文章目录
一.json.hpp库下载及安装
1.1 开源地址及引入方法
??nlohmann json的开源项目地址,其中有对json使用方法的详细说明:
https://github.com/nlohmann/json#serialization–deserialization
??对于我们项目中要使用nlohmann json工具,只需要引入json.hpp这一个文件,其中包含所有接口函数,正如其文档中所述json.hpp文件在single_include/nlohmann目录下,我们只需要下载该文件即可:
git clone https://github.com/nlohmann/json/blob/develop/single_include/nlohmann/json.hpp
 如上图片所示,使用json.hpp文件需要关注两点:
如上图片所示,使用json.hpp文件需要关注两点:
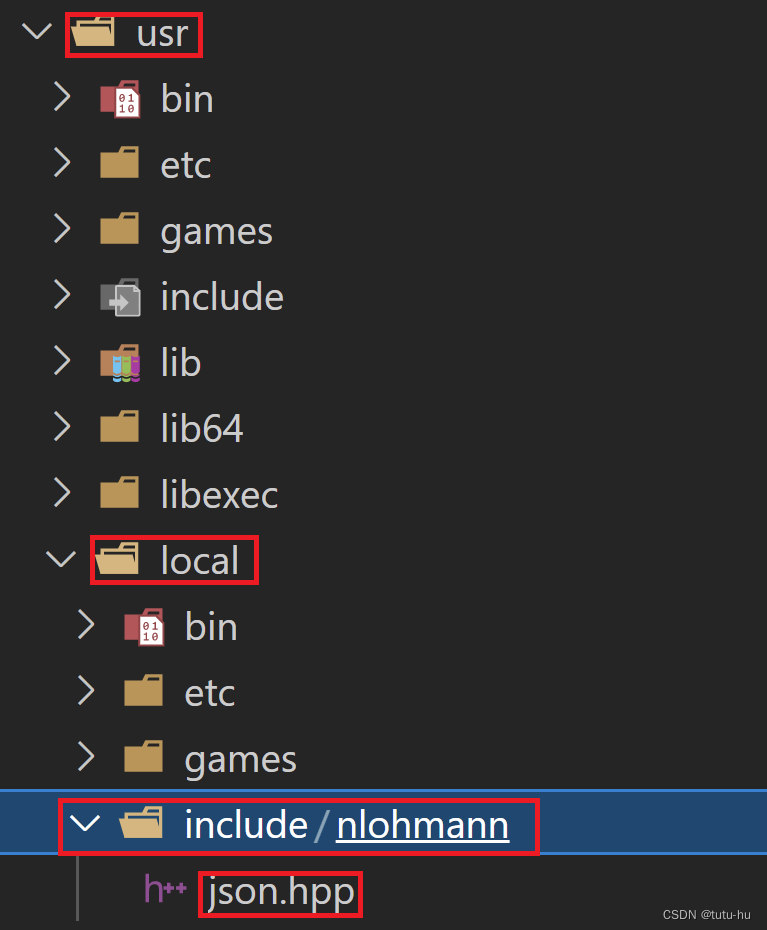
??一是:#include <nlohmann/json.hpp>头文件路径的引入,这里将json.hpp文件放到linux系统中的/usr/local/include路径下,这是系统默认头文件路径,在编译时系统会自动查找该路径。我们在/usr/local/include路径下创建/nlohmann/json.hpp,如下图所示:
 ??二是:在编译时需要指定c++11标准,-std=c++11。
??二是:在编译时需要指定c++11标准,-std=c++11。
1.2 demo程序测试
jsontest.cpp:
#include <iostream>
#include <nlohmann/json.hpp> //引入json.hpp,该文件已经放在系统默认路径:/usr/local/include/nlohmann/json.hpp
using namespace std;
// for convenience
using json = nlohmann::json;
int main()
{
auto config_json = json::parse(R"({"happy": true, "pi": 3.141})"); //构建json对象
cout << config_json << endl; //输出json对象值
return 0;
}
编译:
g++ jsontest.cpp -std=c++11
输出结果:
{“happy”:true,“pi”:3.141}
二.nlohmann json基本操作
2.1 由basic value创建json
两种方式创建json对象:赋值构造+直接构造
jsontest.cpp:
#include <iostream>
#include <nlohmann/json.hpp> //引入json.hpp,该文件已经放在系统默认路径:/usr/local/include/nlohmann/json.hpp
using namespace std;
using json = nlohmann::json; // for convenience
int main()
{
//方式一:赋值构造
json j1;
j1["name"]="LeBorn Jame";//字符串
j1["number"]=23; //整数
j1["man"]=true; //布尔值
j1["children"]={"LeBorn Jr","Bryce Maximus","Zhuri"};//数组
j1["behavior"]["funny"]="gigigigigigi"; //对象中元素值
j1["wife"]={{"name","Savannah Brinson"},{"man",false}};//对象
//方式二:直接构造
json j2={
{"name","LeBorn Jame"},
{"number",23},
{"man",true},
{"children",{"LeBorn Jr","Bryce Maximus","Zhuri"}},
{"behavior",{{"funny","gigigigigigi"}}},
{"wife",{{"name","Savannah Brinson"},{"man",false}}}
};
cout << "j1: "<<j1 << endl; //输出json对象值
cout << "j2: "<<j2 << endl; //输出json对象值
return 0;
}
编译:
g++ jsontest.cpp -std=c++11
输出结果:
j1: {“behavior”:{“funny”:“gigigigigigi”},“children”:[“LeBorn Jr”,“Bryce Maximus”,“Zhuri”],“man”:true,“name”:“LeBorn Jame”,“number”:23,“wife”:{“man”:false,“name”:“Savannah Brinson”}}
j2: {“behavior”:{“funny”:“gigigigigigi”},“children”:[“LeBorn Jr”,“Bryce Maximus”,“Zhuri”],“man”:true,“name”:“LeBorn Jame”,“number”:23,“wife”:{“man”:false,“name”:“Savannah Brinson”}}
2.2 由json对象得到basic value
