百度定义:设计模式(Design pattern)是一套被反复使用、多数人知晓的、经过分类编目的、代码设计经验的总结。使用设计模式是为了可重用代码、让代码更容易被他人理解、保证代码可靠性。 毫无疑问,设计模式于己于他人于系统都是多赢的,设计模式使代码编制真正工程化,设计模式是软件工程的基石,如同大厦的一块块砖石一样。设计模式分为三种类型,分别是:创建型模式、结构型模式,行为型模式。
其实设计模式是跟某个工程结合的应用的,不能只是某个程序,所以此文的程序只是停留在一个概念理解的层面。设计模式其实有二十三种,此文只是介绍了最常用的十几种
创建型模式
单例模式:
Instance办法返回_ intance对象,_ instance对象就是唯一的对象

#include<iostream>
#include<thread>
#include<mutex>
using namespace std;
class Singleton{
public:
static Singleton* Instance(){
if (_instance == nullptr) {
_mxt.lock();
if (_instance == nullptr) {
_instance = new Singleton();
}
_mxt.unlock();
}
return _instance;
}
private:
Singleton(){
std::this_thread::sleep_for(std::chrono::milliseconds(1));
}
Singleton(const Singleton&) = delete;
Singleton(Singleton &&) = delete;
static mutex _mxt;
static Singleton* _instance;
};
Singleton *Singleton::_instance = nullptr;
std::mutex Singleton::_mxt;
void creatSingleton() {
Singleton* p = Singleton::Instance();
cout << p << endl;
}
int main() {
//Singleton *p = Singleton::Instance();
std::thread t1(creatSingleton);
std::thread t2(creatSingleton);
std::thread t3(creatSingleton);
std::thread t4(creatSingleton);
t1.join();
t2.join();
t3.join();
t4.join();
return 0;
}
工厂模式
前提是有一个类似产品基类,派生出多个产品子类,然后要有工厂类,工厂类来实例产品子类
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-oEdVRw7f-1640406317780)(C:\Users\86166\AppData\Roaming\Typora\typora-user-images\image-20211207111502567.png)]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/855e25d17efa4b86b7fce61b072350df.png?x-oss-process=image/watermark,type_d3F5LXplbmhlaQ,shadow_50,text_Q1NETiBA5YuH5pWi54uX54uX77yM5LiN5oCV5Zuw6Zq-,size_20,color_FFFFFF,t_70,g_se,x_16)
#include<iostream>
//#include<thread>
#include<mutex>
using namespace std;
class AbstractProduct {
public:
virtual ~AbstractProduct(){};
virtual void print() = 0;
};
class Product1 : public AbstractProduct {
void print() override {
cout << "this id product 1" << endl;
}
};
class Product2 : public AbstractProduct {
void print() override {
cout << "this id product 2" << endl;
}
};
class Product3 : public AbstractProduct {
void print() override {
cout << "this id product 3" << endl;
}
};
//单例工厂。相反的就是抽象工厂模式,以一个工厂基类派生多个工厂
class Factory {
public:
static Factory* Instance() {
if (Factory::_instance == nullptr) {
_mtx.lock();
if (_instance == nullptr) {
_instance = new Factory();
}
_mtx.unlock();
}
return _instance;
}
AbstractProduct* getProducr(std::string name) {
if (name == "A") {
return new Product1;
} else if (name == "B") {
return new Product2;
} else if (name == "C") {
return new Product3;
} else {
return nullptr;
}
}
private:
Factory(){}
Factory(const Factory&) = delete;
Factory(Factory &&) = delete;
static Factory* _instance;
static mutex _mtx;
};
Factory* Factory::_instance = nullptr;
std::mutex Factory::_mtx;
int main() {
AbstractProduct* products[10];
products[0] = Factory::Instance()->getProducr("A");
products[1] = Factory::Instance()->getProducr("B");
products[2] = Factory::Instance()->getProducr("C");
products[3] = Factory::Instance()->getProducr("A");
products[4] = Factory::Instance()->getProducr("A");
products[5] = Factory::Instance()->getProducr("B");
products[6] = Factory::Instance()->getProducr("C");
products[7] = Factory::Instance()->getProducr("B");
products[8] = Factory::Instance()->getProducr("A");
products[9] = Factory::Instance()->getProducr("E");
for (auto p : products) {
if (p) {
p->print();
} else {
cout << "product is nullptr" << endl;
}
}
return 0;
}
建造者模式
类似于工厂模式,工厂模式重点在于创建产品,而建造者模式重点在产品的创建过程。
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-QESZBQhf-1640406317781)(C:\Users\86166\AppData\Roaming\Typora\typora-user-images\image-20211207114309494.png)]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/be75d5978f01460aa82a8efafd9e17d2.png?x-oss-process=image/watermark,type_d3F5LXplbmhlaQ,shadow_50,text_Q1NETiBA5YuH5pWi54uX54uX77yM5LiN5oCV5Zuw6Zq-,size_15,color_FFFFFF,t_70,g_se,x_16)
原型模式
通过自身来拷贝构造自己
