微软官方文档
Event Tracing - Win32 apps | Microsoft Docs
etw相关工具(目前主要用到logman查询providers)
Event Tracing Tools - Win32 apps | Microsoft Docs
简述:
windows事件跟踪也就是windows event trace(etw)。主要分为三个模块:事件提供者(provider)、事件控制器(controller)、事件订阅者(consumer)。普通程序员一般用系统提供的事件用来监听诸如文件操作,注册表操作。所以我们一般写的代码是consumer。但是事件提供者不会直接给订阅者发送消息,所以我们还要写一个控制器controller用来打开事件,让consumer接收事件。
所以我们要自己实现一个controller和一个consumer,可以在同一个程序里面实现,也可以在两个程序里面实现。
controller的实现
commonDef.h
#pragma once
// 这个名字就是控制器的名字
#define LOGSESSION_NAME L"My Event Trace Session 5"//KERNEL_LOGGER_NAMEW//
// 控制器的guid,唯一标识,重复打开会报错183
#define SESSION_GUID { 0xae44cb98, 0xbd11, 0x4069, { 0x80, 0x93, 0x77, 0xe, 0xc9, 0x25, 0x8a, 0x14 } }
#define ARR_SIZE(arr) (sizeof(arr)/sizeof(arr[0]))
// 下面两个guid,经过测试,发现微软官方文档里面mof class中的guid不能实现事件监听,consumer中的回调从来没有被调用过,logman查询当前系统中存在的provider,然后复制对应的guid是可以监听到事件的
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/windows/win32/etw/fileio
mof class fileio
{90cbdc39-4a3e-11d1-84f4-0000f80464e3}
//DEFINE_GUID(
// FILE_IO_PROVIDER_GUID,
// 0x90cbdc39, 0x4a3e, 0x11d1, 0x84, 0xf4, 0x00, 0x00, 0xf8, 0x04, 0x64, 0xe3
//);
// logman query providers | findstr -i file
// EDD08927-9CC4-4E65-B970-C2560FB5C289
DEFINE_GUID(
FILE_IO_PROVIDER_GUID,
0xEDD08927, 0x9CC4, 0x4E65, 0xB9, 0x70, 0xC2, 0x56, 0x0F, 0xB5, 0xC2, 0x89
);
**********
微软官方文档里面mof class中的guid不能实现事件监听,consumer中的回调从来没有被调用过,logman查询当前系统中存在的provider,然后复制对应的guid是可以监听到事件的
***********
main.c
#include <stdio.h>
#include "commonDef.h"
int testController();
void testConsumer();
int main()
{
testController();
//testConsumer();
return 0;
}testController.cpp
#include <windows.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <conio.h>
#include <strsafe.h>
#include <wmistr.h>
#include <evntrace.h>
#include "commonDef.h"
// tracerpt.exe c:\aetw.etl -o c:\aetw.xml -of XML
// 把etl格式文件转为可读的xml文件
const GUID SessionGuid = SESSION_GUID;
const GUID FileIoProviderGuid = FILE_IO_PROVIDER_GUID;
int testController()
{
ULONG status = ERROR_SUCCESS;
TRACEHANDLE SessionHandle = 0;
EVENT_TRACE_PROPERTIES* pSessionProperties = NULL;
ULONG BufferSize = 0;
BOOL TraceOn = TRUE;
// Allocate memory for the session properties. The memory must
// be large enough to include the log file name and session name,
// which get appended to the end of the session properties structure.
BufferSize = sizeof(EVENT_TRACE_PROPERTIES) + 2*MAX_PATH*sizeof(WCHAR);
pSessionProperties = (EVENT_TRACE_PROPERTIES*)malloc(BufferSize);
if (NULL == pSessionProperties)
{
wprintf(L"Unable to allocate %d bytes for properties structure.\n", BufferSize);
goto cleanup;
}
// Set the session properties. You only append the log file name
// to the properties structure; the StartTrace function appends
// the session name for you.
