如何在c里面调用c++库(C/C++混合编程)
一、概述
在实际开发中经常会遇到需要c/c++混合编程的情况。这种可以分为两类
1. C++程序调用C库
这种情况直接调用就行,c++兼容c
2. C程序调用C++库
C++相比C多了class,多了函数重载,因此在C++的编译器中,为了适应这种变化,会在编译过程中自动给函数增加前缀和后缀。这样导致生成的库文件中的函数名与头文件里面的函数名不对应,因此C程序调用C++库时,会提示找不到函数
我们可以用编译器自带的nm来查看.a内部的信息,比如Xilinx自带的工具为arm-none-eabi-nm
执行命令
arm-none-eabi-nm C:/debug/libLeoTest/Debug/liblibLeoTest.a
这是C编译器的结果
00000000 T getLibVersion
0000001c T getSum
这是C++编译器的结果
00000000 T _Z13getLibVersionv
0000001c T _Z6getSumii
2. extern "C"的用法
要实现这个目的,最重要的就是在要引出的函数名前面增加 extern “C”
如果是批量增加,可以使用
extern "C" {
}
而在c语言里面引用的头文件是不需要加这个的,所以一般我们会用宏定义把这块保护起来
#ifdef __cplusplus
extern "C" {
#endif
.....
.....
.....
#ifdef __cplusplus
}
#endif
在C++里面宏__cplusplus默认是生效的,函数都被extern “C” { }包起来了
在C里面宏__cplusplus未定义,忽略了这几行
这样就实现了C和C++共用同一个头文件,避免写两遍重复的代码
下面我们创建一个例子来实际操作一下
二、创建C++ demo库
1. 创建工程
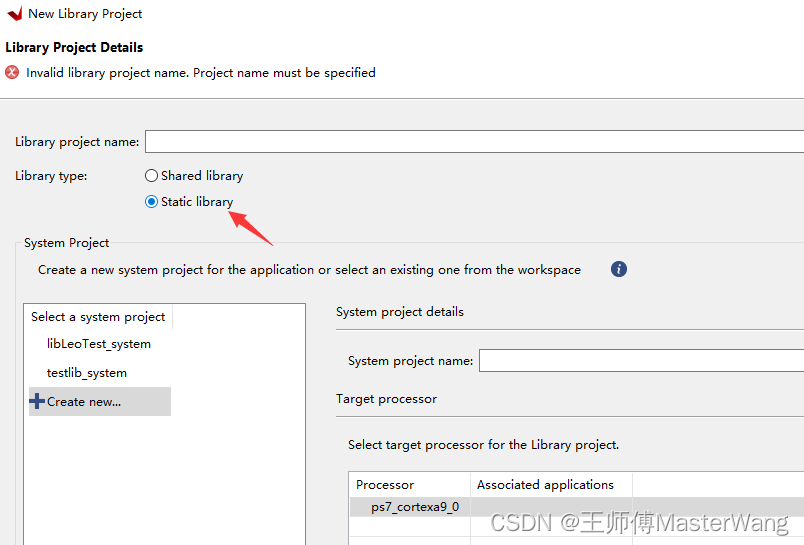
Vitis里面选File -> New -> Library Project
库的类型改为Static library(静态库,扩展名.a)
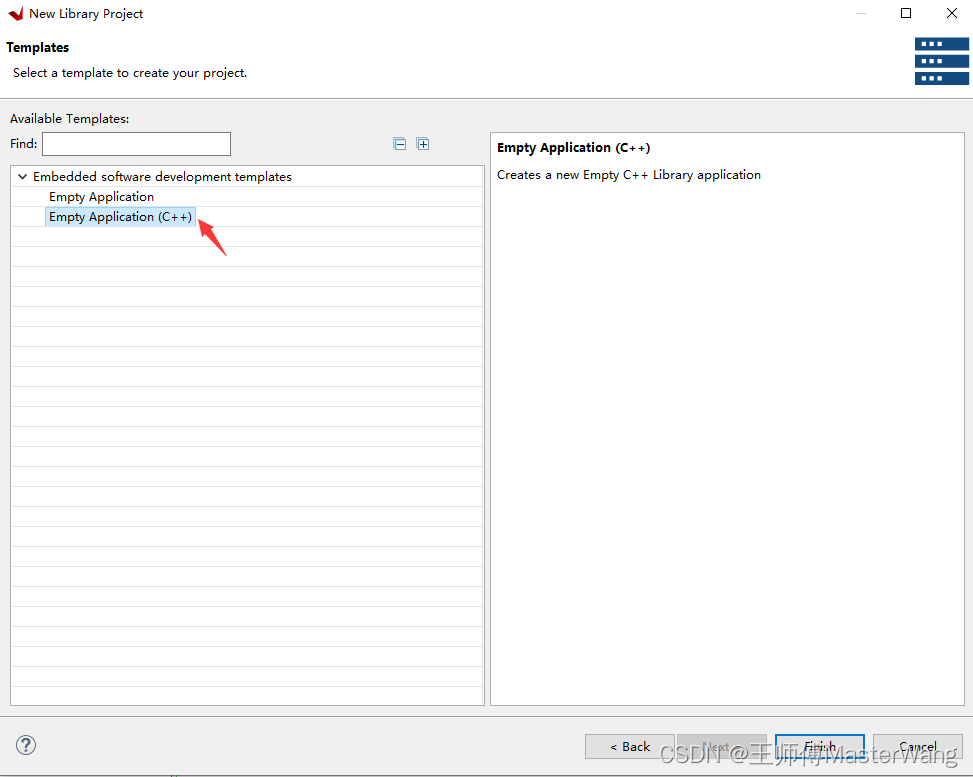
模板选C++
2. 库源文件
libmain.cpp
#include "libLeoTest.h"
int getLibVersion(void)
{
return 123;
}
int getSum(int a, int b)
{
return a + b;
}
libclass.h
#ifndef SRC_LIBCLASS_H_
#define SRC_LIBCLASS_H_
class test_class
{
public:
int a;
int b;
int sum(){
return a+b;
}
};
#endif
libclass.cpp
#include "libclass.h"
extern "C" int getClassSum(int a, int b)
{
test_class class1;
class1.a = a;
class1.b = b;
return class1.sum();
