STL之string的使用
文章目录
string 简介
- string是表示字符串的字符串类
- 该类的接口与常规容器的接口基本相同,再添加了一些专门用来操作string的常规操作。
- string在底层实际是:basic_string模板类的别名,typedef basic_string<char, char_traits, allocator>
string; - 不能操作多字节或者变长字符的序列。
string的基本使用
string的构造
| 函数名称 | 功能说明 |
|---|---|
| string() | 构造空string类对象,即空字符串 |
| string(const char*s) | 用C-string来构造string类对象 |
| string(size_t n,char c) | string类对象中包括n个字符c |
| string(const string&s) | 拷贝构造函数 |
//空构造
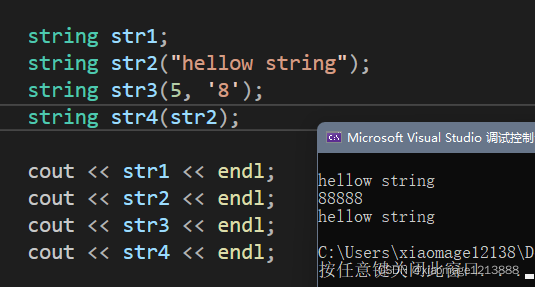
string str1;
//用字符串来构造
string str2("hellow string");
//构造n个字符
string str3(5, '8');
//拷贝构造
string str4(str2);
string的容量操作
| 函数名称 | 功能说明 |
|---|---|
| size() | 返回字符串有效字符长度 |
| length() | 返回字符串有效字符长度 |
| capacity() | 返回总空间大小 |
| empty() | 检测字符串是否为空串,为空返回true,不为空则返回false |
| clear() | 清空字符串 |
| reserve() | 为字符串预留空间(也就是改变capacity的大小) |
| resize() | 将有效字符的个数改成n个(改变size的大小,多出的部分可以用函数的第二个参数进行自定义) |
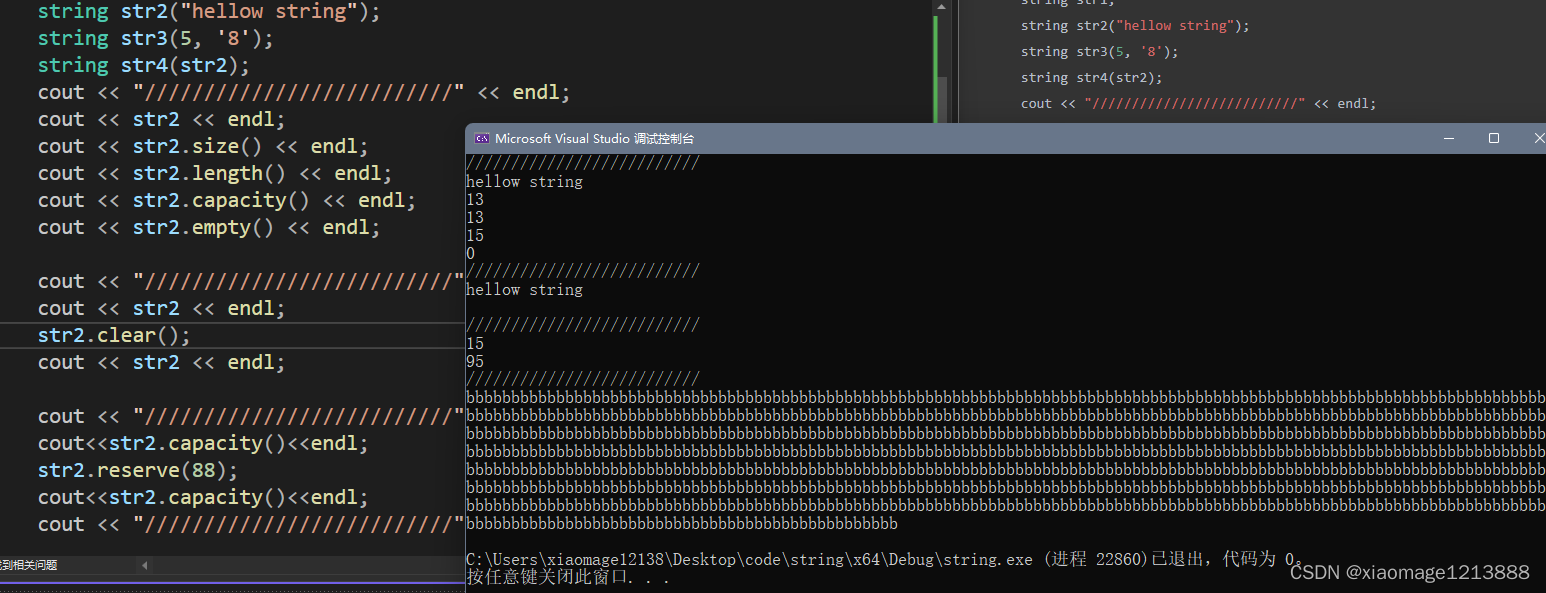
int main() {
string str1;
string str2("hellow string");
string str3(5, '8');
string str4(str2);
cout << "//" << endl;
//打印字符串/有效字符大小/容量/是否为空
cout << str2 << endl;
cout << str2.size() << endl;
cout << str2.length() << endl;
cout << str2.capacity() << endl;
cout << str2.empty() << endl;
cout << "//" << endl;
//打印clear前后字符串的区别
cout << str2 << endl;
str2.clear();
cout << str2 << endl;
cout << "//" << endl;
//打印预留空间前后str2的容量变化
cout<<str2.capacity()<<endl;
str2.reserve(88);
cout<<str2.capacity()<<endl;
cout << "//" << endl;
