前言
C++类的成员变量是否含有“指针类型”直接决定了“Big Five”函数(就是标题中的5个函数)的编写!有无指针类型”成员变量造成Big Five函数实现完全不一样,因此我们需要分别讨论这两种情形。
注:C++11标准才引入移动语义,即才有本文讨论的“移动构造函数”。
注:很多同仁将类的“拷贝赋值函数”称为“赋值构造函数”,个人认为不恰当!故坚持使用“拷贝赋值函数”。
正文
成员变量无“指针类型”
class Human
{
public:
Human();
Human(const Human& human);
Human& operator=(const Human& human);
Human(const Human&& human); // 没有指针类型的成员属性,移动构造函数存在的意义不大。
~Human(); // 成员变量无指针类型,可以不用自行编写析构函数,使用编译器默认提供的即可。
private:
int age;
string name;
};成员变量有“指针类型”
class Human
{
public:
Human();
Human(const Human& human);
Human& operator=(const Human& human);
Human(const Human&& human);
~Human(); // 成员变量有“指针类型”,必须自行实现析构函数,用于释放内存
private:
int age;
string* name;
};1.构造函数(Constructor)
成员变量无“指针类型”:?
Human::Human() : age(0), name()
{
}成员变量有“指针类型”:
Human::Human():age(0), name(nullptr)
{
}2.拷贝构造函数(Copy Constructor)
成员变量无“指针类型”: (可以使用编译器默认提供的版本)
Human::Human(const Human& human)
{
this->age = human.age; // 或,age = human.age;
}成员变量有“指针类型”:
Human::Human(const Human& human)
{
this->age = human.age;
this->name = new string(*human.name);
}3.拷贝赋值函数(拷贝赋值运算符, Copy assignment)
当一个类的对象向该类的另一个对象赋值时,就会用到该类的拷贝赋值函数。当没有重载拷贝赋值函数(赋值运算符)时,通过默认拷贝赋值函数来进行赋值操作。关于“拷贝赋值函数”的使用方法及注意事项参看《【C++】类的拷贝赋值函数》
成员变量无“指针类型”:?(可以使用编译器默认提供的版本)
Human& operator=(const Human& rhs) {
if (this == &rhs) // 避免自我赋值
return *this;
this->age = rhs.age; // 注意:同class的不同对象间互为友元(friend),因此能直接访问rhs对象的private成员age。
return *this;
}成员变量有“指针类型”:
Human& operator=(const Human& rhs) {
if (this == &rhs) // 避免自我赋值
return *this;
this->age = rhs.age; // 注意:同class的不同对象间互为友元(friend),因此能直接访问rhs对象的private成员age。
delete this->name; // 必须先释放内存,否则会引发内存泄漏
this->name = new string(*rhs.name);
return *this;
}4.移动构造函数(Move Constructor, C++11引入)
成员变量无“指针类型”:?(可以使用编译器默认提供的版本)
此种情况下移动构造函数存在的意义不大!
Human::Human(const Human&& human) // human在函数体中没有被修改,因此可以加const限制
{
this->age = human.age;
this->name = human.name;
}成员变量有“指针类型”:
避免成员指针指向的内存重复释放和申请才是移动构造函数存在的最大价值!
Human::Human(Human&& human) // human在函数体中被修改,因此不可以加const限制
{
this->age = human.age;
this->name = human.name;
human.name = nullptr; // 必须置空,否则human.name被析构函数释放,this->name也被释放!
}5.移动赋值函数(Move assignment)
?成员变量无“指针类型”:
成员变量有“指针类型”:
Human& Human::operator=(Human&& human)
{
cout << "Move assignment" << endl;
if (&human == this)
return *this;
this->age = human.age;
delete this->name;
this->name = human.name;
human.name = nullptr;
}6.析构函数(Destructor)
成员变量无“指针类型”:?(可以使用编译器默认提供的版本)
Human::~Human()
{
}成员变量有“指针类型”:
Human::~Human()
{
delete name; // 无需判断name是否为nullptr,因为delete操作符会执行判断(实为编译器会执行加判断是否为空代码)
}完整例子
注:2种情况下的代码差别请注意标有“差异”的代码注释处。?
