一、继承访问权限测试
1.1 Inherit.cpp
a. 设计类A具有public, protected, private等不同属性的成员函数或变量:
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
class A
{
public:
int pub = 1;
protected:
int pro = 2;
private:
int pri = 3;
};
b. 类B通过不同方式继承A,在类B的成员函数中测试访问A的成员函数或变量;
并在类B中添加public, protected, private等不同属性的成员函数或变量,在外部测试访问B的各个成员函数或变量;
以public方式继承:
class Pub_B : public A
{
public:
void Test()
{
cout << pub << endl;
cout << pro << endl;
//cout << pri << endl; 成员"A::pri" 不可访问
}
int pub_pub = 4;
protected:
int pub_pro = 5;
private:
int pub_pri = 6;
};
以protected方式继承:
class Pro_B : protected A
{
public:
void Test()
{
cout << pub << endl;
cout << pro << endl;
//cout << pri << endl; 成员"A::pri" 不可访问
}
int pro_pub = 7;
protected:
int pro_pro = 8;
private:
int pro_pri = 9;
};
以private方式继承:
class Pri_B : private A
{
public:
void Test()
{
cout << pub << endl;
cout << pro << endl;
//cout << pri << endl; 成员"A::pri" 不可访问
}
int pri_pub = 10;
protected:
int pri_pro = 11;
private:
int pri_pri = 12;
};
c. B以private方式继承A,尝试把A中的部分public成员提升为public。
class newPri_B : private A
{
public:
void Test() {
cout << pub << endl;
cout << pro << endl;
//cout << pri << endl; 成员"A::pri" 不可访问
}
int nPri_pub = 13;
using A::pub;
protected:
int nPri_pro = 14;
private:
int nPri_pri = 15;
};
- B以private方式继承A,用{using A::_a; }把A中的部分public成员提升为public
- 如果想让这些继承而来的数据成员作为public或者protected成员,可以用using重新声明。using声明语句中名字的访问权限由该using声明语句之前的访问说明符决定。
d. 访问权限测试
void test()
{
A a;
cout << a.pub << endl;
//cout << a.pro << endl; 成员"A::pro" 不可访问
//cout << a.pri << endl; 成员"A::pri" 不可访问
cout << endl;
Pub_B B1;
B1.Test();
cout << B1.pub << endl;
//cout << B1.pro << endl; 成员"A::pro" 不可访问
//cout << B1.pri << endl; 成员"A::pri" 不可访问
cout << B1.pub_pub << endl;
//cout << B1.pub_pro << endl; 成员"Pub_B::pub_pro" 不可访问
//cout << B1.pub_pri << endl; 成员"Pub_B::pub_pri" 不可访问
cout << endl;
Pro_B B2;
B2.Test();
//cout << B2.pub << endl; 成员"A::pub" 不可访问
//cout << B2.pro << endl; 成员"A::pro" 不可访问
//cout << B2.pri << endl; 成员"A::pri" 不可访问
cout << B2.pro_pub << endl;
//cout << B2.pro_pro << endl; 成员"Pro_B::pro_pro" 不可访问
//cout << B2.pro_pri << endl; 成员"Pro_B::pro_pri" 不可访问
cout << endl;
Pri_B B3;
B3.Test();
//cout << B3.pub << endl; 成员"A::pub" 不可访问
//cout << B3.pro << endl; 成员"A::pro" 不可访问
//cout << B3.pri << endl; 成员"A::pri" 不可访问
cout << B3.pri_pub << endl;
//cout << B3.pri_pro << endl; 成员"Pri_B::pri_pro" 不可访问
//cout << B3.pri_pri << endl; 成员"Pri_B::pri_pri" 不可访问
cout << endl;
newPri_B B4;
B4.Test();
cout << B4.pub << endl;
//cout << B4.pro << endl; 成员"A::pro" 不可访问
//cout << B4.pri << endl; 成员"A::pri" 不可访问
