目录
目录
基本线程管理
启动线程
启动线程,我这里总结了三种方法,第一种是最简单的使用匿名函数的方式,第二种使用小括号,第三种是使用大括号。
线程在创建的时候就已经启动了,不用显示启动。这里跟python不一样,python的线程我记得还得显示的启动才可以。
看代码:
#include <iostream>
#include <thread>
using namespace std;
void func2()
{
cout << " -- thread-2 cout --" << endl;
}
void func3()
{
cout << " -- thread-3 cout --" << endl;
}
int main()
{
std::thread t1([]() {
cout << " -- thread-1 cout --" << endl;
});
std::thread t2(func2);
std::thread t3{func3};
cout << "-- main cout --" << endl;
if (t1.joinable())
{
t1.join();
}
t2.join();
t3.join();
return 0;
}结果:

等待线程完成
等待线程完成就是调用jion函数。
t1.join();
t2.join();
t3.join();如果没有这三个函数,代码有可能会崩。

?因为有可能新建的线程还没有运行完,但是主函数已经运行完了,当线程函数运行完要回到主函数中,发现主函数运行完了,内存中没有主函数了,所以就崩了。有了join函数,主函数会阻塞到线程函数执行完返回主函数,主函数才会继续运行。如果不想线程函数再回到主函数,也可以把线程函数分离出去,这就下面说的在后台运行线程。或者称为守护线程。
if (t1.joinable())
{
t1.join();
}joinable()函数是检查t1是否还需要等待,用来判断是否能够调用join()或者detach(),可以返回true,不可以返回false.
注意同一个线程不能同时调用jion()和detach()--分离线程的。
因为有时候创建完线程后,主线程取干其他的了,当再调用join函数的时候要是子线程运行的快,或者代码少,子线程其实这时候都运行完了,就不需要join了,所以用joinable函数判断一下,避免子线程运行完还在join子线程。
在后台运行线程
#include <iostream>
#include <thread>
using namespace std;
void func2()
{
cout << " -- thread-2 cout --" << endl;
}
void func3()
{
cout << " -- thread-3 cout --" << endl;
}
int main()
{
std::thread t1([]() {
cout << " -- thread-1 cout --" << endl;
});
std::thread t2(func2);
std::thread t3{func3};
cout << "-- main cout --" << endl;
if (t1.joinable())
{
t1.join();
}
t2.detach();
if (t3.joinable())
{
t3.detach();
}
return 0;
}这段代码其实t2和t3是分离了的线程,意思是子线程运行完不回归主线程了,即使主线程运行完了,子线程依然还在运行也可以,也不会出现上面的错误情况。这种情况一般称子线程为守护线程。当然子线程运行完了也不会通知主线程。相当于两个线程互不干扰。
传递参数给线程函数
总结一下给线程传参的例子:
总代码:分析例子的时候一个一个一个分析:
#include <iostream>
#include <thread>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
void func2(int i)
{
std::cout << " -- thread-2 i = " << i << " cout --" << endl;
}
void func3(string& str)
{
std::cout << " -- thread-3 str = " << str << " cout --" << endl;
}
void func4(int i ,string* sstr,string& str)
{
std::cout << " -- thread-3 i = " << i << " sstr = " << *sstr << " str = " << str << " cout --" << endl;
}
int main()
{
int a = 10;
string str = "qwe";
string* pstr = &str;
const string* cpstr = &str;
string& ppstr = str;
const string& cssstr = "zxc";
std::thread t1([](const string* sstr) {
std::cout << " -- thread-1 sstr = " << *sstr << " cout --" << endl;
}, cpstr);
std::thread t2(func2,a);
std::thread t3{ func3,ref(str) };
std::thread t4([](const string& ssstr) {
std::cout << " -- thread-4 ssstr = " << ssstr << " cout --" << endl;
}, cref(cssstr));
std::thread t5{ func4,a,pstr,ref(ppstr) };
std::cout << "-- main cout --" << endl;
if (t1.joinable())
{
t1.join();
}
if (t2.joinable())
{
t2.detach();
}
if (t3.joinable())
{
t3.detach();
}
if (t4.joinable())
{
t4.join();
}
if (t5.joinable())
{
t5.join();
}
return 0;
}上面的代码是我运行过的,没问题,但是比较乱,下面一个类型一个类型的分析。
传一个参数
传值
t1是一个匿名函数传值的demo ,t2是一个普通函数传值的demo
#include <iostream>
#include <thread>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
void func(int i)
{
std::cout << " -- thread-2 i = " << i << " cout --" << endl;
}
int main()
{
int a = 10;
std::thread t1([](int a) {
std::cout << " -- thread-1 a = " << a << " cout --" << endl;
}, a);
std::thread t2(func, a);
std::cout << "-- main cout --" << endl;
if (t1.joinable())
{
t1.join();
}
if (t2.joinable())
{
t2.detach();
}
return 0;
}
传引用
强调一点,线程传引用需要ref()这个是引用或者cref()这个是const引用函数。如果传引用不用这两个函数回出错。因为thread在传递参数时,是以右值传递的。
很明显的右值引用,那么我们该如何传递一个左值呢?std::ref和std::cref很好地解决了这个问题。std::ref?可以包装按引用传递的值。std::cref?可以包装按const引用传递的值。
#include <iostream>
#include <thread>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
void func(string& str)
{
std::cout << " -- thread-2 str = " << str << " cout --" << endl;
}
int main()
{
string a = "qwe";
string& str = a;
std::thread t1([](string& str) {
std::cout << " -- thread-1 a = " << str << " cout --" << endl;
}, ref(str));
std::thread t2(func, ref(str));
std::cout << "-- main cout --" << endl;
if (t1.joinable())
{
t1.join();
}
if (t2.joinable())
{
t2.detach();
}
return 0;
}传指针
#include <iostream>
#include <thread>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
void func(string* str)
{
std::cout << " -- thread-2 str = " << *str << " cout --" << endl;
}
int main()
{
string a = "qwe";
string* str = &a;
std::thread t1([](string* str) {
std::cout << " -- thread-1 a = " << *str << " cout --" << endl;
}, str);
std::thread t2(func, str);
std::cout << "-- main cout --" << endl;
if (t1.joinable())
{
t1.join();
}
if (t2.joinable())
{
t2.detach();
}
return 0;
}
传多个参数
#include <iostream>
#include <thread>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
void func(int i, string* pstr, string& sstr)
{
std::cout << " -- thread-2 i = " << i << " pstr = " << *pstr << " sstr = " << sstr << " cout --" << endl;
}
int main()
{
int i = 10;
string a = "qwe";
string* pstr = &a;
string& sstr = a;
std::thread t1([](int i, string* pstr, string& sstr) {
std::cout << " -- thread-1 i = " << i << " pstr = " << *pstr << " sstr = " << sstr << " cout --" << endl;
}, i, pstr, ref(sstr));
std::thread t2(func, i, pstr, ref(sstr));
std::cout << "-- main cout --" << endl;
if (t1.joinable())
{
t1.join();
}
if (t2.joinable())
{
t2.detach();
}
return 0;
}转移线程的所有权
假设你想要编写一个函数,它创建一个后台运行的线程,但是向调用函数回传新线程的所有权,而非等待其完成,又或者你想要反过来做,创建一个线程,并将所有权传递到要等待它完成的函数,在任意一种情况下,你都需要将所有权从一个地方转移到另外一个地方。
#include <iostream>
#include <thread>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
void func()
{
cout << "thread1" << endl;
}
int main()
{
thread t1(func);
thread t2 = move(t1);
if (t2.joinable())
{
t2.join();
}
if (t1.joinable())
{
t1.join();
}
return 0;
}运行结果,t2拥有t1线程的所有权,而t1则指向的nullptr所以,t2.joinable()函数返回的是true,而t1.joinable()函数返回的是false,不执行t1.join()函数。因为某种意义上已经不存在t1线程了。
在运行时选择线程的数量
要运行的线程数小于硬件线程数量。超过及就超额订阅。因为上下文切切换将占用线程,会降低性能。
一般你启动的线程要比硬件线程少一个,因为已经有一个主线程了。
我现在用的CPU是4核4线程的。所以返回的值是4.

