1.各种数据类型的长度
int main(void)
{
using namespace std;
int n(3); // C++还可以这么赋值
int m{6};
int f = {8};
int n_int = INT_MAX; //声明变量同时赋值=初始化
short n_short = SHRT_MAX;
long n_long = LONG_MAX;
long long n_llong = LLONG_MAX;
cout << "n = " << n << endl;
cout << "m = " << m << endl;
cout << "f = " << f << endl;
cout << "int is " << sizeof(int) << " bytes." << endl; // sizeof是运算符不是clmits中的函数.INT_MAX是
cout << "short is " << sizeof n_short << " bytes." << endl; //函数必须带括号,sizeof(运算符)在这里可以不跟括号,但查看数据类型必须加括号
cout << "long is " << sizeof n_long << " bytes." << endl;
cout << "long long is " << sizeof n_llong << " bytes." << endl;
cout << "Maximum values: " << endl;
cout << "int: " << n_int << endl;
cout << "short: " << n_short << endl;
cout << "long: " << n_long << endl;
cout << "long long: " << n_llong << endl;
return 0;
}
2. 无符号数据类型及cout进制显示
2.1 无符号数据类型及溢出
#include <iostream>
#include <climits> //可以查看数据类型最大值最小值
int main(void)
{
using namespace std;
short sam = SHRT_MAX; //-32768-32767 (16位) longlong > long(至少32位)> int > short(至少16位)
unsigned short sue = sam; // 0-65535
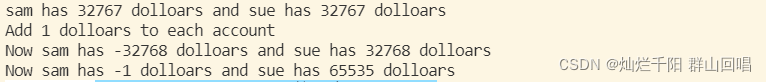
cout << "sam has " << sam << " dolloars and sue has " << sue << " dolloars" << endl;
cout << "Add 1 dolloars to each account" << endl;
sam = sam + 1;
sue = sue + 1;
cout << "Now sam has " << sam << " dolloars and sue has " << sue << " dolloars" << endl;
sam = 0;
sue = 0;
sam = sam - 1;
sue = sue - 1;
cout << "Now sam has " << sam << " dolloars and sue has " << sue << " dolloars" << endl;
return 0;
}
2.2 cout十六进制显示
#include <iostream>
int main(void)
{
using namespace std;
int cheat = 42; //十进制
int waist = 0x42; //十六进制
int inseam = 042; //八进制
cout << hex; //修改cout显示整数的方式
cout << "cheat = " << cheat << " 42 (in decimal)" << endl;
cout << "waist = " << waist << " 0x42 (in hexadicimal)" << endl;
cout << "inseam = " << inseam << " 042 (in octal)" << endl; // cout默认以十进制显示整数
return 0;
}
 2.3 cout 八进制十进制十六进制显示?
2.3 cout 八进制十进制十六进制显示?
#include <iostream>
int main(void)
{
using namespace std;
int cheat = 42;
int waist = 0x42;
int inseam = 042;
cout << "cheat = " << cheat << " 42 (in decimal)" << endl; // cout默认十进制显示
cout << hex; //修改cout为十六进制显示
cout << "waist = " << waist << " 0x42 (in hexadicimal)" << endl;
cout << oct; //修改cout为八进制显示
cout << "inseam = " << inseam << " 042 (in octal)" << endl;
return 0;
}
3.char、ASCII、\n
3.1 char类型
#include <iostream>
int main(void)
{
using namespace std;
char ch;
cout << "Enter a character:" << endl;
cin >> ch; //cin将键盘输入的M转换为77
cout << "Hello, thanks you for the " << ch << " character." << endl; //cout将77转换为M,cin和cout的行为由变量类型引导
return 0;
}
3.2 ASCII与char、cout.put()
#include <iostream>
int main()
{
using namespace std;
char ch = 'M';
int i = ch;
cout << "The ASCII code for " << ch << " is " << i << endl;
cout << "Add one to the character code:" << endl;
ch = ch + 1; //显示下一个字符
i = ch;
cout << "The ASCII code for " << ch << " is " << i << endl;
cout << "Displaying char ch using cout.put(ch)" << endl; // iostream类(数据以及操作数据的方法)的对象cin、cout 矩形(对象)平移(方法)
cout.put(ch); //用对象访问类里面的操作方法(函数)、
cout.put('!');
cout.put('A');
cout << "Done" << endl;
return 0;
}cin与cout的行为由变量引导?