?1.类成员属性没有指针类型
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
class Human
{
public:
Human();
Human(string name, int age);
Human(const Human& human);
Human& operator=(const Human& human);
Human(const Human&& human);
~Human(); // 成员变量无指针类型,可以不用自行编写析构函数,使用编译器默认提供的即可。
private:
int age;
string name;
};
Human::Human() : age(0), name()
{
cout << "Constructor" << endl;
}
Human::Human(string name, int age) : age(age), name(name)
{
cout << "Constructor with parameters" << endl;
}
Human::Human(const Human& human)
{
cout << "Copy constructor" << endl;
this->age = human.age;
this->name = human.name;
}
Human& Human::operator= (const Human& human)
{
cout << "Copy assignment" << endl;
if (&human == this)
return *this;
this->age = human.age;
this->name = human.name;
}
Human::Human(const Human&& human)
{
this->age = human.age;
this->name = human.name;
cout << "Move constructor" << endl;
}
Human::~Human()
{
cout << "Destructor" << endl;
}
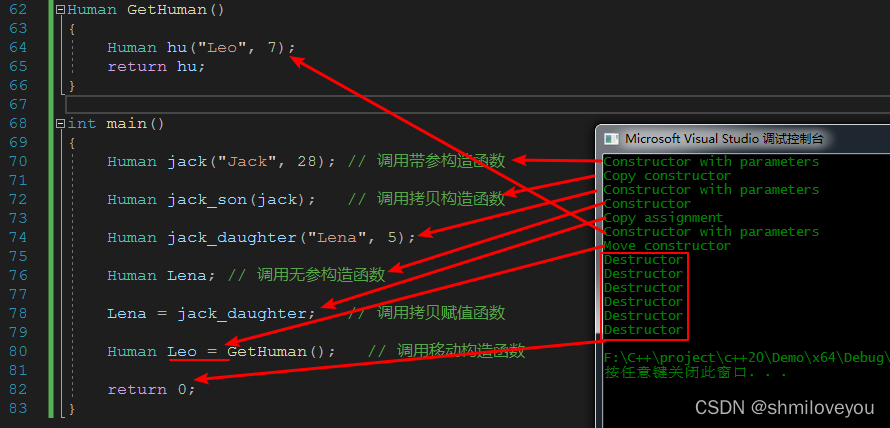
Human GetHuman()
{
Human hu("Leo", 7);
return hu;
}
int main()
{
Human jack("Jack", 28); // 调用带参构造函数
Human jack_son(jack); // 调用拷贝构造函数
Human jack_daughter("Lena", 5);
Human Lena; // 调用无参构造函数
Lena = jack_daughter; // 调用拷贝赋值函数
Human Leo = GetHuman(); // 调用移动构造函数
return 0;
}
?2.类成员属性有指针类型?
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
class Human
{
public:
Human();
Human(string *name, int age);
Human(const Human& human);
Human& operator=(const Human& human);
Human& operator=(Human&& human);
Human(Human&& human); // 差异,无const限制
~Human(); // 成员变量无指针类型,可以不用自行编写析构函数,使用编译器默认提供的即可。
private:
int age;
string *name; // 差异
};
Human::Human() : age(0), name(nullptr)
{
cout << "Constructor" << endl;
}
Human::Human(string *name, int age) : age(age), name(name)
{
cout << "Constructor with parameters" << endl;
}
Human::Human(const Human& human)
{
cout << "Copy constructor" << endl;
this->age = human.age;
this->name = new string(*human.name); // 差异
}
Human& Human::operator= (const Human& human)
{
cout << "Copy assignment" << endl;
if (&human == this)
return *this;
this->age = human.age;
delete this->name; // 差异; 必须先释放内存,否则会引发内存泄漏
this->name = new string(*human.name); // 差异
}
Human& Human::operator=(Human&& human)
{
cout << "Move assignment" << endl;
if (&human == this)
return *this;
this->age = human.age;
delete this->name;
this->name = human.name;
human.name = nullptr;
}
Human::Human(Human&& human)
{
this->age = human.age;
this->name = human.name;
human.name = nullptr; // 差异; 必须置空,否则human.name被析构函数释放,this->name也被释放!
