? ? ? ? 作为小学上课偷偷和同桌在草稿本上玩的小游戏-井字棋,如今在电脑上也可以自己写出来玩。如图:
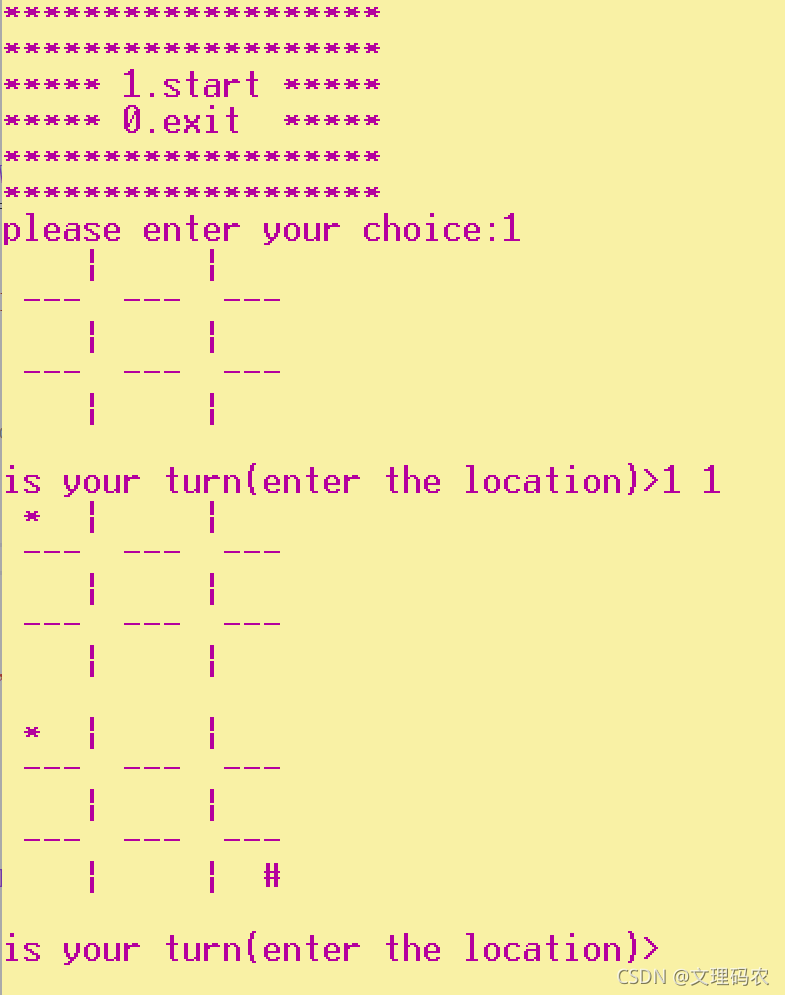
不要惊讶,下面我们来看看怎么实现这个代码。(正文开始)
1.菜单界面:用多个printf 来打印即可,注意中间最好是空的不要连着字。
void menu() {
printf("*******************\n");
printf("*******************\n");
printf("***** 1.start *****\n");
printf("***** 0.exit *****\n");
printf("*******************\n");
printf("*******************\n");
}?2.游戏界面:不同于扫雷,我们只需要一个二维数组即可完成这个游戏,我们需要一个3*3的二维数组,用一个函数将数组初始化全为空格,然后打印数组,然后你会发现啥也没有,因为那些横竖的线并不在数组中,那么如果要打印出格子的话需要在打印数组的同时打印格子。代码以及展示图如下。
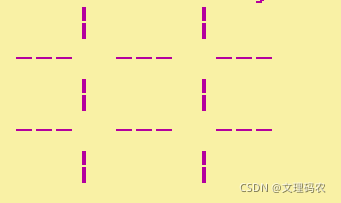
void displayboard(char board[ROW][LINE]) {
int i;
int j;
int k;
for (i = 0; i < ROW; i++) {
for (j = 0; j < LINE; j++)
{
printf(" %c ", board[i][j]);
if (j < (LINE - 1)) {
printf(" | ");
}//除每一行最后一个不打印,其余都打印空格
}
printf("\n");
if (i < (ROW - 1))
{
for (k = 0; k < LINE; k++) {
printf(" --- ");
}//除第一行和最后一行不打印
}
printf("\n");
}
}?3.用户操作:接下来就是用户来下棋了,我们只需要用户选择需要下的位置,然后将空格换成标识符就可以了,但是还需要判断这个位置有没有被占用,或者这个是否是个合法坐标。
if (board[x - 1][y - 1] != ' ') {
printf("the location is used\n");
}else if (x > 0 && x <=ROW && y <= LINE && y>0) {
board[x - 1][y - 1] = '*';
}
else {
printf("illagle location\n");
}?4.电脑下棋:不要妄想电脑会堵你的路,作为“人工智障”他只会下棋,我们只让他随机下棋就可以了,那么就需要头文件<stdlib.h>和<time.h>,然后判断这个位置是否被占用,如果没被占用就是这个位置啦。
void computer_move(char board[ROW][LINE]) {
int x;
int y;
x = rand() % ROW+1;
y = rand() % LINE+1;
while (1)
{
if (board[x][y] == ' ') {
board[x][y] = '#';
break;
}
}
5.判断输赢:如何判断输赢呢,我们需要判断三个标识符是否连成一条线,那么就会用三种情况,横着的,竖着的,斜着的那么我们可以用if来判断,每次在用户下完,和电脑下完都需要检验。
//ROw win
for(i=0;i<ROW;i++){
if (board[i][0] == board[i][1] && board[i ][1] == board[i][2] && board[i][0] == '*') {
return 'p';
}
else if (board[i][0] == board[i][1] && board[i][1] == board[i][2] && board[i][0] == '#') {
return 'c';
}
}
//line win
for (i = 0; i < LINE; i++) {
if (board[0][i] == board[1][i] && board[1][i] == board[2][i] && board[i][i]== '*') {
return 'p';
}
else if (board[0][i] == board[1][i] && board[1][i] == board[2][i] && board[i][i] == '#') {
return 'c';
}
}
if (board[0][0] == board[1][1] && board[1][1] == board[2][2] && board[0][0] == '*') {
return 'p';
}
else if (board[0][0] == board[1][1] && board[1][1] == board[2][2] && board[0][0] == '#') {
return 'c';
}返回值在主函数中判断
if (w == 'p') {
printf("\nplayer win\n");
break;
}
else if (w == 'c'){
printf("\ncomputer win\n");
break;
}
computer_move(board);
w = is_win(board);
displayboard(board);
if (w == 'p') {
printf("\nplayer win\n");
break;
}
else if (w == 'c'){
printf("\ncomputer win\n");
break;
}(这里判断有点冗余了还需要改进)
反思和改进
????????这个程序最大的问题就是电脑下棋的不智能性,只能随便下棋,当然如果要需要更高级的只有人工智能才能解决了,这个后续还会持续学习的;第二个就是在判断的时候条件的冗余,这个后续还需要改进。
(下面是完整代码展示)
game.h
#pragma once
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<time.h>
#define ROW 3
#define LINE 3
void iniboard(char board[ROW][LINE]);
void displayboard(char board[ROW][LINE]);
void player_move(char board[ROW][LINE]);
