一:题目:
In many research areas, one important target of analyzing data is to find the best “peak shape” out of a huge amount of raw data full of noises. A “peak shape” of length L is an ordered sequence of L numbers { D
1
?
, ?, D
L
?
} satisfying that there exists an index i (1<i<L) such that D
1
?
<?<D
i?1
?
<D
i
?
D
i+1
?
?>D
L
?
.
Now given N input numbers ordered by their indices, you may remove some of them to keep the rest of the numbers in a peak shape. The best peak shape is the longest sub-sequence that forms a peak shape. If there is a tie, then the most symmetric (meaning that the difference of the lengths of the increasing and the decreasing sub-sequences is minimized) one will be chosen.
Input Specification:
Each input file contains one test case. For each case, the first line gives an integer N (3≤N≤10
4
). Then N integers are given in the next line, separated by spaces. All the integers are in [?10000,10000].
Output Specification:
For each case, print in a line the length of the best peak shape, the index (starts from 1) and the value of the peak number. If the solution does not exist, simply print “No peak shape” in a line. The judge’s input guarantees the uniqueness of the output.
Sample Input1:
20
1 3 0 8 5 -2 29 20 20 4 10 4 7 25 18 6 17 16 2 -1
结尾无空行
Sample Output1:
10 14 25
结尾无空行
Sample Input2:
5
-1 3 8 10 20
Sample Output2:
No peak shape
二:翻译:
在许多研究领域中,分析数据的一个重要目标就是从大量充满噪声的原始数据中找到最佳的“峰形”。长度为L的“峰形”是L数{D的有序序列
1
?
?D
l
?
},满足存在一个索引i (1
1
?
< < D?
?1
?
< D
我
?
D
我+ 1
?
?> D
l
?
。
现在给定N个输入数字,按照它们的索引排序,你可以删除其中的一些数字,以保持其余数字的峰值形状。最佳峰形是形成峰形的最长子序列。如果有一个平局,那么将选择最对称的(即增加子序列和减少子序列的长度之差是最小的)一个。
输入规格:
每个输入文件包含一个测试用例。对于每种情况,第一行给出整数N(3≤N≤10)
4
). 然后在下一行给出N个整数,用空格隔开。所有整数的取值范围为[?10000,10000]。
输出规范:
对于每种情况,在一行中打印最佳峰值形状的长度、索引(从1开始)和峰值数的值。如果不存在解决方案,只需在一行中打印“无峰形”。法官的输入保证了输出的唯一性。
示例Input1:
20.
1 3 0 8 5 -2 29 20 20 4 10 4 7 25 18 6 17 16 2 -1
结尾无空行
示例Output1:
10 14 25
结尾无空行
示例Input2:
5
1 3 8 10 20
示例Output2:
No peak shape
三:分析题意+思路
分析题意:1.想要求一个带有峰值的 最长峰形,即峰值前面的数小于峰值,
