arrayone.cpp?
// arrayone.cpp -- small arrays of integers
#include <iostream>
int main()
{
using namespace std;
int yams[3]; // creates array with three elements
yams[0] = 7; // assign value to first element
yams[1] = 8;
yams[2] = 6;
int yamcosts[3] = { 20, 30, 5 }; // create, initialize array
// NOTE: If your C++ compiler or translator can't initialize
// this array, use static int yamcosts[3] instead of
// int yamcosts[3]
cout << "Total yams = ";
cout << yams[0] + yams[1] + yams[2] << endl;
cout << "The package with " << yams[1] << " yams costs ";
cout << yamcosts[1] << " cents per yam.\n";
int total = yams[0] * yamcosts[0] + yams[1] * yamcosts[1];
total = total + yams[2] * yamcosts[2];
cout << "The total yam expense is " << total << " cents.\n";
cout << "\nSize of yams array = " << sizeof yams;
cout << " bytes.\n";
cout << "Size of one element = " << sizeof yams[0];
cout << " bytes.\n";
// cin.get();
return 0;
}
执行结果:
Total yams = 21
The package with 8 yams costs 30 cents per yam.
The total yam expense is 410 cents.
Size of yams array = 12 bytes.
Size of one element = 4 bytes.strings.cpp?
// strings.cpp -- storing strings in an array
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring> // for the strlen() function
int main()
{
using namespace std;
const int Size = 15;
char name1[Size]; // empty array
char name2[Size] = "C++owboy"; // initialized array
// NOTE: some implementations may require the static keyword
// to initialize the array name2
cout << "Howdy! I'm " << name2;
cout << "! What's your name?\n";
cin >> name1;
cout << "Well, " << name1 << ", your name has ";
cout << strlen(name1) << " letters and is stored\n";
cout << "in an array of " << sizeof(name1) << " bytes.\n";
cout << "Your initial is " << name1[0] << ".\n";
name2[3] = '\0'; // set to null character
cout << "Here are the first 3 characters of my name: ";
cout << name2 << endl;
// cin.get();
// cin.get();
return 0;
}
执行结果:
?
Howdy! I'm C++owboy! What's your name?
Basicman
Well, Basicman, your name has 8 letters and is stored
in an array of 15 bytes.
Your initial is B.
Here are the first 3 characters of my name: C++?instr1.cpp
// instr1.cpp -- reading more than one string
#include <iostream>
int main()
{
using namespace std;
const int ArSize = 20;
char name[ArSize];
char dessert[ArSize];
cout << "Enter your name:\n";
cin >> name;
cout << "Enter your favorite dessert:\n";
cin >> dessert;
cout << "I have some delicious " << dessert;
cout << " for you, " << name << ".\n";
// cin.get();
// cin.get();
return 0;
}
执行结果:
Enter your name:
Alistair Dreab
Enter your favorite dessert:
I have some delicious Dreab for you, Alistair.instr2.cpp?
// instr2.cpp -- reading more than one word with getline
#include <iostream>
int main()
{
using namespace std;
const int ArSize = 20;
char name[ArSize];
char dessert[ArSize];
cout << "Enter your name:\n";
cin.getline(name, ArSize); // reads through newline
cout << "Enter your favorite dessert:\n";
cin.getline(dessert, ArSize);
cout << "I have some delicious " << dessert;
cout << " for you, " << name << ".\n";
// cin.get();
return 0;
}
执行结果:
Enter your name:
Dirk Hammernose
Enter your favorite dessert:
Radish Torte
I have some delicious Radish Torte for you, Dirk Hammernose.instr3.cpp?
// instr3.cpp -- reading more than one word with get() & get()
#include <iostream>
int main()
{
using namespace std;
const int ArSize = 20;
char name[ArSize];
char dessert[ArSize];
cout << "Enter your name:\n";
cin.get(name, ArSize).get(); // read string, newline
cout << "Enter your favorite dessert:\n";
cin.get(dessert, ArSize).get();
cout << "I have some delicious " << dessert;
cout << " for you, " << name << ".\n";
// cin.get();
return 0;
}
执行结果:
Enter your name:
Mai Parfait
Enter your favorite dessert:
Chocolate Mousse
I have some delicious Chocolate Mousse for you, Mai Parfait.numstr.cpp?
