前言
去年寒假前我的一个亲戚问我如何做一个五分频的分频器。我想这还不简单,不就是个计数器吗,但是发现并没有那么简单,因为偶数分频器根据上升沿计数就可以了,但是奇数分频器也可以,但是没法做到50%占空比。今天课上老师完美的解决了这个问题。
偶分频
我们之前学习过计数器,偶分配无非就是个计数器嘛,用信号做中间变量要注意他是滞后变值,所以修改的时候要考虑清除。这点没什么好说的直接上代码。
library ieee;
use ieee.std_logic_1164.all;
use ieee.std_logic_unsigned.all;
entity Test is
generic(constant N:integer:=6);
port(signal clk:in std_logic;signal cout:out std_logic);
end Test;
architecture even of Test is
signal temp:integer:=0;
constant half:integer:=N/2;
begin
process(clk)
begin
if rising_edge(clk) then
temp<=temp+1;
if temp<half then
cout<='1';
elsif temp<N-1 then
cout<='0';
else
temp<=0;
cout<='0';
end if;
end if;
end process;
end even;
这里我们可以实现一个偶数分频。这个想必大家都没问题,那么我们继续看奇数分频
奇数分频
我们很容易想到奇数分频的50%的占空比肯定是和上升沿和下降沿都有关系,那么我们对上升沿和下降沿都做计数,来看一下效果。
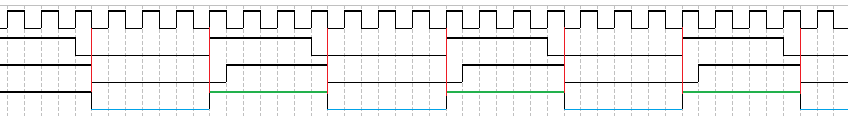
我们发现只有当两个方向的状态均为0时才为0
因为正方向看,他会有半个时钟周期的延迟,这样就可以做到3.5个周期的高电平了。那么剩下的自然就是低电平。
library ieee;
use ieee.std_logic_1164.all;
use ieee.std_logic_unsigned.all;
entity div_any is
generic(constant N:integer:=5);
port(signal clk:in std_logic;signal cout:out std_logic);
end div_any;
architecture even of div_any is
signal tempA,tempB:integer:=0;
signal coutA,coutB:std_logic;
constant half:integer:=N/2;
begin
process(clk)
begin
if rising_edge(clk,coutA,coutB) then
tempA<=tempA+1;
if tempA<half then
coutA<='1';
elsif tempA<N-1 then
coutA<='0';
else
tempA<=0;
coutA<='0';
end if;
elsif falling_edge(clk) then
tempB<=tempB+1;
if tempB<half then
coutB<='1';
elsif tempB<N-1 then
coutB<='0';
else
tempB<=0;
coutB<='0';
end if;
end if;
cout<=coutA or coutB;
end process;
end even;
任意分频
那么如何实现任意分频呢?
我们可以发现,如果当前是偶数,那么直接与上升沿的一样就可以了。不过我们这里做一下特判,1的情况。
下面代码通过输入分频值来更改分频状态。
library ieee;
use ieee.std_logic_1164.all;
use ieee.std_logic_unsigned.all;
entity div_any is
port(signal clk:in std_logic;
signal scaler:in integer range 0 to 63;
signal clk_out,clk_f,clk_r:out std_logic);
end div_any;
architecture DIV of div_any is
signal f_count:integer range 0 to 63:=0;
signal r_count:integer range 0 to 63:=0;
signal half:integer;
signal even:integer;
signal clk_f_temp,clk_r_temp:std_logic;
begin
half<=scaler/2;
even<= scaler rem 2;
with even*scaler select
clk_out<=clk_r_temp when 0,
clk when 1,
clk_f_temp or clk_r_temp when others;
process(clk,scaler)
begin
if rising_edge(clk) then
r_count<=r_count+1;
if r_count<half then
clk_r_temp<='1';
elsif r_count<scaler-1 then
clk_r_temp<='0';
else
clk_r_temp<='0';
r_count<=0;
end if;
elsif falling_edge(clk) then
f_count<=f_count+1;
if f_count<half then
clk_f_temp<='1';
elsif f_count<scaler-1 then
clk_f_temp<='0';
else
clk_f_temp<='0';
f_count<=0;
end if;
end if;
end process;
clk_f<=clk_f_temp;
clk_r<=clk_r_temp;
end DIV;
