OOP
拷贝构造函数
A(const A & a);
- const:防止修改
- &:不仅为了节省空间,更为了防止递归!这里是值传递。
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class CExample
{
int m_nTest;
public:
CExample(int x):m_nTest(x) //带参数构造函数 使用了初始化表的形式
{
cout << "constructor with argument/n";
}
CExample(const CExample & ex) //拷贝构造函数 不写时有默认拷贝构造函数
{
m_nTest = ex.m_nTest;
cout << "copy constructor/n";
}
CExample& operator = (const CExample &ex)//赋值函数(赋值运算符重载) 传值
{
cout << "assignment operator/n";
m_nTest = ex.m_nTest;
return *this;
}
void myTestFunc(CExample ex)
{
}
};
int main()
{
CExample aaa(2); //constructor with argument
CExample bbb(3); //constructor with argument
bbb = aaa; //assignment operator 因为bbb已经实例化,不需要构造,只调用赋值函数
CExample ccc = aaa; //copy constructor 但是ccc还没有实例化,因此调用的是拷贝构造函数
bbb.myTestFunc(aaa); //是aaa作为参数传递给bbb.myTestFunc(CExample ex), 即CExample ex = aaa;和第四个一致,所以还是拷贝构造函数
return 0;
}
假如拷贝构造函数参数不是引用类型的话, 则是值传递。由bbb.myTestFunc可知递归的后果。
使得 ccc.CExample(aaa)变成aaa传值给ccc.CExample(CExample ex),即CExample ex =
aaa,因为 ex 没有被初始化, 所以 CExample ex = aaa 继续调用拷贝构造函数,接下来的是构造ex,也就是
ex.CExample(aaa),必然又会有aaa传给CExample(CExample ex), 即 CExample ex =
aaa;那么又会触发拷贝构造函数,就会永远递归下去。
什么时候需要自定义拷贝构造函数?深拷贝。
浅拷贝与深拷贝
浅拷贝案例:
如果析构掉s1,abcd也被析构,s2变成悬挂指针(指向的地址不知道存了什么东西),很不好。
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
using namespace std;
class String{
private:
char *p;
public:
String(char *str){//这是自定义构造函数
p=new char[strlen(str)+1];
strcpy(p,str);
}
~String(){
delete[] p;
}
};
int main() {
String s1("abcd");
String s2 = s1;//没有自定义拷贝构造函数,所以默认拷贝构造函数会将指针指向同一空间
//浅拷贝:s2和s1这两个指针指向堆里的同一空间,再销毁对象时,两个对象的析构函数将同一个内存空间释放两次,这就是错误所在
}
深拷贝修改:
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
using namespace std;
class String{
private:
char *p;
public:
String(char *str){//这是自定义构造函数
p=new char[strlen(str)+1];
strcpy(p,str);
cout << "constructor" << endl;
}
String(const String & c){//这是自定义拷贝构造函数
p=new char[strlen(c.p)+1];
strcpy(p,c.p);
cout << "copy constructor" << endl;
}
~String(){
delete[] p;
}
};
int main() {
String s1("abcd");
String s2 = s1;//没有实例化,调用自定义拷贝构造函数,所以默认拷贝构造函数会将指针指向同一空间
//深拷贝:s1和s2各自指向一段内存空间,他们指向的空间具有相同的内容
//输出内容:
//constructor
//copy constructor
}
易错1:显式调用成员对象的默认构造函数
自定义拷贝构造函数会调用成员对象的默认构造函数!因为编译器以为你懂!

所以程序员需要显式调成员对象的拷贝构造函数!
