14.1节

14.1答
不同点:
重载操作符必须具有至少一个class或枚举类型的操作数。
重载操作符不保证操作数的求值顺序,例如对&&和| | 的重载版本不再具有“短路求值”的特征,两个操作数,两个操作数都要进行求值,而且不规定操作数的求值顺序。
相同点:?
? ? ? ? 对于优先级和结合性及操作数的数目都不变。
14.2 答:
文件sales_data.cc
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include "Sales_data.h"
using namespace std;
Sales_data operator+(const Sales_data &lhs,const Sales_data &rhs)
{
Sales_data data = lhs;
data += rhs;
return data;
}
Sales_data& Sales_data::operator+=(const Sales_data &s)
{
this->units_sold += s.units_sold;
this->revenue += s.revenue;
return *this;
}
istream & operator>>(istream &is,Sales_data &s)
{
is >> s.bookNo >> s.units_sold >> s.revenue;
return is;
}
ostream & operator<<(ostream &os,const Sales_data &s)
{
os << s.bookNo << s.units_sold << s.revenue;
return os;
}
文件? Sales_data.h?
class Sales_data {
friend Sales_data operator+(const Sales_data &,const Sales_data &);
friend istream & operator>>(istream &is,Sales_data &);
friend ostream & operator<<(ostream &os,const Sales_data &);
public:
Sales_data &operator+=(const Sales_data &);
std::string bookNo;
unsigned units_sold = 0;
double revenue = 0.0;
};
注意:切记不可在友元函数的前面加Sales_data::,否则编译器回提示,C++:‘std::ostream& String::operator<<(std::ostream&, const Sales_data &)’ must take exactly one argument
14.3
答:
(a)使用了c++内置版本的const char *版本的 ‘==’运算符。
字符串字面量是 const char* 类型
(b)string类型的"=="运算符
(c)vector类型的"=="运算符
(d)首先const char *类型的"stone"转换为 string,然后使用string类型的“=="
14.4
答:
(a)%通常定义为非成员,因为可以左右调换
(b)%=会改变自身状态,成员
(c)++成员
(d)->必须为成员
(e)&&非成员,一般不建议重载(&&和| |重载后,短路求值属性会失效)
(f)<<非成员,因为左操作数必须是 ostream类型。
(g)==? 一般定义为非成员
(h)()必须为成员,否则编译器会报错。
赋值运算符,下标运算符,调用运算符,成员运算符必须是成员运算符,其余没有强制要求。
14.5
答:
我们以Date类为例,为其定义重载的输出运算符,输入运算符可参照实现,显然,为Date定义输入输出运算符,可以让我们像输入输出内置类型对象那样输入输出Date,在易用性和代码的可读性上有明显的好处。因此,定义这两个重载运算符是合理的。
文件date.h
#ifndef DATE_H
#define DATE_H
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
class Date
{
public:
Date(){}
Date(int y,int m,int d){year = y;month = m;day = d;}
friend ostream & operator<< (ostream &os,const Date &dt);
private:
int year,month,day;
};
#endif
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include "date.h"
using namespace std;
ostream & operator<<(ostream & os,const Date &dt)
{
const char sep = '\t';
os << "year:"<< dt.year << sep << "month:"<< dt.month<<sep << "day:"<<dt.day;
return os;
}
int main()
{
Date d(2021,11,14);
cout << d << endl;
return 0;
}14.2节
14.2.1习题
习题14.6

14.7
/*
* This file contains code from "C++ Primer, Fifth Edition", by Stanley B.
* Lippman, Josee Lajoie, and Barbara E. Moo, and is covered under the
* copyright and warranty notices given in that book:
*
* "Copyright (c) 2013 by Objectwrite, Inc., Josee Lajoie, and Barbara E. Moo."
*
*
* "The authors and publisher have taken care in the preparation of this book,
* but make no expressed or implied warranty of any kind and assume no
* responsibility for errors or omissions. No liability is assumed for
* incidental or consequential damages in connection with or arising out of the
* use of the information or programs contained herein."
*
* Permission is granted for this code to be used for educational purposes in
* association with the book, given proper citation if and when posted or
* reproduced.Any commercial use of this code requires the explicit written
* permission of the publisher, Addison-Wesley Professional, a division of
* Pearson Education, Inc. Send your request for permission, stating clearly
* what code you would like to use, and in what specific way, to the following
* address:
*
* Pearson Education, Inc.
