A. Doors and Keys
判读大写字母出现前是否出现过对应的小写字母即可。
AC代码
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define ll long long
#define endl "\n"
const double eps = 1e-8;
const ll INF=0x3f3f3f3f;
const ll mod=998244353;
const int maxn = 1e7 + 5;
using namespace std;
#define PI acos(-1)
#define ld long double
int main(){
int ncase;
cin >> ncase;
while(ncase--){
string s;
cin >> s;
int r = 0, g = 0, b = 0, res = 1;
for(int i = 0; i < 6; i++){
if(s[i] == 'r') r = 1;
if(s[i] == 'g') g = 1;
if(s[i] == 'b') b = 1;
if(s[i] == 'R' && r == 0) res = 0;
if(s[i] == 'B' && b == 0) res = 0;
if(s[i] == 'G' && g == 0) res = 0;
}
if(res) cout << "Yes" << endl;
else cout << "No" << endl;
}
return 0;
}
B. Anti-Fibonacci Permutation
题意:
构造 n 个满足要求的排列(
i
≥
3
,
p
i
?
2
+
p
i
?
1
≠
p
i
i \geq 3, p_{i-2}+p_{i-1} \ne p_i
i≥3,pi?2?+pi?1??=pi?)。
构造方法:
把 2 到 n 降序放置(都降序了一定不满足斐波那契数列的性质),把 1 插入这 n-1 个数的不同位置即可。
eg:当 n = 5 时,有:
5 4 3 2 1
5 4 3 1 2
5 4 1 3 2
5 1 4 3 2
1 5 4 3 2
AC代码
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define ll long long
#define endl "\n"
const double eps = 1e-8;
const ll INF=0x3f3f3f3f;
const ll mod=998244353;
const int maxn = 1e7 + 5;
using namespace std;
#define PI acos(-1)
#define ld long double
int main(){
int ncase;
cin >> ncase;
while(ncase--){
int n;
cin >> n;
// 赛中先写了一个额外的构造
for(int i = 2; i <= n; i++) cout << i << " ";
cout << "1" << endl;
// 这个是题解里边的思想
for(int j = 1; j < n; j++){
for(int i = 1; i < n; i++){
cout << n-i+1 << " ";
if(i == j) cout << "1 ";
}
cout << endl;
}
}
return 0;
}
C. Increase Subarray Sums
题意:
给一个大小为 n 的数组,其价值为
m
a
x
(
0
,
m
a
x
(
a
i
+
0
+
…
+
a
i
+
j
)
)
(
1
≤
i
≤
i
+
j
≤
n
)
max(0, max(a_{i+0} + … + a_{i+j})) (1 \leq i \leq i+j \leq n)
max(0,max(ai+0?+…+ai+j?))(1≤i≤i+j≤n)。
对于任意的 k (
0
≤
k
≤
n
0 \leq k \leq n
0≤k≤n),选择 k 个不同的位置,给对应的元素加 x。依次输出操作后的数组的价值。
思路:
贪心,要增加的 k 个数交给的最大值所在区间即可。
定义
f
i
f_i
fi? 表示数组长度为 i 的连续子序列和的最大值,则
r
e
s
=
f
i
+
m
i
n
(
i
,
k
)
?