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-40mpBYKX-1640406317781)(C:\Users\86166\AppData\Roaming\Typora\typora-user-images\image-20211207132017453.png)]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/6746152ab3a24aa4a5f645444c14e27e.png?x-oss-process=image/watermark,type_d3F5LXplbmhlaQ,shadow_50,text_Q1NETiBA5YuH5pWi54uX54uX77yM5LiN5oCV5Zuw6Zq-,size_15,color_FFFFFF,t_70,g_se,x_16)
建造者和原型模式代码演示:
实现汽车生产过程;
#include<iostream>
#include<shared_mutex>
#include<memory>
using namespace std;
//工厂模式的工厂
class Car {
public:
Car() {}
virtual ~Car(){}
virtual Car* copy() = 0;
virtual void setColor(long color) = 0;
virtual void setEngine(long engine) = 0;
virtual void setSeat(long seat) = 0;
virtual void print() {
cout << "color = " << _color << " engine = " << _engine << " seat = " << _seat << endl;
}
protected:
long _color;
int _seat;
float _engine;
};
//工厂模式的产品
class BMW : public Car {
Car *copy() override {
return new BMW(*this);
}
virtual void setColor(long color) override {
cout << "BMW set color" << endl;
this->_color = color;
}
virtual void setEngine(long engine) override {
cout << "BMW set engine" << endl;
this->_engine = engine;
}
virtual void setSeat(long seat) override {
cout << "BMW set seat" << endl;
this->_seat = seat;
}
};
//工厂模式的产品
class BENZ : public Car {
Car *copy() override {
return new BENZ(*this);
}
virtual void setColor(long color) override {
cout << "BENZ set color" << endl;
this->_color = color;
}
virtual void setEngine(long engine) override {
cout << "BENZ set engine" << endl;
this->_engine = engine;
}
virtual void setSeat(long seat) override {
cout << "BENZ set seat" << endl;
this->_seat = seat;
}
};
//工厂模式的产品
class AUDI : public Car {
Car *copy() override {
return new AUDI(*this);
}
virtual void setColor(long color) override {
cout << "AUDI set color" << endl;
this->_color = color;
}
virtual void setEngine(long engine) override {
cout << "AUDI set engine" << endl;
this->_engine = engine;
}
virtual void setSeat(long seat) override {
cout << "AUDI set seat" << endl;
this->_seat = seat;
}
};
//UML中的Builder
class AbstractBuilder {
public:
AbstractBuilder(){};
virtual ~AbstractBuilder(){}
virtual void buildColor(shared_ptr<Car>) = 0;
virtual void buildSeat(shared_ptr<Car>) = 0;
virtual void buildEngine(shared_ptr<Car>) = 0;
virtual shared_ptr<Car> buildCar() = 0;
};
//UML中的ConcreteBuilder
class BMWBuilder : public AbstractBuilder {
public:
void buildColor(shared_ptr<Car> p) override {
p->setColor(0x0000ff);
}
void buildSeat(shared_ptr<Car> p) override {
p->setSeat(2);
}
void buildEngine(shared_ptr<Car> p) override {
p->setEngine(3.0f);
}
shared_ptr<Car> buildCar() override {
shared_ptr<Car> p = make_shared<BMW>();
this->buildColor(p);
this->buildEngine(p);
this->buildSeat(p);
return p;
}
};
//UML中的ConcreteBuilder
class BENZBuild : public AbstractBuilder {
public:
void buildColor(shared_ptr<Car> p) override {
p->setColor(0x000000);
}
void buildSeat(shared_ptr<Car> p) override {
p->setSeat(5);
}
void buildEngine(shared_ptr<Car> p) override {
p->setEngine(1.0f);
}
shared_ptr<Car> buildCar() override {
shared_ptr<Car> p = make_shared<BENZ>();
this->buildEngine(p);
this->buildSeat(p);
this->buildColor(p);
return p;
}
};
//UML中的ConcreteBuilder
class AUDIBuilder : public AbstractBuilder {
public:
void buildColor(shared_ptr<Car> p) override {
p->setColor(0x0000ff);
}
void buildSeat(shared_ptr<Car> p) override {
p->setSeat(3);
}
void buildEngine(shared_ptr<Car> p) override {
p->setEngine(4.0f);
}
shared_ptr<Car> buildCar() override {
shared_ptr<Car> p = make_shared<AUDI>();
this->buildEngine(p);
this->buildColor(p);
this->buildSeat(p);
return p;
}
};
class Boss {
public:
Boss(){}
virtual ~Boss(){
_builder.reset();
}
void setBuilder(shared_ptr<AbstractBuilder> p) {
_builder = p;
p.reset();
}
shared_ptr<Car> getCar() {
return _builder ? _builder->buildCar() : nullptr;
}
private:
shared_ptr<AbstractBuilder> _builder;
};
int main() {
shared_ptr<AbstractBuilder> pBuilder[3];
pBuilder[0] = make_shared<BENZBuild>();
pBuilder[1] = make_shared<BENZBuild>();
pBuilder[2] = make_shared<BENZBuild>();
for (auto p : pBuilder) {
shared_ptr<Car> pCar = p->buildCar();
pCar->print();
//原型模式
Car *pCopy = pCar->copy();
pCopy->print();
}
cout << "//" << endl;
shared_ptr<Boss> boss = make_shared<Boss>();