cout << B4.nPri_pub << endl;
//cout << B4.nPri_pro << endl; 成员"newPri_B::nPri_pro" 不可访问
//cout << B4.nPri_pri << endl; 成员"newPri_B::nPri_pri" 不可访问
}
int main() {
test();
return 0;
}

1.2 小结
- 派生类内不管是 public、protected、private 继承,总是可以 public、protected 成员,基类中的private 成员永远不能再派生类内直接访问,不论通过哪种方式。
- 派生类对象仅当 public 派生时,对基类中的 public 成员有可访问/可修改的权限,其他都为不可访问/不可修改。
另外,继承方式会改变从基类继承的成员在派生类的访问权限:
- public 继承不改变基类成员的访问权限
- protected 继承将基类中 public 成员变为子类的 protected 成员,其它成员的访问权限不变
- private 继承使得基类所有成员在子类中的访问权限变为 private
二、友元类继承测试
2.1 Inherit_Friend.cpp
a. 设计类A含有私有变量a,在类A中友元给类C;
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
/**
*设计类A含有私有变量a,在类A中友元给类C
*/
class A
{
private:
int _a = 1;
friend class C;
};
b. 设计类B继承A,添加私有变量b;在类C中测试访问类B的成员变量a, b;
/**
*设计类B继承A,添加私有变量b
*/
class B : public A
{
private:
int _b = 2;
};
c. 设计类C,测试访问类B的成员变量a,b
/**
*类C:测试访问类B的成员变量a,b
*/
class C
{
public:
void Test()
{
B b;
cout << b._a << endl;
//cout << b._b << endl; 成员"B::_b"不可访问
return;
}
};
此时类C中访问不到类B的私有成员量b,但是访问得到成员量a。
d. 设计类D继承C,在D的成员函数中测试访问类A的成员变量a,类B的成员变量a, b。
/**
*设计类D继承C
*测试访问类A的成员变量a,类B的成员变量a, b
*/
class D : public C
{
public:
void Test()
{
A a;
//cout << a._a << endl; 成员"A::_a"不可访问
B b;
//cout << b._a << endl; 成员"A::_a"不可访问
//cout << b._b << endl; 成员"B::_b"不可访问
}
};
对于类D来说,A的成员变量a,类B的成员变量a, b均不可访问。
2.2 小结
- 友元关系不能继承。基类的友元对派生类的成员没有特殊访问权限
- 如果基类被授予友元关系,则只有基类具有特殊访问权限,该基类的派生类不能访问授予友元关系的类
- 友元关系是单向的,不具有交换性,友元关系也不具有传递性。
三、多态性综合运用
3.1 多态性
多态性(polymorphism)可以简单地概括为“一个接口,多种方法”(相当于上级说一个命令,A,B,C,D等人都做出反应,一个命令,多个反应),它是面向对象编程领域的核心概念。
多态性指相同对象收到不同消息或不同对象收到相同消息时产生不同的实现动作。C++支持两种多态性:编译时多态性,运行时多态性。面向对象的多态性可以分为4类:重载多态,强制多态,包含多态,参数多态。前面两种统称专用多态,后面两种统称通用多态。
- 编译时多态性(静态多态):通过重载函数实现:先期联编 early binding
- 运行时多态性(动态多态):通过虚函数实现 :滞后联编 late binding
C++运行时多态性是通过虚函数来实现的,虚函数允许子类重新定义成员函数,而子类重新定义父类的做法称为覆盖(Override),或者称为重写。
多态的目的:封装可以使得代码模块化,继承可以扩展已存在的代码,它们的目的都是为了代码重用。而多态的目的则是为了“接口重用”。也即,不论传递过来的究竟是类的哪个对象,函数都能够通过同一个接口调用到适应各自对象的实现方法。
3.2 一般多态性函数
输入输出参数完全一样,在父类中添加virtual
新建CAnimal类,Move()是其内部虚函数,新建CCat类、CEagle类、COwl类继承CAnimal类,并重写其内部的虚函数Move()的实现方法以实现多态的效果。
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class CAnimal
{
public:
//无参构造函数
CAnimal() {
m_nLegs = 2;
}
CAnimal(int nLeg) {
m_nLegs = nLeg;
}
//虚函数
virtual void Move() {
cout << "I can crawl or fly!" << endl;
}
protected:
int m_nLegs;
};
class CCat : virtual public CAnimal
{
public:
//无参构造函数
CCat() {
m_nLegs = 4;
}
CCat(int nLegs) {
m_nLegs = nLegs;
}
virtual void Move() {
cout << "I am a cat,I can crawl!" << endl;
}
};
class CEagle : virtual public CAnimal
{
public:
//无参构造函数
CEagle() {