* Rights and Permissions Department
* One Lake Street
* Upper Saddle River, NJ 07458
* Fax: (201) 236-3290
*/
#ifndef STRING_H
#define STRING_H
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cstddef>
#include <iostream>
#include <initializer_list>
#include <iostream>
#include <memory>
class String {
friend String operator+(const String&, const String&);
friend String add(const String&, const String&);
friend std::ostream &print(std::ostream&, const String&);
friend std::ostream &operator<<(ostream &os,const String &);
public:
String() = default;
// cp points to a null terminated array,
// allocate new memory & copy the array
String(const char *cp) :
sz(std::strlen(cp)), p(a.allocate(sz))
{ std::uninitialized_copy(cp, cp + sz, p); }
// copy constructor: allocate a new copy of the characters in s
String(const String &s):sz(s.sz), p(a.allocate(s.sz))
{ std::uninitialized_copy(s.p, s.p + sz , p); }
// move constructor: copy the pointer, not the characters,
// no memory allocation or deallocation
String(String &&s) noexcept : sz(s.size()), p(s.p)
{ s.p = 0; s.sz = 0; }
String(size_t n, char c) : sz(n), p(a.allocate(n))
{ std::uninitialized_fill_n(p, sz, c); }
// allocates a new copy of the data in the right-hand operand;
// deletes the memory used by the left-hand operand
String &operator=(const String &);
// moves pointers from right- to left-hand operand
String &operator=(String &&) noexcept;
// unconditionally delete the memory because each String has its own memory
~String() noexcept { if (p) a.deallocate(p, sz); }
// additional assignment operators
String &operator=(const char*); // car = "Studebaker"
String &operator=(char); // model = 'T'
String &
operator=(std::initializer_list<char>); // car = {'a', '4'}
const char *begin() { return p; }
const char *begin() const { return p; }
const char *end() { return p + sz; }
const char *end() const { return p + sz; }
size_t size() const { return sz; }
void swap(String &s)
{ auto tmp = p; p = s.p; s.p = tmp;
auto cnt = sz; sz = s.sz; s.sz = cnt; }
private:
std::size_t sz = 0;
char *p = nullptr;
static std::allocator<char> a;
};
String make_plural(size_t ctr, const String &, const String &);
inline
void swap(String &s1, String &s2)
{
s1.swap(s2);
}
#endif/*
* This file contains code from "C++ Primer, Fifth Edition", by Stanley B.
* Lippman, Josee Lajoie, and Barbara E. Moo, and is covered under the
* copyright and warranty notices given in that book:
*
* "Copyright (c) 2013 by Objectwrite, Inc., Josee Lajoie, and Barbara E. Moo."
*
*
* "The authors and publisher have taken care in the preparation of this book,
* but make no expressed or implied warranty of any kind and assume no
* responsibility for errors or omissions. No liability is assumed for
* incidental or consequential damages in connection with or arising out of the
* use of the information or programs contained herein."
*
* Permission is granted for this code to be used for educational purposes in
* association with the book, given proper citation if and when posted or
* reproduced.Any commercial use of this code requires the explicit written
* permission of the publisher, Addison-Wesley Professional, a division of
* Pearson Education, Inc. Send your request for permission, stating clearly
* what code you would like to use, and in what specific way, to the following
* address:
*
* Pearson Education, Inc.