#include <iostream>
#include <thread>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
void func()
{
cout << "thread1" << endl;
}
int main()
{
thread t1(func);
thread t2 = move(t1);
if (t2.joinable())
{
t2.join();
}
if (t1.joinable())
{
t1.join();
}
int a = std::thread::hardware_concurrency();
cout << "thread num = " << a << endl;
return 0;
}结果
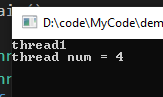
标识线程
线程标识符是std::thread::id类型的,并且有两种获取方式。其一,线程的标识符可以通过std::thread对象中通过get_id()成员函数来获得。如果std::thread对象没有相关联的执行线程,对get_id()的调用返回一个默认构造函的std::thread::id对象,表示没有线程。
另外当前线程的标识符,可以通过std::this_thread::get_id()获得,这也定义在<thread>头文件中。
std::thread::id类型的对象可以自由地复制和比较,否则他们作为标识符就没什么大用处。如果两个std::thread::id类型的对象相等,则它们代表着同一个线程,或者两者都具有“没有线程”的值。
#include <iostream>
#include <thread>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
void func()
{
cout << "thread1" << endl;
}
int main()
{
thread t1(func);
thread t2 = move(t1);
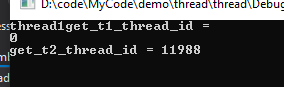
cout << "get_t1_thread_id = " << t1.get_id() << endl;
cout << "get_t2_thread_id = " << t2.get_id() << endl;
if (t2.joinable())
{
t2.join();
}
if (t1.joinable())
{
t1.join();
}
return 0;
}
#include <iostream>
#include <thread>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
void func()
{
cout << "thread1 id = " << std::this_thread::get_id() << endl;
}
int main()
{
thread t1(func);
thread t2 = move(t1);
cout << "get_t1_thread_id = " << t1.get_id() << endl;
cout << "get_t2_thread_id = " << t2.get_id() << endl;
cout << "2_get_t1_thread_id = " << std::this_thread::get_id() << endl;
if (t2.joinable())
{
t2.join();
}
if (t1.joinable())
{
t1.join();
}
return 0;
}
?总结:
td::this_thread::get_id()?是在函数体内用的得到的是当前线程的id,在哪里用就是求当前线程的id,不能求别的线程id。
cout << "get_t2_thread_id = " << t2.get_id() << endl;?这个是求t2线程的id可以在主线程求子线程的id。