ZeroMemory(pSessionProperties, BufferSize);
pSessionProperties->Wnode.BufferSize = BufferSize;
pSessionProperties->Wnode.Flags = WNODE_FLAG_TRACED_GUID;
pSessionProperties->Wnode.ClientContext = 1; //1:QPC clock resolution,
pSessionProperties->Wnode.Guid = SessionGuid;
// https://stackoverflow.com/questions/68646731/etw-realtime-consuming-of-event-trace
pSessionProperties->LogFileMode = EVENT_TRACE_REAL_TIME_MODE;// | EVENT_TRACE_SYSTEM_LOGGER_MODE; //
pSessionProperties->MaximumFileSize = 1024; // 1 MB
pSessionProperties->FlushTimer = 1;
// https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/windows/win32/etw/fileio
//pSessionProperties->EnableFlags = EVENT_TRACE_FLAG_PROCESS | EVENT_TRACE_FLAG_PROCESS_COUNTERS | EVENT_TRACE_FLAG_DISK_FILE_IO | EVENT_TRACE_FLAG_DISK_IO | EVENT_TRACE_FLAG_DISK_IO_INIT | EVENT_TRACE_FLAG_FILE_IO | EVENT_TRACE_FLAG_FILE_IO_INIT;
pSessionProperties->LoggerNameOffset = sizeof(EVENT_TRACE_PROPERTIES);
//pSessionProperties->LogFileNameOffset = sizeof(EVENT_TRACE_PROPERTIES) + sizeof(WCHAR)*MAX_PATH;
wcscpy_s((WCHAR*)((char*)pSessionProperties + pSessionProperties->LoggerNameOffset), ARR_SIZE(LOGSESSION_NAME), LOGSESSION_NAME);
//StringCbCopy((LPWSTR)((char*)pSessionProperties + pSessionProperties->LogFileNameOffset), sizeof(LOGFILE_PATH), LOGFILE_PATH);
// Create the trace session.
status = StartTrace(&SessionHandle, LOGSESSION_NAME, pSessionProperties);
if (ERROR_SUCCESS != status)
{
wprintf(L"StartTrace() failed with %lu\n", status);
if (status == ERROR_ALREADY_EXISTS) {
status = ::ControlTrace(
(TRACEHANDLE)NULL,
LOGSESSION_NAME,
pSessionProperties,
EVENT_TRACE_CONTROL_STOP);
wprintf(L"stop trace return : %d\n", status);
if (SUCCEEDED(status)) {
status = ::StartTrace(
(PTRACEHANDLE)&SessionHandle,
LOGSESSION_NAME,
pSessionProperties);
wprintf(L"again starttrace return : %d\n", status);
}
}
}
if (ERROR_SUCCESS != status) {
goto cleanup;
}
wprintf(L"StartTrace get session handle:%p\n", SessionHandle);
// Enable the providers that you want to log events to your session.