峰值后面的数大于峰值
2.如果出现长度一样的峰型,则考虑比较对称的峰形,
即峰值左右数的个数相差比较少的
思路:我们要求的结果的过程是动态的也就是在变化,所以这类题是动态规划
统计每个数值的最佳峰形长度,最后求出最大值
那么在统计每个数值的峰形长度 = 数值前面比起小的个数 + 本身(1)+ 后面比起大的数
下标为 i 的数值 前面比起小的数
m_first[i] = max(m_first[i],m_first[前面的数] + 1),这里加一是表示统计第一次前面有数比起小的时候为1
下标为 i 的数值 后面比起小的数
m_last[i] = max(m_last[i],m_last[后面的数] + 1)
四:上码
/**
分析题意:1.想要求一个带有峰值的 最长峰形,即峰值前面的数小于峰值,
峰值后面的数大于峰值
2.如果出现长度一样的峰型,则考虑比较对称的峰形,
即峰值左右数的个数相差比较少的
思路:我们要求的结果的过程是动态的也就是在变化,所以这类题是动态规划
统计每个数值的最佳峰形长度,最后求出最大值
那么在统计每个数值的峰形长度 = 数值前面比起小的个数 + 本身(1)+ 后面比起大的数
下标为 i 的数值 前面比起小的数
m_first[i] = max(m_first[i],m_first[前面的数] + 1),这里加一是表示统计第一次前面有数比起小的时候为1
下标为 i 的数值 后面比起小的数
m_last[i] = max(m_last[i],m_last[后面的数] + 1)
*/
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int main(){
int m_first[10010];//存的是m[i] 前面比起小的个数
int m_last[10010]; //存的是m[i] 后面比起小的个数
int m[10010];// 存放的输入的数值
memset(m_first,0,sizeof(m_first));
memset(m_last,0,sizeof(m_last));
memset(m,0,sizeof(m));
int N;
cin >> N;
for(int i = 1; i <= N; i++){
cin >> m[i];
}
//统计 峰值 前面的递增的序列当中的数个数
for(int i = 1; i <= N; i++){
for(int j = 1; j <= i - 1; j++){
if(m[j] < m[i])
m_first[i] = max(m_first[i],m_first[j] + 1);//这里的每次更新,会将有的数值均前面比起大的 也就是m_first[i] = 0,那么后面的数统计到这时候会均比0大
}
}
//从后往前 也就是峰值后面的递减序列
for(int i = N; i >= 1; i--){
for(int j = N; j >= i + 1; j--){
if(m[j] < m[i]){
m_last[i] = max(m_last[i],m_last[j] + 1);
}
}
}
//开始统计不同下标下的个数
int max = 0;
for(int i = 1; i <= N; i++){
int temp = m_first[i] + m_last[i];
int maxx = m_first[max] + m_last[max];
if(m_first[i] == 0 || m_last[i] == 0)//如果出现递增或递减序列 那么其m_last[i] == 0, m_first[i] == 0;
continue;
else if(temp > maxx)
max = i;
//这种情况就是 长度一致,我们要选择更加对称的
else if(temp == maxx && (abs(m_first[i] - m_last[i])) < (abs(m_first[max] - m_last[max])) )
max = i;
}
//如果出现递增或是递减的序列则 m_first[max] + m_last[max] == 0;
if(m_first[max] + m_last[max] > 0){
cout << m_first[max] + 1 + m_last[max] << ' ' << max << ' ' << m[max];
}else{
cout << "No peak shape";
}
}
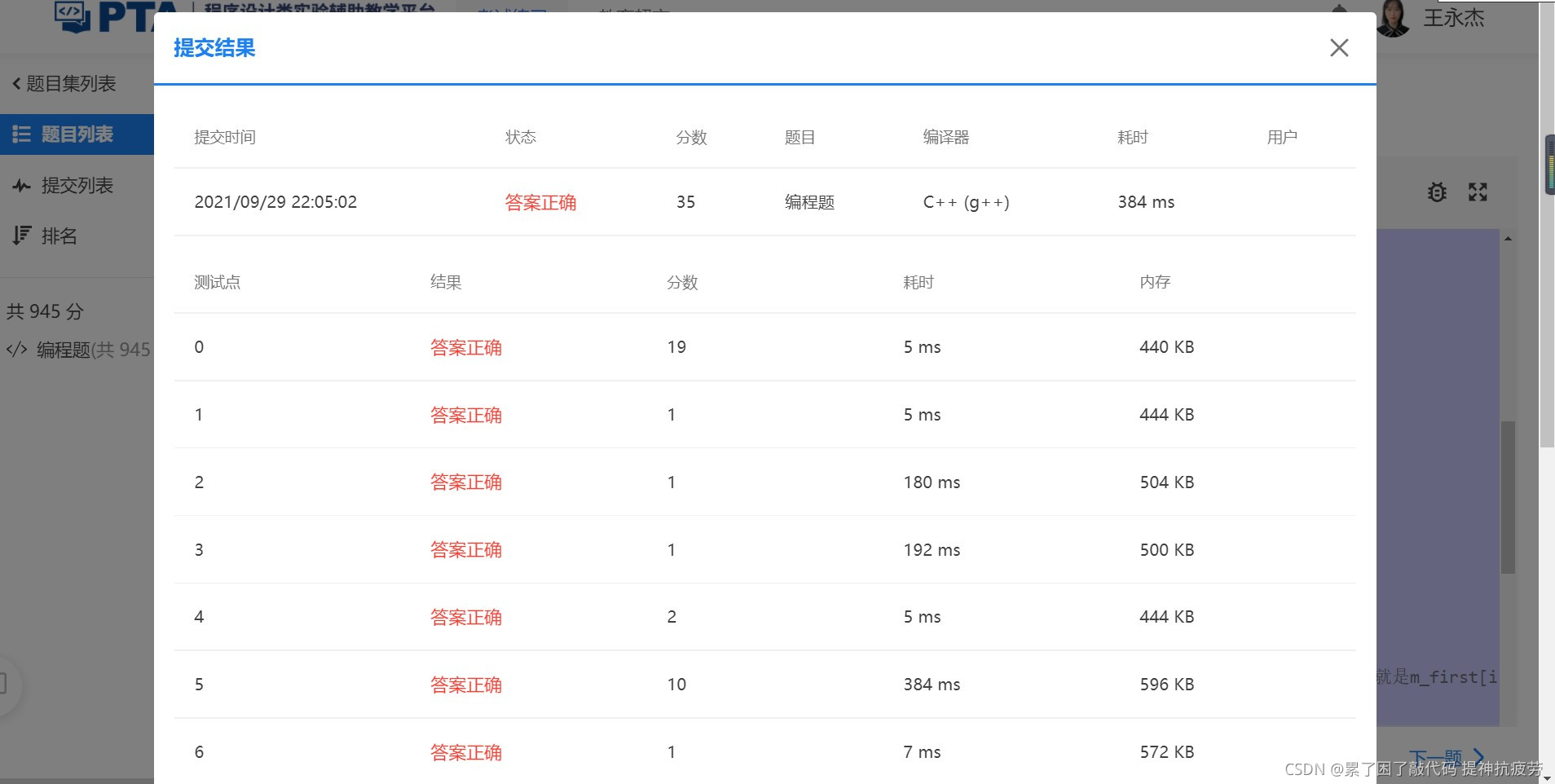
加油陌生人,我们共勉!如有疑问欢迎留言!!!!!!!