文章目录
1 浅拷贝
简单的赋值拷贝操作
2 深拷贝
在堆区重新申请空间,进行拷贝操作
3 对比:是否delete堆区的数据
栈区的数据在使用完毕后由编译器自动释放对应的内存;堆区的数据由程序员自己开辟,自己释放,即在使用完毕后不会自动释放。如果忘记对堆区的数据释放,会造成内存泄漏,直到整个程序执行完毕后,堆区的数据才被回收。
分别在栈区开辟一块内存,存放变量a;在堆区开辟一块内存,存放成员变量b。
错误示范:没有手动释放堆区的数据
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int *g_a;
int *g_b;
void test()
{
int a = 10; //a存放于栈区,test函数执行完毕后,由编译器自动释放内存
int *b = new int(20); //b存放与堆区,test函数执行完毕后,编译器不会自动释放,需要用户自己回收 delete,否则会造成内存泄漏
cout << "a = " << a << endl;
cout << "b = " << *b << endl;
g_a = &a;
g_b = b;
cout << "test函数执行完毕!" << endl;
}
int main()
{
test();
//由于栈区中的a在test函数执行完毕后自动释放,所以a对应的内存的值不为10
cout << "a = " << *g_a << endl;
cout << "a = " << *g_a << endl;
cout << "a = " << *g_a << endl;
//由于堆区中的b在test函数执行完毕后没有被释放,所以b对应的内存的值仍为20
cout << "b = " << *g_b << endl;
cout << "b = " << *g_b << endl;
cout << "b = " << *g_b << endl;
return 0;
}
输出结果:
a = 10
b = 20
test函数执行完毕!
a = -858993460
a = -858993460
a = -858993460
b = 20
b = 20
b = 20
正确示范:堆区的数据使用完毕后,执行delete操作
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int *g_a;
int *g_b;
void test()
{
int a = 10; //a存放于栈区,test函数执行完毕后,由编译器自动释放内存
int *b = new int(20); //b存放与堆区,test函数执行完毕后,编译器不会自动释放,需要用户自己回收 delete,否则会造成内存泄漏
cout << "a = " << a << endl;
cout << "b = " << *b << endl;
g_a = &a;
g_b = b;
delete b; //释放堆区中的数据 b
cout << "test函数执行完毕!" << endl;
}
int main()
{
test();
//由于栈区中的a在test函数执行完毕后自动释放,所以a对应的内存的值不为10
cout << "a = " << *g_a << endl;
cout << "a = " << *g_a << endl;
cout << "a = " << *g_a << endl;
//堆区中的b在test函数执行完毕后,被delete释放,所以b对应的内存的值不为20
cout << "b = " << *g_b << endl;
cout << "b = " << *g_b << endl;
cout << "b = " << *g_b << endl;
return 0;
}
输出结果:
a = 10
b = 20
test函数执行完毕!
a = -858993460
a = -858993460
a = -858993460
b = -572662307
b = -572662307
b = -572662307
4 浅拷贝与深拷贝
4.1 浅拷贝造成的错误
代码:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Person
{
public:
Person(int age,int height)
{
m_age = age;
m_height = new int (height); //在堆区开辟一块内存,存放成员变量 m_height;需要手动释放,即需要自定义一个析构函数
cout << "Person 有参构造函数调用" << endl;
}