 3.3 转义字符换行
3.3 转义字符换行
#include <iostream>
int main(void)
{
using namespace std;
int n = 10;
cout << "Hello world!" << endl;
cout << "Good morning!\n";//使用转义字符换行,显示字符串这种方法简单一点,\n是一个字符哦(换行符)
cout << "What's your name?" << '\n';
cout << "What's your name?" << "\n";
cout << "n = " << n << endl;
cout << "n = " << n << "\n";
return 0;
}
 4.const
4.const
#include <iostream>
int main()
{
using namespace std;
const int toes = 10; //必须在声明时赋值(之后不准修改)(对const初始化)
/*const int toes;
toes = 10;这种是错误的*/
return 0;
}5.浮点数(整数部分+小数部分)?
#include <iostream>
int main()
{
using namespace std;
cout.setf(ios_base::fixed, ios_base::floatfield);
float tub = 10.0 / 3.0;
const float million = 1.0E6;
cout << "tub = " << tub << endl; // cout默认输出小数点后六位
cout << "A million tubs = " << million * tub << endl; // float精度达不到
cout << "Ten million tubs = " << 10 * million * tub << endl; // float精度达不到
double mint = 10.0 / 3.0;
cout << "A million mint = " << million * mint << endl;
cout << "Ten million mint = " << 10 * million * mint << endl; // double精度比float高
return 0;
}6. 比较大的浮点数
#include <iostream>
int main()
{
using namespace std;
float a = 2.34E22; // 2.34e/E+22 2.34*10^22
float b = a + 1.0;
cout << "a = " << a << endl;
cout << "b = " << b << endl; //a = b
cout << "b - a = " << b - a << endl; // float位数只有前六位或前七位有效
return 0;
}
7.float与double的精度
float单精度 至少32位 double双精度 至少48位
浮点数在内存中如何存储的? ? ? ? ??int 类型 5 以0101二进制存储这个好理解
float 8.25 单精度 内存中32位(bit) ? ? ? double 64位 ? ?计算机存浮点数都是以科学计数法的方式存储的 ? IEEE标准
8.25 科学计数法 8.25 * 10^0 ? ? ? ? ?112.5 ? 科学计数法 ? 1.125 * 10^2 ? ?十进制的科学计数法 ?但是计算机只认识二进制的科学计数法
8.25 二进制的科学计数法(分成整数部分(倒序)+小数部分(正序)) ?1000.01 ? ?转换为科学计数法 为1.00001*2^3
50.25 整数部分(32+16+2) ? 110010.01 ? ? ? ? 任何一个浮点数二进制科学计数法为 ? ? 1.?????*2^x ? ?整数部分一定为1
符号占1bit ?正数为 0,负数为 1; ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?1.00001*2^3 ? ? 指数3表示小数点右移 ? ? ?
0 - 255 ? 中间127 ?0-126(负次幂) 127-255(代表正次幂)
8.25在内存中的表示: 符号位0? ? ? ? ? ?8位指数位 为127+3=130(3次幂) ? ?130 -- 10000010 ? ? ? 0(符号位) ? ?10000010(指数位) ?00001(小数位,23位) 000000000000000000(18个0)
整数部分1位,小数部分23位,共24位(二进制) ? ? 4位对应一个十进制的数 ? ?24/4=6 ? 对应十进制有效位6位 ? 二进制32位 ? 课本56页
double类型: 十进制13(52/4)位有效位 ? 二进制64位 ? 符号位1 ? ? ?指数位11 ? 小数位 52
11.17? ? 二进制? ? ? ?1011.001010111100001........(小数部分很难取整,无限长 ) ? 而float最多表示32位小数部分, 二进制超过32位就不对了,十进制超过6位就不对了
26.0在内存中如何存储的? 0100000110100000............
11010.00000000............
1.10100.......0 * 2 ^ 4
符号位:0? ??指数位:127 + 4 = 131 二进制:10000011??小数位:010000000000...........
0.75 二进制 0.110000.............
1.10*(2^-1)
符号位:0? ??指数位:127 + (-1)?= 126?二进制:01111110??小数位:1000000000...........
-2.5 二进制 10.1
-1.01*2^1
符号位:1? ??指数位:127 + 1?= 128?二进制:10000000??小数位:0100000000...........
8.float的误差
/*
* @Description:
* @Date: 2022-02-14 13:25:40
* @LastEditTime: 2022-02-14 13:56:58
* @FilePath: \C++\第三章\class6\6_1.cpp
*/
// 26.0在内存中如何存储的? 11010.00000000............ 1.10100.......0 * 2 ^ 4 符号位:0 指数位:127 + 4 = 131 二进制:10000011 小数位:010000000000...........
#include <iostream>
int main(void)
{
using namespace std;
float hats, heads;
cout.setf(ios_base::fixed, ios_base::floatfield); //可以强制打印小数点后六位(没办法四舍五入),去掉这一句就可以四舍五入,输出61.42000000.......0可以不显示
cout << "Enter a number: "; // 50.25
cin >> hats;
cout << "Enter another number: "; // 11.17
cin >> heads;
cout << "hats = " << hats << " heads = " << heads << endl;
cout << "hats + heads = " << hats + heads << endl; // 61.42 的小数部分 0.42 二进制01101...........无限,但是float二进制小数部分只有23位有效,十进制六位61.4199(近似有效)
cout << "hats - heads = " << hats - heads << endl;
cout << "hats * heads = " << hats * heads << endl;
cout << "hats / heads = " << hats / heads << endl; // folat精度不够,二进制只能显示小数点后23位,所以不准,去掉setf()可四舍五入
return 0;
}
注视掉?cout.setf()

