插入元素到容器中的指定位置
// 在 pos 前插入 value
iterator insert( iterator pos, const T& value ); (C++11 前)
iterator insert( const_iterator pos, const T& value ); (C++11 起)
iterator insert( const_iterator pos, T&& value ); (C++11 起)
//在 pos 前插入 value 的 count 个副本
void insert( iterator pos, size_type count, const T& value );(C++11 前)
iterator insert( const_iterator pos, size_type count, const T& value );(C++11 起)
//在 pos 前插入来自范围 [first, last) 的元素。
template< class InputIt >
void insert( iterator pos, InputIt first, InputIt last); (C++11 前)
template< class InputIt >
iterator insert( const_iterator pos, InputIt first, InputIt last ); (C++11 起)
插入元素到容器中的指定位置。
1-2) 在 pos 前插入 value 。
3) 在 pos 前插入 value 的 count 个副本。
4) 在 pos 前插入来自范围 [first, last) 的元素。
若 InputIt 为整数类型,则此重载与重载 (3) 拥有相同效果。 (C++11 前)
此重载仅若 InputIt 足以为遗留输入迭代器 (LegacyInputIterator) 才参与重载决议,以避免与重载 (3) 有歧义。 (C++11 起)
若 first 和 last 是指向 *this 中的迭代器,则行为未定义。
若新 size() 大于旧 capacity() 则导致重分配。 若新的 size() 大于 capacity() ,则所有迭代器和引用都被非法化。否则,仅在插入点前的迭代器和引用保持合法。尾后迭代器亦被非法化。
参数
pos - 将内容插入到其前的迭代器。 pos 可为 end() 迭代器
value - 要插入的元素值
first, last - 要插入的元素范围,不能是指向调用 insert 所用的容器中的迭代器
ilist - 要插入的值来源的 initializer_list
类型要求
为使用重载 (1) , T 必须满足可复制赋值 (CopyAssignable) 和 可复制插入 (CopyInsertable) 的要求。
为使用重载 (2) , T 必须满足可移动赋值 (MoveAssignable) 和 可移动插入 (MoveInsertable) 的要求。
为使用重载 (3) , T 必须满足可复制赋值 (CopyAssignable) 和 可复制插入 (CopyInsertable) 的要求。 为使用重载 (4,5) , T 必须满足可就位构造 (EmplaceConstructible) 的要求。
为使用重载 (4) , T 必须满足可移动赋值 (MoveAssignable) 和 可移动插入 (MoveInsertable) 的要求。仅若 InputIt 满足遗留输入迭代器 (LegacyInputIterator) 但不满足遗留向前迭代器 (LegacyForwardIterator) 才要求。(C++17 前)
为使用重载 (4,5) , T 必须满足可交换 (Swappable) 、 可移动赋值 (MoveAssignable) 、 可移动构造 (MoveConstructible) 和 可移动插入 (MoveInsertable) 的要求。(C++17 起)
返回值
1-2) 指向被插入 value 的迭代器。
3) 指向首个被插入元素的迭代器,或若 count0 则为 pos 。
4) 指向首个被插入元素的迭代器,或若 firstlast 则为 pos 。
5) 指向首个被插入元素的迭代器,或若 ilist 为空则为 pos 。
复杂度
1-2) 常数,加上 pos 与容器结尾的距离成线性。
3) 与 count 成线性,加上 pos 与容器结尾的距离成线性。
4) 与 std::distance(first, last) 成线性,加上 pos 与容器结尾的距离成线性。
异常
若在尾端插入单个元素时抛出异常,且 T 为可复制插入 (CopyInsertable) 或 std::is_nothrow_move_constructible::value 为 true ,则无效果(强异常保证)。
用例
std::vector<std::string> words {"I", "am", "the", "most", "handsome", "programmer"};
printVector("words: ", words);
// 在 pos 前插入 value。
words.insert(words.begin() + 2, "HH");
printVector("words insert value : ", words);
// 在 pos 前插入 value 的 count 个副本。
words.insert(words.begin() + 3, 2, "KK");
printVector("words insert n value : ", words);
std::vector<std::string> words1 {"JJ", "GG", "LL"};
// 在 pos 前插入来自范围 [first, last) 的元素。
