前言:C++不像python,创建变量的时候必须指定类型,这样才能给变量分配一个合适的内存空间。
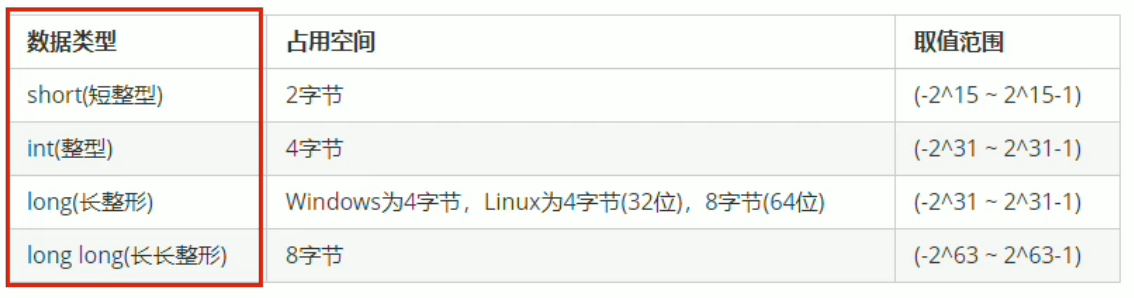
2.1 整型
作用:整型变量表示的是整型类型的数据
整型的数据类型有4种(最常用的是int),其区别在于所占内存空间不同:
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
//整型
//1.短整型
short num1 = 32768;
//2.整型
int num2 = 10;
//3.长整型
long num3 = 10;
//4.长长整型
long long num4 = 10;
cout << "num1=" << num1 << endl;
cout << "num2=" << num2 << endl;
cout << "num3=" << num3 << endl;
cout << "num4=" << num4 << endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
}
因为短整型取值范围为-32768-32767,所以注意数值溢出,当数值溢出时,取补码。
当如下定义时:
short num1 = 32768
输出为
num1=-32768
2.2 sizeof关键字
作用:利用siezeof关键字可以统计数据类型所占内存大小
语法:sizeof{ 数据类型 / 变量 }
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
//利用sizeof求出数据类型占用大小
short num1 = 10;
int num2 = 10;
long num3 = 10;
long long num4 = 10;
cout << "short占用内存空间为:" << sizeof(short) << endl;
cout << "num1占用内存空间为:" << sizeof(num1) << endl;
cout << "int占用内存空间为:" << sizeof(int) << endl;
cout << "num2占用内存空间为:" << sizeof(num2) << endl;
cout << "long占用内存空间为:" << sizeof(long) << endl;
cout << "num3占用内存空间为:" << sizeof(num3) << endl;
cout << "long long占用内存空间为:" << sizeof(long long) << endl;
cout << "num4占用内存空间为:" << sizeof(num4) << endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
}
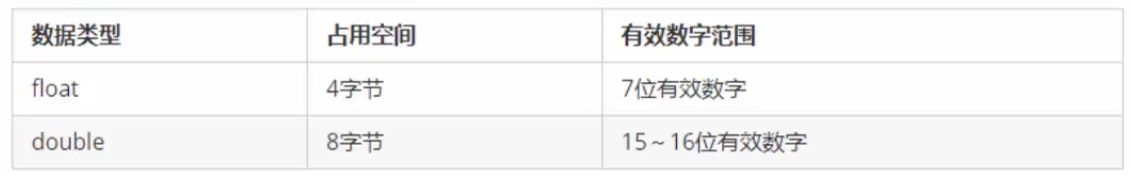
2.3 实型(浮点型)
作用:用于表示小数
浮点型变量分为两种:
单精度float, 双精度double
区别在于表示的有效数字范围不同。
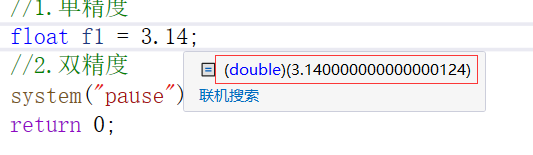
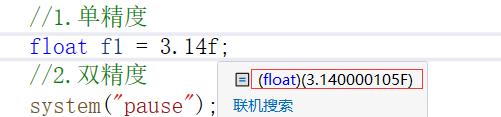
在使用时,使用方法通常为
float f1 = 3.14f
如果不加f,默认是double型变量:
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{ //默认情况下,输出一个小数,会显示最多6位有效数字
//1.单精度
float f1 = 3.1415926f;
cout << "f1=" << f1 << endl;
//2.双精度
double d1 = 3.1415926;
cout << "d1=" << d1 << endl;
//占用内存查看
cout << "float占用内存空间为:" << sizeof(float) << endl;
cout << "double占用内存空间为:" << sizeof(double) << endl;
//科学计数法
float f2 = 3e2f;
cout << "f2=" << f2 << endl;
float f3 = 3e-2f;
cout << "f3=" << f3 << endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
}
2.4 字符型
作用:字符变量用于显示单个字符
语法: char ch=‘a’;
- C和C++中字符型变量只占用1个字节。
- 字符型变量并不是把字符本身放到内存中存储,而是将对应的ASCII编码放入到存储单元。
注:用单引号不要用双引号;单引号内只能有一个字符,不可以是字符串。
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
//字符型变量创建方式
char ch = 'a';
cout << ch << endl;
//字符型变量所占内存大小
