什么是 SPJ
SPJ 是 Special Judge 的意思。
什么时候使用 SPJ
当题目答案不止一个的时候,我们就必须使用 SPJ。
如何使用 SPJ
题目中打开 SPJ
首先,我们需要在出题的时候,增加 SPJ 选项,如下图所示。
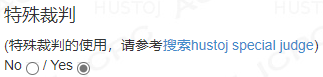
题目保存后,就显示有 SPJ,如下图所示。

编写 SPJ 程序
SPJ 程序,也就是一个标准 C 或者 C++ 程序,根据题目的要求,读取测试文件(*.in),标准输出文件(*.out),用户输出文件(user.out),进行比较。
使用带参数输入。
SPJ 模板代码
//
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
using LL=long long;
const int AC=0;
const int WA=1;
int main(int argc,char *args[]) {
ios::sync_with_stdio(0);
cin.tie(0);
cout.tie(0);
//读取三个文件,注意 arg 顺序不能变
ifstream f_in;
f_in.open(args[1]);
ifstream f_out;
f_out.open(args[2]);
ifstream f_user;
f_user.open(args[3]);
int ret=AC;
/**************自己写判题逻辑**************/
/************************************/
f_in.close();
f_out.close();
f_user.close();
return 0;
}
上传 spj.cc 到对应的题目目录
假设我们题目题号为
6387
6387
6387,那么对应的路径就是 /home/judge/data/6387。将 spj.cc 上传到对应目录,如下图。
spj.cc 文件名可以任意命名。

编译 spj 可执行文件
执行
g++ -o spj 6387_spj.cpp -std=c++14
这样我们就可以得到对应的可执行文件 spj。
修改所有者
将 spj 所有者改为 www-data。
sudo chown www-data:judge spj
权限设置好如下图。
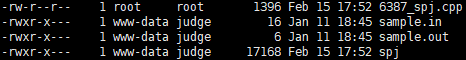
设置可执行
sudo chmod +x spj
测试
自己建立一个 user.out 文件。
./spj sample.in sample.out user.out
查看执行结果
echo $?
如下图。

显示
0
0
0 表示结果正确。显示非零一般是
1
1
1 表示结果失败。
SPJ 编写样例
SPJ 编写的难度在于题目的逻辑判断。
我们使用 MYOJ 题号
6387
6387
6387 为例子。
该题是有向图的拓扑序列,就是给一个有向图,输出对应的拓扑序列。如果是一个
D
A
G
DAG
DAG 输出任意一个合理的序列,如果不是
D
A
G
DAG
DAG 输出
?
1
-1
?1。
情景分析
不是 D A G DAG DAG
我们应该输出
?
1
-1
?1。用户可能有两种错误。
情况一:输出
?
1
?
2...
-1\ 2 ...
?1?2...。用户输出了
?
1
-1
?1,但是也输出多个数据。
情况二:输出
?
2
-2
?2。用户输出非
?
1
-1
?1。
是 D A G DAG DAG
我们读取用户的输出,然后根据拓扑排序的性质,对每个输出进行合法性分析。
用户可能有两种错误。
情况一:不是一个合法的拓扑排序。也就是输出到某个顶点
u
u
u 的时候,该顶点
u
u
u 的入度不为
0
0
0。
情况二:用户输出了比
n
n
n 更多的顶点。
样例代码
//
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
using LL=long long;
const int AC=0;
const int WA=1;
const int N=1e5+10;
LL h[N], in[N];
LL ans[N];
const int M=2e5+10;
LL e[M], ne[M], idx;
LL que[M];
LL hh, tt;
LL n;
void add(LL a, LL b) {
e[idx]=b;
ne[idx]=h[a];
h[a]=idx++;
//更新入度
in[b]++;
}
int main(int argc,char *args[]) {
#if 1
ios::sync_with_stdio(0);
cin.tie(0);
cout.tie(0);
#endif
ifstream f_in;
f_in.open(args[1]);
ifstream f_out;
f_out.open(args[2]);
ifstream f_user;
f_user.open(args[3]);
int ret=AC;
/**************自己写判题逻辑**************/
memset(h, -1, sizeof h);
LL m;
f_in>>n>>m;
for (LL i=1; i<=m; i++) {
LL a,b;
f_in>>a>>b;
add(a,b);
}
LL cnt=0;
LL u;
while (f_user>>u) {
//cout<<"u="<<u<<"\n";
++cnt;
if (cnt>n) {
return WA+6;
}
if (u>0) {
if (in[u]!=0) {
return WA+1;
}
//遍历u的所有边
for (LL i=h[u]; i!=-1; i=ne[i]) {
LL v=e[i];
in[v]--;
}
} else if (u!=-1) {
return AC+2;
}
}
if (cnt!=n) {
return WA+5;
}
/************************************/
f_in.close();
f_out.close();
f_user.close();
return 0;
}