文章目录
前言
??下面的文章小王留着以后复盘用,比较通俗易懂了属于是。考完研已经快一个月了,小王必须尽快恢复状态,不开心的就让他过去吧,学业一定不可以落下,纵有疾风起,人生不言弃,与诸君共勉!

第一天感觉很实用的快捷键
第一次用vs
(自动对齐)快捷键:Ctrl+K+D(三个键同时按下)
注释:Ctrl + K + C
取消注释:Ctrl + K + U
一、常识
注:一个工程下面不可两个及以上cpp文件中出现main函数,也就是你只能在一个cpp里有main函数
A01打印c++HelloWorld.cpp
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
/*
1月24日,今天是不开心的一天,但也是开心的一天
不开心的是还是会想不开心的人 时间是一种解药 一定可以走出来哒!
开心的是考完研到现在已经堕落快一个月了,不过现在振作了
估计是考研花光了那半年的所有力气,导致现在干啥都没劲
*/
// main只能有一个,因为做人不能三心二意
int main() {
//在屏幕中输出helloworld
cout << "helloworld" << endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
}
https://blog.csdn.net/hanhanwanghaha宝藏女孩的成长日记 欢迎您的关注!
欢迎关注微信公众号:宝藏女孩的成长日记 让这个可爱的宝藏女孩在努力的道路上与你一起同行! 如有转载,请注明出处(如不注明,盗者必究)
A02变量.cpp
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
//创建变量的语法:数据类型 变量名 = 变量初始值
int num = 10;
//num在内存中为10
cout << "num为" << num << endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
}
A03常量.cpp
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
/*
常量
作用:用于记录程序中不可更改的数据
定义方式有两种:注意后面不要加“;”
1、#define 宏常量
1、const 修饰的变量
*/
//第一种定义方式:年龄为23
#define age 23
int main() {
/*常量不可以改变,否则会报错
age = 18;*/
cout << "目前我的年龄为:" << age << endl;
//第二种定义方式
const int mouth = 12;
/*常量不可以改变,否则会报错
mouth = 18;*/
cout << "一年有多少个月" << mouth << endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
}
A04标识符命名规则.cpp
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
/*
标识符命名规则
1、标识符不可以是关键字
2、标识符是字母,数字,下划线构成
3、标识符第一个字母只能是字母、下划线组成
4、标识符是区分大小写的
*/
int main() {
//1、标识符不可以是关键字
//int int 10;
//2、标识符是字母,数字,下划线构成
int _aaa = 888;
int aaa = 666;
//3、标识符第一个字母只能是字母、下划线组成,要是以数字开头要报错
//int 1kk = 33;
//4、标识符是区分大小写的,输出时就不能用AAA
//int aaa = 666;
cout << aaa << endl;
//在起名的时候,最好能够做到见名知意
int num1 = 10;
int num2 = 56;
int sum = num1 + num2;
cout << sum << endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
}
A05整型.cpp
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
//short 短整形 2个字节 (-2的15次方到2的15次方-1)超过这个范围会报错
short num1 = 32768;
//int整形 4个字节 (-2的31次方到2的31次方-1)超过这个范围会报错
int num2 = 32769;
//long长整形 4个字节 (-2的31次方到2的31次方-1)超过这个范围会报错
long num3 = 32770;
//long long长整形 8个字节 (-2的63次方到2的63次方-1)超过这个范围会报错
int num4 = 32771;
cout << num1 << endl;
cout << num2 << endl;
cout << num3 << endl;
cout << num4 << endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
}
A06sizeof的用法.cpp
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
//short(2字节) int(4字节) long(windows:4字节 linux32位:4字节;linux64位:8字节)
//longlong(8字节)
short num1 = 888;
cout << "short所长字节为:" << sizeof(num1) << endl;
int num2 = 999;
cout << "short所长字节为:" << sizeof(999) << endl;
long num3 = 666;
cout << "long所长字节为:" << sizeof(666) << endl;
long long num4 = 966;
cout << "short所长字节为:" << sizeof(long long) << endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
}
https://blog.csdn.net/hanhanwanghaha 宝藏女孩的成长日记 欢迎您的关注!
