学习方法:见专栏的第一篇
温馨提示:-----只看剥离的精华------,主要内容只是为了大致的了解这章的内容,方便以后查找。希望可以抛砖引玉
主要的内容
● 函数——strlen();
● 关键字——const;
● 字符串;
● 如何创建、存储字符串;
● 如何使用strlen()函数获取字符串的长度;
● 用C预处理器指令#define和ANSIC的const修饰符创建符号常量。
本章重点介绍输入和输出。与程序交互和使用字符串可以编写个性化的程序,本章将详细介绍C语言的两个输入/输出函数:scanf()和printf()。学会使用这两个函数,不仅能与用户交互,还可根据个人喜好和任务要求格式化输出。最后,简要介绍一个重要的工具——C预处理器指令,并学习如何定义、使用符号常量。
剥离的精华
1.#define?
#define指令可以让你需要的值都可以完整地保存在程序中,不受其他变量的影响。并且方便修改
#include<stdio.h> #include <string.h> #define density 62.4 int main(void) { float weight,volume; int size,letters; char name[40]; printf(" hi! what is your name \n"); scanf("%s",name); printf("%s,what is your weights\n",name); scanf("%f",&weight); size=sizeof(name); letters=strlen(name); volume=weight/density; printf("well, %s,your volume is %2.2f cubic feet \n",name,volume); printf("also,your first name has %d letters.\n",letters); printf("and we have %d bytes to store it \n",size); return 0; }#define指令还可定义字符和字符串常量。前者使用单引号,后者使用双引号。//个人感觉没用,我自己再写一个输出函数不香吗?
#include <stdio.h> #define praise "you are an extraorfinary being" int main(void) { char name[40]; printf("what is your name?\n"); scanf("%s",name); printf("hello %s,%s\n",name,praise); printf("hello %s,you are an extraorfinary being",name); //不能说毫无关联,只能说一模一样 return 0; }2.printf和scanf的一些小技巧
? ?2.1scanf()函数在%s的情况下,scanf()只会读取字符串中的一个单词,而不是一整句。C语言还有其他的输入函数(如,fgets()),用于读取一般字符串
#include <stdio.h> #define praise "you are an extraorfinary being" int main(void) { char name[40]; printf("what is your name?\n");//当你没有连续的输入你的名字之后,看一看结果。eg //jikl和j ikl scanf("%s",name); printf("hello %s,%s\n",name,praise); printf("hello %s,you are an extraorfinary being",name); //不能说毫无关联,只能说一模一样 return 0; }2.2printf()和scanf()函数的*运算符
printf()函数如果你不想预先指定字段宽度,希望通过程序来指定,那么可以用*修饰符代替字段宽度。但还是要用一个参数告诉函数,字段宽度应该是多少。也就是说,如果转换说明是%*d,那么参数列表中应包含*和d对应的值。这个技巧也可用于浮点值指定精度和字段宽度
#include <stdio.h> int main(void) { int width ,precision; int number =256; double weight =242.5; printf("输入第一数字的宽度\n"); scanf("%d",&width); printf("the number is %*d",width,number); printf("请输入浮点数的宽度及其精度\n"); scanf("%d,%d",&width,&precision); printf("weight=%*.*f\n",width,precision,weight); printf("done!\n"); return 0; }scanf()函数与printf()函数则不一样,scanf()函数的*省去对应的对象,直接最后一个输入,即可。
#include <stdio.h>//scanf()函数的*的作用 int main(void) { int n; printf("请输入三个整数\n"); scanf("%*d %*d %d",&n); printf("最后一个整数是%d\n",n); return 0; }2.3printf()函数的数据的美观,就是当想数据更加美观的话,可以考虑尽量大的字符宽度。但是一点就是这几个数据的宽度足够大的同时并且相等。
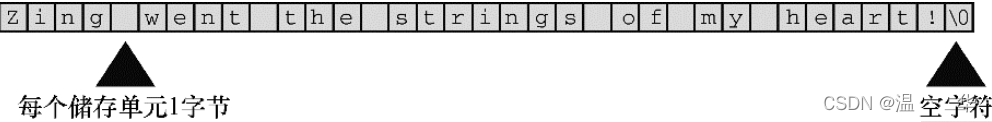
#include <stdio.h> #include <string.h> int main(void) { int num1; int num2; char name1[20]; char name2[20]; printf("请输入姓\n"); scanf("%s",name1); printf("请输入名\n"); scanf("%s",name2); num1=strlen(name1); num2=strlen(name2); printf("%9s %9s\n",name1,name2); printf("%9d %9d\n",num1,num2); printf("%-9s %-9s\n",name1,name2);//瞧我这思维转换 printf("%-9d %-9d\n",num1,num2); return 0; }3.字符串都被存储在char类型的数组中,看一张图足矣
4.strlen()函数和sizeof()函数
strlen()函数针对字符串的长度,sizeof()函数计算其类型的大小。
#include <stdio.h> #include <string.h> #define praise "you are an extraorfinary being." int main(void) { char name[40]; printf("what is your name?\n"); scanf("%s",name); printf("hello %s,%s\n",name,praise); printf("your name of %zd letter occupies %zd memory cells.\n",strlen(name),sizeof(name)); printf("the phrase of praise has %zd letters\n",strlen(praise)); printf("and occupies %zd memeory cells\n",sizeof praise);//最后两行函数的比较体现出来了字符串的最后一位是多少 return 0; }5.多行书写代码的时候的两种简单的方法
就改善上面的程序来体现。
#include <stdio.h> #include <string.h> #define praise "you are an extraorfinary being." int main(void) { char name[40]; printf("what is your name?\n"); scanf("%s",name); printf("hello %s,%s\n",name,praise); printf("your name of %zd letter occupies\ %zd memory cells.\n",strlen(name),sizeof(name));//这是断行 书写规则就是/加enter printf("the phrase of praise" " has %zd letters\n",strlen(praise));//这是另一种断行方式。 书写规则就是""+""字符串的相加 printf("and occupies %zd memeory cells\n",sizeof praise);//最后两行函数的比较体现出来了字符串的最后一位是多少 return 0; }
代码练习
编写一个程序,提示用户输入名和姓,然后以“名,姓”的格式打印出来。
#include <stdio.h> int main(void) { char name[20]; char fir[20]; printf("请输入姓\n"); scanf("%s",name); printf("请输入名\n"); scanf("%s",fir); printf("下面是得到的结果\n"); printf("%s,%s\n",name,fir); return 0; }6.编写一个程序,先提示用户输入名,然后提示用户输入姓。在一行打印用户输入的名和姓,下一行分别打印名和姓的字母数。字母数要与相应名和姓的结尾对齐,如下所示接下来,再打印相同的信息,但是字母个数与相应名和姓的开头对齐,如下所
#include <stdio.h> #include <string.h> int main(void) { int num1; int num2; char name1[20]; char name2[20]; printf("请输入姓\n"); scanf("%s",name1); printf("请输入名\n"); scanf("%s",name2); num1=strlen(name1); num2=strlen(name2); printf("%9s %9s\n",name1,name2); printf("%9d %9d\n",num1,num2); printf("%-9s %-9s\n",name1,name2);//瞧我这思维转换 printf("%-9d %-9d\n",num1,num2); return 0; }