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <nlohmann/json.hpp> //引入json.hpp,该文件已经放在系统默认路径:/usr/local/include/nlohmann/json.hpp
using namespace std;
using json = nlohmann::json; // for convenience
int main()
{
//构建一个json对象hututu
json hututu = {
{"name","hututu"},
{"age",18},
{"gender",'m'},
{"score",88.99},
{"location",{"aaa","bbb","ccc"}},
};
//方式一
auto name = hututu["name"].get<std::string>(); //获取“name”对应的value值,并转为string类型
cout<<"name = "<<name<<endl;
cout<<"type name = "<<typeid(name).name()<<endl;
cout<<"----------------------"<<endl;
//方式二
auto location0 = hututu["location"][0].get<std::string>();
auto location1 = hututu["location"][1].get<std::string>();
auto location2 = hututu["location"].at(2).get<std::string>();
cout<<"location0 = "<<location0<<endl;
cout<<"location1 = "<<location1<<endl;
cout<<"location2 = "<<location2<<endl;
return 0;
}
输出结果:
name = hututu
type name = Ss
location0 = aaa
location1 = bbb
location2 = ccc
2.3 像操作stl container一样操作json value
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <nlohmann/json.hpp> //引入json.hpp,该文件已经放在系统默认路径:/usr/local/include/nlohmann/json.hpp
using namespace std;
using json = nlohmann::json; // for convenience
int main()
{
//构建一个json对象animalArray
json animalArray={"cat","dog"};//定义一个数组类型的json对象
animalArray.push_back("pig");//添加元素
animalArray.emplace_back("duck");//C++11新方式添加元素,减少申请内存
cout<<"animalArray: "<<animalArray<<endl;
//使用is_array()函数判断对象类型,使用empty函数判断数量是否为空
if(animalArray.is_array() && !animalArray.empty())
{
auto size=animalArray.size(); //使用size函数获取元素数量
cout<<"animalArray size: "<<size<<endl;
auto animalLast=animalArray.at(size-1).get<std::string>();
cout<<"animalArray[size-1]: "<<animalLast<<endl;
cout<<"/--------------------/"<<endl;
}
json animalObject={{"kind","dog"},{"height",50}};//定义一个对象类型的json对象
animalObject.push_back({"color","red"});//插入元素
animalObject.erase("kind");//删除键值
cout<<"animalObject: "<<animalObject<<endl;
animalObject["height"] = 99; //通过key修改value值
//判断是否含有某个键值方式一
if(animalObject.contains("height"))//通过contains函数判断是否包含某个key
{
auto height=animalObject["height"].get<double>();
cout<<"方式一:height: "<<height<<endl;
}
//判断是否含有某个键值方式二
auto size=animalObject.count("height");//通过count函数计算某一个键的数量
if(size>0)
{
cout<<"方式二:存在height键值"<<endl;
}
//判断是否含有某个键值方式三
auto iter=animalObject.find("height");//通过find函数查找某个键的迭代器
if(iter!=animalObject.end())
{
cout<<"方式三:存在height键值"<<endl;
}
//遍历输出键值方式1
cout<<"遍历输出键值方式1:"<<endl;
for(auto item:animalObject.items())
{