m_nLegs = 2;
}
CEagle(int nLegs) {
m_nLegs = nLegs;
}
virtual void Move() {
cout << "I am an eagle,I can fly!" << endl;
}
};
class COwl : public CCat, public CEagle
{
public:
//无参构造函数
COwl() {
m_nLegs = 2;
}
COwl(int nLegs) {
m_nLegs = nLegs;
}
virtual void Move() {
cout << "I am an owl,I can also fly!" << endl;
}
};
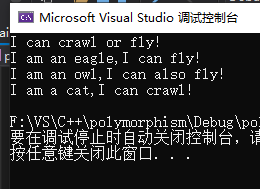
void TestAnimal()
{
CAnimal* pAnimal[4];
pAnimal[0] = new CAnimal(2);
pAnimal[1] = new CCat(4);
pAnimal[2] = new CEagle(2);
pAnimal[3] = new COwl(2);
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++)
{
pAnimal[i]->Move();
}
}
int main() {
TestAnimal();
return 0;
}

3.3 特殊多态性函数
输入或输出参数在子类中是父类的指针或基类的引用,在子类中对于的是子类的指针或子类的引用
此处的特殊多态性含义为函数的参数是父类的指针(引用)或者子类的指针(引用)(即在运行过程中实现虚函数的绑定(运行时多态))。
void callMove(CAnimal* pAn) {
pAn->Move();
}
void TestAnimal()
{
CAnimal animal;
CEagle eagle;
COwl owl;
CCat cat;
callMove(&animal);
callMove(&eagle);
callMove(&owl);
callMove(&cat);
}
3.4 析构函数的多态性
我们在应用C++的多态特性时,常常会碰到一种情况,就是当指向基类的指针被释放时,派生类的析构函数其实没有被调用,导致在派生类中申请的空间没有被释放,导致内存泄漏。
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Base {
public:
Base() {cout << "Base constructor... \n";}
~Base() {cout << "Base destructor... \n";}
virtual void fun() const {cout << "Base functoin...\n";}
};
class Derived :public Base {
public:
Derived() {
p = new int(0);
cout << "Derived Constructor...\n";
}
~Derived() {
cout << "Derived destructor...\n";
delete p;
}
void fun() const {cout << "Derived function...\n";}
private:
int *p;
};
int main() {
Base* pd = new Derived;
pd->fun();
delete pd;
return 0;
}

我们可以看到派生类的析构函数没有调用,派生类的构造函数申请的空间泄漏了。
为防止这种情况出现,我们将代码改为:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Base {
public:
Base() {cout << "Base constructor... \n";}
virtual ~Base() {cout << "Mammal destructor... \n";}
virtual void fun() const {cout << "Base functoin...\n";}
};
class Derived :public Base {
public:
Derived() {
p = new int(0);
cout << "Derived Constructor...\n";
}
~Derived() {
cout << "Derived destructor...\n";
delete p;
}
void fun() const {cout << "Derived function...\n";}
private:
int *p;
};
int main() {
Base* pd = new Derived;
pd->fun();
delete pd;
return 0;
}

通过将基类的析构函数声明为虚析构函数,成功的通过基类指针调用了派生类的析构函数,完成了内存的释放。
3.5 多继承
c++不仅可以单继承,也可以多继承。
多继承的概念: 如果一个派生类从多个基类继承, 则称为多继承。
多继承的声明:
class 派生类名:访问控制 基类名1, 访问控制 基类名2, …
{
成员列表
}
注意:
- 多个基类的派生类的构造函数执行的顺序与单继承的情况类似,执行顺序取决于定义派生类时指定的继承基类的顺序。
- 一个派生类对象拥有多个基类的成员。 不同名成员访问不会出现二义性; 如果不同的基类拥有同名成员, 派生类对象访问时应该加以识别。
- 如果派生类声明了一个和基类成员同名的新成员, 派生的新成员就覆盖了基类同名成员, 直接使用成员名只能访问到派生类的成员。
虚继承:
class A
{
public:
int a;
};
class B : public A