cout << "char字符型变量所占内存:" << sizeof(char) << endl;
//字符型变量常见错误
// char ch2="b";
// char ch2='abc';
//字符型变量对应ASCII编码
cout <<"字符A的ASCII码值为:"<<(int)'A' << endl;
cout << "变量ch的ASCII码值为:" << (int)ch << endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
}
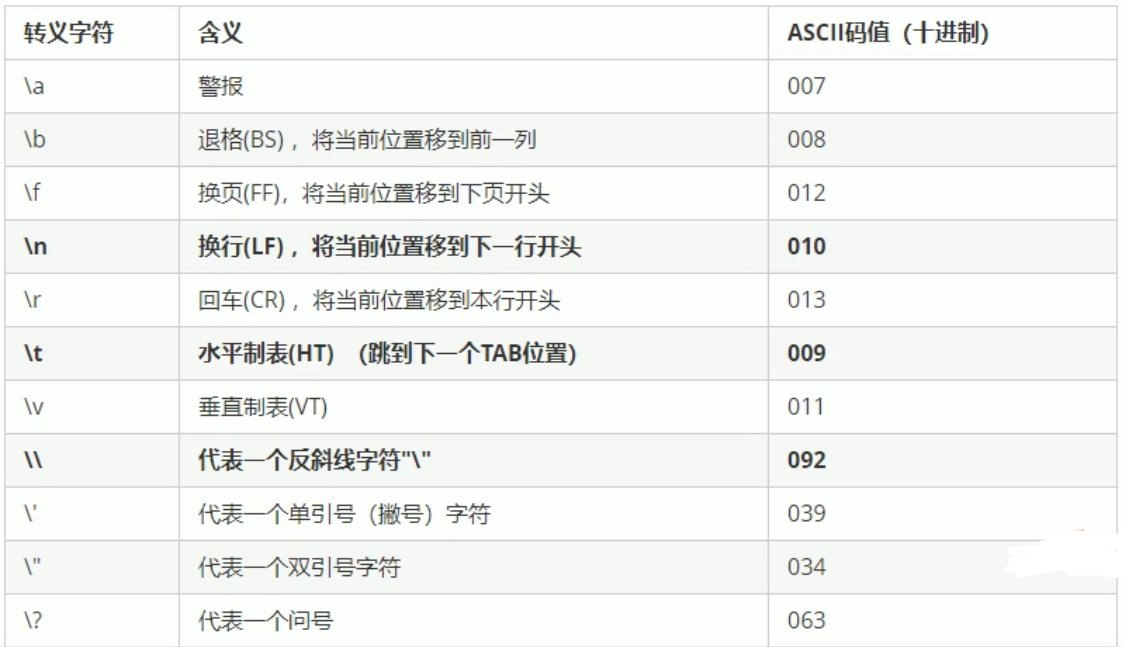
2.5 转义字符
作用:用于表示一些不能显示出来的ASCII字符
常用的就下面这些,其余可自行百度
语法:使用cout时直接加在字符串中。
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{ //换行符 \n
cout << "hello world\n"<<endl;
//反斜杠 \
cout << "\\" << endl;
/*水平制表符 \t
使用空格补齐位置,使得所占位置为8的倍数
输入正好为8个时,输出会多8个空格 */
cout << "aaaa\ttheworld" << endl;
cout << "aaa\ttheworld" << endl;
cout << "aaaaaaaa\ttheworld" << endl;
cout << "aaaaaaaaa\ttheworld" << endl;
cout << "aaaaaaaaaaa\ttheworld" << endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
}
2.6 字符串型
作用:用于表示一串字符。
两种风格
-
C风格的字符串:char 变量名[ ] = “字符串值”; ——注意加[ ],不加[ ]的时候默认的是字符。
-
C++风格字符串:string 变量名 = “字符串值”;——注意加头文件#include
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
//1.C风格字符串,注意加中括号[]
char str[] = "hello world";
cout << str << endl;
//2.C++风格字符串,注意加头文件#include<string>
string str2 = "hello world";
cout << str2 << endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
}
2.7 布尔类型 bool
作用:布尔数据类型代表真或假的值
bool类型只有两个值:
- true 真
- false 假
bool类型占一个字节
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
//1.创建bool数据类型
bool flag = true;
cout << flag << endl;
flag = false;
cout << flag << endl;
//本质是1就是真,0就是假。
//2.查看bool类型所占内存空间
cout <<"bool类型所占内存空间为:" << sizeof(bool) << endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
}
2.8 数据的输入
作用:从键盘获取数据
关键字:cin
语法:cin >> 变量
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
//1.整型
int a = 0; //尽量初始化,如果不初始化在使用或者打印它时都会报错。
cout << "请给整型变量a赋值:" << endl;
cin >> a;
cout << "整型变量a=" << a << endl;
//2.浮点型
float f = 0.f;
cout << "请给浮点型变量f赋值:" << endl;
cin >> f;
cout << "浮点型变量f=" << f << endl;
//3.字符型
char ch = ' ';
cout << "请给字符型变量ch赋值:" << endl;
cin >> ch;
cout << "字符型变量f=" << ch << endl;
//4.字符串型
string str = "abc";
cout << "请给字符串型变量str赋值:" << endl;
cin >> str;
cout << "字符串型变量str=" << str << endl;
//5.布尔型,用数字表示真假,只要输入不是0,那么就是1
bool flag = false;
cout << "请给布尔型变量flag赋值:" << endl;
cin >> flag;
cout << "布尔型变量flag=" << flag << endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
}