// numstr.cpp -- following number input with line input
#include <iostream>
int main()
{
using namespace std;
cout << "What year was your house built?\n";
int year;
cin >> year;
// cin.get();
cout << "What is its street address?\n";
char address[80];
cin.getline(address, 80);
cout << "Year built: " << year << endl;
cout << "Address: " << address << endl;
cout << "Done!\n";
// cin.get();
return 0;
}
执行结果:
What year was your house built?
1966
What is its street address?
Year built: 1966
Address:
Done!?strtype1.cpp??
// strtype1.cpp -- using the C++ string class
#include <iostream>
#include <string> // make string class available
int main()
{
using namespace std;
char charr1[20]; // create an empty array
char charr2[20] = "jaguar"; // create an initialized array
string str1; // create an empty string object
string str2 = "panther"; // create an initialized string
cout << "Enter a kind of feline: ";
cin >> charr1;
cout << "Enter another kind of feline: ";
cin >> str1; // use cin for input
cout << "Here are some felines:\n";
cout << charr1 << " " << charr2 << " "
<< str1 << " " << str2 // use cout for output
<< endl;
cout << "The third letter in " << charr2 << " is "
<< charr2[2] << endl;
cout << "The third letter in " << str2 << " is "
<< str2[2] << endl; // use array notation
// cin.get();
// cin.get();
return 0;
}
执行结果:
Enter a kind of feline: ocelot
Enter another kind of feline: tiger
Here are some felines:
ocelot jaguar tiger panther
The third letter in jaguar is g
The third letter in panther is nstrtype2.cpp?
// strtype2.cpp -- assigning, adding, and appending
#include <iostream>
#include <string> // make string class available
int main()
{
using namespace std;
string s1 = "penguin";
string s2, s3;
cout << "You can assign one string object to another: s2 = s1\n";
s2 = s1;
cout << "s1: " << s1 << ", s2: " << s2 << endl;
cout << "You can assign a C-style string to a string object.\n";
cout << "s2 = \"buzzard\"\n";
s2 = "buzzard";
cout << "s2: " << s2 << endl;
cout << "You can concatenate strings: s3 = s1 + s2\n";
s3 = s1 + s2;
cout << "s3: " << s3 << endl;
cout << "You can append strings.\n";
s1 += s2;
cout << "s1 += s2 yields s1 = " << s1 << endl;
s2 += " for a day";
cout << "s2 += \" for a day\" yields s2 = " << s2 << endl;
//cin.get();
return 0;
}
执行结果:
You can assign one string object to another: s2 = s1
s1: penguin, s2: penguin
You can assign a C-style string to a string object.
s2 = "buzzard"
s2: buzzard
You can concatenate strings: s3 = s1 + s2
s3: penguinbuzzard
You can append strings.
s1 += s2 yields s1 = penguinbuzzard
s2 += " for a day" yields s2 = buzzard for a daystrtype3.cpp?
// strtype3.cpp -- more string class features
#include <iostream>
#include <string> // make string class available
#include <cstring> // C-style string library
#pragma warning(disable:4996)
int main()
{
using namespace std;
char charr1[20];
char charr2[20] = "jaguar";
string str1;
string str2 = "panther";
// assignment for string objects and character arrays
str1 = str2; // copy str2 to str1
strcpy(charr1, charr2); // copy charr2 to charr1
// appending for string objects and character arrays
str1 += " paste"; // add paste to end of str1
strcat(charr1, " juice"); // add juice to end of charr1
// finding the length of a string object and a C-style string
int len1 = str1.size(); // obtain length of str1
int len2 = strlen(charr1); // obtain length of charr1
cout << "The string " << str1 << " contains "
<< len1 << " characters.\n";
cout << "The string " << charr1 << " contains "
<< len2 << " characters.\n";
// cin.get();
return 0;
}
执行结果:
The string panther paste contains 13 characters.
The string jaguar juice contains 12 characters.?ERROR解决:
?? ?'strcpy': This function or variable may be unsafe. Consider using strcpy_s instead. To disable deprecation, use _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS. See online help for details.?? ?