words.insert(words.begin() + 5, words1.begin(), words1.end());
printVector("words insert other value : ", words);
直接于 pos 前插入元素到容器中
template< class... Args >
iterator emplace( const_iterator pos, Args&&... args ); (C++11 起 )
直接于 pos 前插入元素到容器中。通过 std::allocator_traits::construct 构造元素,它典型地用布置 new 在容器所提供的位置原位构造元素。将参数 args… 作为 std::forward(args)… 转发给构造函数。
若新的 size() 大于 capacity() ,则所有迭代器和引用都被非法化。否则,仅在插入点前的迭代器和引用保持合法。尾后迭代器亦被非法化。
参数
pos - 将构造新元素到其前的迭代器
args - 转发给元素构造函数的参数
类型要求
T (容器元素类型) 必须满足可移动赋值 (MoveAssignable) 、 可移动插入 (MoveInsertable) 和 可就位构造 (EmplaceConstructible) 的要求。
返回值
指向被安置的元素的迭代器。
复杂度
与 pos 和容器尾的距离成线性。
异常
若 value_type 的复制构造函数、移动构造函数、赋值运算符或移动赋值运算符以外的操作抛异常,或若在用 emplace 在尾部插入单个元素时抛异常,且 value_type 为可复制插入 (CopyInsertable) 或可不抛出移动构造,则无效果(强异常保证)。
否则,效果未指定。
注意
特化 std::vector 在 C++14 前无 emplace() 成员。
用例
// 直接于 pos 前插入元素到容器中
std::vector<std::string> words {"I", "am", "the", "most", "handsome", "programmer"};
printVector("words: ", words);
words.emplace(words.begin() + 2, "HH");
printVector("words emplace: ", words);
添加新元素到容器尾
template< class... Args >
void emplace_back( Args&&... args ); (C++11 起)(C++17 前)
template< class... Args >
reference emplace_back( Args&&... args ); (C++17 起)
添加新元素到容器尾。元素通过 std::allocator_traits::construct 构造,它典型地用布置 new 于容器所提供的位置原位构造元素。参数 args… 以 std::forward(args)… 转发到构造函数。
若新的 size() 大于 capacity() ,则所有迭代器和引用(包含尾后迭代器)都被非法化。否则仅尾后迭代器被非法化。
参数 args - 转发到元素构造函数的参数
类型要求 value_type 必须满足可移动插入 (MoveInsertable) 和 可就位构造 (EmplaceConstructible) 的要求。
返回值 (无) (C++17 前)
到被插入元素的引用。 (C++17 起)
复杂度 均摊常数。
异常
若抛出异常,则此函数无效果(强异常保证)。 若 T 的移动构造函数非 noexcept 且非可复制插入 (CopyInsertable) 到 *this ,则 vector 将使用抛出的移动构造函数。若它抛出,则保证被舍弃,且效果未指定。
注意
因为可能发生再分配, emplace_back 对 vector 要求元素类型为可移动插入 (MoveInsertable) 。
特化 std::vector 在 C++14 前无 emplace_back() 成员。
用例
std::vector<std::string> words {"I", "am", "the", "most", "handsome", "programmer"};
printVector("words: ", words);
// 添加新元素到容器尾
words.emplace_back("HH");
printVector("words emplace_back : ", words);
迭代器
- 指向容器首元素的迭代器
iterator begin(); (C++11 前)
iterator begin() noexcept; (C++11 起)
const_iterator begin() const; (C++11 前)
const_iterator begin() const noexcept; (C++11 起)
const_iterator cbegin() const noexcept; (C++11 起)
返回指向容器首元素的迭代器。
若容器为空,则返回的迭代器将等于 end() 。
参数 (无)
返回值 指向首元素的迭代器。
复杂度 常数。
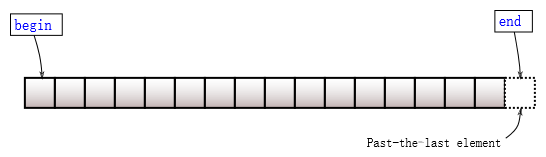
- 指向容器末元素后一元素的迭代器
iterator end(); (C++11 前)
iterator end() noexcept; (C++11 起)
const_iterator end() const; (C++11 前)
const_iterator end() const noexcept; (C++11 起)
const_iterator cend() const noexcept;(C++11 起)
返回指向容器末元素后一元素的迭代器。