shared_ptr<BMWBuilder> pp1 = make_shared<BMWBuilder>();
shared_ptr<BENZBuild> pp2 = make_shared<BENZBuild>();
boss->setBuilder(pp1);//boss->setBuilder(shared_ptr<BMWBuilder>()).....x
shared_ptr<Car> p1 = boss->getCar();
p1->print();
boss->setBuilder(pp2);
shared_ptr<Car> p2 = boss->getCar();
p2->print();
return 0;
}
结构型模式
桥接模式
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-E5fhXLtT-1640406317782)(C:\Users\86166\AppData\Roaming\Typora\typora-user-images\image-20211207134441636.png)]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/386269e16c8e4be1b8920390c5046faf.png?x-oss-process=image/watermark,type_d3F5LXplbmhlaQ,shadow_50,text_Q1NETiBA5YuH5pWi54uX54uX77yM5LiN5oCV5Zuw6Zq-,size_20,color_FFFFFF,t_70,g_se,x_16)
例子:实现以上UML图
通过一个游戏属性把手机类和游戏类桥接起来
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
class Game {
public:
Game(){}
virtual ~Game(){}
virtual void run() = 0;
};
class Phone {
public:
Phone(){};
virtual ~Phone(){};
virtual void installGame(Game *p) = 0;
virtual void runGame() = 0;
protected:
Game *_game;//通过一个游戏属性把手机类和游戏类桥接起来
};
class PhoneA : public Phone {
public:
void installGame(Game *p) override {
this->_game = p;
}
void runGame() override {
if (this->_game) {
cout << "Phone start launch game!" << endl;
this->_game->run();
} else {
cout << "Phone not found any game!" << endl;
}
}
};
class PhoneB : public Phone {
public:
void installGame(Game *p) override {
this->_game = p;
}
void runGame() override {
if (this->_game) {
cout << "Phone start launch game!" << endl;
this->_game->run();
} else {
cout << "Phone not found any game!" << endl;
}
}
};
class GameA : public Game{
public:
void run() override {
cout << "GameA is starting!" << endl;
}
};
class GameB : public Game{
public:
void run() override {
cout << "GameA is starting!" << endl;
}
};
int main() {
Phone *phone1 = new PhoneA();
Phone *phone2 = new PhoneB();
Game *game1 = new GameA();
Game *game2 = new GameB();
phone1->installGame(game1);
phone2->installGame(game2);
phone1->runGame();
phone2->runGame();
delete phone1;
delete phone2;
return 0;
}
适配器模式
类适配器:比如客户端要访问Target类中的Request办法,而Adaptee类中的specific Request办法是真实要访问的,这时候就要有一个适配器,这个适配器Adapter的Request办法可以调Adaptee中的specific Request办法
对象适配器:比如客户端要访问Target类中的Request办法,而Adaptee类中的specific Request办法是真实要访问的,这时候就要有一个适配器,适配器Adapter继承Target类,而Adaptee类作为一个对象放在Adapter类中
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-q2YMhZYF-1640406317782)(C:\Users\86166\AppData\Roaming\Typora\typora-user-images\image-20211212081607915.png)]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/d676fff69171440a933fd0c558923a5b.png?x-oss-process=image/watermark,type_d3F5LXplbmhlaQ,shadow_50,text_Q1NETiBA5YuH5pWi54uX54uX77yM5LiN5oCV5Zuw6Zq-,size_20,color_FFFFFF,t_70,g_se,x_16)
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
//客户想要的类实现
class Target{
public:
Target(){}
virtual ~Target(){}
virtual int request() = 0;
};
//存在的类实现
class Adaptee {
public:
Adaptee() {}
virtual ~Adaptee() {}
virtual int otherRequest() {
cout << "Adaptee Run otherRequest!" << endl;
return 999;
}
};
//第二个存在类实现
class AAdaptee : public Adaptee {
public:
AAdaptee() {}
virtual ~AAdaptee() {}
int otherRequest() {
cout << "AAdaptee Run otherRequest!" << endl;
return 888;
}
};
//类适配器,通过访问存在的类的办法,直接继承的方式耦合性太高
class Adapter : public Target, public Adaptee {
public:
int request() override{
this->otherRequest();
}
};
//对象适配器,通过传存在的类的对象,灵活绑定需要适配的对象,也就是客户的类要绑定哪个就绑定哪个
class AAdapter : public Target {
private:
Adaptee* _adaptee;
public:
AAdapter() = delete;
AAdapter(Adaptee *p) : _adaptee(p) {
}
virtual ~AAdapter() {
delete _adaptee;
}
int request() override {
return this->_adaptee->otherRequest();
}
};
int main() {
Adapter *adapter = new Adapter();
auto ret = adapter->request();
cout << " ret = " << ret << endl;
Target *p = new AAdapter(new Adaptee());
auto i = p->request();
cout << "ret = " << i << endl;
//对象适配器在多个存在类情况下,只需要传存在的类就可以,如果是类适配器就有得写一个类
Target *pp = new AAdapter(new AAdaptee());
auto j = pp->request();
cout << "ret = " << j << endl;
return 0;
}
装饰器模式
某个类已经实现了一些功能,而再有一些类对存在的这个类实现装饰加内容或修改功能