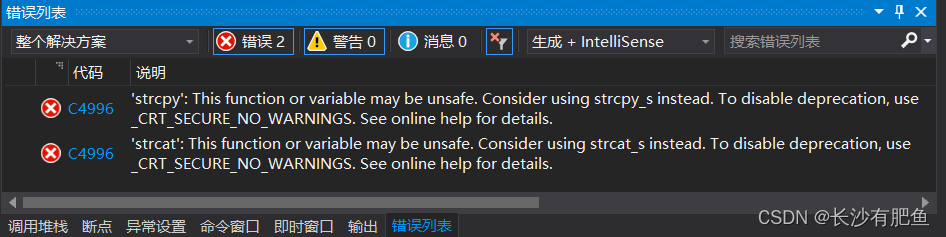
?strtype4.cpp
// strtype4.cpp -- line input
#include <iostream>
#include <string> // make string class available
#include <cstring> // C-style string library
int main()
{
using namespace std;
char charr[20];
string str;
cout << "Length of string in charr before input: "
<< strlen(charr) << endl;
cout << "Length of string in str before input: "
<< str.size() << endl;
cout << "Enter a line of text:\n";
cin.getline(charr, 20); // indicate maximum length
cout << "You entered: " << charr << endl;
cout << "Enter another line of text:\n";
getline(cin, str); // cin now an argument; no length specifier
cout << "You entered: " << str << endl;
cout << "Length of string in charr after input: "
<< strlen(charr) << endl;
cout << "Length of string in str after input: "
<< str.size() << endl;
// cin.get();
return 0;
}
执行结果:
Length of string in charr before input: 31
Length of string in str before input: 0
Enter a line of text:
peanut butter
You entered: peanut butter
Enter another line of text:
blueberry jam
You entered: blueberry jam
Length of string in charr after input: 13
Length of string in str after input: 13structur.cpp?
// structur.cpp -- a simple structure
#include <iostream>
struct inflatable // structure declaration
{
char name[20];
float volume;
double price;
};
int main()
{
using namespace std;
inflatable guest =
{
"Glorious Gloria", // name value
1.88, // volume value
29.99 // price value
}; // guest is a structure variable of type inflatable
// It's initialized to the indicated values
inflatable pal =
{
"Audacious Arthur",
3.12,
32.99
}; // pal is a second variable of type inflatable
// NOTE: some implementations require using
// static inflatable guest =
cout << "Expand your guest list with " << guest.name;
cout << " and " << pal.name << "!\n";
// pal.name is the name member of the pal variable
cout << "You can have both for $";
cout << guest.price + pal.price << "!\n";
// cin.get();
return 0;
}
执行结果:
Expand your guest list with Glorious Gloria and Audacious Arthur!
You can have both for $62.98!assgn_st.cpp?
// assgn_st.cpp -- assigning structures
#include <iostream>
struct inflatable
{
char name[20];
float volume;
double price;
};
int main()
{
using namespace std;
inflatable bouquet =
{
"sunflowers",
0.20,
12.49
};
inflatable choice;
cout << "bouquet: " << bouquet.name << " for $";
cout << bouquet.price << endl;
choice = bouquet; // assign one structure to another
cout << "choice: " << choice.name << " for $";
cout << choice.price << endl;
// cin.get();
return 0;
}
执行结果:
bouquet: sunflowers for $12.49
choice: sunflowers for $12.49arrstruc.cpp?
// arrstruc.cpp -- an array of structures
#include <iostream>
struct inflatable
{
char name[20];
float volume;
double price;
};
int main()
{
using namespace std;
inflatable guests[2] = // initializing an array of structs
{
{"Bambi", 0.5, 21.99}, // first structure in array
{"Godzilla", 2000, 565.99} // next structure in array
};
cout << "The guests " << guests[0].name << " and " << guests[1].name
<< "\nhave a combined volume of "
<< guests[0].volume + guests[1].volume << " cubic feet.\n";
// cin.get();
return 0;
}
执行结果:
The guests Bambi and Godzilla
have a combined volume of 2000.5 cubic feet.?address.cpp?
// address.cpp -- using the & operator to find addresses
#include <iostream>
int main()
{
using namespace std;
int donuts = 6;
double cups = 4.5;
cout << "donuts value = " << donuts;
cout << " and donuts address = " << &donuts << endl;
// NOTE: you may need to use unsigned (&donuts)
// and unsigned (&cups)
cout << "cups value = " << cups;
cout << " and cups address = " << &cups << endl;
// cin.get();
return 0;
}
执行结果:
donuts value = 6 and donuts address = 010FFD90
cups value = 4.5 and cups address = 010FFD80
pointer.cpp?