}
libLeoTest.h
#ifndef SRC_LIBLEOTEST_H_
#define SRC_LIBLEOTEST_H_
#ifdef __cplusplus
extern "C" {
#endif
int getSum(int a, int b);
int getClassSum(int a, int b);
int getLibVersion(void);
#ifdef __cplusplus
}
#endif
#endif
三、创建c主程序
1. 创建工程并增加main函数
按照hello world的模板创建一个C工程
hellloworld.c
#include <stdio.h>
#include "platform.h"
#include "xil_printf.h"
#include "libLeoTest.h"
int main()
{
int version;
int sum;
int classsum;
version = getLibVersion();
sum = getSum(1, 2);
sumclass = getClassSum(3, 4);
return 0;
}
2. 设置库文件的搜索路径
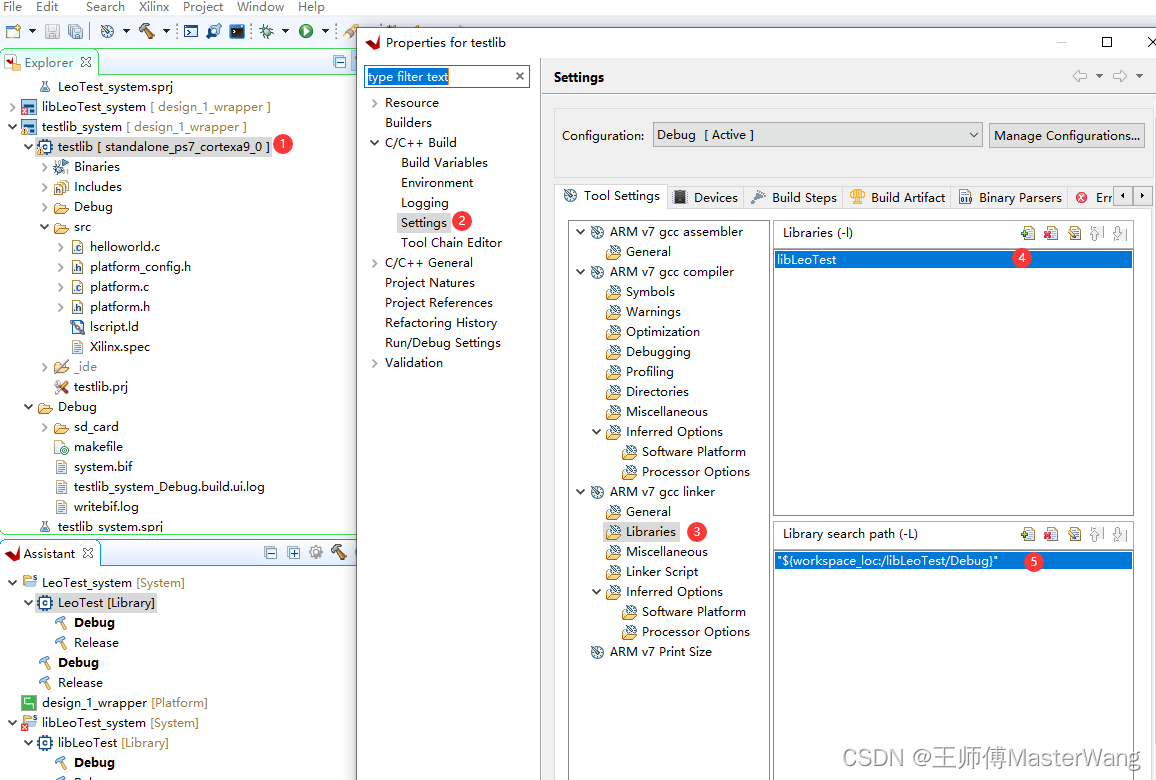
2. 1 在工程名上右键,选择Properties(注意不要选上面的xxxx_system)
2. 2 选择Settings -> ARM v7 gcc linker -> Libraries
2. 3 增加库名称
注意如果库的文件名是liblibLeoTest.a,则输入的库名称应该是libLeoTest
2. 4 增加库搜索路径
选择库文件所在的路径
3. 编译
然后编译就可以正常使用c++的库文件了
附录: nm的用法
nm --help
Usage: nm [option(s)] [file(s)]
List symbols in [file(s)] (a.out by default).
The options are:
-a, --debug-syms Display debugger-only symbols
-A, --print-file-name Print name of the input file before every symbol
-B Same as --format=bsd
-C, --demangle[=STYLE] Decode low-level symbol names into user-level names
The STYLE, if specified, can be `auto' (the default),
`gnu', `lucid', `arm', `hp', `edg', `gnu-v3', `java'
or `gnat'
--no-demangle Do not demangle low-level symbol names
-D, --dynamic Display dynamic symbols instead of normal symbols
--defined-only Display only defined symbols