{
public:
int b;
};
class C : public A
{
public:
int c;
};
class D :public B, public C
{
public:
int d;
void fun()
{
d = a;
}
};
此时出现二义性,应将 class B : virtual public A,class C : virtual public A,运用虚继承消除二义性
3.6 应用
设计矢量图,运用多继承设计组合图形,要求具备创建不同类型矢量图、选择图形、移动图形、用不同颜色显示图形(表示选中与否),用vector或数组管理图形。
CShape.h
#ifndef CSHAPE_H
#define CSHAPE_H
#include<string>
#include<math.h>
using namespace std;
class CPoint;
class CRect;
class CShape
{
public:
CShape();
CShape(const CShape& shape);
virtual ~CShape();
virtual double GetArea() const;
virtual bool ptIn(const CPoint& pt) const;
virtual bool InRect(const CRect& rc) const;
virtual void Draw() const;
virtual void DrawColor();
virtual CShape* Clone() const;
virtual CShape& Move(int nOffsetX, int nOffsetY);
protected:
string m_sName;
};
class CPoint :public CShape {
public:
int m_nPosX;
int m_nPosY;
CPoint() {
m_nPosX = 0;
m_nPosY = 0;
}
CPoint(int nPosX, int nPosY);
CPoint(const CPoint& pt);
virtual ~CPoint();
double GetArea() const;
bool ptIn(const CPoint& pt) const;
bool InRect(const CRect& rc) const;
void Draw() const;
void DrawColor();
CPoint* Clone() const;
CPoint& Move(int nOffsetX, int nOffsetY);
};
class CTriangle :virtual public CShape {
public:
CTriangle() {}
CTriangle(const CPoint& pt1, const CPoint& pt2, const CPoint& pt3);
CTriangle(const CTriangle& rc);
CTriangle(const CPoint& pt);
virtual ~CTriangle();
double GetArea() const;
bool ptIn(const CPoint& pt) const;
bool InRect(const CRect& rc) const;
void Draw() const;
void DrawColor();
CShape* Clone() const;
CShape& Move(int nOffsetX, int nOffsetY);
CPoint m_pts[3];
};
class CRect :virtual public CShape {
public:
CRect() {}
CRect(CPoint pt1, CPoint pt2);
CRect(const CRect& rc);
CRect(CPoint pt1);
virtual ~CRect();
double GetArea() const;
bool ptIn(const CPoint& pt) const;
bool InRect(const CRect& rc) const;
void Draw() const;
void DrawColor();
CShape* Clone() const;
CShape& Move(int nOffsetX, int nOffsetY);
CPoint m_ptLT;
CPoint m_ptBR;
};
class Comgraphics :public CRect, public CTriangle {
public:
Comgraphics(const CRect& pt1);
Comgraphics(const Comgraphics& rc);
Comgraphics(const CPoint pt1);
virtual ~Comgraphics();
double GetArea() const;
bool ptIn(const CPoint& pt) const;
bool InRect(const CRect& rc) const;
void Draw() const;
void DrawColor();
CShape* Clone() const;
CShape& Move(int nOffsetX, int nOffsetY);
CPoint m_pt1;
CPoint m_pt2;
};
#endif
CShape.cpp
#include "CShape.h"
#include "graphics.h"
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
//CShape
CShape::CShape()
{
}
CShape::CShape(const CShape& shape) {