std::cout<<item.key()<<" "<<item.value()<<std::endl;
}
//遍历输出键值方式2
cout<<"遍历输出键值方式2:"<<endl;
for(auto iter=animalObject.begin();iter!=animalObject.end();++iter)
{
cout<<iter.key()<<" "<<iter.value()<<std::endl;
}
return 0;
}
输出结果:
animalArray: [“cat”,“dog”,“pig”,“duck”]
animalArray size: 4
animalArray[size-1]: duck
/--------------------/
animalObject: {“color”:“red”,“height”:50}
方式一:height: 99
方式二:存在height键值
方式三:存在height键值
遍历输出键值方式1:
color “red”
height 99
遍历输出键值方式2:
color “red”
height 99
三.json序列化与反序列化
3.1 json value和string
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <nlohmann/json.hpp> //引入json.hpp,该文件已经放在系统默认路径:/usr/local/include/nlohmann/json.hpp
using namespace std;
using json = nlohmann::json; // for convenience
int main()
{
//反序列化构建json对象,两种方式
json hututu1 = "{\"name\":\"hututu\",\"age\":18,\"score\":88.99}"_json;//方式1,通过"_json"实现反序列化
auto temp = R"({"name":"hututu","age":18,"score":88.99})";//使用原生字符串关键字R来避免转移字符,但这一句并没有序列化,hututu2只保存字符串而已,需要结合方式3实现反序列化
json hututu2 = json::parse(temp);//方式2,通过静态函数"parse"实现反序列化
cout<<"/----------反序列化-----------/"<<endl;
cout<<"hututu1 = "<<hututu1<<endl;
cout<<"hututu2 = "<<hututu2<<endl;
cout<<"/----------序列化-----------/"<<endl;
//序列化(Serialization):dump(number),number为打印出的空格数
std::string hututu1_string=hututu1.dump();//animal1值为{"kind":"dog","height":50}
std::string hututu2_string=hututu2.dump(4);
cout<<"hututu1_string = "<<hututu1_string<<endl;
cout<<"hututu2_string = "<<hututu2_string<<endl;
return 0;
}
输出结果:
/----------反序列化-----------/
hututu1 = {“age”:18,“name”:“hututu”,“score”:88.99}
hututu2 = {“age”:18,“name”:“hututu”,“score”:88.99}
/----------序列化-----------/
hututu1_string = {“age”:18,“name”:“hututu”,“score”:88.99}
hututu2_string = {
“age”: 18,
“name”: “hututu”,
“score”: 88.99
}
3.2 json对象和文件输入输出转换
#include <iostream> //文件操作头文件
#include <string>
#include <fstream>
#include <nlohmann/json.hpp> //引入json.hpp,该文件已经放在系统默认路径:/usr/local/include/nlohmann/json.hpp
using namespace std;
using json = nlohmann::json; // for convenience
int main()
{
//上述操作适用于istream和ostream的子类,比如我们经常会用到的ifstream和ofstream
//从.json文件中读取内容到json对象中
std::ifstream in("./person.json");//打开文件,关联到流in
json hututu={"111","222"}; //定义一个json对象为hututu,有初始内容,但是会被覆盖
in>>hututu; //从流in中(也就是./person.json文件)读取内容到json对象中,会覆盖之前内容
in.close(); //关闭文件流in
hututu["aaa"]="bbb"; //添加json对象内容
cout << hututu << endl; //输出json对象值
//输出json对象内容到文件中,并生成新的文件
std::ofstream out("./new.json"); //创建文件./new.json,并关联到流out
