#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int n,post[100001],in[100001],dd[100001],a,b,c,d;
struct node{
node *lchild,*rchild;
int deep;
int data;
};
node *newnode(int yuy){
node *Node=new node;
Node->data=yuy;
Node->lchild=NULL;
Node->rchild=NULL;
return Node;
}
void build(int inl,int inr,int postl,int postr,node* &root,int dep){
if(postl>postr){
root=NULL;
return ;}
int index;
for(int i=inl;i<=inr;i++){
if(post[postr]==in[i]){
index=i;
break;
}
}
//printf("%d ",post[postr]);
root=newnode(in[index]);
root->deep=dep;
dd[dep]++;
build(inl,index-1,postl,postl+index-inl-1,root->lchild,dep+1);
build(index+1,inr,postl+index-inl,postr-1,root->rchild,dep+1);
}
int main(){
scanf("%d",&n);
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)scanf("%d",&in[i]);
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)scanf("%d",&post[i]);
node *root=NULL;
build(1,n,1,n,root,1);
// dfs(root,1);
queue<node*>q;
q.push(root);
int ans[100001],kk=0;
while(!q.empty()){
node *ui=q.front();
q.pop();
//printf("%d ",ui->data);
ans[++kk]=ui->data;
// if(ui->deep%2==1){
if(ui->lchild)q.push(ui->lchild);
if(ui->rchild)q.push(ui->rchild);
}
int ygg=1,u=1;
while(dd[ygg]){
if(ygg%2==0)for(int i=u;i<=u+dd[ygg]-1;i++)printf("%d ",ans[i]);
else for(int i=u+dd[ygg]-1;i>=u;i--)printf("%d ",ans[i]);
u+=(dd[ygg]);
++ygg;
}
return 0;
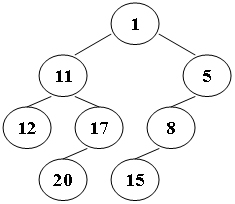
}Suppose that all the keys in a binary tree are distinct positive integers. A unique binary tree can be determined by a given pair of postorder and inorder traversal sequences. And it is a simple standard routine to print the numbers in level-order. However, if you think the problem is too simple, then you are too naive. This time you are supposed to print the numbers in "zigzagging order" -- that is, starting from the root, print the numbers level-by-level, alternating between left to right and right to left. For example, for the following tree you must output: 1 11 5 8 17 12 20 15.
Input Specification:
Each input file contains one test case. For each case, the first line gives a positive integer N (≤30), the total number of nodes in the binary tree. The second line gives the inorder sequence and the third line gives the postorder sequence. All the numbers in a line are separated by a space.
Output Specification:
For each test case, print the zigzagging sequence of the tree in a line. All the numbers in a line must be separated by exactly one space, and there must be no extra space at the end of the line.