解决办法:用double? ?可显示二进制小数点后53位,十进制13位,我们用setf()显示6位显然也是准确的

9.乘除法
#include <iostream>
int main(void)
{
using namespace std;
cout.setf(ios_base::fixed, ios_base::floatfield); //显示小数点后六位
cout << "Integer division : 9/5 = " << 9 / 5 << endl; //整数相除结果取出整数部分
cout << "Float division : 9.0/5.0 = " << 9.0 / 5.0 << endl;
cout << "Mixed division : 9.0/5 = " << 9.0 / 5 << endl; //混合类型
cout << "Mixed division : 9/5.0 = " << 9 / 5.0 << endl; //混合类型 浮点型精度高于整型,提升精度为浮点型
cout << "Double division : 1e7 / 9.0 = " << 1e7 / 9.0 << endl; //都当成double类型来处理(精度高) 一般定义浮点数用double,编译器默认当成double处理,除非你强制float
cout << "FLoat constance division : 1e7f / 9.0f = " << 1e7f / 9.0f << endl; //都当成float类型来处理
return 0;
}
 10.求模运算符
10.求模运算符
#include <iostream>
int main(void)
{
using namespace std;
const int pounds_per_stone = 14; //声明整型类型常量 14榜(pounds)=1英石(stone)
cout << "Enter your weight in pounds: ";
int lbs;
cin >> lbs;
int stone = lbs / pounds_per_stone;
int pounds = lbs % pounds_per_stone;
cout << lbs << "pounds = " << stone << " stone, " << pounds << " pounds." << endl;
return 0;
} 11.数值转换
11.数值转换
#include <iostream>
int main(void)
{
using namespace std;
cout.setf(ios_base::fixed, ios_base::floatfield);
float tree = 3;
int guess(3.9832); // C++特有赋值方式,这里取出小数的整数部分
int debt = 6.2E22; //超过了整型的取值范围,结果不确定,对于int(32位 -2^31---2^31-1)太大了
cout << "tree = " << tree << endl;
cout << "guess = " << guess << endl;
cout << "debt = " << debt << endl;
return 0;
} 12.强制类型转换?
12.强制类型转换?
#include <iostream>
int main(void)
{
using namespace std;
int auks, bats, coots;
auks = 19.99 + 11.99; //计算机用double类型相加计算再转换为整型,结果取整=31
bats = (int)19.99 + (int)11.99; // C语言格式
coots = int(19.99) + int(11.99); // C++语言格式
cout << "auks = " << auks << endl;
cout << "bats = " << auks << endl;
cout << "coots = " << auks << endl;
char ch = 'Z';
cout << "The code for " << ch << " is " << int(ch) << endl;
cout << static_cast<int>(ch) << endl; //强制类型转换
return 0;
} 13.复习题,课本67页
13.复习题,课本67页

