今天我们学习的是链栈,也就是说栈的链式结构,我们运用顺序链的方式来实现。首先呢,链栈是不存在存储空间满的情况的,所以可以说它是个无底洞,然而我们之前学的顺序栈是有额定空间的。
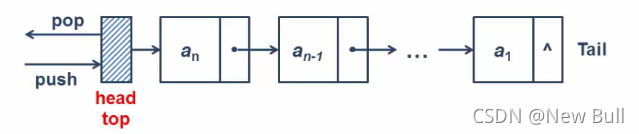
?栈顶指针总是指向栈顶前面的头节点(head top)。在链式栈中,我们也需要使用空间申请的方式来获取空间内存,当然了,如果我们进行出栈操作后,我们就得释放空间。
我们先定义个数据类型:
typedef int StackElementType;
typedef int Belongs_NewBull;链式栈的定义:
对于链栈的定义的话,我们要严格使用typedef struct node { }; 注意这里的node字段不可以写成Node或者其他的。(我也不知道为啥,有大神知到希望可以留言告知)(详情看代码注释)
typedef struct node {//注意这里只能用node而不能用Node或者其他,不然会报错
StackElementType data;//定义一个数据存储data
struct node* next;//指向下一个节点的指针
}SNode; typedef SNode* LinkStack;
LinkStack top;//top指针用于指向next或者data的链栈的初始化:初始化呢我们首先要申请一个动态空间top,然后将下一个节点设为NULL(详情看代码注释)
Belongs_NewBull InitStack() {//在这里我们一般习惯性的怎加*在top前面,这样的话会,后续代码会报错
top = (LinkStack)malloc(sizeof(SNode));//为top申请动态空间
if (top == NULL) {//判断是否申请动态内存成功
printf("初始化错误!!!");
return 0;
}
top->next = NULL;//申请成功后,将top的下一个空间为空NIULL
return 1;
}链栈的Push操作:Push操作时,我们需要为临时定义的p获取动态内存。(详情看代码注释)
Belongs_NewBull Push() {
SNode* p;
int n,i=0;
StackElementType temp;
printf("请输入你要输入数据的个数:");
scanf_s("%d",&n);
for (i; i < n; i++) {
p = (SNode*)malloc(sizeof(SNode));//为p申请动态空间,每次输入都需要给p开辟新的空间,不然则无法赋值
scanf_s("%d", &temp);//将要输入的第某个数据赋值给temp
p->data = temp;//将temp的值赋值给p暂时储存下来,这里的p用的是 SNode*p中的p
p->next = top->next;//将此时的top的地址空间传给p
top->next = p;//将上面开辟的空间传给top
}
return 1;
}链栈的Pop操作:Pop操作完成后我们需要进行对栈顶出栈后的元素占的空间释放,采用函数free()(详情看代码注释)
Belongs_NewBull Pop() {
SNode* p;
StackElementType d;
p = top->next;//将栈顶(top)的地址传给p,用以判断链栈是否为空
if (p == NULL) {
printf("链栈为空,程序退出!!!\n");
return 0;
}
top->next = p->next;//将此时的top的地址传给p
d = p->data;//将要删除的数据交给d存下来
printf("已经出栈掉:%d", d);
free(p);//将top在上面传给p的空间释放
return 1;
}获取链栈的高度(长度):使用新定义的p指针,将头节点前的地址指针传给p(p=top->next),使用while循环对len累加,然后打印出长度。(详情看代码注释)
Belongs_NewBull get_length_Stack() {
SNode* p;
int len=0;
p = top->next;//将栈顶(top)的地址传给p(也可以说成头节点前的位置信息)
while (p != NULL) {
len++;
p = p->next;//从上至下,随着while的循环p所指的地址(高度)往下传
}
printf("链栈的长度为:%d\n", len);
return 1;
}链栈的输出语句:使用新定义的p指针,将头节点前的地址指针传给p(p=top->next)(详情看代码注释)
Belongs_NewBull Display() {
int temp;
SNode* p;
p = top->next;//将头节点前的位置的参数传给p
if (top->next == NULL) {
printf("链表为空!!\n");
return 0;
}
printf("链栈的数据为:\n");
while (p!= NULL) {
temp = p->data;//将此时的p对应的数据赋值给temp便于输出
printf("%d ", temp);
p = p->next;//位置参数将依次由while循环向下传导
}
printf("\n");
return 1;
}整体代码:
#include<stdio.h>
#include<iostream>
#include<malloc.h>
#include<cstring>
using namespace std;
typedef int StackElementType;
typedef int Belongs_NewBull;
typedef struct node {//注意这里只能用node而不能用Node或者其他,不然会报错
StackElementType data;//定义一个数据存储data
struct node* next;//指向下一个节点的指针
}SNode; typedef SNode* LinkStack;