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-Jpq7V0Zr-1640406317783)(C:\Users\86166\Desktop\截图\装饰者模式捕获.PNG)]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/ca4bb60ef2fd424ead76f61280e58d24.png?x-oss-process=image/watermark,type_d3F5LXplbmhlaQ,shadow_50,text_Q1NETiBA5YuH5pWi54uX54uX77yM5LiN5oCV5Zuw6Zq-,size_20,color_FFFFFF,t_70,g_se,x_16)
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
class AbstractPerson {
public:
virtual ~AbstractPerson(){}
virtual void run() = 0;
virtual void walk() = 0;
};
class Person : public AbstractPerson {
public:
Person(){}
~Person(){}
void run() override {
cout << "Person Run!" << endl;
}
void walk() override {
cout << "Person Walk!" << endl;
}
};
class AbstractDecoratorPerson : public AbstractPerson {
public:
AbstractDecoratorPerson(AbstractPerson *p) : _person(p){}
~AbstractDecoratorPerson(){}
void run() override {
cout << " Decorator Person run!" << endl;
}
void walk() override {
cout << " Decorator Person walk!" << endl;
}
protected:
AbstractPerson *_person;
};
class DecoratorPersonBlack : public AbstractDecoratorPerson {
public:
DecoratorPersonBlack(AbstractPerson *p) : AbstractDecoratorPerson(p) {
}
~DecoratorPersonBlack(){}
void run() override {
cout << "Black Person running fastly!" << endl;
_person->run();
_person->run();
}
};
class DecoratorPersonOld : public AbstractDecoratorPerson {
public:
DecoratorPersonOld(AbstractPerson *p) : AbstractDecoratorPerson(p) {
}
~DecoratorPersonOld(){}
void run() override {
cout << " old Person cannot run!" << endl;
this->help();
}
void walk() override {
cout << "Old Person Walk Very Slowly!" << endl;
}
void help() {
cout << " Old Person Need Help" << endl;
}
};
int main() {
AbstractPerson *p = new Person();
p->run();
p->walk();
DecoratorPersonOld *p1 = new DecoratorPersonOld(p);
DecoratorPersonBlack *p2 = new DecoratorPersonBlack(p);
delete p;
delete p1;
delete p2;
return 0;
}
外观模式
当数据来时,需要把数据注入多个系统中,如果没有统一接口,那么这个数据就要多次注入数据,多次注入数据很有可能导致某一次注入失败,客户端这样出现问题,那么就会导致服务端出现问题。外观模式就是提供一个注入接口,客户端调这个接口就可以
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-ISJeY4dz-1640406317783)(C:\Users\86166\Desktop\截图\外观模式捕获.PNG)]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/55983351c1254af7bffdbff75780d378.png?x-oss-process=image/watermark,type_d3F5LXplbmhlaQ,shadow_50,text_Q1NETiBA5YuH5pWi54uX54uX77yM5LiN5oCV5Zuw6Zq-,size_20,color_FFFFFF,t_70,g_se,x_16)
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;
class AbstractFaced {
public:
virtual ~AbstractFaced(){}
virtual void Register() = 0;
virtual void Login() = 0;
};
class SystemA : public AbstractFaced {
public:
SystemA(){}
virtual ~SystemA(){}
void Register() override {
cout << "SystemA Reginster!" << endl;
}
void Login() override {
cout << "SystemA Login!" << endl;
}
};
class SystemB : public AbstractFaced {
public:
SystemB(){}
virtual ~SystemB(){}
void Register() override {
cout << "SystemB Reginster!" << endl;
}
void Login() override {
cout << "SystemB Login!" << endl;
}
};
class Facede : public AbstractFaced {
private:
vector<AbstractFaced*> systemArray;
public:
Facede() {
systemArray.push_back(new SystemA());
systemArray.push_back(new SystemB());
}
~Facede() {
for (auto p : systemArray) {
delete p ;
}
}
void Register() override {
for (auto p : systemArray) {
p->Register();
}
}
void Login() override {
for (auto p : systemArray) {
p->Login();
}
}
};
int main() {
Facede facede;
facede.Register();
facede.Login();
return 0;
}
代理模式/委托模式
可以通过中间类Proxy来访问subject类
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-PJasaQlZ-1640406317783)(C:\Users\86166\Desktop\截图\代理模式捕获.PNG)]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/d4d4cfad673548c9af507c1fbb84328f.png?x-oss-process=image/watermark,type_d3F5LXplbmhlaQ,shadow_50,text_Q1NETiBA5YuH5pWi54uX54uX77yM5LiN5oCV5Zuw6Zq-,size_20,color_FFFFFF,t_70,g_se,x_16)
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
class Person {
protected:
Person *_proxy;
public:
Person(){}
virtual ~Person(){}
virtual void rentHouse() = 0;
virtual void setDelegate(Person *p) {
_proxy = p;
}
};
class Proxy : public Person {
public:
Proxy(){}
virtual ~Proxy(){}
void rentHouse() override {
if (_proxy) {
cout << "Proxy Need To Rent House!" << endl;