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class A{
private:
int x, y;
public:
A(){//默认构造函数 注意未提供构造函数时系统才会自动提供
x=y=0;
}
void inc(){
x++;
y++;
}
void print(){
cout << " x= " << x << " y= " << y << endl;
}
};
class B{
int z;
A a;
public:
B(){
z=0;
}
// 这里IDE逼着我对成员变量a进行接管 而没有默认调a的构造函数
//所以我需要显式调用a的默认拷贝构造函数a(b.a)
B(const B &b): a(b.a){
z = b.z;
}
void inc(){
z++;
a.inc();
}
void print(){
a.print();
cout << "z= " << z << endl;
}
};
int main() {
B b1;
b1.print();//x= 0 y= 0 z= 0
b1.inc();
b1.print();//x= 1 y= 1 z= 1
B b2(b1);
b2.print();//x= 1 y= 1 z= 1
}
易错2:NRVO(命名返回值优化)
而关于ppt上表示拷贝构造函数复杂性,用于引出移动构造函数的例子,经过代码测试并没有2次或3次构造对象,其实只有一次。原因是编译器优化了返回副本。这称为 NRVO(命名返回值优化)。下面两份代码可以证明。
NRVO参考链接
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class X {
public:
X() { cout << "Default Constructor" << endl; }
X(const X&) { cout << "Copy Constructor" << endl; }
};
X f(X x) { return x; }
X g() {
X y;
return y;
}
int main() {
cout << "First create an object" << endl;
X a;//a调用构造函数 输出Default Constructor
cout << "Call f()" << endl;
f(a);//传参时x=a调用拷贝构造函数 输出Copy Constructor return时temp=x调用拷贝构造函数 输出Copy Constructor
// 因为x是函数参数,所以有复制/移动 输出了2个Copy Constructor
cout << "Call g()" << endl;
g();//y调用构造函数 y的类型恰好是X 进行了优化 输出1次Default Constructor
// 输出:
// First create an object
// Default Constructor
// Call f()
// Copy Constructor
// Copy Constructor
// Call g()
// Default Constructor
}
这里主要证明了NRVO中函数或 catch 子句参数不会被优化。
in a return statement in a function with a class return type, when the expression is the name of a non-volatile automatic object (other than a function or catch-clause parameter) with the same cv-unqualified type as the function return type, the copy/move operation can be omitted by constructing the automatic object directly into the function’s return value
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
using namespace std;
class String{
private:
char *p;
public:
String(char *str){//这是自定义构造函数
p=new char[strlen(str)+1];
strcpy(p,str);
cout << " constructor " << p << endl;