// pointer.cpp -- our first pointer variable
#include <iostream>
int main()
{
using namespace std;
int updates = 6; // declare a variable
int * p_updates; // declare pointer to an int
p_updates = &updates; // assign address of int to pointer
// express values two ways
cout << "Values: updates = " << updates;
cout << ", *p_updates = " << *p_updates << endl;
// express address two ways
cout << "Addresses: &updates = " << &updates;
cout << ", p_updates = " << p_updates << endl;
// use pointer to change value
*p_updates = *p_updates + 1;
cout << "Now updates = " << updates << endl;
// cin.get();
return 0;
}
? ?执行结果:
Values: updates = 6, *p_updates = 6
Addresses: &updates = 010FFE2C, p_updates = 010FFE2C
Now updates = 7init_ptr.cpp
// init_ptr.cpp -- initialize a pointer
#include <iostream>
int main()
{
using namespace std;
int higgens = 5;
int * pt = &higgens;
cout << "Value of higgens = " << higgens
<< "; Address of higgens = " << &higgens << endl;
cout << "Value of *pt = " << *pt
<< "; Value of pt = " << pt << endl;
// cin.get();
return 0;
}
执行结果:
Value of higgens = 5; Address of higgens = 004FFC38
Value of *pt = 5; Value of pt = 004FFC38use_new.cpp?
// use_new.cpp -- using the new operator
#include <iostream>
int main()
{
using namespace std;
int nights = 1001;
int * pt = new int; // allocate space for an int
*pt = 1001; // store a value there
cout << "nights value = ";
cout << nights << ": location " << &nights << endl;
cout << "int ";
cout << "value = " << *pt << ": location = " << pt << endl;
double * pd = new double; // allocate space for a double
*pd = 10000001.0; // store a double there
cout << "double ";
cout << "value = " << *pd << ": location = " << pd << endl;
cout << "location of pointer pd: " << &pd << endl;
cout << "size of pt = " << sizeof(pt);
cout << ": size of *pt = " << sizeof(*pt) << endl;
cout << "size of pd = " << sizeof pd;
cout << ": size of *pd = " << sizeof(*pd) << endl;
// cin.get();
return 0;
}
执行结果:
nights value = 1001: location 010FFA38
int value = 1001: location = 0138CEC8
double value = 1e+07: location = 01386038
location of pointer pd: 010FFA20
size of pt = 4: size of *pt = 4
size of pd = 4: size of *pd = 8arraynew.cpp?
// arraynew.cpp -- using the new operator for arrays
#include <iostream>
int main()
{
using namespace std;
double * p3 = new double [3]; // space for 3 doubles
p3[0] = 0.2; // treat p3 like an array name
p3[1] = 0.5;
p3[2] = 0.8;
cout << "p3[1] is " << p3[1] << ".\n";
p3 = p3 + 1; // increment the pointer
cout << "Now p3[0] is " << p3[0] << " and ";
cout << "p3[1] is " << p3[1] << ".\n";
p3 = p3 - 1; // point back to beginning
delete [] p3; // free the memory
// cin.get();
return 0;
}
执行结果:
p3[1] is 0.5.
Now p3[0] is 0.5 and p3[1] is 0.8.addpntrs.cpp?