cout << "Move constructor" << endl;
}
Human::~Human()
{
delete name; // 差异
cout << "Destructor" << endl;
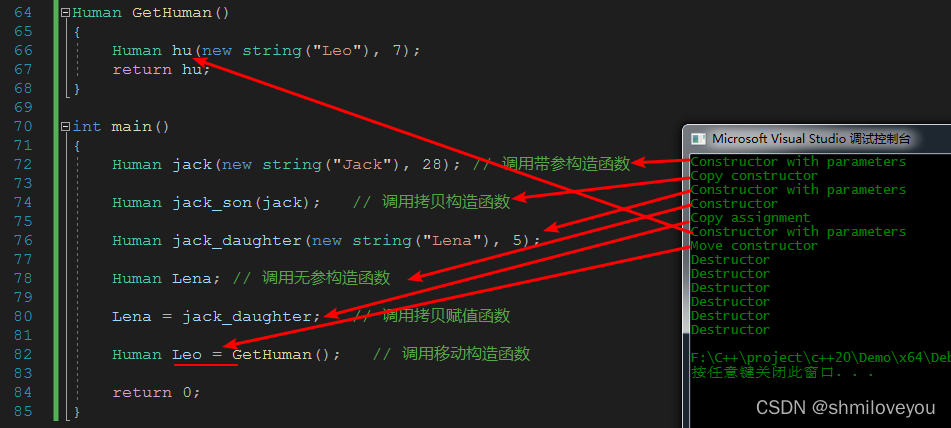
}测试1:?
Human GetHuman()
{
Human hu(new string("Leo"), 7);
return hu;
}
int main()
{
// 测试1
Human jack(new string("Jack"), 28); // 调用带参构造函数
Human jack_son(jack); // 调用拷贝构造函数
Human jack_daughter(new string("Lena"), 5);
Human Lena; // 调用无参构造函数
Lena = jack_daughter; // 调用拷贝赋值函数
Human Leo = GetHuman(); // 调用移动构造函数
return 0;
}
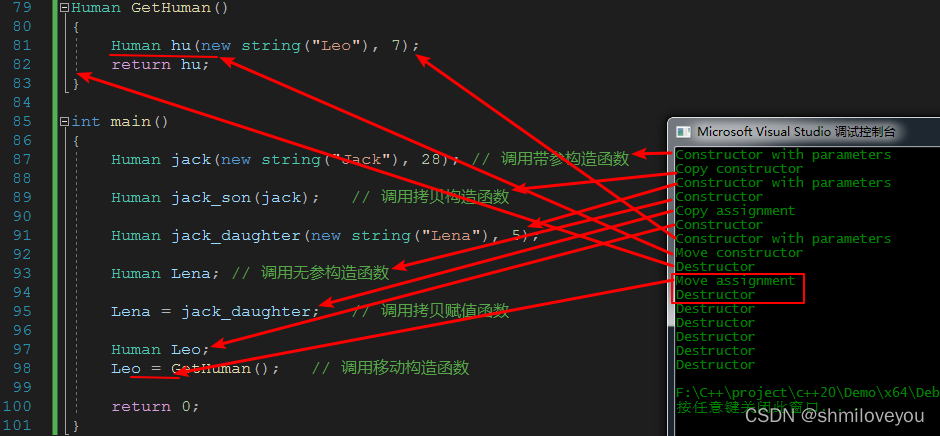
测试2:
Human GetHuman()
{
Human hu(new string("Leo"), 7);
return hu;
}
int main()
{
Human jack(new string("Jack"), 28); // 调用带参构造函数
Human jack_son(jack); // 调用拷贝构造函数
Human jack_daughter(new string("Lena"), 5);
Human Lena; // 调用无参构造函数
Lena = jack_daughter; // 调用拷贝赋值函数
Human Leo;
Leo = GetHuman(); // 调用移动构造函数和移动赋值函数
return 0;
}
?