欢迎关注微信公众号:宝藏女孩的成长日记 让这个可爱的宝藏女孩在努力的道路上与你一起同行! 如有转载,请注明出处(如不注明,盗者必究)
A07实型.cpp
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
/* 1、单精度 float
2、双精度 double;
*/
cout <<"默认情况下,输入一个小数最多会显示6位有效数字" << endl;
float f1 = 3.1415926;
cout << "f1=" << f1 << endl;
double d1 = 1.1415927;
cout << "d1=" << d1 << endl;
//用sizeof来统计float和double占用的内存空间
cout << "float的内存占用空间为" << sizeof(float) << endl;
cout << "double的内存占用空间为" << sizeof(double) << endl;
//科学技术法(不要求掌握,但是遇到了会认出这是什么)
float f2 = 3e2; //3*10的2次方
cout << "f2为" << f2 << endl;
float f3 = 3e-2; //3*0.1的2次方
cout << "f3为" << f3 << endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
}
A08字符型.cpp
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
//1、字符型变量创建方式
char ch = 'B';
cout << "ch为" << ch << endl;
//2、字符型变量所占内存大小
cout << "char字符变量所占内存为" << sizeof(char) << endl;
//3、字符变量常见错误
//char ch2 = "c";//创建字符型变量的时候,要用单引号
//char ch3 = 'jbgdjsnixc';//创建字符变量时,单引号内只能有一个字符
//4、字符变量对应的ASCLL编码
//a-97 A-65 剩下的可以推 例如 B-66
cout << "ch对应ASCLL编码为" << (int)ch << endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
}
A09转义字符.cpp
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
//常用转义字符
//换行符: \n
cout << "hello world\n";
//反斜杠: \\
cout << "\\" << endl;
//水平制表符: \t (作用:可以整齐输出数据)
cout << "aaaaa\thello world" << endl;
cout << "aaa\thello world" << endl;
cout << "a\thello world" << endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
}
A10字符串类型.cpp
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
#include <string> //用C++风格的字符串时,需包含这个头文件
int main() {
string str1 = "hello \nworld \n换了个行哈哈哈哈哈哈";
cout << str1 << endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
}
A11布尔类型.cpp
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
//1、创建bool数据类型
bool flag = true;//true代表真
cout << flag << endl;
flag = false;
cout << flag << endl;
//本质上 1代表真 0代表假
//2、查看bool类型所占空间
cout << "bool类型所占空间为:" << sizeof(bool) << endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
}
A12数据的输入.cpp
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
#include <string>//string的头文件
int main() {
//1、整型
int num1 = 0;
cout << "请给整型变量num1赋值" << endl;
cin >> num1;
cout << "赋值后的整型变量为" << num1 << endl;
