互斥锁pthread_mutex_t
在linux中,互斥锁的出现是为了限制多个线程同时对临界资源区进行访问。通过互斥锁对临界资源区进行保护,只有拥有锁的线程才可以访问临界区,没有的锁的线程如果要访问临界区则需要等到锁的释放后,竞争到锁的拥有权后,才能进入临界区。 但这里会出现一个问题:单纯加锁也会导致一直是一个线程访问临界资源的问题,个别线程竞争力很强,可能会一直占据锁的使用权,导致其他线程的无法进入临界区。 这就需要引入另一个机制 条件变量
条件变量pthread_cond_t
条件变量被用于线程间的同步,条件变量通过允许线程阻塞和等待另一个线程发送信号来弥补互斥锁的不足,条件变量是利用线程间共享的全局变量,进行同步的一种机制,主要包括两个动作:一个线程等待"条件变量的条件成立"而挂起;另一个线程使"条件成立"(给出条件成立信号)。条件变量的使用总是和一个互斥锁结合在一起,用来防止互斥锁引起的线程竞争的现象
条件变量的使用
主要的应用函数
/*pthread_cond_t cond; 变量cond只有两种取值1、0。*/
int pthread_cond_init(pthread_cond_t *restrict cond, const pthread_condattr_t *restrict attr); //功能:初始化一个条件变量
int pthread_cond_wait(pthread_cond_t *restrict cond, pthread_mutex_t *restrict mutex);
/*
功能:阻塞等待一个条件变量
函数作用:
阻塞等待条件变量cond(参1)满足
释放已掌握的互斥锁(解锁互斥量)相当于pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex);
*/
int pthread_cond_timedwait(pthread_cond_t *restrict cond, pthread_mutex_t *restrict mutex, const struct timespec *restrict abstime); //功能:限时等待一个条件变量
int pthread_cond_signal(pthread_cond_t *cond); //功能:唤醒至少一个阻塞在条件变量上的线程
int pthread_cond_broadcast(pthread_cond_t *cond); //功能:唤醒全部阻塞在条件变量上的线程
int pthread_cond_destroy(pthread_cond_t *cond); // 功能:销毁一个条件变量
互斥锁的使用
主要应用函数
//锁的初始化
int pthread_mutex_init(pthread_mutex_t *mutex, const pthread_mutexattr_t * attr)
//锁操作
int pthread_mutex_lock(pthread_mutex_t *mutex)
int pthread_mutex_unlock(pthread_mutex_t *mutex)
int pthread_mutex_trylock(pthread_mutex_t *mutex)
int pthread_mutex_trylock(pthread_mutex_t *mutex) /*语义与pthread_mutex_lock()类似,不同的是在锁已经被占据时返回EBUSY而不是挂起等待*/
//锁的释放
int pthread_mutex_destory(pthread_mutex_t *mutex)
条件变量和互斥锁的应用实例
#include<stdio.h>
#include<pthread.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
pthread_mutex_t lock;
pthread_cond_t cond;
void*Run(void*arg)
{
//pthread_detach(pthread_self());
while(1){
char*Str=(char*)arg;
// printf("%s is Run\n" , Str);
pthread_mutex_lock( &lock ) ;
pthread_cond_wait(&cond,&lock);//默认不满足条件,线程会阻塞等待条件变量就绪
printf("%s is open\n" , Str) ;
pthread_mutex_unlock( &lock ) ;
sleep(4) ;
}
}
int main()
{
pthread_mutex_init(&lock,NULL);//初始化锁
pthread_cond_init(&cond,NULL);//初始化条件变量
pthread_t tid1,tid2;
pthread_create(&tid1,NULL,Run,(void*)"tid1");
pthread_create(&tid2,NULL,Run,(void*)"tid2");
while(1)
{
pthread_cond_signal(&cond);//唤醒线程
sleep(2) ;
}
pthread_mutex_destroy(&lock);
pthread_cond_destroy(&cond);
return 0;
}
二个线程进入临界区时调用pthread_cond_wait被阻塞,按照被阻塞的先后顺序放入等待队列中,当主函数执行pthread_cond_signal,条件就绪。条件变量中的等待队列中队列头的线程被唤醒打印,之后循环又调用了pthread_cond_wait阻塞。这个线程被挂到条件变量等待队列末尾。
主线程又一次执行pthread_cond_signal,条件又一次就绪。这时条件变量中的等待队列中队列头的线程被唤醒打印。从而实现了线程的有序访问临界资源。实验结果如下
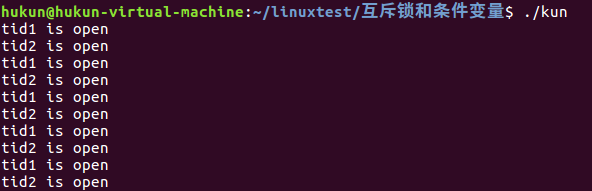
线程又一次执行pthread_cond_signal,条件又一次就绪。这时条件变量中的等待队列中队列头的线程被唤醒打印。从而实现了线程的有序访问临界资源。实验结果如下