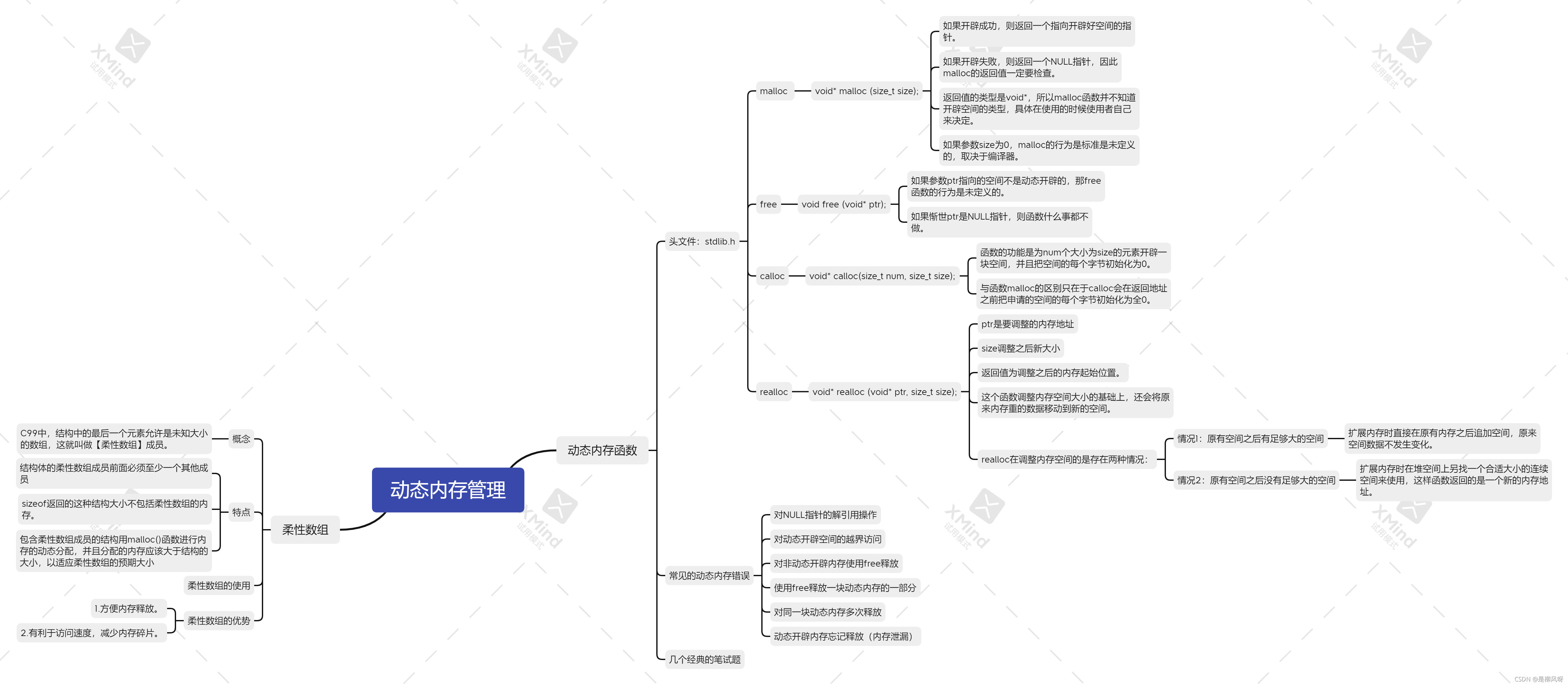
测试malloc函数
int main()
{
//申请空间
int* p = (int*)malloc(40);
if (p == NULL)
{
return -1;
}
//开辟成功了
int i = 0;
for (i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
*(p + i) = i;
}
//释放空间
free(p);
p = NULL;
return 0;
}
测试calloc函数和realloc函数
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<string.h>
#include<errno.h>
int main()
{
//申请10个int的空间
int* p = (int*)calloc(10, sizeof(int));
if (p == NULL)
{
printf("%s\n", strerror(errno));
return -1;
}
//申请成功
int i = 0;
for (i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
*(p + i) = i;
}
//空间不够了,增加至20个int
int* ptr = (int*)realloc(p, 20 * sizeof(int));
if (ptr != NULL)
{
p = ptr;
}
else
{
return -1;
}
for (i = 10; i < 20; i++)
{
*(p + i) = i;
}
//打印
for (i = 0; i < 20; i++)
{
printf("%d ", *(p + i));
}
//释放空间
free(p);
p = NULL;
return 0;
}
对NULL指针的解引用操作
void main()
{
int* p = (int*)malloc(4000000000000000000000);
*p = 20; //如果p的值是NULL,就会有问题。所以malloc的返回值一定要检查.