x
res = f_i + min(i, k) * x
res=fi?+min(i,k)?x。
AC代码
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define ll long long
#define endl "\n"
const double eps = 1e-8;
const ll INF=0x3f3f3f3f;
const ll mod=998244353;
const int maxn = 1e7 + 5;
using namespace std;
#define PI acos(-1)
#define ld long double
ll a[5005], f[5005];
int main(){
int ncase;
cin >> ncase;
while(ncase--){
ll n, x;
cin >> n >> x;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++) cin >> a[i], f[i] = -1e9;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++){
ll sum = 0;
for(int j = i; j <= n; j++){
sum += a[j];
f[j-i+1] = max(sum, f[j-i+1]);
}
}
for(int i = 0; i <= n; i++){
ll res = 0;
for(int j = 1; j <= n; j++){
res = max(res, f[j] + min(j, i) * x);
}
cout << res << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
return 0;
}
D. Cross Coloring
题意:
给一个 n * m 的网格进行 q 次染色。
第 i 次染色将在 k 中颜色中任选一种,染给第
x
i
x_i
xi? 行和第
y
i
y_i
yi?列。
问最后将得到多少种染色结果。
思路:
q 次操作结束后,没有被完全覆盖的操作对应的格子的颜色可以在 k 个颜色中任选。统计有几次操作不会被完全覆盖即可。
后边的操作一定不会被前边的操作覆盖。倒着统计 q 次颜色,对于第 i 次染色的行或列没有被颜色时,本次操作染色的格子将不会被完全覆盖。注意,当行或列都被染过后就不需要统计。
在 2 * 10 的格子中,最后两次操作分别染第一行和第二行,这时全部的行都被染色,前 q-2 次染色结果一定被覆盖。
设:没有被完全覆盖的操作数为
c
n
t
,
r
e
s
=
k
c
n
t
cnt, res = k ^{cnt}
cnt,res=kcnt
ps:注意初始化,我这里处理了一下初始化的代码(109ms),不处理初始化的代码会TLE

AC代码
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define ll long long
#define endl "\n"
const double eps = 1e-8;
const ll INF=0x3f3f3f3f;
const ll mod=998244353;
const int maxn = 1e6 + 5;
using namespace std;
#define PI acos(-1)
#define ld long double
#define IOS cin.tie(0), ios::sync_with_stdio(false)
template<class T>inline void read(T &res)
{
char c;T flag=1;
while((c=getchar())<'0'||c>'9')if(c=='-')flag=-1;res=c-'0';
while((c=getchar())>='0'&&c<='9')res=res*10+c-'0';res*=flag;
}
ll h[maxn], w[maxn], x[maxn], y[maxn];
ll qpow(ll a, ll b){
ll res = 1;
while(b){
if(b & 1) res *= a;
res %= mod;
a = a * a % mod;
b >>= 1;
}
return res;