//打印改变有效字符后字符串的变化
str2.resize(888,'b');
cout << str2 << endl;
return 0;
}
注意:
- size()与length()方法底层实现原理完全相同,引入size()的原因是为了与其他容器的接口保持一致,一般情况下基本都是用size()。
- clear()只是将string中有效字符清空,不改变底层空间大小。
- resize(size_t n) 与 resize(size_t n, char c)都是将字符串中有效字符个数改变到n个,不同的是当字
符个数增多时:resize(n)用0来填充多出的元素空间,resize(size_t n, char c)用字符c来填充多出的
元素空间。resize在改变元素个数时,如果是将元素个数增多,可能会改变底层容量的大
小,如果是将元素个数减少,底层空间总大小不变。 - reserve(size_t res_arg=0):为string预留空间,不改变有效元素个数,当reserve的参数小于string的底层空间总大小时,reserver不会改变容量大小。
string类对象访问及遍历操作
| 函数名称 | 功能说明 |
|---|---|
| operator[] () | 返回pos位置的字符,const string类对象调用 |
| begin()/end() | begin获取第一个字符的迭代器/end获取最后一个字符下一个位置的迭代器 |
| rbegin()/rend() | rbegin获取倒数第一个字符的迭代器/rend获取第一个字符上一个位置的迭代器 |
| 范围for | C++11支持更简洁的范围for的新遍历方式 |
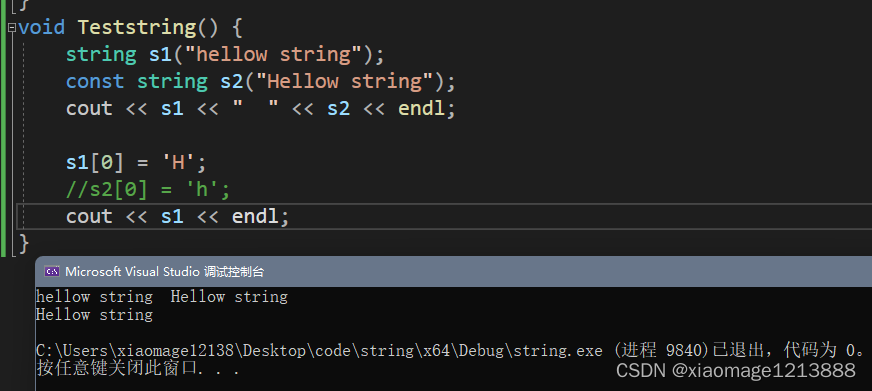
void Teststring() {
string s1("hellow string");
const string s2("Hellow string");
cout << s1 << " " << s2 << endl;
s1[0] = 'H';
//s2[0] = 'h';//const类型对象不能修改
cout << s1 << endl;
}
string的三种遍历操作
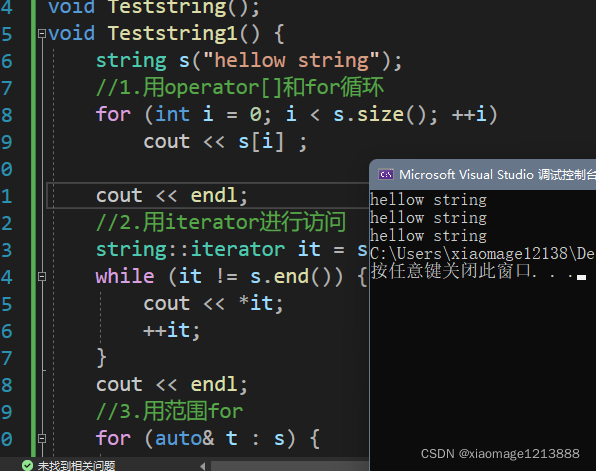
void Teststring1() {
string s("hellow string");
//1.用operator[]和for循环
for (int i = 0; i < s.size(); ++i)
cout << s[i] ;
cout << endl;
//2.用iterator进行访问
string::iterator it = s.begin();
while (it != s.end()) {
cout << *it;
++it;
}
cout << endl;
//3.用范围for
for (auto& t : s) {
cout << t;
}
}
string类对象的修改操作
| 函数名称 | 功能说明 |
|---|---|
| push_back() | 在字符串后插字符 |
| append() | 字符串后追加字符 |
| operator+=() | 字符串后追加字符串 |
