1.为什么需要unique_ptr
与shared_ptr作用类似,需要解决内存泄漏的问题,但是却不需要使用shared_ptr的引用计数,所以为了减少消耗,就需要一个这样的智能指针。但是使用已被废弃的auto_ptr的话就会有新的问题,auto_ptr在使用过程中如果被拷贝构造或者赋值的话,被复制的auto_ptr就失去了作用,这个时候就需要在auto_ptr的基础上禁用拷贝构造以及赋值操作,也就成了unique_ptr。
2.什么是unique_ptr
一个unique_ptr独享它指向的对象。也就是说,同时只有一个unique_ptr指向同一个对象,当这个unique_ptr被销毁时,指向的对象也随即被销毁。
使用unique_ptr需要引入<memory.h>
3.unique_ptr特性
unique_ptr禁用了拷贝构造以及赋值操作,也就导致了下面的这些操作无法完成。
void testFunction(std::unique_ptr<Test> t){
t->getString();
}
void features(){
// Disable copy from lvalue.
// unique_ptr(const unique_ptr&) = delete;
// unique_ptr& operator=(const unique_ptr&) = delete;
//不能进行拷贝构造以及赋值运算,也就表示不能作为函数参数传递
std::unique_ptr<Test> t(new Test);
std::unique_ptr<Test> t2 = t; //编译报错
std::unique_ptr<Test> t3(t);//编译报错
testFunction(t);//编译报错
}
4.如何使用unique_ptr
4.1简单使用
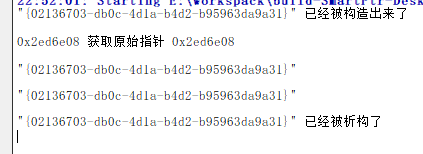
void simpleUse(){
Test *test = new Test;
std::unique_ptr<Test> t(test);
qDebug() << test <<"获取原始指针"<< t.get() <<endl;
// t.release(); //释放其关联的原始指针的所有权,并返回原始指针,没有释放对象
// t.reset();// 释放对象
t->getString();
std::unique_ptr<Test> t2 = std::move(t); //交换使用权到t2;
t2->getString();
}
4.2指向数组
和shared_ptr需要注意的地方一样,指向数组时要注意模板书写的方式,以及如何使用自定义删除器
错误写法:会导致内存泄露
void customRemover(){
std::unique_ptr<Test> t(new Test[5]);
}
正确写法:
void customRemover(){
std::unique_ptr<Test[]> t(new Test[5]);
std::unique_ptr<Test, void(*)(Test *)> p2(new Test[5],[](Test *t){
delete []t;
});
}
5.unique_ptr需要注意什么
不要多个unique_ptr指向同一个对象
例如:
void repeatPointsTo(){
Test *test = new Test;
std::unique_ptr<Test> t(test);
std::unique_ptr<Test> t2(test);
//两个unique_ptrzhi'xi指向同一个对象,会导致这个对象被析构两次,导致问题出现
}
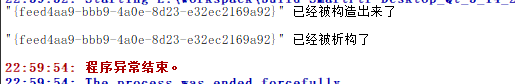
会导致对象会被多次析构,导致崩溃