//默认拷贝函数,如果不提供拷贝构造,编译器就会提供下面的默认拷贝函数,为浅拷贝
Person(const Person& p)
{
m_age = p.m_age;
m_height = p.m_height; //浅拷贝,只复制p.m_height的地址,复制前后的地址指向同一块内存
cout << "Person 默认拷贝构造函数调用" << endl;
}
//自定义的析构函数,用于回收堆区的数据
~Person()
{
//析构,将堆区开辟的内存释放
//如果m_height不为空指针,则释放m_height指向的内存,并将m_height赋值为空指针。
if (m_height != NULL)
{
delete m_height;
m_height = NULL;
}
cout << "Person 析构函数调用" << endl;
}
int m_age; //年龄(存放于栈区)
int *m_height; //身高(存放于堆区)
};
void test()
{
Person p1(18, 180);
Person p2(p1);
cout << "p1的年龄: " << p1.m_age << " 身高: " << *p1.m_height << endl;
cout << "p2的年龄: " << p2.m_age << " 身高: " << *p2.m_height << endl;
}
int main()
{
test();
return 0;
}
输出结果:
Person 有参构造函数调用
Person 拷贝构造函数调用
p1的年龄: 18 身高: 180
p2的年龄: 18 身高: 180
Person 析构函数调用
运行中断,报错如下。
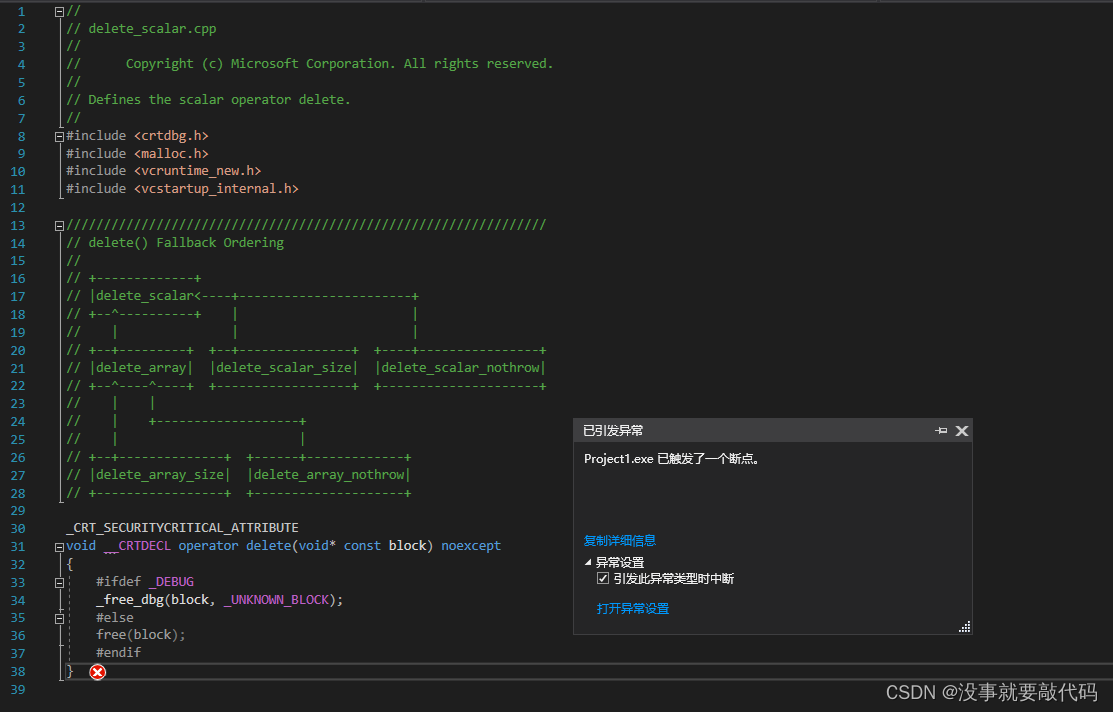
这就是浅拷贝带来的问题!
4.2 如果类成员有在堆区开辟的,一定要自己提供拷贝构造函数(深拷贝),防止浅拷贝带来的问题
代码:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Person
{
public:
//有参构造
Person(int age,int height)
{
m_age = age;
m_height = new int (height); //在堆区开辟一块内存,存放成员变量 m_height;需要手动释放,即需要自定义一个析构函数
cout << "Person 有参构造函数调用" << endl;
}
//自定义的拷贝构造函数
Person(const Person& p)
{
m_age = p.m_age;
m_height = new int(*p.m_height); //深拷贝,重新在堆区开辟一块内存存放拷贝后的数据
cout << "Person (自定义)拷贝构造函数调用" << endl;
}
//自定义的析构函数,用于回收堆区的数据
~Person()
{
//析构,将堆区开辟的内存释放
//如果m_height不为空指针,则释放m_height指向的内存,并将m_height赋值为空指针。
if (m_height != NULL)
{
delete m_height;
m_height = NULL;
}
cout << "Person 析构函数调用" << endl;
}
int m_age; //年龄(存放于栈区)
int *m_height; //身高(存放于堆区)
};
void test()
{
Person p1(18, 180);
Person p2(p1);
cout << "p1的年龄: " << p1.m_age << " 身高: " << *p1.m_height << endl;
cout << "p2的年龄: " << p2.m_age << " 身高: " << *p2.m_height << endl;
}
int main()
{
test();
return 0;
}
输出结果:
Person 有参构造函数调用
Person (自定义)拷贝构造函数调用
p1的年龄: 18 身高: 180
p2的年龄: 18 身高: 180
Person 析构函数调用
Person 析构函数调用
4.3 浅拷贝与深拷贝图解
浅拷贝,只是将地址复制,拷贝前后两份地址指向同一块内存,p1调用析构函数,会立马释放该内存空间;当p2调用析构函数时,没有内存可以释放,故发生错误。

深拷贝,在堆区开辟一块内存,存放拷贝后的数据,这样,p1、p2调用析构函数时就不会互相干扰。

如果还是不明白,请参考https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1et411b73Z?p=110