m_sName = shape.m_sName;
}
CShape::~CShape()
{
}
double CShape::GetArea() const {
return 0;
}
bool CShape::ptIn(const CPoint& pt) const {
return false;
}
bool CShape::InRect(const CRect& rc) const {
return false;
}
void CShape::Draw() const
{
}
void CShape::DrawColor()
{
}
CShape* CShape::Clone() const {
return new CShape(*this);
}
CShape& CShape::Move(int nOffsetX, int nOffsetY) {
return *this;
}
//CPoint
CPoint::CPoint(int nPosX, int nPosY) {
m_nPosX = nPosX;
m_nPosY = nPosY;
}
CPoint::CPoint(const CPoint& pt) {
m_nPosX = pt.m_nPosX;
m_nPosY = pt.m_nPosY;
}
CPoint::~CPoint() {
//cout << "CPoint::~CPoint()\n";
}
double CPoint::GetArea() const {
return 0;
}
bool CPoint::ptIn(const CPoint& pt) const {
return false;
}
bool CPoint::InRect(const CRect& rc) const {
return rc.ptIn(*this);
}
void CPoint::Draw() const {
circle(m_nPosX, m_nPosY, 2);
}
void CPoint::DrawColor()
{
}
CPoint* CPoint::Clone() const {
return new CPoint(*this);
}
CPoint& CPoint::Move(int nOffsetX, int nOffsetY) {
m_nPosX += nOffsetX;
m_nPosY += nOffsetY;
return *this;
}
//CTriangle
CTriangle::CTriangle(const CTriangle& tri) {
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
m_pts[i] = tri.m_pts[i];
}
}
CTriangle::~CTriangle() {
//cout << "CTriangle::~CTriangle()\n";
}
CTriangle::CTriangle(const CPoint& pt1, const CPoint& pt2, const CPoint& pt3) {
m_pts[0] = pt1;
m_pts[1] = pt2;
m_pts[2] = pt3;
}
CTriangle::CTriangle(const CPoint& pt)
{
CPoint* pt1 = new CPoint(pt.m_nPosX + 100, pt.m_nPosY + 90);
CPoint* pt2 = new CPoint(pt.m_nPosX, pt.m_nPosY + 90);
m_pts[0] = pt;
m_pts[1] = *pt1;
m_pts[2] = *pt2;
}
CShape& CTriangle::Move(int nOffsetX, int nOffsetY) {
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
m_pts[i].Move(nOffsetX, nOffsetY);
}
return *this;
}
double CTriangle::GetArea() const {
int x1, y1, x2, y2, x3, y3;
x1 = m_pts[0].m_nPosX;
y1 = m_pts[0].m_nPosY;
x2 = m_pts[1].m_nPosX;
y2 = m_pts[1].m_nPosY;
x3 = m_pts[2].m_nPosX;
y3 = m_pts[2].m_nPosY;
double bottomLine = sqrt(pow(x1 - x2, 2) + pow(y1 - y2, 2));
double verticalLine1 = abs((y1 - y2) * x3 - (x1 - x2) * y3 + (x1 - x2) * y2 - (y1 - y2) * x2);
double verticalLine2 = sqrt(pow(y1 - y2, 2) + pow(x1 - x2, 2));
double verticalLine = verticalLine1 / verticalLine2;
return (verticalLine * bottomLine) / 2.0;
}
bool CTriangle::ptIn(const CPoint& pt) const {
CTriangle c1 = CTriangle(m_pts[0], m_pts[1], pt);
CTriangle c2 = CTriangle(m_pts[1], m_pts[2], pt);
CTriangle c3 = CTriangle(m_pts[2], m_pts[0], pt);
double totalArea = c1.GetArea() + c2.GetArea() + c3.GetArea();