//2、浮点型
float f = 3.14f;
cout << "请给浮点型f赋值" << endl;
cin >> f;
cout << "赋值后的f为:" << f << endl;
//3、字符型
char ch = 'a';
cout << "请给字符型ch赋值" << endl;
cin >> ch;
cout << "赋值后的ch为:" << ch << endl;
//4、字符串型
string str1 = "sweety";
cout << "请给字符串型str1赋值" << endl;
cin >> str1;
cout << "赋值后的str1为:" << str1 << endl;
//5、布尔类型 (点0或1)
bool flag = "flase";
cout << "请给布尔类型flag赋值" << endl;
cin >> flag;
cout << "赋值后的flag为:" << flag << endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
}
二、算术运算符
A13算术运算符.cpp
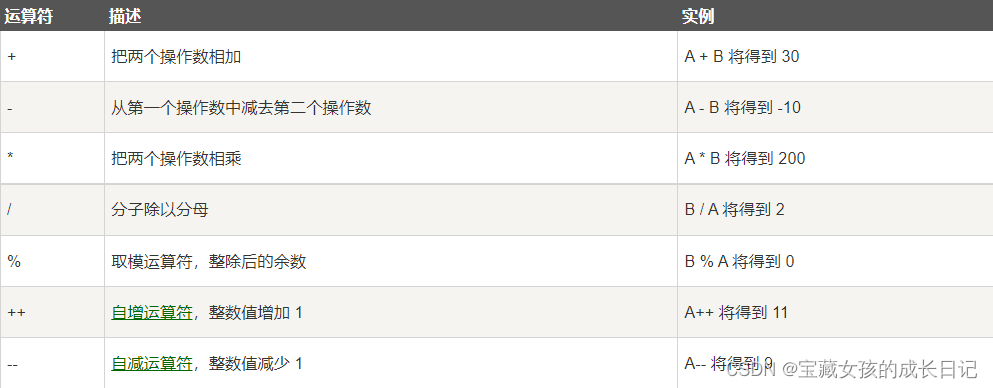
加减乘除与取模、自增和自减
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
//加减乘除
int num1 = 6;
int num2 = 6;
cout << num1 + num2 << endl;
cout << num1 - num2 << endl;
cout << num1 * num2 << endl;
cout << num1 / num2 << endl;
//两个整数相除,结果依然是整数,将小数部分去掉
int a = 10;
int b = 20;
cout << a / b << endl;
//两个数相除,除数不可以为0,若为0,则会报错,同理也取不了余数(本质就是除法)
int c = 9;
int d = 0;
//cout << c / d << endl;
//两个小数可以相除
double e = 0.01;
double f = 0.3;
cout << e / f << endl;
//取模的本质就是取余数,注意:小数不可以取模
int g = 8;
int h = 3;
cout << "8%3的余数为" << g % h << endl;
cout << "\n前置和后置++及其区别\n" << endl;
//1、前置递增
int A1 = 7;
++A1;//让变量+1
cout << "前置定增后的A1为" << A1 << endl;
//2、后置递增
int A2 = 7;
A2++;//让变量+1
cout << "后置定增后的A1为" << A2 << endl;
//3、前置递增和后置递增的区别
cout << "前置递增是先让变量加1,再进行表达式的运算" << endl;
int A3 = 5;
int B3 = ++A3 * 2;
cout << "A3=" << A3 << endl;
cout << "B3=" << B3 << endl;
cout << "后置递增是先进行表达式的运算,再让变量加1" << endl;
int A4 = 5;
int B4 = A4++ * 2;
cout << "A4=" << A4 << endl;
cout << "B4=" << B4 << endl;
//自减同理
system("pause");
return 0;
}
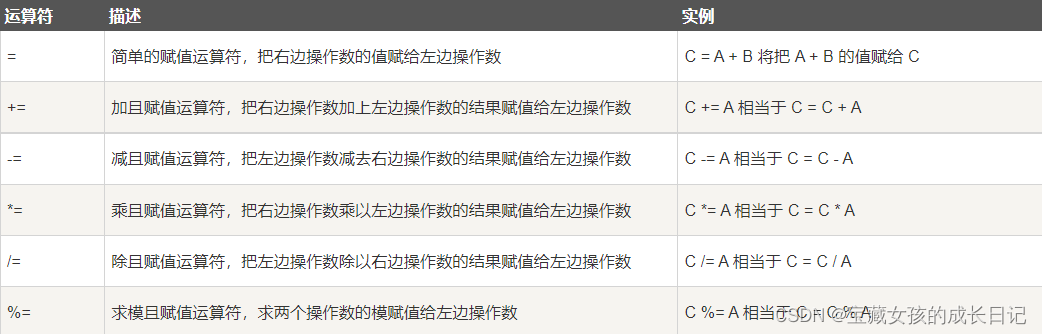
A14赋值运算符.cpp
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
// =
int a = 2;
a = 999;
cout << "a的值为" << a << endl;
//+=
int b = 4;
b += 4;
cout << "b的值为" << b << endl;
//-=
int c = 10;
c -= 2;
cout << "c的值为" << c << endl;
//*=
int d = 33;
d *= 2;
cout << "d的值为" << d << endl;
// /=
int e = 81;
e /= 9;
cout << "e的值为" << e << endl;
// %=
int f = 13;
f %= 7;
cout << "f的值为" << f << endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
}
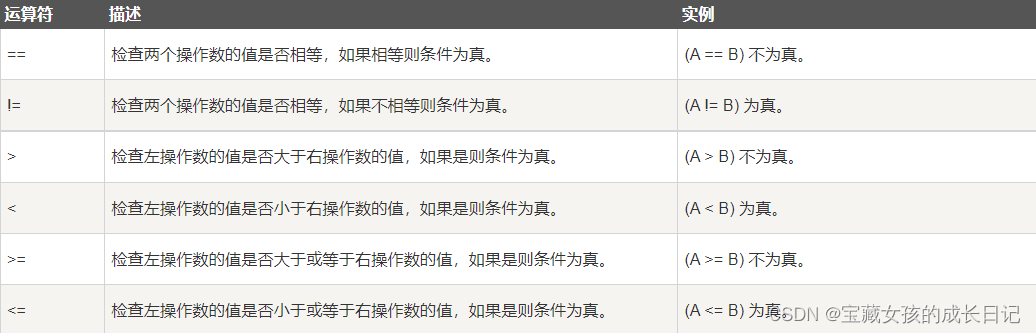
A15比较运算符.cpp
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