_proxy->rentHouse();
cout << "Proxy Need To Charge As Intermidary!" << endl;
}
}
};
class Master : public Proxy {
public:
Master(){}
virtual ~Master(){}
void rentHouse() override {
cout << "Master Need Rent House!" << endl;
}
};
int main() {
Person *p = new Master();
Person *proxy = new Proxy();
proxy->setDelegate(p);
proxy->rentHouse();
delete proxy;
delete p;
return 0;
}
行为型模式
模板办法模式
将逻辑/算法放在抽象基类中,并定义好需要实现细节的接口,子类实现细节
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-ltrOjNUk-1640406317784)(C:\Users\86166\Desktop\截图\模板办法模式.PNG)]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/5cf412db5f2c4e9283b5de64c5273227.png?x-oss-process=image/watermark,type_d3F5LXplbmhlaQ,shadow_50,text_Q1NETiBA5YuH5pWi54uX54uX77yM5LiN5oCV5Zuw6Zq-,size_17,color_FFFFFF,t_70,g_se,x_16)
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
class factory {
public:
virtual ~factory() {};
virtual void buildCar() {
this->buildA();
this->buildB();
this->buildC();
this->buildD();
cout << "Build Finised!" << endl;
}
virtual void buildA() = 0;
virtual void buildB() = 0;
virtual void buildC() = 0;
virtual void buildD() = 0;
};
class FactoryBMW : public factory {
public:
void buildA() override {
cout << "BuildA With BMW " << endl;
}
void buildB() override {
cout << "BuildB With BMW " << endl;
}
void buildC() override {
cout << "BuildC With BMW " << endl;
}
void buildD() override {
cout << "BuildD With BMW " << endl;
}
};
class FactoryBENZ : public factory {
public:
void buildA() override {
cout << "BuildA With BENZ " << endl;
}
void buildB() override {
cout << "BuildB With BENZ " << endl;
}
void buildC() override {
cout << "BuildC With BENZ " << endl;
}
void buildD() override {
cout << "BuildD With BENZ " << endl;
}
};
class FactoryTOYOTA : public factory {
public:
void buildCar() {
this->buildA();
this->buildB();
this->buildD();
this->buildC();
this->buildE();
cout << "Build Finised!" << endl;
}
void buildA() override {
cout << "BuildA With TOYOTA " << endl;
}
void buildB() override {
cout << "BuildB With TOYOTA " << endl;
}
void buildC() override {
cout << "BuildC With TOYOTA " << endl;
}
void buildD() override {
cout << "BuildD With TOYOTA " << endl;
}
void buildE() {
cout << "BuildE With TOYOTA " << endl;
}
};
int main() {
factory *p1 = new FactoryBMW();
factory *p2 = new FactoryBENZ();
factory *p3 = new FactoryTOYOTA();
p1->buildCar();
p2->buildCar();
p3->buildCar();
delete p1, p2, p3;
return 0;
}
策略模式
Strategy模式和Template模式要解决的问题是相同(类似)的,都是为了给业务逻辑(算法)具体实现和抽象接口之间的解耦。Strategy模式将逻辑(算法)封装到一个类(Context)里面,通过组合的方式将具体算法的实现在组合对象中实现,再通过委托的方式将抽象接口的实现委托给组合对象实现。
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-1U77BBx2-1640406317784)(C:\Users\86166\AppData\Roaming\Typora\typora-user-images\image-20211224202613711.png)]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/7ce0c3240f67416f8bb821acd7d07de5.png?x-oss-process=image/watermark,type_d3F5LXplbmhlaQ,shadow_50,text_Q1NETiBA5YuH5pWi54uX54uX77yM5LiN5oCV5Zuw6Zq-,size_20,color_FFFFFF,t_70,g_se,x_16)
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
class Stratefy {
public:
virtual ~Stratefy() {}
virtual void sort(int arr[], int N) = 0;
};
class Context {
private:
Stratefy* _strategy;
int *_arr;
int _size;
public:
Context() : _arr(nullptr), _size(0), _strategy(nullptr) {}
Context(int arr[], int n) : _arr(arr), _size(n){}
void setData(int arr[], int n) {
this->_arr = arr;
this->_size = n;
}
void setSortStrategy(Stratefy *p) {
this->_strategy = p;
}
void sort() {
this->_strategy->sort(_arr, _size);
}
void print() {
for (int i = 0; i < _size; i++) {
cout << _arr[i] << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
};
class BubbleSort : public Stratefy{
public:
BubbleSort(){}
~BubbleSort(){}
void sort(int arr[], int N) override {
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < N - i - 1; j++) {
if (arr[j] > arr[j + 1]) {
int temp = arr[j];
arr[j] = arr[j + 1];
arr[j + 1] = temp;
}
}
}
}
};
class SelectionSort : public Stratefy{
public:
SelectionSort(){}
~SelectionSort(){}
void sort(int arr[], int N) override {
int k;
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
k = i;