}
int main(){
IOS;
int ncase;
read(ncase);
for(int _ = 1; _ <= ncase; _++){
ll n, m, k, q;
read(n); read(m); read(k); read(q);
int tmp = max(n, m);
for(int i = 1; i <= q; i++) read(x[i]), read(y[i]);
int cnt = 0;
int a = 0, b = 0;
for(int i = q; i >= 1; i--){
if(w[x[i]] != _ || h[y[i]] != _) cnt++;
if(w[x[i]] != _) w[x[i]] = _, a++;
if(h[y[i]] != _) h[y[i]] = _, b++;
if(a == n || b == m) break;
}
cout << qpow(k, cnt) << endl;
}
return 0;
}
E. Expand the Path
题意:
有一个 n * n 的网格和一个机器人,机器人在 (1,1)并且只会根据指令移动。
- 指令D:x++
- 指令R:y++
给出一个指令串s(只饱含D 和 R),在机器人移动前可以对指令串进行若干次操作(选择一个指令,进行复制。即 D 变为DD,R 变为 RR),问机器人可以走过的格子数是多少。
分析:
对于10*10的网格和指令RDRRDR。
我们来分析机器人每一步可能到达的位置:
- 位置一:机器人最终落脚的位置为原指令停止位置(x, y) 到 (n, n) 所表示的矩形中.
- 位置二:此处是由指令D 到达,复制指令D,将可能走过如图所示的格子(注意位置四,并不一定每次都会走到头)。
- 位置三:此处是由指令R 到达,复制指令R,将可能走过如图所示的格子。
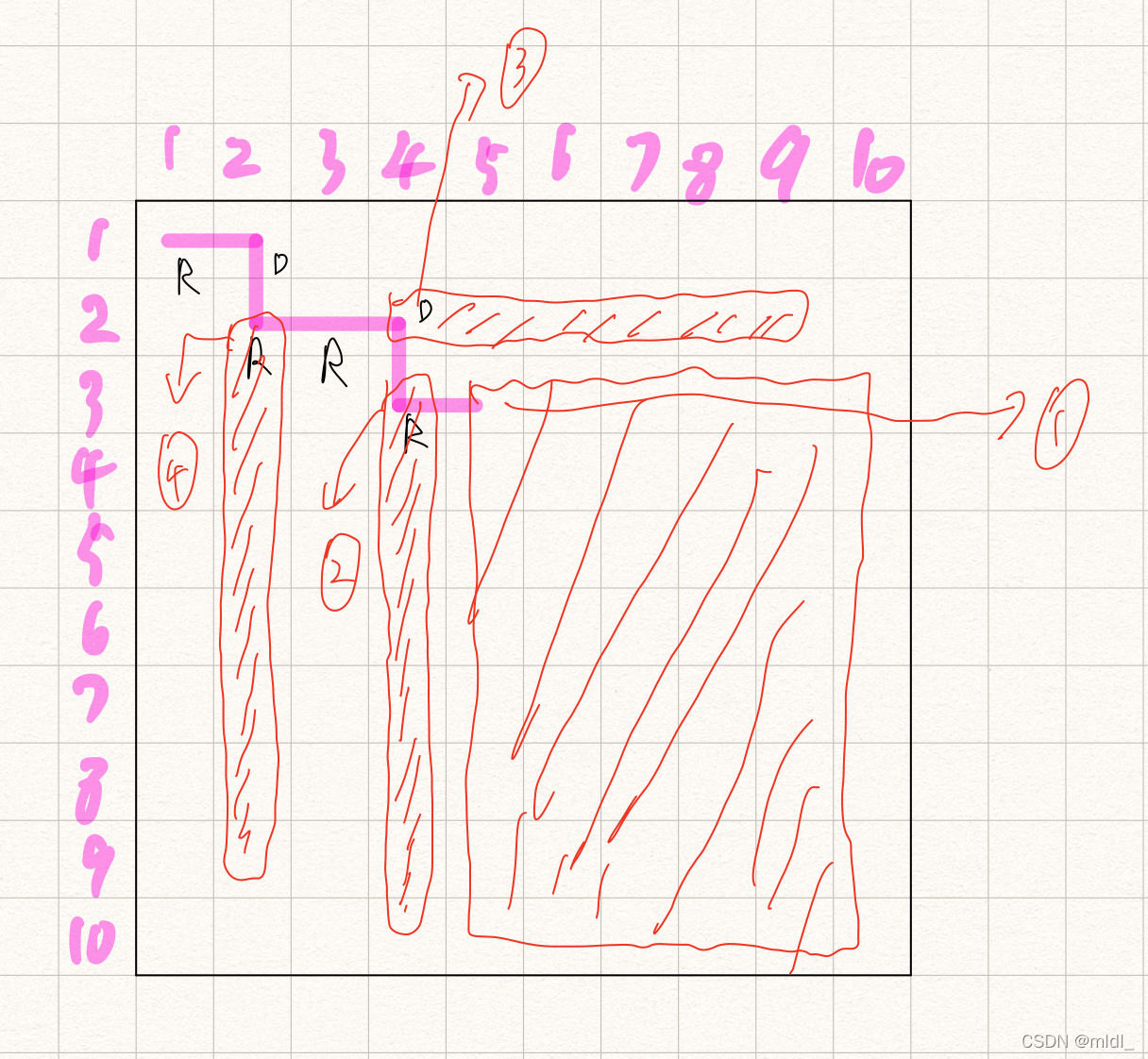
注意,上述的规律成立的前提是此处可以通过一个指令R或者一个指令D复制过来,因此有两种不适用于的情况:
- 只有指令D或只有指令R的情况。
- 机器人在第一行,不能通过复制指令D 实现往下走
- 机器人在第一列,不能通过复制指令R 实现往右走
代码里边有解释,可以看一下代码解释。
AC代码
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define ll long long
#define endl "\n"
const double eps = 1e-8;
const ll INF=0x3f3f3f3f;
const ll mod=998244353;
const int maxn = 2e5 + 5;
using namespace std;
#define PI acos(-1)
#define ld long double
#define IOS cin.tie(0), ios::sync_with_stdio(false)
int main(){
IOS;
int ncase;
cin >> ncase;
while(ncase--){
ll n;
cin >> n;
string s;
cin >> s;
ll x = 1, y = 1;
for(auto c : s){
if(c == 'R') y++;
else x++;
}
if(x == 1 || y == 1){ // 只有D或R
cout << n << endl;
continue;
}
ll res = (n - x + 1) * (n - y + 1) + 1; // 结尾
ll r = 0, d = 0;
for(int i = s.size()-1; i > 0; i--){
char c = s[i];
if(c == 'R'){
y--; r++;
// x != 1 说明前边还有指令D,可以通过复制指令D,让当前格向下移动
// d 表示已经出现了几次下移(不能走出去),x 是现在在哪
if(x != 1) res += (n - d) - x + 1;
else res++;
}
else{
x--; d++;
// y != 1 说明前边还有指令R,可以通过复制指令R,让当前格向右移动
if(y != 1) res += (n - r) - y + 1;
else res++;
}
}
cout << res << endl;
}
return 0;
}