printf("%d", *p);
free(p);
}
对动态内存空间的越界访问
int main()
{
int* p = (int*)malloc(200);//只申请了200个字节
if (p == NULL)
{
return -1;
}
//使用
int i = 0;
//越界访问
for (i = 0; i < 80; i++) //访问了80*4个字节的空间
{
*(p + i) = i;
}
for (i = 0; i < 80; i++)
{
printf("%d\n", *(p + i));//即使能打印出来,也不代表代码是正确的。
}
//释放
free(p);
p = NULL;
return 0;
}
对非动态内存使用free释放
int main()
{
int a = 10;
int* p = &a;
free(p);
p = NULL;
return 0;
}
使用free释放一块动态开辟内存的一部分
int main()
{
int* p = (int*)malloc(10 * sizeof(int));
if (p == NULL)
{
return -1;
}
//使用
int i = 0;
for (i = 0; i < 5;i++)
{
*p++ = i;
}
//释放
free(p);
p = NULL;
return 0;
}
对同一块动态内存的多次释放
int main()
{
int* p = (int*)malloc(40);
if (p == NULL)
{
return -1;
}
//使用
//...
//2次释放是错误的
free(p);
free(p);
return 0;
}
动态开辟内存忘记释放
void test()
{
//开辟一个动态内存空间
int* p = (int*)malloc(100);
if (NULL != p)
{
*p = 20;
}
}
//出去后,p被销毁,而开辟的内存空间还在,这样无法被找到,无法使用,造成内存泄漏。
野指针
int main()
{
int* = (int*)malloc(40);
if (p == NULL)
{
return -1;
}
//使用
//释放
free(p);
//p就是一个野指针,它所指向的内存空间已经被回收。
p = NULL;
//p就NULL,不是野指针。
}
实现一个通讯录
test.c
//实现一个通讯录:
//1.存放1000个人的信息
//信息:名字+性别+年龄+电话+住址
//2.增加联系人
//3.删除联系人
//4.查找联系人
//5.修改联系人
//6.排序
//7.存文件
//test.c
//测试通讯录的各个功能
//
//contact.c
//通讯录的实现
//
//contact.h
//通讯录的声明
#include "contact.h "
void menu()
{
printf("*****************************\n");
printf("****1. add 2. del *****\n");
printf("****3. search 4. modify*****\n");
printf("****5. show 6 .sort ****\n");
printf("****0. exit ***\n");
printf("*****************************\n");
}
enum Option
{
EXIT,
ADD,
DEL,
SEARCH,
MODIFY,
SHOW,
SORT
};
int main()
{
int input = 0;
//创建一个通讯录
struct Contact con;
//初始化通讯录
InitContact(&con);
//最多可以放3个人的信息了
//空间不够可以增容
do
{
menu();
printf("请选择:>");
scanf("%d", &input);
switch (input)
{
case ADD:
AddContact(&con);
break;
case DEL:
DelContact(&con);
break;
case SEARCH:
SearchContact(&con);
break;
case MODIFY:
ModifyContact(&con);
break;
case SHOW:
ShowContact(&con);
break;
case EXIT:
//销毁通讯录
DestoryContact(&con);
printf("退出通讯录\n");
break;
default:
printf("选择错误\n");
break;
}
} while (input);
return 0;
}
contact.h
#pragma once
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include<stdio.h>
#include<string.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#define DEFAULT_SZ 3
#define NAME_MAX 20
#define SEX_MAX 5
#define TELE_MAX 12
#define ADDR_MAX 30
#define MAX 1000
//描述人的信息
struct PeoInfo
{
char name[NAME_MAX];
int age;
char sex[SEX_MAX];
char tele[TELE_MAX];
char addr[ADDR_MAX];
};
//通讯录 - 静态版本
//struct Contact
//{
//1000个人的数据存放在data数组中
// struct PeoInfo data[MAX];
// //记录当前通讯录有效信息的个数
// int sz;
//};
//动态增长的版本
struct Contact
{
struct PeoInfo* data;
int sz;//通讯录中当前有效元素的个数
int capacity;//通讯录的当前最大容量
};
//初始化通讯录
void InitContact(struct Contact* pc);
//销毁通讯录
void DestoryContact(struct Contact* pc);
//增加联系人
void AddContact(struct Contact* pc);
//显示所有的联系人
void ShowContact(struct Contact* pc);
//删除指定联系人
void DelContact(struct Contact* pc);
//查找指定联系人
void SearchContact(struct Contact* pc);
//修改指定联系人
void ModifyContact(struct Contact* pc);
contact.c
#include "contact.h"
//静态的版本
//void InitContact(struct Contact* pc)
//{
// pc->sz = 0;//默认没有信息
// /*memset(pc->data, 0, MAX * sizeof(struct PeoInfo));*/