// addpntrs.cpp -- pointer addition
#include <iostream>
int main()
{
using namespace std;
double wages[3] = { 10000.0, 20000.0, 30000.0 };
short stacks[3] = { 3, 2, 1 };
// Here are two ways to get the address of an array
double * pw = wages; // name of an array = address
short * ps = &stacks[0]; // or use address operator
// with array element
cout << "pw = " << pw << ", *pw = " << *pw << endl;
pw = pw + 1;
cout << "add 1 to the pw pointer:\n";
cout << "pw = " << pw << ", *pw = " << *pw << "\n\n";
cout << "ps = " << ps << ", *ps = " << *ps << endl;
ps = ps + 1;
cout << "add 1 to the ps pointer:\n";
cout << "ps = " << ps << ", *ps = " << *ps << "\n\n";
cout << "access two elements with array notation\n";
cout << "stacks[0] = " << stacks[0]
<< ", stacks[1] = " << stacks[1] << endl;
cout << "access two elements with pointer notation\n";
cout << "*stacks = " << *stacks
<< ", *(stacks + 1) = " << *(stacks + 1) << endl;
cout << sizeof(wages) << " = size of wages array\n";
cout << sizeof(pw) << " = size of pw pointer\n";
// cin.get();
return 0;
}
执行结果:
pw = 0070FDE4, *pw = 10000
add 1 to the pw pointer:
pw = 0070FDEC, *pw = 20000
ps = 0070FDD4, *ps = 3
add 1 to the ps pointer:
ps = 0070FDD6, *ps = 2
access two elements with array notation
stacks[0] = 3, stacks[1] = 2
access two elements with pointer notation
*stacks = 3, *(stacks + 1) = 2
24 = size of wages array
4 = size of pw pointerptrstr.cpp?
// ptrstr.cpp -- using pointers to strings
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring> // declare strlen(), strcpy()
#pragma warning(disable:4996)
int main()
{
using namespace std;
char animal[20] = "bear"; // animal holds bear
const char * bird = "wren"; // bird holds address of string
char * ps; // uninitialized
cout << animal << " and "; // display bear
cout << bird << "\n"; // display wren
// cout << ps << "\n"; //may display garbage, may cause a crash
cout << "Enter a kind of animal: ";
cin >> animal; // ok if input < 20 chars
// cin >> ps; Too horrible a blunder to try; ps doesn't
// point to allocated space
ps = animal; // set ps to point to string
cout << ps << "!\n"; // ok, same as using animal
cout << "Before using strcpy():\n";
cout << animal << " at " << (int *) animal << endl;
cout << ps << " at " << (int *) ps << endl;
ps = new char[strlen(animal) + 1]; // get new storage
strcpy(ps, animal); // copy string to new storage
cout << "After using strcpy():\n";
cout << animal << " at " << (int *) animal << endl;
cout << ps << " at " << (int *) ps << endl;
delete [] ps;
// cin.get();
// cin.get();
return 0;
}
执行结果:
bear and wren
Enter a kind of animal: fox
fox!
Before using strcpy():
fox at 010FF91C
fox at 010FF91C
After using strcpy():
fox at 010FF91C
fox at 01339380newstrct.cpp?
// newstrct.cpp -- using new with a structure
#include <iostream>
struct inflatable // structure definition
{
char name[20];
float volume;
double price;
};
int main()
{
using namespace std;
inflatable * ps = new inflatable; // allot memory for structure
cout << "Enter name of inflatable item: ";
cin.get(ps->name, 20); // method 1 for member access
cout << "Enter volume in cubic feet: ";
cin >> (*ps).volume; // method 2 for member access
cout << "Enter price: $";
cin >> ps->price;
cout << "Name: " << (*ps).name << endl; // method 2
cout << "Volume: " << ps->volume << " cubic feet\n"; // method 1
cout << "Price: $" << ps->price << endl; // method 1
delete ps; // free memory used by structure
// cin.get();
// cin.get();
return 0;
}
执行结果:
Enter name of inflatable item: Febulous Frodo
Enter volume in cubic feet:
7
Enter price: $27.99
Name: Febulous Frodo
Volume: 7 cubic feet
Price: $27.99delete.cpp?
// delete.cpp -- using the delete operator
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring> // or string.h
using namespace std;
char * getname(void); // function prototype
int main()
{
char * name; // create pointer but no storage
name = getname(); // assign address of string to name
cout << name << " at " << (int *)name << "\n";
delete[] name; // memory freed
name = getname(); // reuse freed memory
cout << name << " at " << (int *)name << "\n";
delete[] name; // memory freed again
// cin.get();
// cin.get();
return 0;
}
char * getname() // return pointer to new string
{
char temp[80]; // temporary storage
cout << "Enter last name: ";
cin >> temp;
char * pn = new char[strlen(temp) + 1];
strcpy(pn, temp); // copy string into smaller space
return pn; // temp lost when function ends
}
执行结果:
?
Enter name of inflatable item: Febulous Frodo
Enter volume in cubic feet:
7
Enter price: $27.99
Name: Febulous Frodo
Volume: 7 cubic feet
Price: $27.99