LinkStack top;//top指针用于指向next或者data的
Belongs_NewBull InitStack() {//在这里我们一般习惯性的怎加*在top前面,这样的话会,后续代码会报错
top = (LinkStack)malloc(sizeof(SNode));//为top申请动态空间
if (top == NULL) {//判断是否申请动态内存成功
printf("初始化错误!!!");
return 0;
}
top->next = NULL;//申请成功后,将top的下一个空间为空NIULL
return 1;
}
Belongs_NewBull Push() {
SNode* p;
int n,i=0;
StackElementType temp;
printf("请输入你要输入数据的个数:");
scanf_s("%d",&n);
for (i; i < n; i++) {
p = (SNode*)malloc(sizeof(SNode));//为p申请动态空间,每次输入都需要给p开辟新的空间,不然则无法赋值
scanf_s("%d", &temp);//将要输入的第某个数据赋值给temp
p->data = temp;//将temp的值赋值给p暂时储存下来,这里的p用的是 SNode*p中的p
p->next = top->next;//将此时的top的地址空间传给p
top->next = p;//将上面开辟的空间传给top
}
return 1;
}
Belongs_NewBull Pop() {
SNode* p;
StackElementType d;
p = top->next;//将栈顶(top)的地址传给p,用以判断链栈是否为空
if (p == NULL) {
printf("链栈为空,程序退出!!!\n");
return 0;
}
top->next = p->next;//将此时的top的地址传给p
d = p->data;//将要删除的数据交给d存下来
printf("已经出栈掉:%d", d);
free(p);//将top在上面传给p的空间释放
return 1;
}
Belongs_NewBull get_length_Stack() {
SNode* p;
int len=0;
p = top->next;//将栈顶(top)的地址传给p
while (p != NULL) {
len++;
p = p->next;//从上至下,随着while的循环p所指的地址(高度)往下传
}
printf("链栈的长度为:%d\n", len);
return 1;
}
Belongs_NewBull Display() {
int temp;
SNode* p;
p = top->next;//将栈顶(top)的位置的参数传给p
if (top->next == NULL) {
printf("链表为空!!\n");
return 0;
}
printf("链栈的数据为:\n");
while (p!= NULL) {
temp = p->data;//将此时的p对应的数据赋值给temp便于输出
printf("%d ", temp);
p = p->next;//位置参数将依次由while循环向下传导
}
printf("\n");
return 1;
}
Belongs_NewBull main() {
int i;
string answer;
while (true) {
start:
printf("===========功能如下==========\n");
printf("======1.建立并初始化链栈======\n");
printf("======2.向链栈进行Push操作======\n");
printf("======3.将链栈中的数据输出======\n");
printf("======4.对链栈进行Pop操作======\n");
printf("======5.获取链栈的长度======\n");
printf("======6.清空链栈======\n");
printf("======0.退出程序======\n");
printf("学号:204010110 姓名:程兰昌\n");
printf("请输入数字进行操作:\n");
scanf_s("%d", &i);
switch(i){
case 1://建立链栈并初始化
InitStack();
system("pause");
system("cls");
goto start;
case 2:
Push();
system("pause");
system("cls");
goto start;
case 3:
Display();
system("pause");
system("cls");
goto start;
case 4:
Pop();
system("pause");
system("cls");
goto start;
case 5:
get_length_Stack();
system("pause");
system("cls");
goto start;
case 6:
InitStack();
system("pause");
system("cls");
goto start;
case 0://退出整个程序的代码
printf("确定退出程序吗?(yes or no):");
cin >> answer;
if (answer == "yes" || answer == "YES")exit(0);
if (answer == "no" || answer == "NO") {
system("pause");
system("cls");
goto start;
}
else {
printf("输入指令有误,程序继续!!\n");
system("pause");
system("cls");
goto start;
}
}
}
return 0;
}版权属于作者 New Bull? ? ? ?未经允许不可转载,否者将追究版权问题