status = EnableTraceEx2(
SessionHandle,
(LPCGUID)&FileIoProviderGuid,
EVENT_CONTROL_CODE_ENABLE_PROVIDER,
TRACE_LEVEL_INFORMATION,
0,
0,
0,
NULL
);
if (ERROR_SUCCESS != status)
{
wprintf(L"EnableTrace() failed with %lu\n", status);
TraceOn = FALSE;
goto cleanup;
}
wprintf(L"Run the provider application. Then hit any key to stop the session.\n");
_getch();
cleanup:
if (SessionHandle)
{
if (TraceOn)
{
status = EnableTraceEx2(
SessionHandle,
(LPCGUID)&FileIoProviderGuid,
EVENT_CONTROL_CODE_DISABLE_PROVIDER,
TRACE_LEVEL_INFORMATION,
0,
0,
0,
NULL
);
}
status = ControlTrace(SessionHandle, LOGSESSION_NAME, pSessionProperties, EVENT_TRACE_CONTROL_STOP);
if (ERROR_SUCCESS != status)
{
wprintf(L"ControlTrace(stop) failed with %lu\n", status);
}
}
if (pSessionProperties)
{
free(pSessionProperties);
pSessionProperties = NULL;
}
return 0;
}pSessionProperties->LogFileMode设置位EVENT_TRACE_REAL_TIME_MODE表示实时监听,而不是存储为文件
如上代码编译出来的程序重命名位controller.exe
consumer的实现
main.c
#include <windows.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include "commonDef.h"
int testController();
void testConsumer();
int main()
{
//testController();
testConsumer();
return 0;
}testConsumer.cpp
#include <windows.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <conio.h>
#include <comutil.h>
#include <wbemidl.h>
#include <wmistr.h>
#include <evntrace.h>
#include <tdh.h>
#include <in6addr.h>
#include "commonDef.h"
#pragma comment(lib, "tdh.lib")
// Used to calculate CPU usage
ULONG g_TimerResolution = 0;
// Used to determine if the session is a private session or kernel session.
// You need to know this when accessing some members of the EVENT_TRACE.Header
// member (for example, KernelTime or UserTime).
BOOL g_bUserMode = FALSE;
// Handle to the trace file that you opened.
TRACEHANDLE g_hTrace = 0;
// Callback that receives the events.
VOID WINAPI ProcessEvent(PEVENT_RECORD pEvent)
{
wprintf(L"ProcessEvent:processID:%d\n", pEvent->EventHeader.ProcessId);
}
void testConsumer()
{
TDHSTATUS status = ERROR_SUCCESS;
EVENT_TRACE_LOGFILE trace;
HRESULT hr = S_OK;
TRACE_LOGFILE_HEADER* pHeader = &trace.LogfileHeader;
// Identify the log file from which you want to consume events
// and the callbacks used to process the events and buffers.
ZeroMemory(&trace, sizeof(EVENT_TRACE_LOGFILE));
trace.LogFileName = NULL;
trace.LoggerName = (LPWSTR)LOGSESSION_NAME;
trace.EventRecordCallback = ProcessEvent;
trace.ProcessTraceMode = PROCESS_TRACE_MODE_EVENT_RECORD | PROCESS_TRACE_MODE_REAL_TIME;
g_hTrace = OpenTrace(&trace);
if (INVALID_PROCESSTRACE_HANDLE == g_hTrace)
{
wprintf(L"OpenTrace failed with %lu\n", GetLastError());
goto cleanup;
}
//g_bUserMode = pHeader->LogFileMode & EVENT_TRACE_PRIVATE_LOGGER_MODE;
if (pHeader->TimerResolution > 0)
{
g_TimerResolution = pHeader->TimerResolution / 10000;
}
wprintf(L"OpenTrace return: %p\n", g_hTrace);
wprintf(L"Number of events lost: %lu\n", pHeader->EventsLost);
// Use pHeader to access all fields prior to LoggerName.
// Adjust pHeader based on the pointer size to access
// all fields after LogFileName. This is required only if
// you are consuming events on an architecture that is
// different from architecture used to write the events.