}
String(const String & c){//这是自定义拷贝构造函数
p=new char[strlen(c.p)+1];
strcpy(p,c.p);
cout << "copy constructor " << p << endl;
}
String& operator = (const String &c)//赋值函数(赋值运算符重载) 传值 并没有被调用
{
cout << "assignment operator" << endl;
p = c.p;
return *this;
}
~String(){
delete[] p;
}
};
String generate(){
return String("test");
// return "test";和上面意义一样
}
String generate1(){
String s("test");
return s;
}
String generate2(String s){
return s;
}
int main() {
String tmp = generate();//调用1次构造函数 constructor test
String S = tmp;//调用1次拷贝构造函数 copy constructor test
String S2 = generate1();//调用1次构造函数 constructor test
String S3 = generate2(S2);//s=S2 有一次拷贝构造 返回时tmp=s又有一次拷贝构造 输出2次copy constructor test
//constructor test
//copy constructor test
//constructor test
//copy constructor test
//copy constructor test
}
为什么tmp=generate()并不会多执行一次拷贝构造?因为编译器先把tmp的指针传进generate,然后在返回的时候先把结果store进tmp的指针指向的内容,然后再调用拷贝构造函数。即构造函数时的对象指针就是用的tmp,不是额外新开的内存。
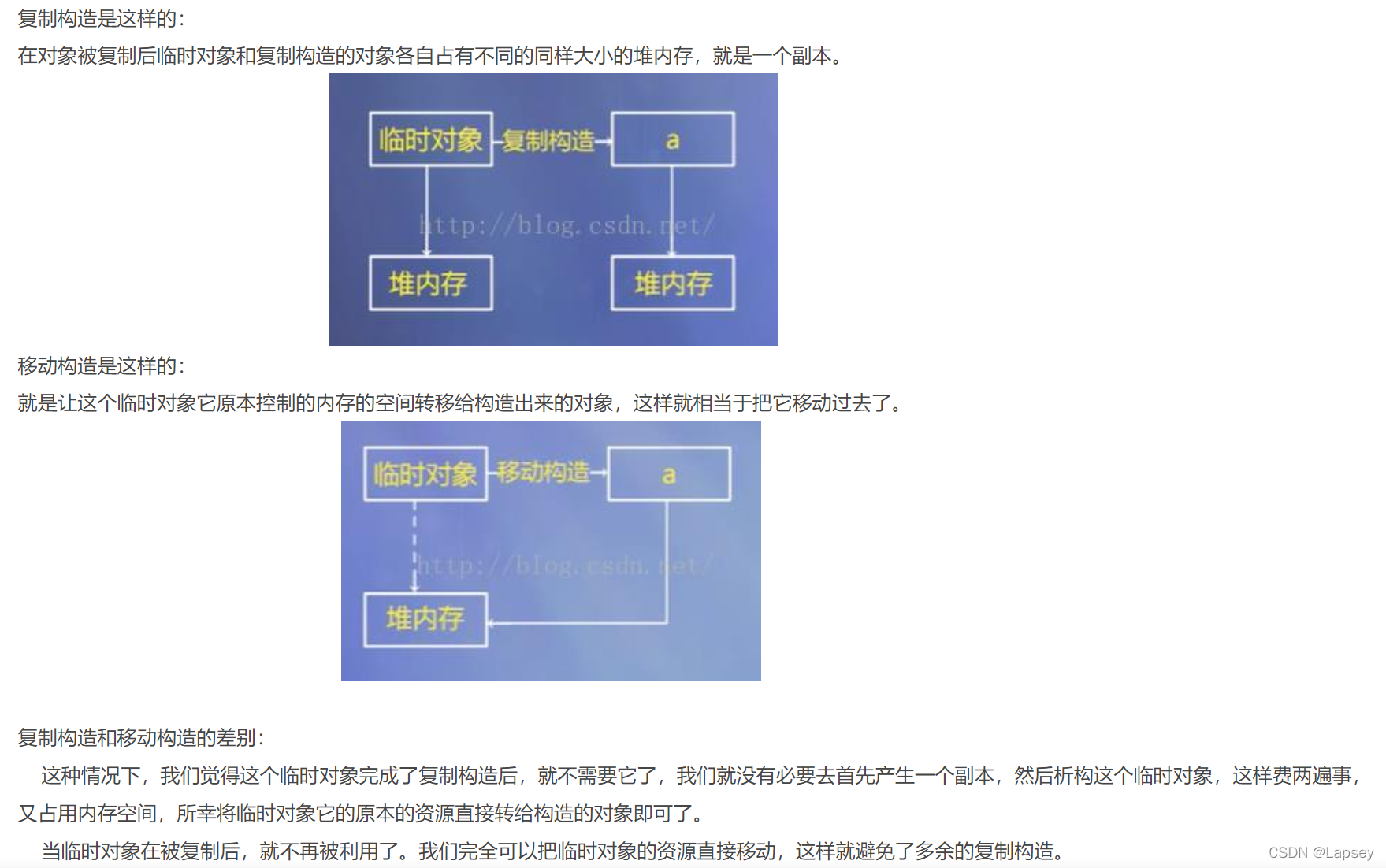
移动构造函数
若没有自定义拷贝构造、拷贝赋值、析构函数,编译器会合成默认的移动构造函数和移动赋值函数。
- 拷贝构造有变,一般移动构造也会变
- 析构函数管理额外申请的资源,编译器不负责,所以没有默认的函数
触发时机: 如果临时对象即将消亡,并且它里面的资源是需要被再利用的,这个时候我们就可以触发移动构造。
如下面的代码只有S=S2后,S3=S时使用了移动构造函数,因为S是即将消亡的临时对象,且资源可以被利用。
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
using namespace std;
class String{
private:
char *p;
public:
String(char *str){//这是自定义构造函数
p=new char[strlen(str)+1];
strcpy(p,str);
cout << " constructor " << p << endl;
}
String(const String & c){//这是自定义拷贝构造函数
p=new char[strlen(c.p)+1];
strcpy(p,c.p);
cout << "copy constructor " << p << endl;
}
String(String &&s):p(s.p){
s.p = nullptr;
cout << "move constructor " << p << endl;
}
String& operator = (const String &c)//赋值函数(赋值运算符重载) 传值 并没有被调用
{
cout << "assignment operator" << endl;
p = c.p;
return *this;
}
~String(){
delete[] p;
}
};
String generate(){
return String("test");
}
String generate1(){
String s("test");
return s;
}
String generate2(String s){
return s;
}
int main() {
String tmp = generate();//调用1次构造函数 constructor test