-e (ignored)
-f, --format=FORMAT Use the output format FORMAT. FORMAT can be `bsd',
`sysv' or `posix'. The default is `bsd'
-g, --extern-only Display only external symbols
-l, --line-numbers Use debugging information to find a filename and
line number for each symbol
-n, --numeric-sort Sort symbols numerically by address
-o Same as -A
-p, --no-sort Do not sort the symbols
-P, --portability Same as --format=posix
-r, --reverse-sort Reverse the sense of the sort
--plugin NAME Load the specified plugin
-S, --print-size Print size of defined symbols
-s, --print-armap Include index for symbols from archive members
--size-sort Sort symbols by size
--special-syms Include special symbols in the output
--synthetic Display synthetic symbols as well
-t, --radix=RADIX Use RADIX for printing symbol values
--target=BFDNAME Specify the target object format as BFDNAME
-u, --undefined-only Display only undefined symbols
-X 32_64 (ignored)
@FILE Read options from FILE
-h, --help Display this information
-V, --version Display this program's version number
nm: supported targets: elf64-x86-64 elf32-i386 elf32-iamcu elf32-x86-64 a.out-i386-linux pei-i386 pei-x86-64 elf64-l1om elf64-k1om elf64-little elf64-big elf32-little elf32-big pe-x86-64 pe-bigobj-x86-64 pe-i386 plugin srec symbolsrec verilog tekhex binary ihex
Report bugs to <http://www.sourceware.org/bugzilla/>.
