Placement new is a variation new operator in C++. Normal new operator does two things : (1) Allocates memory (2) Constructs an object in allocated memory.?
Placement new allows us to separate above two things. In placement new, we can pass a preallocated memory and construct an object in the passed memory.?
?
new vs?placement new
- Normal new allocates memory in heap and constructs objects there whereas using placement new, object construction can be done at known address.
- With normal new, it is not known that, at what address or memory location it’s pointing to, whereas the address or memory location that it’s pointing is known while using placement new.
- The deallocation is done using delete operation when allocation is done by new but there is no placement delete, but if it is needed one can write it with the help of destructor
Syntax:?
?
new (address) (type) initializer As we can see, we can specify an address where we want a new object of given type to be constructed.
When to prefer using placement new?
As it allows to construct an object on memory that is already allocated, it is required for optimizations as?it is faster not to re-allocate all the time. There may be cases when it is required to re-construct an object multiple times so, placement new operator might be more efficient in these cases.
|
|
Output:?
?
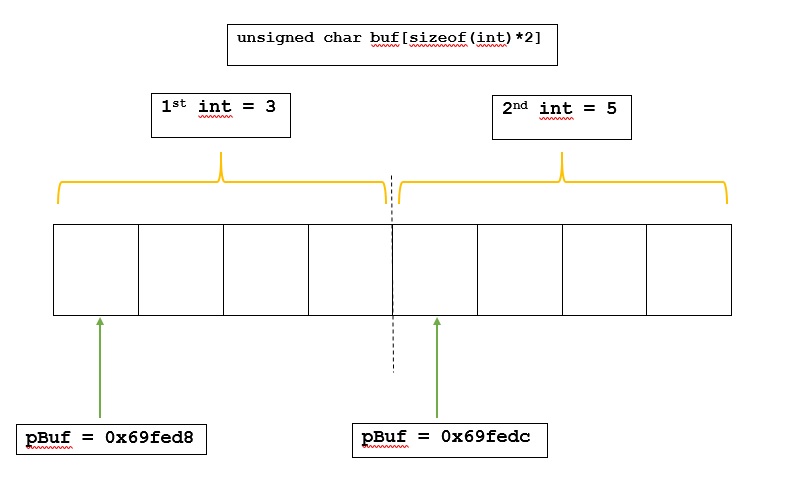
Buff Addr Int Addr 0x69fed8 0x69fed8 0x69fedc 0x69fedc ------------------------------ 1st Int 2nd Int 3 5
The diagram below pictorially shows what is actually happening in above C++ program.
?
Below is a another simple implementation in C++ to illustrate the use of placement new in C++ :
|
|
Output:?
?
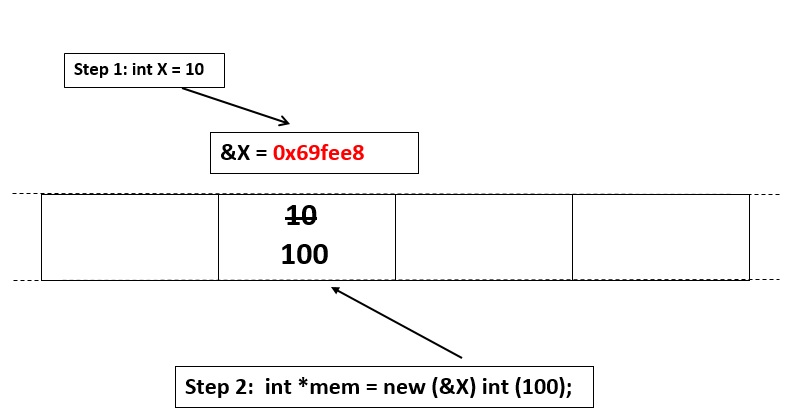
Before placement new : X : 10 &X : 0x69fee8 After placement new : X : 100 mem : 0x69fee8 &X : 0x69fee8
Explanation: Here, it is clear that a new value of x is assigned at the address of x with the help of placement new operator. This is clear by the fact that the value of &X and mem is equal.?
The diagram below pictorially shows what is actually happening in above C++ program.
?
How to delete the memory allocated by placement new ?
The operator delete can only delete the storage created in heap, so when placement new is used delete operator cannot be used to delete the storage. In the case of memory allocation using placement new operator , since it is created in stack the compiler knows when to delete it and it will handle deallocation of the memory automatically. If required, one can write it with the help of destructor as shown below.
|
|
Output:?
?
Constructor : (4.2, 5.3) Constructor : (0, 0) Constructor : (0, 0) Constructor : (2.6, 3.9) |4.2 +j5.3 | = 6.7624 |0 +j0 | = 0 |0 +j0 | = 0 |2.6 +j3.9 | = 4.68722 Destructor : (4.2, 5.3) Destructor : (0, 0) Destructor : (0, 0) Destructor : (2.6, 3.9)
Explanation: Here the destructor is explicitly called because here it cannot be packaged within the delete operator because delete will need to release the memory which you do not have here and it cannot be implicit as it is a dynamic process which we want to manage yourself.?
?
When will?placement new operator show segmentation fault?
The placement new operator should be used with care. The address which is passed can be a reference or a pointer pointing to a valid memory location. It may?show an error when the address passed is :?
?
- A pointer such as NULL pointer.
- A pointer that is not pointing to any location.
- It cannot be a void pointer unless it points to some location.
|
|
Segmentation fault
Advantages of placement new operator over new operator
- The address of memory allocation is known before hand.
- Useful when building a memory pool, a garbage collector or simply when performance and exception safety are paramount.
- There’s no danger of allocation failure since the memory has already been allocated, and constructing an object on a pre-allocated buffer takes less time.
- This feature becomes useful while working in an environment with limited resources.
This article is contributed by MAZHAR IMAM KHAN. If you like GeeksforGeeks and would like to contribute, you can also write an article using write.geeksforgeeks.org or mail your article to review-team@geeksforgeeks.org. See your article appearing on the GeeksforGeeks main page and help other Geeks.
Please write comments if you find anything incorrect, or you want to share more information about the topic discussed above.
?
Want to learn from the best curated videos and practice problems, check out the C++ Foundation Course for Basic to Advanced C++ and C++ STL Course for foundation plus STL.? To complete your preparation from learning a language to DS Algo and many more,? please refer Complete Interview Preparation Course.