String S = tmp;//调用1次拷贝构造函数 copy constructor test
String S2 = generate1();//调用1次构造函数 constructor test
String S3 = generate2(S2);//调用1次拷贝构造传参 再调用移动构造生成S
// 触发时机: 如果临时对象即将消亡,并且它里面的资源是需要被再利用的,这个时候我们就可以触发移动构造。
// constructor test
//copy constructor test
// constructor test
//copy constructor test
//move constructor test
}
另外,vector分配内存时也需要注意标记noexcept:
为了避免这种潜在的问题,除非vector知道元素类型的移动构造函数不会抛出异常,否则在重新分配内存的过程中,它就必须使用拷贝构造函数而不是移动构造函数。如果希望在vector重新分配内存这类情况下对我们自定义类型的对象进行移动而不是拷贝,就必须显示的告诉标准库我们的移动构造函数可以安全使用。我们通过将移动构造函数(及移动赋值运算符)标记为noexcept来做到这一点。——《C++ primer》
下面是有noexcept的情况:
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
class Test
{
public:
Test(const string& s = "hello world") :str(new string(s)) { cout << "constructor" << endl; };//构造函数
Test(const Test& t);
Test& operator=(const Test& t);
Test(Test&& t) noexcept;
Test& operator=(Test&& t) noexcept;
~Test();
public:
string * str;
};
Test::Test(const Test& t)//拷贝构造函数
{
str = new string(*(t.str));
cout << "copy constructor" << endl;
}
Test& Test::operator=(const Test& t)//拷贝赋值运算符
{
cout << "assignment" << endl;
return *this;
}
Test::Test(Test&& t)noexcept//移动构造函数
{
str = t.str;
t.str = nullptr;
cout << "move constructor" << endl;
}
Test& Test::operator=(Test&& t)noexcept//移动赋值运算符
{
cout << "move assignment" << endl;
return *this;
}
Test::~Test()//析构函数
{
cout << "destructor" << endl;
}
int main()
{
vector<Test> vec(1);
Test t("what");
vec.push_back(std::move(t));//写move,会把左值显式变成右值引用,调移动构造函数move constructor what move constructor hello world
vec.push_back(t);//t传参调用拷贝构造函数 copy constructor what move constructorhello world
return 0;
//输出:
//constructor vector<Test> vec(1) 所以事先使用默认构造函数构造了一个Test对象
//constructor Test t 使用默认构造函数构造了一个对象
//中间两行见上
//destructor 重新分配内存后,原来的内存将被销毁,所以输出一个“析构函数”
//destructor 执行了return 0, 内存被释放,vec 和 t 都被析构,所以输出三个 “析构函数”(vec里面有2个对象)先销毁t
//destructor 先销毁vec的第一个元素hello world
//destructor 再销毁vec的第二个元素what
}
当不写noexcept时:
- vec.push_back(t);//都是copy constructor
- vec.push_back(std::move(t));//第一个是move 第二个是copy 因为move显式将左值变右值 调移动构造函数