int a = 6;
int b = 8;
cout << (a == b) << endl;//0
cout << (a != b) << endl;//1
cout << (a > b) << endl;//0
cout << (a < b) << endl;//1
cout << (a >= b) << endl;//0
cout << (a <= b) << endl;//1
system("pause");
return 0;
}
A16逻辑运算符.cpp

#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
//逻辑运算:与&& (两个为真才能为真,有一个不为真就是假)
//在c++中,除了0都为真
int a = 9;
int b = 6;
cout << (a && b) << endl;//两个都为真,结果就是1
a = 9;
b = 0;
cout << (a && b) << endl;//有一个不为真,那么结果就是假(0)
a = 0;
b = 0;
cout << (a && b) << endl;//两个都为假,结果更加为假啦
//逻辑运算:或||(有一个为真就是真)
int c = 6;
int d = 6;
cout << (c||d) << endl;//两个都为真,结果肯定为真
c = 0;
d = 6;
cout << (c || d) << endl;//有一个为真,结果为真
c = 6;
d = 0;
cout << (c || d) << endl;//有一个为真,结果为真
c = 0;
d = 0;
cout << (c || d) << endl;//两个都为假,则结果为假
//逻辑运算 非!
int e = 9;
cout << !e << endl;//0
cout << !!e << endl;//1
system("pause");
return 0;
}
三、选择结构
A17选择结构.cpp
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
//用户输入高考分数,如果分数大于550,考上重本
int score = 0;
cout << "请输入您的高考分数" << endl;
//1、用户输入分数
cin >> score;
//2、打印用户输入的分数
cout << "您输入的分数为" << score << endl;
//3、判断分数是否大于550,如果是,就输出
/*
//选择结构 单行if语句
if (score >= 550) {
cout << "您可以四川选择一本的大学" << endl;
}*/
//选择结构 多行if语句(讲人话:就是加了一个else)
/*if(score >= 550) {
cout << "您可以四川选择一本的大学" << endl;
}
else {
cout << "您的分数未达到550,走不了一本" << endl;
}*/
选择结构 多条件if语句(讲人话:就是加了一个或多个else if,最后再来个else)
/*if (score >= 550) {
cout << "您可以四川选择一本的大学" << endl;
}
else if(score >500)
{
cout << "您的分数在500到550之间,可以选择二本的大学" << endl;
}
else if (score > 470) {
cout << "您的分数在470到500之间,可以选择民办院校" << endl;
}
else {
cout << "亲亲,这边建议您复读" << endl;
}*/
//嵌套if语句
if (score >= 550) {
cout << "恭喜您!您可以选择很多一本的大学" << endl;
if (score > 650) {
cout << "建议直接报考顶尖985" << endl;
}
else if (score > 600) {
cout << "并且您可以选择很多985 211" << endl;
}
}
else if (score > 500)
{
cout << "您的分数在500到550之间,可以选择二本的大学" << endl;
}
else if (score > 470) {
cout << "您的分数在470到500之间,可以选择民办院校" << endl;
if (score > 490) {
cout << "您还可以看看好一点的民办院校" << endl;
}
}
else {
cout << "亲亲,这边建议您复读" << endl;
}
system("pause");
return 0;
}
}
A18选择结构的应用.cpp
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
//1、创建三个娃娃成绩的默认值
int score1 = 89;
int score2 = 95;
