a drawing program
- data
- center
- operatons
- render
- move
- resize
Inheritance in C++
- can define one class in term of another
- can capture the notion that
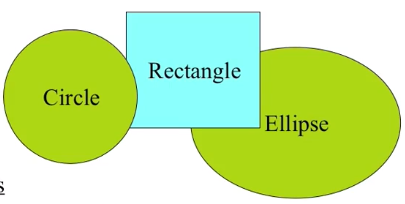
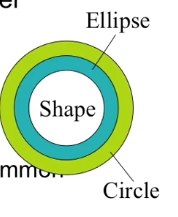
- an ellipse is a shape
- a circle is a special kind of ellipse
- a rectangle is a different shape
- circles,ellipses,and rectangles share common
- attributes
- services
- circles,ellipses,and rectangles are not identical(同一的)
conceptual(概念) model
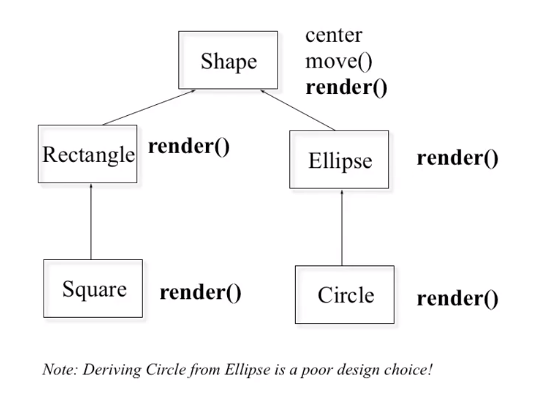
?render 不同
shape
-
define the general properties of shape
class XYPos{...};//x,y point class shape{ public: Shape(); virtual ~Shape(); virtual void render(); // virtual 子类和父类的同名函数联系在一起 void move(const XYPos&); virtual void resize(); protected: XYPos center; }
add new shapes
class Ellipse:public Shape{
public:
Ellipse(float maj,float mint);
virtual void render();//will define own virtual不加也是virtual的,好习惯,不用看shape
protected:
float major_axis,minor_axis;
};
class Circls:public Ellipse{
public:
Circle(float radius):Ellispse(radius,radius){}
virtual void render();
};
Example
void render(Shape* p){ // 通用函数
p->render(); //calls correct render function for given shape
}
// p的静态类型是 shape 的指针;p的动态类型指的是 p当时指的对象的类型是什么。如果render是virtual 是动态绑定,取决于render;不是virtual是静态绑定。
void func(){
Ellipse ell(10,20);
ell.render();
Circle circ(40);
circ.render();
render(&ell); // virtual作用:运行时候确定调用哪个函数,这里调用 ell 的函数
reder(&circ);
}
p是多态的,p指的谁,变成谁的形态。
poly多morphism形态 (多态性)
-
upcast: take an object of the derived class as an object of base one
- Ellipse can be treaded as a Shape
upcast: 把子类对象当作父类看待
-
dynamic binging(动态绑定)
- binding:which function to be called
- static binding:call the function as the code
- dynamic binding:call the function of the object
- binding:which function to be called
绑定:调用函数时候应调用哪个函数,叫做绑定
静态绑定:调的函数在编译时候确定
动态绑定:运行时候才知道调用哪个函数,根据指针所指的对象决定