此元素表现为占位符;试图访问它导致未定义行为。
参数 (无)
返回值 指向后随最后元素的迭代器。
复杂度 常数。
- 指向逆向容器首元素的逆向迭代器
reverse_iterator rbegin(); (C++11 前)
reverse_iterator rbegin() noexcept; (C++11 起)
const_reverse_iterator rbegin() const; (C++11 前)
const_reverse_iterator rbegin() const noexcept; (C++11 起)
const_reverse_iterator crbegin() const noexcept;(C++11 起)
返回指向逆向容器首元素的逆向迭代器。它对应非逆向容器的末元素。
参数 (无)
返回值 指向首元素的逆向迭代器。
复杂度 常数。
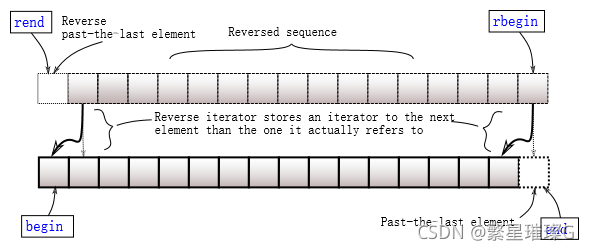
- 指向逆向容器末元素后一元素的逆向迭代器
reverse_iterator rend(); (C++11 前)
reverse_iterator rend() noexcept; (C++11 起)
const_reverse_iterator rend() const; (C++11 前)
const_reverse_iterator rend() const noexcept;(C++11 起)
const_reverse_iterator crend() const noexcept;(C++11 起)
返回指向逆向容器末元素后一元素的逆向迭代器。它对应非逆向容器首元素的前一元素。此元素表现为占位符,试图访问它导致未定义行为。
参数 (无)
返回值 指向末元素后一元素的逆向迭代器。
复杂度 常数。
用例:
std::vector<std::string> words1 {"I", "am", "the", "most", "handsome", "programmer"};
for(std::vector<std::string>::const_iterator it = words1.cbegin(); it != words1.cend(); it ++)
{
std::cout << *it << " ";
}
std::cout << std::endl;
for(std::vector<std::string>::const_reverse_iterator it = words1.crbegin(); it != words1.crend(); it ++)
{
std::cout << *it << " ";
}
std::cout << std::endl;
操作符
operator==,!=,<,<=,>,>=(std::vector)
template< class T, class Alloc >
bool operator==( const std::vector<T,Alloc>& lhs,
const std::vector<T,Alloc>& rhs ); (1)
template< class T, class Alloc >
bool operator!=( const std::vector<T,Alloc>& lhs,
const std::vector<T,Alloc>& rhs ); (2)
template< class T, class Alloc >
bool operator<( const std::vector<T,Alloc>& lhs,
const std::vector<T,Alloc>& rhs ); (3)
template< class T, class Alloc >
bool operator<=( const std::vector<T,Alloc>& lhs,
const std::vector<T,Alloc>& rhs ); (4)
template< class T, class Alloc >
bool operator>( const std::vector<T,Alloc>& lhs,
const std::vector<T,Alloc>& rhs ); (5)
template< class T, class Alloc >
bool operator>=( const std::vector<T,Alloc>& lhs,
const std::vector<T,Alloc>& rhs ); (6)
比较二个容器的内容。
1-2) 检查 lhs 与 rhs 的内容是否相等,即它们是否拥有相同数量的元素且 lhs 中每个元素与 rhs 的同位置元素比较相等。
3-6) 按字典序比较 lhs 与 rhs 的内容。由等价于 std::lexicographical_compare 的函数进行比较。
参数
lhs, rhs - 要比较内容的容器
为使用重载 (1-2) , T 必须满足可相等比较 (EqualityComparable) 的要求。
为使用重载 (3-6) , T 必须满足可小于比较 (LessThanComparable) 的要求。顺序关系必须建立全序。
返回值
- 若容器内容相等则为 true ,否则为 false
- 若容器内容不相等则为 true ,否则为 false
- 若 lhs 的内容按字典序小于 rhs 的内容则为 true ,否则为 false
- 若 lhs 的内容按字典序小于或等于 rhs 的内容则为 true ,否则为 false
- 若 lhs 的内容按字典序大于 rhs 的内容则为 true ,否则为 false
- 若 lhs 的内容按字典序大于或等于 rhs 的内容则为 true ,否则为 false
复杂度
1-2) 若 lhs 与 rhs 的大小不同则为常数,否则与容器大小成线性
3-6) 与容器大小成线性