ubuntu、Makefile操作
要求
??编写一个主程序文件 main1.c 和一个子程序文件 sub1.c, 要求:子程序sub1.c 包含一个算术运算函数 float x2x(int a,int b)
??x2x 函数功能为对两个输入整型参数做某个运算,将结果做浮点数返回;主程序main1.c,定义并赋值两整型变量,然后调用函数 x2x,将x2x的返回结果printf出来。
unbuntu
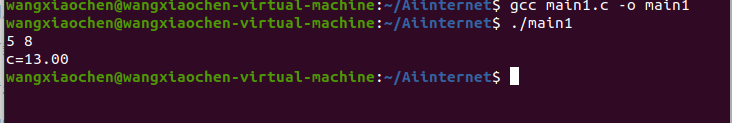
- 在ubuntu系统用gcc 命令行方式编译主程序main1.c 并运行
main1.c
#include<stdio.h>
#include"sub1.c"
float x2x(int a,int b);
int main()
{
int a,b;
scanf("%d",&a);
scanf("%d",&b);
printf("c=%.2f\n",x2x(a,b));
return 0;
}
sub1.c
#include<stdio.h>
float x2x(int a,int b)
{
float c;
c=a+b;
return c;
}
- 终端gcc命令调试运行功能函数
Windows10 Dev c++
#include<stdio.h>
#include"sub1.h"
float x2x(int a,int b) ;
int main(){
int a,b;
scanf("%d,%d",&a,&b);
printf("c=%.2f\n",x2x(a,b));
}

ubuntu使用Makefile进行操作
make是一个命令工具,它解释Makefile 中的指令。在Makefile文件中描述了整个工程所有文件的编译顺序、编译规则。Makefile 有自己的书写格式、关键字、函数。像C 语言有自己的格式、关键字和函数一样。而且在Makefile 中可以使用系统shell所提供的任何命令来完成想要的工作。Makefile在绝大多数的IDE 开发环境中都在使用,已经成为一种工程的编译方法。
makefile使用规则
- 目标文件:[相依文件]
- 命令[注释]
- 命令[注释]
- 程序代码片
#include<stdio.h>
#include"sub1.h"
int main()
{
int a,b;
scanf("%d",&a);
scanf("%d",&b);
float c;
c = x2x(a,b);
printf("c=%f\n",c);
return 0;
}
#ifndef _SUB1_H_
#define _SUB1_H_
float x2x(int a,int b);
#endif
#include"sub1.h"
float x2x(int a,int b)
{
float c;
c=a+b;
return c;
}
- 创建makefile文件,并进行makefile的编辑


- make命令执行

总结
在ubuntu环境下,可用gcc对c语言进行编译,但对于多个文件的维护工作可以由make和makefile来完成
参考:
Ubuntu16.04下C语言的编译及makefile的应用
Ubuntu系统使用gcc和Makefile编译C程序