* Rights and Permissions Department
* One Lake Street
* Upper Saddle River, NJ 07458
* Fax: (201) 236-3290
*/
#include <cstring>
using std::strlen;
#include <algorithm>
using std::copy;
#include <cstddef>
using std::size_t;
#include <iostream>
using std::ostream;
#include <utility>
using std::swap;
#include <initializer_list>
using std::initializer_list;
#include <memory>
using std::uninitialized_copy;
#include "string.h"
// define the static allocator member
std::allocator<char> String::a;
// copy-assignment operator
String & String::operator=(const String &rhs)
{
// copying the right-hand operand before deleting the left handles self-assignment
auto newp = a.allocate(rhs.sz); // copy the underlying string from rhs
uninitialized_copy(rhs.p, rhs.p + rhs.sz, newp);
if (p)
a.deallocate(p, sz); // free the memory used by the left-hand operand
p = newp; // p now points to the newly allocated string
sz = rhs.sz; // update the size
return *this;
}
// move assignment operator
String & String::operator=(String &&rhs) noexcept
{
// explicit check for self-assignment
if (this != &rhs) {
if (p)
a.deallocate(p, sz); // do the work of the destructor
p = rhs.p; // take over the old memory
sz = rhs.sz;
rhs.p = 0; // deleting rhs.p is safe
rhs.sz = 0;
}
return *this;
}
String& String::operator=(const char *cp)
{
if (p) a.deallocate(p, sz);
p = a.allocate(sz = strlen(cp));
uninitialized_copy(cp, cp + sz, p);
return *this;
}
String& String::operator=(char c)
{
if(p) a.deallocate(p, sz);
p = a.allocate(sz = 1);
*p = c;
return *this;
}
String& String::operator=(initializer_list<char> il)
{
// no need to check for self-assignment
if (p)
a.deallocate(p, sz); // do the work of the destructor
p = a.allocate(sz = il.size()); // do the work of the copy constructor
uninitialized_copy(il.begin(), il.end(), p);
return *this;
}
// named functions for operators
ostream &print(ostream &os, const String &s)
{
auto p = s.begin();
while (p != s.end())
os << *p++ ;
return os;
}
String add(const String &lhs, const String &rhs)
{
String ret;
ret.sz = rhs.size() + lhs.size(); // size of the combined String
ret.p = String::a.allocate(ret.sz); // allocate new space
uninitialized_copy(lhs.begin(), lhs.end(), ret.p); // copy the operands
uninitialized_copy(rhs.begin(), rhs.end(), ret.p + lhs.sz);
return ret; // return a copy of the newly created String
}
// return plural version of word if ctr isn't 1
String make_plural(size_t ctr, const String &word,
const String &ending)
{
return (ctr != 1) ? add(word, ending) : word;
}
// chapter 14 will explain overloaded operators
ostream & operator<<(ostream &os,const String &s)
{
for(auto ptr = s.begin(); ptr != s.end(); ++ptr)
os << *ptr << std::endl; //or can be written: print(os,s)
return os;
}
String operator+(const String &lhs, const String &rhs)
{
return add(lhs, rhs);
}
int main()
{
return 0;
}
14.8 同练习14.5
14.2.2重载输入运算符
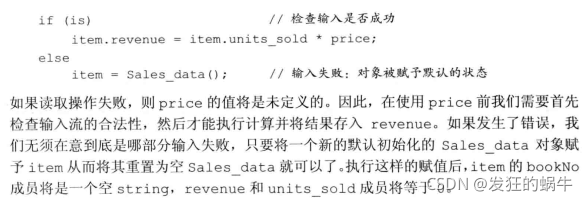
istream & operator>>(istream &is,Sales_data &s)
{
double price;
is >> s.bookNo >> s.units_sold >> price;
if(is)
s.revenue = price * s.units_sold;
else
s = Sales_data(); //input failure,object is set to the default state
return is;
}输入运算符定义注意事项如下:
1.输入后要判断流是否正确,如果正确继续执行往后的操作
2.如果错误,那么把被输入的对象置为默认状态。


?
?
?
?习题14.2.2
习题14.9
istream & operator>>(istream &is,Sales_data &s)
{
double price;
is >> s.bookNo >> s.units_sold >> price;
if(is)
s.revenue = price * s.units_sold;
else
s = Sales_data(); //input failure,object is set to the default state
return is;
}
ostream & operator<<(ostream &os,const Sales_data &s)
{
os << s.bookNo << s.units_sold << s.revenue;
return os;
}
提示:输入运算符必须在输入后立刻判断流的状态,如果流失败(说明读取数据发生错误),那么立刻把被输入的对象置于默认的状态。
14.10
(a)参数中传入的Sales_data 对象将会得到输入的值,其中BookNo、units_sold、price的值分别是:0-201-99999-9、10、24.95,同时,revenue的值是249.5。
(b)输入错误,参数中传入的Sales_data对象会得到默认值。
练习14.11