
cout << endl;
str.clear();
}
return 0;
}11. a+b 若未给出数据范围,你就尽可能用大类型,例如long,避免通过样例漏掉
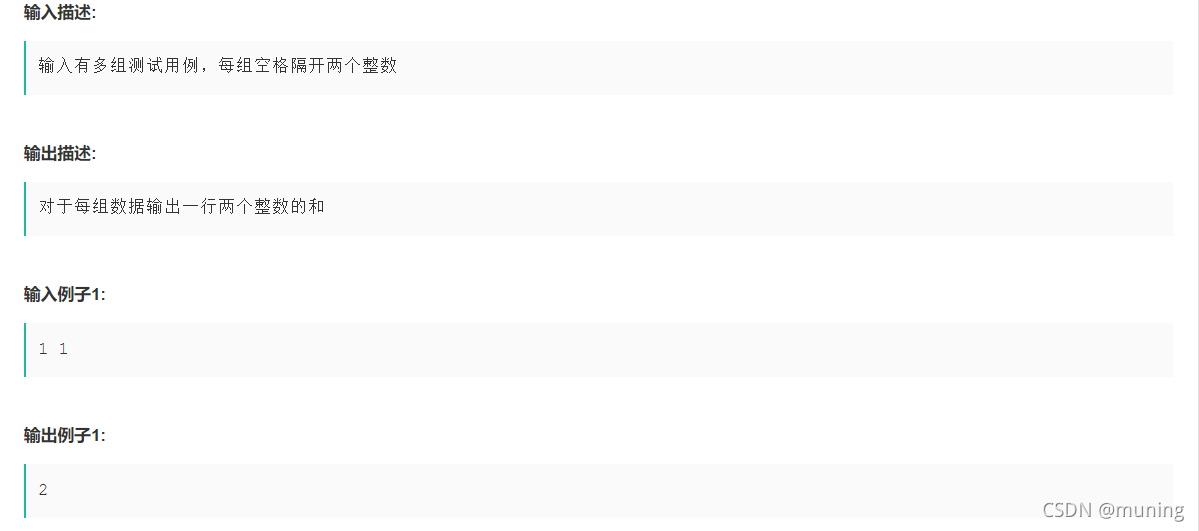
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
// 不要用 int a, b, 因为测试数据会越界,为了效果,所以这个题目故意不在题面说数据范围
// 不要用 int a, b, 因为测试数据会越界,为了效果,所以这个题目故意不在题面说数据范围
// 不要用 int a, b, 因为测试数据会越界,为了效果,所以这个题目故意不在题面说数据范围
// 不要用 int a, b, 因为测试数据会越界,为了效果,所以这个题目故意不在题面说数据范围
// 你可以试试测试用例 12141483647 12141483647,输出结果是否正确
long long a,b;
while(cin >> a >> b)// 注意,如果输入是多个测试用例,请通过while循环处理多个测试用例
cout << a+b << endl;
}