// memset(pc->data, 0, sizeof(pc->data));
//
//}
//动态的版本
void InitContact(struct Contact* pc)
{
pc->sz = 0;
pc->data = (struct PeoInfo*)malloc(DEFAULT_SZ * sizeof(struct PeoInfo));
pc->capacity = DEFAULT_SZ;
}
void DestoryContact(struct Contact* pc)
{
free(pc->data);
pc->data = NULL;
pc->capacity = 0;
pc->sz = 0;
}
//静态的版本
//void AddContact(struct Contact* pc)
//{
// if (pc->sz == MAX)
// {
// printf("通讯录满了\n");
// }
// else
// {
// printf("请输入名字:>");
// scanf("%s", pc->data[pc->sz].name);
// printf("请输入年龄:>");
// scanf("%d", &(pc->data[pc->sz].age));
// printf("请输入性别:>");
// scanf("%s", pc->data[pc->sz].sex);
// printf("请输入电话:>");
// scanf("%s", pc->data[pc->sz].tele);
// printf("请输入地址:>");
// scanf("%s", pc->data[pc->sz].addr);
//
// printf("添加成功\n");
// pc->sz++;
// }
//}
//动态增长的版本
void AddContact(struct Contact* pc)
{
if (pc->sz == pc->capacity)
{
//增加容量
struct PeoInfo* ptr = (struct PeoInfo*)realloc(pc->data, (pc->capacity + 2)*sizeof(struct PeoInfo));
if (ptr != NULL)
{
pc->data = ptr;
pc->capacity += 2;
printf("增容成功\n");
}
else
{
return;
}
}
//录入新增人的信息
printf("请输入名字:>");
scanf("%s", pc->data[pc->sz].name);
printf("请输入年龄:>");
scanf("%d", &(pc->data[pc->sz].age));
printf("请输入性别:>");
scanf("%s", pc->data[pc->sz].sex);
printf("请输入电话:>");
scanf("%s", pc->data[pc->sz].tele);
printf("请输入地址:>");
scanf("%s", pc->data[pc->sz].addr);
printf("添加成功\n");
pc->sz++;
}
void ShowContact(struct Contact* pc)
{
int i = 0;
printf("%15s\t%5s\t%8s\t%15s\t%30s\n\n", "name", "age", "sex", "tele", "addr");
for (i = 0; i < pc->sz; i++)
{
//打印每一个数据
printf("%15s\t%5d\t%8s\t%15s\t%30s\n",pc->data[i].name,
pc->data[i].age, pc->data[i].sex, pc->data[i].tele, pc->data[i].addr);
}
}
int FindContactByName(const struct Contact* pc, const char* name)
{
int i = 0;
for (i = 0; i < pc->sz; i++)
{
if (strcmp(pc->data[i].name, name) == 0)
{
return i;
}
}
//找不到了
return -1;
}
void DelContact(struct Contact* pc)
{
if (pc->sz == 0)
{
printf("通讯录为空,无法删除\n");
return;
}
char name[NAME_MAX] = { 0 };
printf("请输入需要删除人的名字:>");
scanf("%s", name);
//查找
int pos = FindContactByName(pc, name);
if (pos == -1)
{
printf("指定的联系人不存在\n");
}
else
{
//删除
int j = 0;
for (j = pos; j < pc->sz-1; j++)
{
pc->data[j] = pc->data[j + 1];
}
pc->sz--;
//
printf("删除成功\n");
}
}
void SearchContact(const struct Contact* pc)
{
char name[NAME_MAX] = { 0 };
printf("输入要查找人的名字:>");
scanf("%s", name);
int pos = FindContactByName(pc, name);
if (-1 == pos)
{
printf("查无此人");
}
else
{
int i = 0;
printf("%15s\t%5s\t%8s\t%15s\t%30s\n\n", "name", "age", "sex", "tele", "addr");
printf("%15s\t%5d\t%8s\t%15s\t%30s\n",
pc->data[pos].name,
pc->data[pos].age,
pc->data[pos].sex,
pc->data[pos].tele,
pc->data[pos].addr);
}
}
void ModifyContact(struct Contact* pc)
{
char name[NAME_MAX] = { 0 };
printf("输入要修改人的名字:>");
scanf("%s", name);
int pos = FindContactByName(pc, name);
if (-1 == pos)
{
printf("要修改的人不存在");
}
else
{
printf("请输入新的名字:>");
scanf("%s", pc->data[pos].name);
printf("请输入新的年龄:>");
scanf("%d", &(pc->data[pos].age));
printf("请输入新的性别:>");
scanf("%s", pc->data[pos].sex);
printf("请输入新的电话:>");
scanf("%s", pc->data[pos].tele);
printf("请输入新的地址:>");
scanf("%s", pc->data[pos].addr);
}
}
几道经典的面试题
题目1:
请问运行Test 函数会有什么样的结果?