1.
? ?int, short long, long long, unsigned/signed, char(特殊的整型)
? ?目的:根据数据运算的需要选择合适的数据类型和应用进行匹配
2.
a) short a = 80;
b) unsigned int b = 42110;
c) int max = 2147483647= 2^31-1 (32位)
unsigned int c = 3000000000; long c = 3000000000; /long long c = 3000000000;
3.
C++没有提供自动防止超出整数类型溢出的功能,需要程序员自己预估大小并选择合适数据类型,每种数据类型的宽度,C++未作规定,具体的数值由开发平台和编译器决定
4.
33:默认C++整数常量在不超出int类型范围的应用情况下,默认优先使用int,33以int类型存放
33?????L:强制使33以long类型存放整数常量,33ul? 是unigned long
5.
在基于ASCII的平台下,二者是等价的。但是char grade = 65;先将65存储为int类型然后再类型转换,将int转换为char,存储在grade中。char grade = ‘A’是直接存。
6.
1) char ch?= 88;cout << ch << endl;
2) 使用强制类型转换 cout? <<? (char)88 << endl; // cout << char(88) << endl;
7.
不同环境下long longlong不一定对应8bytes 可能4bytes
long 8 bytes? ?64位
double 类型 小数点后52位? ?
long long 64位
不同平台和编译器对应的long longlong 类型是不同的,若long长度为4bytes 则存放在double(53位)类型中不会精度丢失的现象,若long long长度为8bytes则会出现舍入误差
8.
a) 8 * 9 + 2 = 74
b) 6 * 3 / 4 = 4? 取整
c) 3 / 4 * 6 = 0??取整
d) 6.0 * 3/4 = 4.5 都按照double类型处理,提升精度
e) 15%4 = 3
9.
int sum = int(x1) + int (x2);? ?/int sum = (int)x1+ (int)x2;
int sum = int(x1 + x2); / int sum = (int)(x1 + x2)
10.
a) int
b) 强制按照float类型
c) char
d) char 32_t? 书本53页 (不常用)
e) double? ?计算机用double类型计算,精度提升,float/double float---->double
14.编程练习,课本68页
14.1

#include <iostream>
const int FOOT_TO_INCH = 12; //定义常量最好用关键字const,这里是全局的 转换因子
int main(void)
{
using namespace std;
int height;
cout << "Please enter your height int inches_";
cin >> height;
cout << "Your height convert to " << height / FOOT_TO_INCH << " foot and " << height % FOOT_TO_INCH << " inch" << endl;
return 0;
}![]()
14.2

#include <iostream>
const int FOOT_TO_INCH = 12; //常量习惯使用大写
const double INCH_TO_M = 0.0254;
const double KG_TO_POUND = 2.2;
int main(void)
{
using namespace std;
cout << "Please input your height(foot): " << endl;
int height_foot, height_inch; //英尺、英寸 1英尺=12英寸 ,也可以将变量统一声明
cin >> height_foot;
cout << "Please input your height(inch): " << endl;
cin >> height_inch;
cout << height_foot << " foot " << height_inch << " inch " << endl;
double height = (height_foot * FOOT_TO_INCH + height_inch) * INCH_TO_M; //身高可以是小数故用double
cout << "your height are: " << height << "m" << endl;
cout << "Please input your weight(pounds): ";
double weight;
cin >> weight;
weight = weight / KG_TO_POUND;
cout << "your weight are: " << weight << " kg" << endl;
double bmi = weight / (height * height);
cout << "bmi = " << bmi << endl;
return 0;
}
14.3