for (int j = i + 1; j < N; j++) {
if (arr[k] > arr[j]) {
k = j;
}
}
int temp = arr[i];
arr[i] = arr[k];
arr[k] = temp;
}
}
};
class InsertSort : public Stratefy{
public:
InsertSort(){}
~InsertSort(){}
void sort(int arr[], int N) override {
int i, j;
for (i = 1; i < N; i++) {
for (j = i - 1; j >= 0; j--) {
if (arr[i] > arr[j]) {
break;
}
int temp = arr[i];
for (int k = i - 1; k > j; k--) {
arr[k + 1] = arr[k];
}
arr[j + 1] = temp;
}
}
}
};
int main() {
Context* ctx = new Context();
int arr[] = {23, 58, -4, 59, -48, 5987, 85, 85, -4864, 352};
ctx->setData(arr, sizeof(arr) / sizeof(int));
cout << "before sort :";
ctx->print();
Stratefy *p1 = new BubbleSort();
ctx->setSortStrategy(p1);
ctx->sort();
cout << "after bubble sort:";
ctx->print();
Stratefy *p2 = new SelectionSort();
ctx->setSortStrategy(p2);
ctx->sort();
cout << "after SelectionSort sort:";
ctx->print();
Stratefy *p3 = new InsertSort();
ctx->setSortStrategy(p3);
ctx->sort();
cout << "after InsertSort sort:";
ctx->print();
delete ctx, p1, p2, p3;
return 0;
}
观察者模式
Observer模式要解决的问题为:建立一个一(Subject)对多(Observer)的依赖关系,并且做到当“一” 变化的时候,依赖这个“一”的多也能同步改变
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-YdGwNZ4y-1640406317784)(C:\Users\86166\AppData\Roaming\Typora\typora-user-images\image-20211224205522777.png)]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/60c6ddfc434d4943b88b539e977fff4e.png?x-oss-process=image/watermark,type_d3F5LXplbmhlaQ,shadow_50,text_Q1NETiBA5YuH5pWi54uX54uX77yM5LiN5oCV5Zuw6Zq-,size_20,color_FFFFFF,t_70,g_se,x_16)
比如,观察者相对于一个酒店,具体观察者相当于酒店前台,前台等待观察着(前台有多个),如果有客人来就让它登记个人信息。而对象相当于服务员,具体对象相当于具体的房间,在前台登记后就可以叫服务员带它到具体房间入住且服务员记录入住信息。下面注释以上面动作为主。
#include<iostream>
#include <map>
using namespace std;
class AbstracrSubject;
/*&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&& Observer &&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&*/
class AbstractObserser {//酒店,酒店能保存信息和能接收信息
public:
AbstractObserser(string s):name(s){}//保存信息
virtual ~AbstractObserser(){}
virtual void update(AbstracrSubject *p) = 0;//接收信息
inline string getName() {
return name;
}
protected:
string name;
};
/*&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&&*/
/*--------------------- Subject ---------------------------*/
class AbstracrSubject {//服务员,带到房间且保存入住信息
protected:
std::map<string, AbstractObserser*> _observsers;
public:
virtual int getDate() = 0;
virtual void addObserver(AbstractObserser *p) {//带到房间
_observsers[p->getName()] = p;
}
virtual void notify(string s) {//服务员记录入住情况
if (_observsers.find(s) == _observsers.end()) {
cout << "not found any observer!" << endl;
} else {
_observsers[s]->update(this);
}
}
};
/*-------------------------------------------------------*/
/ ConcreteObserverA\B //
class Observer : public AbstractObserser {//前台能 登记信息
public:
Observer(string s) : AbstractObserser(s) {}
~Observer(){}
void update(AbstracrSubject *p) override {
cout << "Update Observer! total = " << p->getDate() << " observer = " << this << endl;
}
};
class Observer2 : public AbstractObserser {
public:
Observer2(string s) : AbstractObserser(s) {}
~Observer2(){}
void update(AbstracrSubject *p) override {
cout << "Update Observer2! total = " << p->getDate() << " observer = " << this << endl;
}
};
///
/****************************** ConcreteSubject ******************************/
class Subject : public AbstracrSubject {//房间,能查询客户房间信息
public:
Subject(){}
~Subject(){}
void add() {
this->total++;
this->notify(to_string(this->total));
}
int getDate() override{
return total;
}
private:
int total;
};
/****************************************************************************/
int main() {
Subject *subject = new Subject();//一个服务员
AbstractObserser *p1 = new Observer("1");//有客人来就登记信息
AbstractObserser *p2 = new Observer2("2");
AbstractObserser *p3 = new Observer("3");
AbstractObserser *p4 = new Observer2("4");
AbstractObserser *p5 = new Observer("5");
AbstractObserser *p6 = new Observer2("6");
AbstractObserser *p7 = new Observer("7");
subject->addObserver(p1);//把客人带到房间入住
subject->addObserver(p2);
subject->addObserver(p3);
subject->addObserver(p4);
subject->addObserver(p5);
subject->addObserver(p6);