hututu["name"]="new name"; //更改hututu对象的内容
out<<std::setw(4)<<hututu; //输出json对象hututu信息到文件./new.json中,std::setw(4)用于设置增加打印空格
out.close(); //关闭文件流out
return 0;
}
./person.json文件内容
{
“name”:“hututu”,
“age”:18,
“gender”:“m”,
“score”:88.99
}
执行程序后,输出的json对象内容如下,也就是从./person.json文件中读取的信息:
{“aaa”:“bbb”,“age”:18,“gender”:“m”,“name”:“hututu”,“score”:88.99}
同时在当前目录下生成新的文件./new.json,内容如下所示:
{
“aaa”: “bbb”,
“age”: 18,
“gender”: “m”,
“name”: “new name”,
“score”: 88.99
}
3.3 json value和自定义对象
??在自定义对象命名空间中定义两个函数即可像basic value一样进行反序列化和序列化:from_json(const json& j,T& value)、to_json(json& j,const T& value)
#include <iostream> //文件操作头文件
#include <string>
#include <nlohmann/json.hpp> //引入json.hpp,该文件已经放在系统默认路径:/usr/local/include/nlohmann/json.hpp
using namespace std;
using json = nlohmann::json;
class person
{
public:
person(){} //默认构造函数
person(string m_name,int m_age,double m_score):name(m_name),age(m_age),score(m_score){};
public:
string name;
int age;
double score;
void display()
{
cout<<"person name = "<<this->name<<endl;
cout<<"person age = "<<this->age<<endl;
cout<<"person score = "<<this->score<<endl;
}
};
//定义from_json(const json& j,T& value)函数,用于序列化
//json对象----->class对象
void from_json(const json& j,person& hututu)
{
hututu.name=j["name"].get<std::string>();
hututu.age=j["age"].get<int>();
hututu.score=j["score"].get<double>();
}
//定义to_json(json& j,const T& value)函数,用于反序列化
//class对象----->json对象
void to_json(json& j,const person& hututu)
{
j["name"]=hututu.name;
j["age"]=hututu.age;
j["score"]=hututu.score;
}
// void to_json(json& j, const person& p)
// {
// j = json{ {"name", p.name}, {"address", p.address}, {"age", p.age} };
// }
// void from_json(const json& j, person& p) {
// j.at("name").get_to(p.name);
// j.at("address").get_to(p.address);
// j.at("age").get_to(p.age);
// }
//main.cpp文件
int main()
{
person hututu{"hututu",18,88.99};//定义一个person对象为hututu
cout<<"/----------to json,方式1:json=class隐式转换-----------/"<<endl;
json j1=hututu; //class to json,隐式调用to_json函数
cout<<"j1 = "<<j1<<endl; //输出json对象值
cout<<"/----------to json,方式2:调用to_json函数-----------/"<<endl;
json j2;
to_json(j2,hututu); //to json,调用to_json函数
cout<<"j2 = "<<j2<<endl; //输出json对象值
cout<<"/----------from json,方式1:调用from_json函数-----------/"<<endl;
j1["name"]="new name"; //修改json对象数据
cout<<"new j1 = "<<j1<<endl; //输出json对象值
person hututu_new;
from_json(j1,hututu_new); //json---->class
hututu_new.display(); //输出person对象内容