#include <iostream>
const int DEGREE_TO_MINUTE = 60;
const int MINUATES_TO_SECONDS = 60; //符号常量的方式
int main(void)
{
using namespace std;
int degrees, minutes, seconds;
double degree_style;
cout << "Enter a latitude in degrees, minutes, and seconds:" << endl;
cout << "First, enter the degrees: ";
cin >> degrees;
cout << "Next, enter the minutes of arc: ";
cin >> minutes;
cout << "Finally, enter the seconds of arc: ";
cin >> seconds;
degree_style = degrees + (double)minutes / DEGREE_TO_MINUTE + (double)seconds / (MINUATES_TO_SECONDS * DEGREE_TO_MINUTE); //使用强制类型转换,注意MINUATES_TO_SECONDS * DEGREE_TO_MINUTE
cout << degrees << " degrees," << minutes << " minutes," << seconds << " seconds = " << degree_style << " degrees" << endl;
return 0;
}
14.4

#include <iostream>
const int DAY_TO_HOUR = 24;
const int HOUR_TO_MINUTES = 60;
const int MINUTES_TO_SECONDS = 60;
int main(void)
{
using namespace std;
long seconds;
int days, hours, minutes, surplus_seconds, surplus_seconds_new;
cout << "Enter a number of seconds: ";
cin >> seconds;
days = seconds / (MINUTES_TO_SECONDS * HOUR_TO_MINUTES * DAY_TO_HOUR);
surplus_seconds = seconds % (MINUTES_TO_SECONDS * HOUR_TO_MINUTES * DAY_TO_HOUR);
hours = surplus_seconds / (MINUTES_TO_SECONDS * HOUR_TO_MINUTES);
surplus_seconds_new = surplus_seconds % (MINUTES_TO_SECONDS * HOUR_TO_MINUTES);
minutes = surplus_seconds_new / MINUTES_TO_SECONDS;
seconds = surplus_seconds % MINUTES_TO_SECONDS;
cout << seconds << " seconds = " << days << " days, " << hours << " hours, " << minutes << " minutes, " << seconds << " seconds " << endl;
return 0;
}![]()
14.5

#include <iostream>
int main()
{
using namespace std;
long long world_population, us_population;
double us_world_pecent;
cout << "Enter the world's population: ";
cin >> world_population;
cout << "Enter the population of the US: ";
cin >> us_population;
us_world_pecent = (double)us_population / world_population * 100;
cout << "The population of the US in " << us_world_pecent << " of the world population." << endl;
return 0;
}
14.6

#include <iostream>
int main(void)
{
using namespace std;
double distance_in_miles, fuel_in_gallon;
double distance_in_kilometer, fuel_in_litre;
double fuel_consume;
cout << "Enter the distance in miles: ";
cin >> distance_in_miles;
cout << "Enter the fuel consume in gallon: ";
cin >> fuel_in_gallon;
fuel_consume = distance_in_miles / fuel_in_gallon;
cout << "The fuel consume is " << fuel_consume << " miles/gallon." << endl;
cout << "Enter the distance in kilometer: ";
cin >> distance_in_kilometer;
cout << "Enter the fuel consume in litre: ";
cin >> fuel_in_litre;
fuel_consume = (fuel_in_litre / distance_in_kilometer) * 100;
cout << "The fuel consume is " << fuel_consume << " L/100km." << endl;
return 0;
}
14.7?

#include <iostream>
const double GALLON_TO_LITRE = 3.875;
const double HKM_TO_MILE = 62.14;
int main(void)
{
using namespace std;
double fuel_consume_eur, fuel_consume_us;
cout << "Enter the fuel consume in europe(L/100Km): "; // ? L/100km = ? * 62.14 *3.875
cin >> fuel_consume_eur;
fuel_consume_us = (GALLON_TO_LITRE * HKM_TO_MILE) / fuel_consume_eur;
cout << "The fuel consume is " << fuel_consume_us << " mile/gallon." << endl;
return 0;
}![]()