subject->addObserver(p7);
subject->add();
cout << "------------------" << endl;
subject->add();
cout << "------------------" << endl;
subject->add();
cout << "------------------" << endl;
subject->add();
cout << "------------------" << endl;
subject->add();
cout << "------------------" << endl;
subject->add();
cout << "------------------" << endl;
return 0;
}
命令模式
Command模式通过将请求封装到一个对象(Command)中,并将请求的接收者存放到具体的ConcreteCommand类中(Receiver)中,从而实现调用操作的对象和操作的具体实现者之间的解耦。
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-CetP1K94-1640406317785)(C:\Users\86166\AppData\Roaming\Typora\typora-user-images\image-20211225100911193.png)]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/4bd2a7e5674148d0bf4348448ddd487c.png?x-oss-process=image/watermark,type_d3F5LXplbmhlaQ,shadow_50,text_Q1NETiBA5YuH5pWi54uX54uX77yM5LiN5oCV5Zuw6Zq-,size_20,color_FFFFFF,t_70,g_se,x_16)
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
class Receiver {
public:
Receiver(){}
virtual ~Receiver(){}
virtual void doCommand(int n) {
if (n <= 1)
cout << "Execute Command! <= 1!" << endl;
else
cout << "Execute Command > 1!" << endl;
}
};
class Receiver2 : public Receiver{
public:
Receiver2(){}
virtual ~Receiver2(){}
void doCommand(int n) override{
if (n < 10)
cout << "Execute Command < 10!" << endl;
else
cout << "Execute Command >= 10 !" << endl;
}
};
class Command {
protected:
Receiver *_receiver;
public:
Command(Receiver *p) : _receiver(p){}
virtual ~Command(){}
virtual void operator()(int n) = 0;
};
class ConcreateCommand : public Command {
public:
ConcreateCommand(Receiver *p) : Command(p){}
void operator()(int n) override {
_receiver->doCommand(n);
}
};
class ConcreateCommand2 : public Command {
public:
ConcreateCommand2(Receiver *p) : Command(p){}
void operator()(int n) override {
_receiver->doCommand(n);
}
};
class Invoker {
private:
Command* _command;
public:
Invoker() : _command(nullptr) {
}
Invoker(Command *p) : _command(p) {
}
virtual ~Invoker(){}
void setCommand(Command *p) {
_command = p;
}
void executeCommand(int n) {
if (_command) {
(*_command)(n);
}
}
};
int main() {
Invoker *invoker = new Invoker();
Receiver *receiver = new Receiver();
Receiver *receiver2 = new Receiver2();
Command *command = new ConcreateCommand(receiver);
Command *command2 = new ConcreateCommand2(receiver2);
invoker->setCommand(command);
invoker->executeCommand(1);
invoker->executeCommand(2);
invoker->setCommand(command2);
invoker->executeCommand(1);
invoker->executeCommand(20);
delete invoker, receiver, command;
return 0;
}
访问者模式
不改变类的前提下定义作用于这些元素的新操作
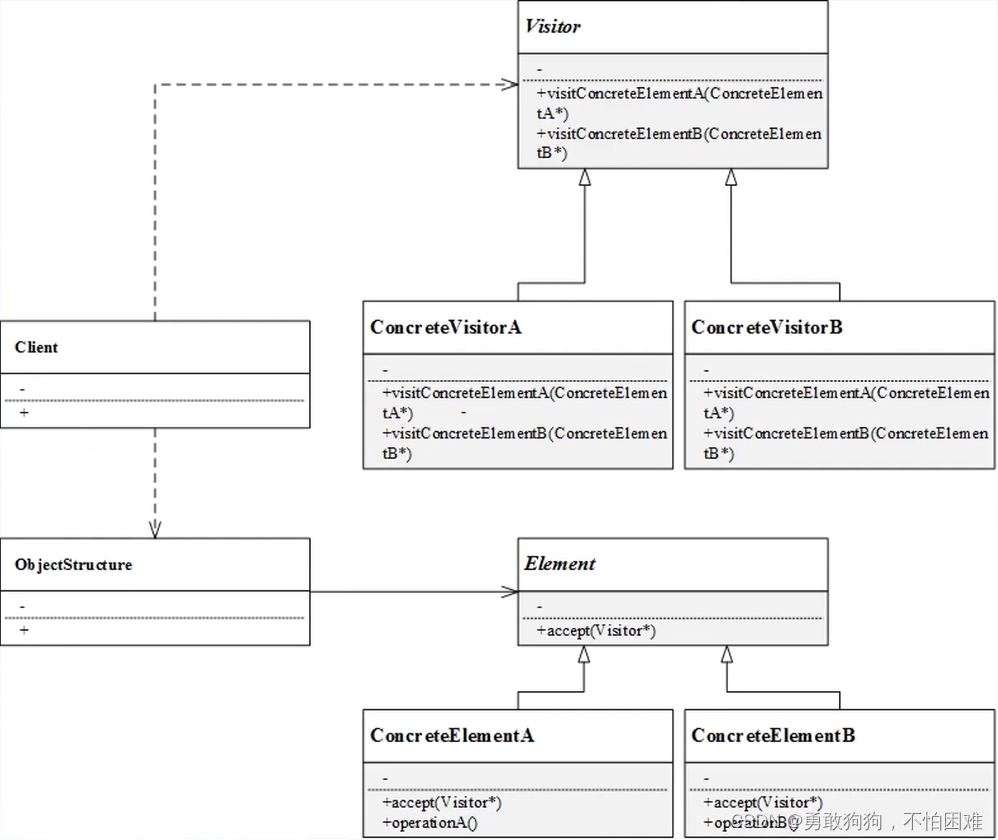
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <map>
/// Element
using namespace std;
class Visotor;
class Node {
public:
virtual ~Node(){}
virtual void accept(Visotor *visitor) = 0;
};
/// Visitor
class Visotor {
public:
virtual ~Visotor(){}
virtual void visit(Node * node) = 0 ;
};
/// ConcentrateElementA
class NodeA : public Node {
friend class VisitorA;
private:
string s;
int n;
public:
NodeA() {
s = "Hello KKB";
n = 666;
}
virtual ~ NodeA(){}
void accept(Visotor* vistor) override {
vistor->visit(this);
}
};
/// ConcentrateElementB
class NodeB : public Node {
friend class VisitorB;
private:
std::map<string, int> _map;
int n;
public:
NodeB() {
_map["aa"] = 34;
_map["bb"] = 54;
_map["cc"] = 32;
}
virtual ~ NodeB(){}
void accept(Visotor* vistor) override {
vistor->visit(this);
}
};
/// ConcreteVisitorA
class VisitorA : public Visotor {
public:
void visit(Node *node) override{
NodeA *p = (NodeA *)node;
cout << "NodeA.s = " << p->s << " NodeA.n = " << p->n << endl;
}
};
/// ConcreteVisitorB
class VisitorB : public Visotor {
public:
void visit(Node *node) override{
NodeB *p = (NodeB *)node;
cout << "-------------- NodeB ---- map begin ------" << endl;
for (auto e : p->_map) {
cout << "key = " << e.first << " value = " << e.second << endl;
}
cout << "-------------- NodeB ---- map end ------" << endl;
}
};
int main() {
Node *p1 = new NodeA();
Node *p2 = new NodeB();
Visotor *p3 = new VisitorA();
Visotor *p4 = new VisitorB();
p1->accept(p3);
p2->accept(p4);
delete p1, p2, p3, p4;
