peterson算法是用软件实现临界区管理的算法
// multithread_count.c
#include <ctype.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include<stdbool.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <pthread.h>
#define NUM 50000
int count = 0;
bool inside[10]={false,false,false};
int turn=0;
void * worker_funcA(void *arg)
{
for (int i = 0; i < NUM; i++) {
//peterson begin
inside[0]=true;
turn=1;
while(inside[1]&&turn==1);
count++;///这句话对应三句汇编指令,这三句汇编指令就是临界区
inside[0]=false;
//peterson end
}
return NULL;
}
void * worker_funcB(void *arg)
{
for (int i = 0; i < NUM; i++) {
//peterson begin
inside[1]=true;
turn=0;
while(inside[0]&&turn==0);
count++;
inside[1]=false;
//peterson end
}
return NULL;
}
int main(void)
{
pthread_t worker1, worker2;
void *worker1_status;
void *worker2_status;
pthread_create(&worker1, NULL, worker_funcA, NULL);
pthread_create(&worker2, NULL, worker_funcB, NULL);
pthread_join(worker1, &worker1_status);
pthread_join(worker2, &worker2_status);
printf("Count: %d\n", count);
return 0;
}
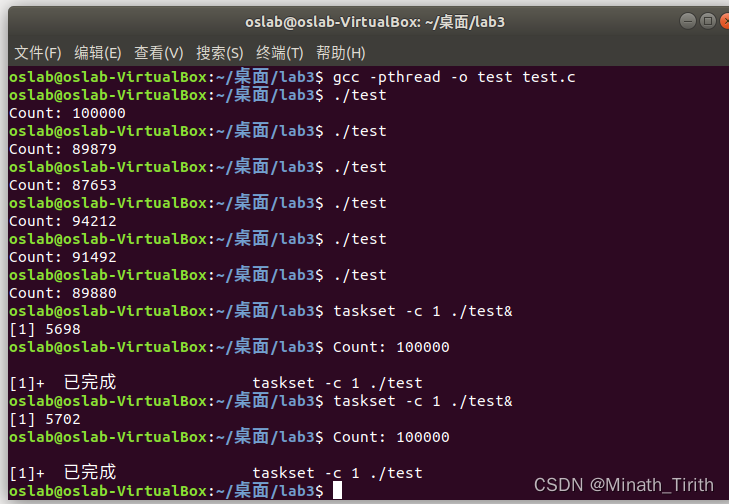
值得一提的是,peterson算法只适用于单核情况,如果是多核模式或者没有使用任何临界区管理方法,那么将得到如下不正确的结果,每次运行的结果都不一样,偶尔能得到正确答案,答案不正确是在执行临界区的三条汇编指令时发生进程切换导致的。使用taskset指令,指定单cpu运行即可得到正确结果