if (totalArea == this->GetArea())
return true;
else
return false;
}
bool CTriangle::InRect(const CRect& rc) const {
return rc.ptIn(m_pts[0]) && rc.ptIn(m_pts[1]) && rc.ptIn(m_pts[2]);
}
void CTriangle::Draw() const {
int poly[8] = { m_pts[0].m_nPosX ,m_pts[0].m_nPosY,m_pts[1].m_nPosX,m_pts[1].m_nPosY,
m_pts[2].m_nPosX,m_pts[2].m_nPosY, m_pts[0].m_nPosX ,m_pts[0].m_nPosY };
setfillcolor(EGERGB(0xFF, 0xFF, 0xFF));
fillpoly(4, poly);
}
void CTriangle::DrawColor() {
int poly[8] = { m_pts[0].m_nPosX ,m_pts[0].m_nPosY,m_pts[1].m_nPosX,m_pts[1].m_nPosY,
m_pts[2].m_nPosX,m_pts[2].m_nPosY, m_pts[0].m_nPosX ,m_pts[0].m_nPosY };
setfillcolor(EGERGB(0xFF, 0xA5, 0x00));
fillpoly(4, poly);
}
CShape* CTriangle::Clone() const {
return new CTriangle(*this);
}
//CRect
CRect::CRect(CPoint pt1, CPoint pt2) {
m_ptLT = CPoint(min(pt1.m_nPosX, pt2.m_nPosX), min(pt1.m_nPosY, pt2.m_nPosY));
m_ptBR = CPoint(max(pt1.m_nPosX, pt2.m_nPosX), max(pt1.m_nPosY, pt2.m_nPosY));
}
CRect::CRect(const CRect& rc) {
m_ptLT = rc.m_ptLT;
m_ptBR = rc.m_ptBR;
}
CRect::CRect(CPoint pt1)
{
m_ptLT = CPoint(pt1.m_nPosX, pt1.m_nPosY);
m_ptBR = CPoint(pt1.m_nPosX + 100, pt1.m_nPosY + 100);
}
CRect::~CRect() {
// cout << "CRect::CRect()\n";
}
double CRect::GetArea() const {
return (m_ptBR.m_nPosX - m_ptLT.m_nPosX) * (m_ptBR.m_nPosY - m_ptLT.m_nPosY);
}
bool CRect::ptIn(const CPoint& pt) const {
return (pt.m_nPosX >= m_ptLT.m_nPosX && pt.m_nPosX <= m_ptBR.m_nPosX) &&
(pt.m_nPosY >= m_ptLT.m_nPosY && pt.m_nPosY <= m_ptBR.m_nPosY);
}
bool CRect::InRect(const CRect& rc) const {
return rc.ptIn(m_ptLT) && rc.ptIn(m_ptBR);
}
void CRect::Draw() const {
// 存储n个顶点的x,y坐标
int pts[10] = { m_ptLT.m_nPosX,m_ptLT.m_nPosY,m_ptBR.m_nPosX,m_ptLT.m_nPosY,
m_ptBR.m_nPosX,m_ptBR.m_nPosY,m_ptLT.m_nPosX,m_ptBR.m_nPosY,m_ptLT.m_nPosX,m_ptLT.m_nPosY };
// 绘制n个顶点的多边形,第一个参数必须要传入n+1,pts最后一个顶点坐标和第一个相同
//drawpoly(5, pts);
setfillcolor(EGERGB(0xFF, 0xFF, 0xFF));
fillpoly(5, pts);
}
void CRect::DrawColor() {
int pts[10] = { m_ptLT.m_nPosX,m_ptLT.m_nPosY,m_ptBR.m_nPosX,m_ptLT.m_nPosY,
m_ptBR.m_nPosX,m_ptBR.m_nPosY,m_ptLT.m_nPosX,m_ptBR.m_nPosY,m_ptLT.m_nPosX,m_ptLT.m_nPosY };
// 绘制n个顶点的多边形,第一个参数必须要传入n+1,pts最后一个顶点坐标和第一个相同
setfillcolor(EGERGB(0xFF, 0xA5, 0x00));
fillpoly(5, pts);
}
CShape* CRect::Clone() const {
return new CRect(*this);
}
CShape& CRect::Move(int nOffsetX, int nOffsetY) {
m_ptLT.Move(nOffsetX, nOffsetY);
m_ptBR.Move(nOffsetX, nOffsetY);
return *this;
}
//Comgraphics
Comgraphics::Comgraphics(const CRect& pt1) {
m_pt1.m_nPosX = pt1.m_ptBR.m_nPosX;