void computer_move(char board[ROW][LINE]);
char is_win(char board[ROW][LINE]);test.cpp
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include"game.h"
void iniboard(char board[ROW][LINE]) {
int i,j;
for (i = 0; i < ROW; i++) {
for ( j = 0; j < LINE; j++)
{
board[i][j] = ' ';
}
}
}
void displayboard(char board[ROW][LINE]) {
int i;
int j;
int k;
for (i = 0; i < ROW; i++) {
for (j = 0; j < LINE; j++)
{
printf(" %c ", board[i][j]);
if (j < (LINE - 1)) {
printf(" | ");
}
}
printf("\n");
if (i < (ROW - 1))
{
for (k = 0; k < LINE; k++) {
printf(" --- ");
}
}
printf("\n");
}
}
void player_move(char board[ROW][LINE]) {
printf("is your turn(enter the location)>");
int x, y;
scanf("%d %d", &x, &y);
if (board[x - 1][y - 1] != ' ') {
printf("the location is used\n");
}
else if (x > 0 && x <=ROW && y <= LINE && y>0) {
board[x - 1][y - 1] = '*';
}
else {
printf("illagle location\n");
}
}
void computer_move(char board[ROW][LINE]) {
int x;
int y;
x = rand() % ROW+1;
y = rand() % LINE+1;
while (1)
{
if (board[x][y] == ' ') {
board[x][y] = '#';
break;
}
}
}
char is_win(char board[ROW][LINE]) {
int i = 0;
//ROw win
for(i=0;i<ROW;i++){
if (board[i][0] == board[i][1] && board[i ][1] == board[i][2] && board[i][0] == '*') {
return 'p';
}
else if (board[i][0] == board[i][1] && board[i][1] == board[i][2] && board[i][0] == '#') {
return 'c';
}
}
//line win
for (i = 0; i < LINE; i++) {
if (board[0][i] == board[1][i] && board[1][i] == board[2][i] && board[i][i]== '*') {
return 'p';
}
else if (board[0][i] == board[1][i] && board[1][i] == board[2][i] && board[i][i] == '#') {
return 'c';
}
}
if (board[0][0] == board[1][1] && board[1][1] == board[2][2] && board[0][0] == '*') {
return 'p';
}
else if (board[0][0] == board[1][1] && board[1][1] == board[2][2] && board[0][0] == '#') {
return 'c';
}
}game.cpp
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include "game.h"
void menu() {
printf("*******************\n");
printf("*******************\n");
printf("***** 1.start *****\n");
printf("***** 0.exit *****\n");
printf("*******************\n");
printf("*******************\n");
}
void game() {
char board[ROW][LINE];
iniboard(board);
displayboard(board);
char w;
while (1) {
player_move(board);
w = is_win(board);
displayboard(board);
if (w == 'p') {
printf("\nplayer win\n");
break;
}
else if (w == 'c'){
printf("\ncomputer win\n");
break;
}
computer_move(board);
w = is_win(board);
displayboard(board);
if (w == 'p') {
printf("\nplayer win\n");
break;
}
else if (w == 'c'){
printf("\ncomputer win\n");
break;
}
}
}
void test() {
int input;
srand((unsigned int)time(NULL));
do{
menu();
printf("please enter your choice:");
scanf("%d", &input);
switch (input)
{
case 1:
game();
break;
case 0:
printf("the game is over");
break;
default:
printf("the choice is fault\n");
break;
}
} while (input);
}
int main() {
test();
}