C语言中操作字符串的函数
一、函数表
| 函数名 | 函数 | 功能 |
|---|---|---|
| strlen | size_t strlen(const char* s); | 返回字符串 s 的长度(不包括结尾的0) |
| strcmp | int strcmp(const char* s1, const char* s2); | 比较两个字符串,返回:如果 s1 == s2,返回 0;如果 s1<s2 则返回小于 0 (如 -1);如果 s1>s2 则返回大于 0 (如 1) |
| strcpy | char* strcpy(char* restrict dst, const char* reestrict src) | 把字符串 src 复制拷贝到字符串 dst,返回 dst,restrict 表明 src 和 dst 不能重叠 |
| strcat | char* stract(char* restrict s1, const char* reestrict s2) | 把字符串 s2 拷贝到字符串 s1 的后面,连接成一个长的字符串,返回 s1 |
| strchr | char* strchr(const char* s, int c) | 返回一个指针,指向字符串 s1 中字符 ch 的第一次出现的位置 |
| strstr | char* strstr(const char* s1, const char* s2) | 返回一个指针,指向字符串 s1 中字符串 s2 的第一次出现的位置 |
二、strlen
实例
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
//自定义 strlen()函数
size_t mylen(const char* s)
{
int idx = 0;
while (s[idx] != '\0') {
idx++;
}
return idx;
}
int main()
{
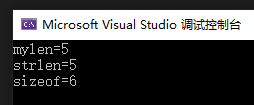
char a[] = "Hello";
printf("mylen=%llu\n", mylen(a));
printf("strlen=%llu\n", strlen(a));// {'H', 'e', 'l', 'l', 'o'};
printf("sizeof=%llu\n", sizeof(a));// {'H', 'e', 'l', 'l', 'o','\0'};
return 0;
}
运行结果
三、strcmp
实例
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
//自定义 strcmp()函数
int mycmp1(const char* s1, const char* s2)
{
int idx = 0;
while (1) {
if (s1[idx] != s2[idx]) {
break;
}
else if (s1[idx] == '\0') {
break;
}
idx++;
}
return s1[idx] - s2[idx];
}
int mycmp2(const char* s1, const char* s2)
{
int idx = 0;
while (s1[idx] == s2[idx] && s1[idx] != 0) {
idx++;
}
return s1[idx] - s2[idx];
}
int mycmp3(const char* s1, const char* s2)
{
int idx = 0;
while (*s1 == *s2 && *s1 != 0) {
s1++;
s2++;
}
return *s1 - *s2;
}
int main()
{
char s1[] = "abc";
char s2[] = "abc";
char s3[] = "abc ";
char s4[] = "bbc";
char s5[] = "Abc";
printf("mycmp1=%d\n", mycmp1(s1, s2));
printf("mycmp2=%d\n", mycmp2(s1, s3));
printf("mycmp3=%d\n", mycmp3(s1, s4));
printf("mycmp3=%d\n", mycmp3(s1, s5));
printf("strlen=%d\n", strcmp(s1, s2));
printf("strlen=%d\n", strcmp(s1, s3));
printf("strlen=%d\n", strcmp(s1, s4));
printf("strlen=%d\n", strcmp(s1, s5));
return 0;
}
运行结果
VS编辑器的原因,库函数 strlen 的结果只有 0, -1, 1 三种结果。

四、strcpy
// 复制一个字符串
char* dst = (char*)malloc(strlen(src)+1);
strcpy(dst,src);
// strlen 查 src 大小 +1 (+1 的原因是加上字符串最后的 ‘\0’, strlen 读取的长度不包括 ‘\0’), 再 malloc 分配空间给 dst, 这样 dst 的空间正好等于 src, 然后再执行 strcpy 复制操作
实例
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
//自定义 strcpy()函数
char* mycpy1(char* dst, const char* src)
{
int idx = 0;
while (src[idx] != '\0') {
dst[idx] = src[idx];
idx++;
}
dst[idx] = '\0';
return dst;
}
char* mycpy2(char* dst, const char* src)
{
char* ret = dst;
while (*src) {
*dst++ = *src++;
}
*dst = '\0';
return ret;
}
int main()
{
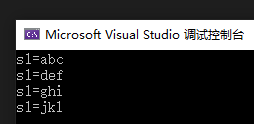
char s1[] = "abc";
char s2[] = "def";
char s3[] = "ghi";
char s4[] = "jkl";
printf("s1=%s\n", s1);
strcpy(s1, s2);
printf("s1=%s\n", s1);
mycpy1(s1, s3);
printf("s1=%s\n", s1);
mycpy2(s1, s4);
printf("s1=%s\n", s1);
return 0;
}
运行结果
五、stract
实例
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
int main()
{
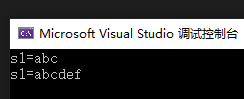
char s1[10] = "abc";
char s2[] = "def";
printf("s1=%s\n", s1);
strcat(s1, s2);
printf("s1=%s\n", s1);
return 0;
}
运行结果
六、strchr
实例
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
int main()
{
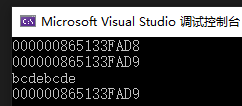
char s1[10] = "abcdebcde";
printf("%p\n", s1);
printf("%p\n", s1 + 1);
char* p = strchr(s1, 'b');
printf("%s\n", p);
printf("%p\n", p);
return 0;
}
运行结果