void GetMemory(char* p)
{
p = (char*)malloc(100);
}
void Test(void)
{
char* str = NULL;
GetMemory(str);
strcpy(str, "hello world");
printf(str);
}
//改法
#include<stdio.h>
#include<string.h>
void Getmemory(char** p)
{
*p = (char*)malloc(100);
}
void Test(void)
{
char* str = NULL;
Getmemory(&str);
strcpy(str, "hello world");
printf(str);
//释放
free(str);
str = NULL;
}
int main()
{
Test();
return 0;
}
题目2:
char *GetMemory(void) {
char p[] = "hello world";
return p; }
void Test(void) {
char *str = NULL;
str = GetMemory();
printf(str);
}
请问运行Test 函数会有什么样的结果?
//出GetMemory()函数体后,str所指向的内存空间还给操作系统了
//所以有可能打印hellow world,也有可能打印时随机值。
题目3:
void GetMemory(char** p, int num)
{
*p = (char*)malloc(num);
}
void Test(void)
{
char* str = NULL;
GetMemory(&str, 100);
strcpy(str, "hello");
printf(str);
}
int main()
{
Test();
return 0;
}
请问运行Test 函数会有什么样的结果?
题目4:
void Test(void)
{
char* str = (char*)malloc(100);
strcpy(str, "hello");
free(str);
//str = NULL;如果释放后置成空指针就没事了。
if (str != NULL)
{
strcpy(str, "world");
printf(str);
}
}
int main()
{
Test();
return 0;
}
请问运行Test 函数会有什么样的结果?
C/C++内存开辟
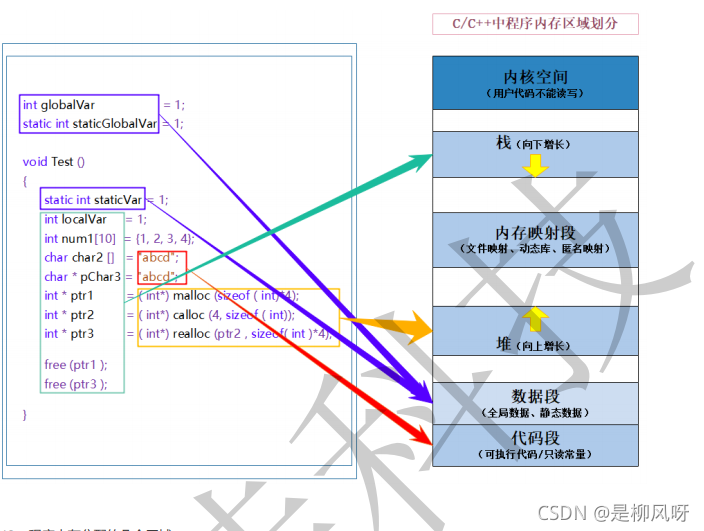
柔性数组
柔性数组的使用
#include<errno.h>
#include<string.h>
struct st_type
{
int i; //4
int a[];//柔性数组成员
};
int main()
{
printf("%d\n", sizeof(struct st_type));//4
struct st_type* ps = (struct st_type*)malloc(sizeof(struct st_type) + 10 * sizeof(int));
if (ps == NULL)
{
printf("%s\n", strerror(errno));
return -1;
}
//开辟成功了
ps->i = 10;
int i = 0;
for (i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
ps->a[i] i;
}
for (i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
printf("%d", ps->a[i]);
}
//a数组的空间不够了,希望调整为20个整形数据
struct st_type* ptr = (struct st_type*)realloc(ps, sizeof(struct st_type) + 20 * sizeof(int));
if (ptr == NULL)
{
printf("扩容失败");
return -1;
}
else
{
ps = ptr;
}
//使用
//释放
free(ps);
ps = NULL;
return 0;
}
//上述st_type,也可以设计为:
#include<string.h>
#include<errno.h>
struct st_type
{
int i;//4
int * a; //4
};
int mian()
{
struct st_type* ps = (struct st_type*)malloc(sizeof(struct st_type));
ps->i = 100;
ps->a = (int*)malloc(10 * sizeof(int));
int i = 0;
for (i = 0;i < 10;i++)
{
ps->a[i] = i;
}
for (i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
printf("%d ", ps->a[i]);
}
//a指向的空间不够了,希望可以调整大小
int* ptr = (int*)realloc(ps->a, 20 * sizeof(int));
if (ptr == 0)
{
printf("扩容失败\n");
return -1;
}
else
{
ps->a = ptr;
}
//使用
//释放
free(ps->a);
ps->a = NULL;
free(ps);
ps = NULL;
return 0;
}