| c_str | 返回c格式字符串 |
| find+npos | 从字符串pos位置开始往后找字符c,返回该字符在字符串中的位置 |
| rfind() | 从字符串pos位置开始往前找字符c,返回该字符在字符串中的位置 |
| substr() | 在str中从pos位置开始,截取n个字符,然后将其返回 |
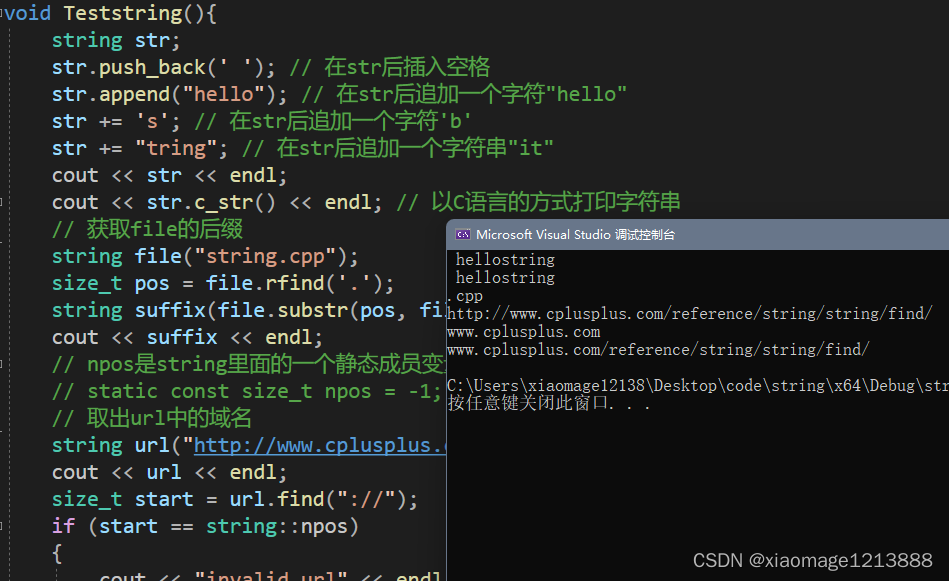
void Teststring(){
string str;
str.push_back(' '); // 在str后插入空格
str.append("hello"); // 在str后追加一个字符"hello"
str += 's'; // 在str后追加一个字符'b'
str += "tring"; // 在str后追加一个字符串"it"
cout << str << endl;
cout << str.c_str() << endl; // 以C语言的方式打印字符串
// 获取file的后缀
string file("string.cpp");
size_t pos = file.rfind('.');
string suffix(file.substr(pos, file.size() - pos));
cout << suffix << endl;
// npos是string里面的一个静态成员变量
// static const size_t npos = -1;
// 取出url中的域名
string url("http://www.cplusplus.com/reference/string/string/find/");
cout << url << endl;
size_t start = url.find("://");
if (start == string::npos)
{
cout << "invalid url" << endl;
return;
}
start += 3;
size_t finish = url.find('/', start);
string address = url.substr(start, finish - start);
cout << address << endl;
// 删除url的协议前缀
pos = url.find("://");
url.erase(0, pos + 3);
cout << url << endl;
}
string类非成员函数
| 函数 | 功能说明 |
|---|---|
| operator+() | 尽量少用,因为传值返回,导致深拷贝效率低 |
| operator>>() | 输入运算符重载 |
| operator<<() | 输出运算符重载 |
| getline() | 获取一行字符串 |
| relational operators | 大小比较 |
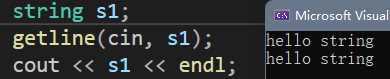
string s ;
//这样输入只能输入不带空格的字符串,如果中间有空格隔开,那么只能输出空格之前的字符串
cin >> s;
cout << s << endl;

string s1;
getline(cin, s1);
cout << s1 << endl;