int score3 = 93;
//2、请用户输入三个娃娃的实际成绩
cout << "请输入第一个娃娃的成绩" << endl;
cin >> score1;
cout << "请输入第二个娃娃的成绩" << endl;
cin >> score2;
cout << "请输入第三个娃娃的成绩" << endl;
cin >> score3;
cout << "第一个娃娃的成绩为" << score1 << endl;
cout << "第二个娃娃的成绩为" << score2 << endl;
cout << "第三个娃娃的成绩为" << score3 << endl;
if (score1 > score2) {
if (score1 > score3) {
cout << "第一个娃娃成绩最好" << endl;
}
else if(score1 > score3) {
cout << "第三个娃娃成绩最好" << endl;
}
else {
cout << "第一个和第三个娃娃成绩相等,且都大于第二个娃娃的成绩" << endl;
}
}
else if(score1<score2) {
if (score2 > score3) {
cout << "第二个娃娃成绩最好" << endl;
}
else if(score2 < score3) {
cout << "第三个娃娃成绩最好" << endl;
}
else {
cout << "第二个和第三个娃娃成绩相等,且都大于第一个娃娃的成绩" << endl;
}
}
else {
if (score2 > score3) {
cout << "第一个和第二个娃娃成绩相等,且都大于第三个娃娃的成绩" << endl;
}
else if (score2 < score3) {
cout << "第一个和第二个娃娃成绩相等,且都大于第三个娃娃的成绩" << endl;
}
else {
cout << "三个娃娃成绩相等" << endl;
}
}
system("pause");
return 0;
}
A19三目运算符.cpp
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
//三目运算符
//创建三个变量abc
//ab作比较,将变量大的值赋值给c
int a = 10;
int b = 90;
int c = 0;
c = (a > b ? a : b);
cout << "ab中最大的值c为" << c << endl;
//在C++中三目运算符返回的是变量,可以继续赋值
(a > b ? a : b) = 100;
cout << "a=" << a << endl;
cout << "b=" << b << endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
}
A20switch语句.cpp
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
//switch语句的学习:给中考某同学的期末等级做评价
// A 顶呱呱了你,快去重高报名吧!
// B 一般的学校可以读!
// C 有学上。
// D 复读吧,,,???????????
//1、提示用户输入成绩等级
cout << "请您录入成绩等级" << endl;
//2、录入成绩等级
char score = 'A';
cin >> score;
cout << "您输入的成绩为"<<score << endl;
//3、根据用户输入的分数来提示用户最后的结果
switch (score)
{
case 'A':
cout << "顶呱呱了你,快去重高报名吧!" << endl;
break;
case 'B':
cout << "一般的学校可以读!" << endl;
break;
case 'C':
cout << "有学上。" << endl;
break;
case 'D':
cout << "复读吧,,,???????????" << endl;
break;
default:
cout << "别搞笑" << endl;
break;
}
/*
总结:
什么时候用if,什么时候用switch
if表示一个区间,switch只能表示整型或者字符型
*/
system("pause");
return 0;
}
总结
https://blog.csdn.net/hanhanwanghaha宝藏女孩的成长日记 欢迎您的关注!
欢迎关注微信公众号:宝藏女孩的成长日记 让这个可爱的宝藏女孩在努力的道路上与你一起同行! 如有转载,请注明出处(如不注明,盗者必究)、
C++大部分和C Python java的语法是差不多的,反正语言都是有贯通性的 ,但还是有一些语法上的差别感觉,
而且很多都是离散数学学过的吧, 第一天接触的都是很基础的东西 明天加大分量。终于干完咯!去看武林外传啦!!!