m_pt1.m_nPosY = pt1.m_ptLT.m_nPosY + (pt1.m_ptBR.m_nPosY - pt1.m_ptLT.m_nPosY) / 2;
m_pt2.m_nPosX = pt1.m_ptLT.m_nPosX + (pt1.m_ptBR.m_nPosX - pt1.m_ptLT.m_nPosX) / 2;
m_pt2.m_nPosY = pt1.m_ptBR.m_nPosY;
m_ptLT = pt1.m_ptLT;
m_ptBR = pt1.m_ptBR;
}
Comgraphics::Comgraphics(const Comgraphics& rc) {
m_pt1 = rc.m_pt1;
m_pt2 = rc.m_pt2;
m_ptBR = rc.m_ptBR;
m_ptLT = rc.m_ptLT;
}
Comgraphics::Comgraphics(const CPoint pt1) {
m_ptLT = CPoint(pt1.m_nPosX, pt1.m_nPosY);
m_ptBR = CPoint(pt1.m_nPosX + 60, pt1.m_nPosY + 80);
}
Comgraphics::~Comgraphics() {
cout << "Comgraphics::~Comgraphics()" << endl;
}
double Comgraphics::GetArea() const {
return 0.0;
}
bool Comgraphics::ptIn(const CPoint& pt) const {
return (pt.m_nPosX >= m_ptLT.m_nPosX && pt.m_nPosX <= m_ptBR.m_nPosX) &&
(pt.m_nPosY >= m_ptLT.m_nPosY && pt.m_nPosY <= m_ptBR.m_nPosY);
}
bool Comgraphics::InRect(const CRect& rc) const const {
return rc.ptIn(m_ptLT) && rc.ptIn(m_ptBR);
}
void Comgraphics::Draw() const {
// 存储n个顶点的x,y坐标
int pts[10] = { m_ptLT.m_nPosX,m_ptLT.m_nPosY,m_ptBR.m_nPosX,m_ptLT.m_nPosY,
m_ptBR.m_nPosX,m_ptBR.m_nPosY,m_ptLT.m_nPosX,m_ptBR.m_nPosY,m_ptLT.m_nPosX,m_ptLT.m_nPosY };
// 绘制n个顶点的多边形,第一个参数必须要传入n+1,pts最后一个顶点坐标和第一个相同
//drawpoly(5, pts);
setfillcolor(GREEN);
fillpoly(5, pts);
line(m_pt1.m_nPosX, m_pt1.m_nPosY, m_pt2.m_nPosX, m_pt2.m_nPosY);
line(m_ptLT.m_nPosX, m_ptLT.m_nPosY, m_pt2.m_nPosX, m_pt2.m_nPosY);
line(m_pt1.m_nPosX, m_pt1.m_nPosY, m_ptLT.m_nPosX, m_ptLT.m_nPosY);
}
void Comgraphics::DrawColor() {
// 存储n个顶点的x,y坐标
int pts[10] = { m_ptLT.m_nPosX,m_ptLT.m_nPosY,m_ptBR.m_nPosX,m_ptLT.m_nPosY,
m_ptBR.m_nPosX,m_ptBR.m_nPosY,m_ptLT.m_nPosX,m_ptBR.m_nPosY,m_ptLT.m_nPosX,m_ptLT.m_nPosY };
// 绘制n个顶点的多边形,第一个参数必须要传入n+1,pts最后一个顶点坐标和第一个相同
setfillcolor(YELLOW);
fillpoly(5, pts);
line(m_pt1.m_nPosX, m_pt1.m_nPosY, m_pt2.m_nPosX, m_pt2.m_nPosY);
line(m_ptLT.m_nPosX, m_ptLT.m_nPosY, m_pt2.m_nPosX, m_pt2.m_nPosY);
line(m_pt1.m_nPosX, m_pt1.m_nPosY, m_ptLT.m_nPosX, m_ptLT.m_nPosY);
}
CShape* Comgraphics::Clone() const {
return new Comgraphics(*(this));
}
CShape& Comgraphics::Move(int nOffsetX, int nOffsetY) {
m_ptLT.Move(nOffsetX, nOffsetY);
m_ptBR.Move(nOffsetX, nOffsetY);
m_pt1.Move(nOffsetX, nOffsetY);
m_pt2.Move(nOffsetX, nOffsetY);
return *this;
}
Main.cpp
#include<vector>
#include "graphics.h"
#include<iostream>
#include "CShape.h"
using namespace std;
int main()
{
//图形画布基础设置
initgraph(640, 480);
setbkcolor(WHITE);
delay_ms(0);
setcolor(BLACK);
setfont(20, 0, "楷体");
setbkmode(TRANSPARENT);
//enter+左击-->新建矩形");
//enter+右击-->新建三角形");