return 0;
}
责任链模式
使多个对象都有机会处理请求,从而避免请求的发送者和接收者之间的耦合关系。将这个对象连成一条链,并沿着这条链传递该请求,直到有一个对象处理它为止。
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-HfDiAssk-1640406317785)(C:\Users\86166\AppData\Roaming\Typora\typora-user-images\image-20211225112049093.png)]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/1b194fdc04d64df3a7d16cbcd7177f35.png?x-oss-process=image/watermark,type_d3F5LXplbmhlaQ,shadow_50,text_Q1NETiBA5YuH5pWi54uX54uX77yM5LiN5oCV5Zuw6Zq-,size_20,color_FFFFFF,t_70,g_se,x_16)
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
class Handler {
private:
protected:
Handler *_nextHandler;
public:
virtual void setNextHandler(Handler *p) {
_nextHandler = p;
}
virtual void dealRequest(int day) = 0;
virtual void request(int day) {
cout << "request for " << day << "days!" << endl;
if (this->_nextHandler)
this->_nextHandler->dealRequest(day);
else
cout << "not need request, because next handler is null!" << endl;
}
};
class Eployee : public Handler {
void dealRequest(int day) override {
cout << "没有权限,需要上级处理审批!" << endl;
if (this->_nextHandler) {
this->_nextHandler->dealRequest(day);
}
}
};
class TeamLeader : public Handler {
public:
void dealRequest(int day) override {
if (day <= 3) {
cout << "少于三天,直接通过审批! " << endl;
} else {
cout << "大于三天,需要上级审批" << endl;
if (this->_nextHandler) {
this->_nextHandler->dealRequest(day);
}
}
}
};
class Mannager : public Handler {
public:
void dealRequest(int day) override {
if (day <= 7) {
cout << "少于7天,直接通过审批! " << endl;
} else {
cout << "大于7天,需要上级审批" << endl;
if (this->_nextHandler) {
this->_nextHandler->dealRequest(day);
}
}
}
};
class CEO : public Handler {
public:
void dealRequest(int day) override {
if (day <= 15) {
cout << "少于15天,直接通过审批! " << endl;
} else {
cout << "大于15天,拒绝申请!" << endl;
}
}
};
int main() {
Handler *p1 = new Eployee();
Handler *p2 = new TeamLeader();
Handler *p3 = new Mannager();
Handler *p4 = new CEO();
p1->setNextHandler(p2);
p2->setNextHandler(p3);
p3->setNextHandler(p4);
p4->setNextHandler(nullptr);
p1->request(3);
p1->request(5);
p1->request(10);
p1->request(30);
delete p1, p2, p3, p4;
return 0;
}
迭代器模式
提供一种顺序访问一个聚合对象中各个元素,而不是暴露该对象的内部表示
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-8pV9cy8y-1640406317786)(C:\Users\86166\AppData\Roaming\Typora\typora-user-images\image-20211225114527920.png)]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/cd6524aa90df483990c6a8ed6308f281.png?x-oss-process=image/watermark,type_d3F5LXplbmhlaQ,shadow_50,text_Q1NETiBA5YuH5pWi54uX54uX77yM5LiN5oCV5Zuw6Zq-,size_15,color_FFFFFF,t_70,g_se,x_16)
#include<iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
namespace master {
template<class T>
class Aggregate {
public:
Aggregate(){}
virtual ~Aggregate(){}
virtual void push(T t) = 0;
virtual T& operator[](int idx) = 0;
virtual int size() = 0;
};
template<class T>
class Iterator {
public:
Iterator(){}
virtual ~Iterator(){}
virtual void begin() = 0;
virtual void next() = 0;
virtual T* currentItem() = 0;
virtual bool end() = 0;
};
template<class T>
class ConcreateAggregate : public Aggregate<T> {
public:
void push(T t) override {
_data.push_back(t);
}
T& operator[](int idx) override {
return _data[idx];
}
int size() override {
return _data.size();
}
private:
std::vector<T> _data;
};
template<class T>
class ConcreteIterator : public Iterator<T> {
private:
Aggregate<T> *_agrg;
int _cursour;
public:
ConcreteIterator(Aggregate<T> *p) : _agrg(p), _cursour(0) {
}
virtual ~ConcreteIterator(){}
void begin() override {
_cursour = 0;
}
virtual void next() {
if (_cursour >= _agrg->size()) return ;
_cursour++;
}
virtual T* currentItem(){
if (_agrg) {
return &((*_agrg)[_cursour]);
} else {
return nullptr;
}
}
bool end() override {
return _cursour >= _agrg->size();
}
};
}
int main() {
master::Aggregate<int> *aggr = new master::ConcreateAggregate<int>();
aggr->push(1);
aggr->push(2);
aggr->push(3);
aggr->push(4);
aggr->push(5);
master::Iterator<int> *it = new master::ConcreteIterator<int>(aggr);
for (it->begin(); !it->end(); it->next()) {
cout << *it->currentItem() << endl;
}
delete aggr, it;
return 0;
}
总结:
设计模式还是面向的是一个工程,理解最好的方式就是自己画UML图去实现一个程序
`