if (pHeader->PointerSize != sizeof(PVOID))
{
pHeader = (PTRACE_LOGFILE_HEADER)((PUCHAR)pHeader +
2 * (pHeader->PointerSize - sizeof(PVOID)));
}
wprintf(L"Number of buffers lost: %lu\n\n", pHeader->BuffersLost);
// https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/windows/win32/api/evntrace/nf-evntrace-processtrace
// This function blocks until processing ends
status = ProcessTrace(&g_hTrace, 1, 0, 0);
if (status != ERROR_SUCCESS && status != ERROR_CANCELLED)
{
wprintf(L"ProcessTrace failed with %lu\n", status);
goto cleanup;
}
wprintf(L"ProcessTrace return: %lu, press any key to quit\n\n", status);
_getch();
cleanup:
if (INVALID_PROCESSTRACE_HANDLE != g_hTrace)
{
status = CloseTrace(g_hTrace);
}
}一个程序实现controller和consumer,但是编译后重命名程序位controller.exe和consumer.exe,先运行controller.exe打开控制器,然后运行consumer.exe订阅事件
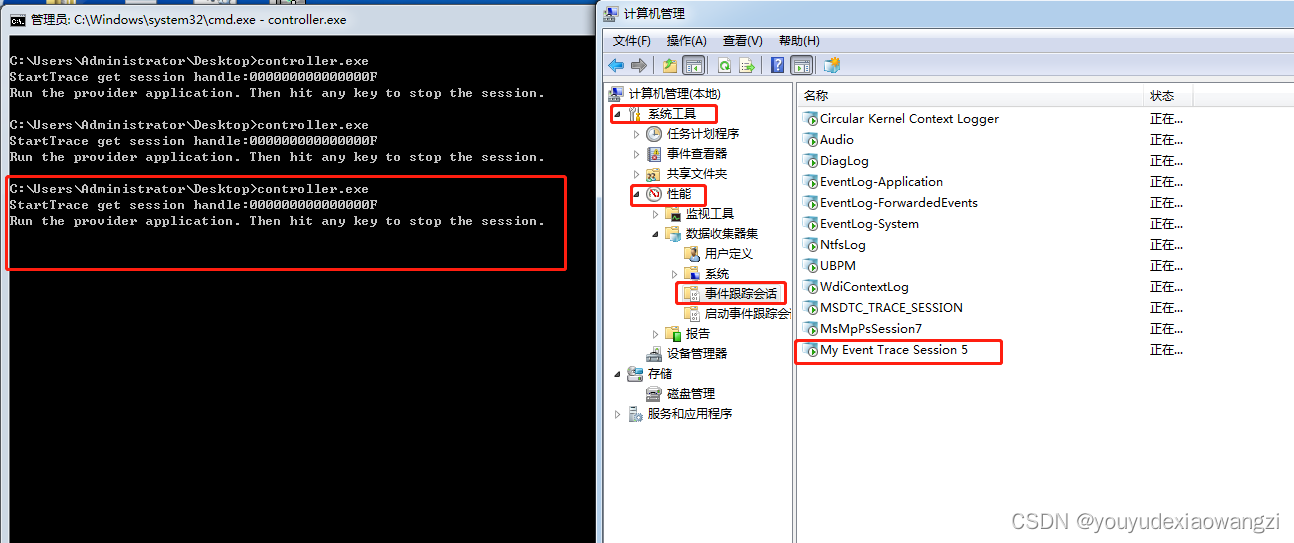
注意事项
- pSessionProperties->LogFileMode = EVENT_TRACE_REAL_TIME_MODE;表示实时监控,如果不是实时监控,需要设置LogFileNameOffset,并且将文件路径复制到Offset对应的位置
- pSessionProperties->Wnode.Guid = SessionGuid;表示自己的控制器对应的guid,如果重复打开会报错183
- StartTrace的第二个参数是session的名字,consumer会根据这个loggerName打开Trace,如上图中的名字
- consumer中的trace.LoggerName = (LPWSTR)LOGSESSION_NAME;要和controller总设置的一样
- trace.ProcessTraceMode = PROCESS_TRACE_MODE_EVENT_RECORD | PROCESS_TRACE_MODE_REAL_TIME;表示实时记录,要与controller中一样
- 执行ProcessTrace之后,如果成功,该线程会阻塞,知道controller结束或者BufferCallback返回false
- 微软官方提供的etw文档里面又mof class的guid,但是如果controller中直接使用该guid,consumer中调用ProcessTrace后就只是卡住,没有ProcessEvent的任何打印。通过logman查询到provider对应的guid是有ProcessEvent的打印的
?