//enter+滚轮中间-->新建组合图形
//ctrl+左击-->复制图形");
//ctrl+右击-->粘贴图形");
vector<CShape*>shapes;
vector<CShape*>shapestmp;
shapes.push_back(new CTriangle(CPoint(320, 320), CPoint(250, 340), CPoint(340, 450)));
//shapes.push_back(new CTriangle(CPoint(10, 10), CPoint(150, 10), CPoint(150, 150)));
shapes.push_back(new CRect(CPoint(200, 200), CPoint(300, 300)));
shapes.push_back(new Comgraphics(CRect(CPoint(250, 50))));
//移动
bool move_flag = false;
bool copy_flag = false;
bool redraw = true;
//鼠标点击时记录它的坐标
int clickX, clickY;
int copyX, copyY;
int checkedid = -1;
int copyid = -1;
for (; is_run(); delay_fps(60)) {
while (mousemsg()) {
mouse_msg msg = getmouse();
//判断鼠标的移动
if (msg.is_move()) {
if (checkedid != -1) {
if (move_flag) {
shapes[checkedid]->Move(msg.x - clickX, msg.y - clickY);
}
}
clickX = msg.x;
clickY = msg.y;
redraw = true;
}
// 判断鼠标左键
else if (msg.is_left()) {
// 判断鼠标左键是否按下
if (msg.is_down()) {
clickX = msg.x;
clickY = msg.y;
CPoint pt = CPoint(clickX, clickY);
int isIn = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < shapes.size(); i++) {
if (shapes[i]->ptIn(pt)) {
isIn = 1;
//如果鼠标在图形区域内就设置移动的flag为true
move_flag = true;
checkedid = i;
redraw = true;
break;
}
}
if (isIn == 0)
checkedid = -1;
}
else {
move_flag = false;
}
}
}
// 重新绘图
if (redraw) {
redraw = false;
cleardevice();
for (int i = 0; i < shapes.size(); i++) {
if (i == checkedid)
shapes[i]->DrawColor();
else
shapes[i]->Draw();
}
}
while (kbmsg()) {
key_msg msgk = getkey();
if (msgk.key == key_enter && msgk.msg == key_msg_down) {
mouse_msg msgm = getmouse();
if (msgm.is_left()) {
// 判断鼠标左键是否按下
if (msgm.is_down()) {
shapes.push_back(new CRect(CPoint(msgm.x, msgm.y)));
redraw = true;
}
}
if (msgm.is_right()) {
// 判断鼠标右键是否按下
if (msgm.is_down()) {
shapes.push_back(new CTriangle(CPoint(msgm.x, msgm.y)));
redraw = true;
}
}
if (msgm.is_mid()) {
CRect r1 = CRect(CPoint(msgm.x, msgm.y));
// 判断鼠标中键是否按下
if (msgm.is_down()) {
shapes.push_back(new Comgraphics(r1));
redraw = true;
}
}
}
if (msgk.key == key_control && msgk.msg == key_msg_down) {
mouse_msg msgm = getmouse();
if (msgm.is_left()) {
// 判断鼠标左键是否按下
if (msgm.is_down()) {
copyX = msgm.x;
copyY = msgm.y;
CPoint pt = CPoint(copyX, copyY);
for (int i = 0; i < shapes.size(); i++) {
if (shapes[i]->ptIn(pt)) {
//如果鼠标在图形区域内就设置移动的flag为true
copy_flag = true;
copyid = i;
break;
}
}
}
}
if (msgm.is_right()) {
// 判断鼠标右键是否按下
if (msgm.is_down()) {
if (copy_flag == true) {
shapes.push_back(&(shapes[copyid]->Clone())->Move(msgm.x - copyX, msgm.y - copyY));
redraw = true;
}
}
}
}
}
}
closegraph();
return 0;
}