cout<<"/----------from json,方式2:调用.get函数-----------/"<<endl;
person hututuNew = j2.get<person>();//像basic value一样通过get函数获取值,将其值直接赋值给自定义对象
hututuNew.display();
return 0;
}
执行结果:
/----------to json,方式1:json=class隐式转换-----------/
j1 = {“age”:18,“name”:“hututu”,“score”:88.99}
/----------to json,方式2:调用to_json函数-----------/
j2 = {“age”:18,“name”:“hututu”,“score”:88.99}
/----------from json,方式1:调用from_json函数-----------/
new j1 = {“age”:18,“name”:“new name”,“score”:88.99}
person name = new name
person age = 18
person score = 88.99
/----------from json,方式2:调用.get函数-----------/
person name = hututu
person age = 18
person score = 88.99
四.NLOHMANN_DEFINE_TYPE_INTRUSIVE宏的使用
4.1 宏的定义
JSON for Modern C++ 中为方便序列化和反序列化定义了两宏,如下
- NLOHMANN_DEFINE_TYPE_NON_INTRUSIVE(name, member1, member2, …) 将在要为其创建代码的类/结构的命名空间内定义。
- NLOHMANN_DEFINE_TYPE_INTRUSIVE(name, member1, member2, …) 将在要为其创建代码的类/结构中定义。 该宏还可以访问私有成员。
进一步查看代码:
/*!
@brief macro
@def NLOHMANN_DEFINE_TYPE_INTRUSIVE
@since version 3.9.0
*/
#define NLOHMANN_DEFINE_TYPE_INTRUSIVE(Type, ...) \
friend void to_json(nlohmann::json& nlohmann_json_j, const Type& nlohmann_json_t) { NLOHMANN_JSON_EXPAND(NLOHMANN_JSON_PASTE(NLOHMANN_JSON_TO, __VA_ARGS__)) } \
friend void from_json(const nlohmann::json& nlohmann_json_j, Type& nlohmann_json_t) { NLOHMANN_JSON_EXPAND(NLOHMANN_JSON_PASTE(NLOHMANN_JSON_FROM, __VA_ARGS__)) }
/*!
@brief macro
@def NLOHMANN_DEFINE_TYPE_NON_INTRUSIVE
@since version 3.9.0
*/
#define NLOHMANN_DEFINE_TYPE_NON_INTRUSIVE(Type, ...) \
inline void to_json(nlohmann::json& nlohmann_json_j, const Type& nlohmann_json_t) { NLOHMANN_JSON_EXPAND(NLOHMANN_JSON_PASTE(NLOHMANN_JSON_TO, __VA_ARGS__)) } \
inline void from_json(const nlohmann::json& nlohmann_json_j, Type& nlohmann_json_t) { NLOHMANN_JSON_EXPAND(NLOHMANN_JSON_PASTE(NLOHMANN_JSON_FROM, __VA_ARGS__)) }
4.2 宏的使用
??可以看出上述的宏主要实现了from_json和to_json两个函数的功能,使用时需要在一个类中调用该宏,并传入(类名,参数1,参数2,参数3…)使用,这样在json对象和class对象之间之间直接赋值可以完成相互转换,具体用法如下:
#include <iostream> //文件操作头文件
#include <string>
#include <nlohmann/json.hpp> //引入json.hpp,该文件已经放在系统默认路径:/usr/local/include/nlohmann/json.hpp
using namespace std;
using json = nlohmann::json;
class person
{
public:
string name;
int age;
double score;
void display()
{
cout<<"person name = "<<this->name<<endl;
cout<<"person age = "<<this->age<<endl;
cout<<"person score = "<<this->score<<endl;
}
// 类名,成员1,成员2,成员3
NLOHMANN_DEFINE_TYPE_INTRUSIVE(person, name, age, score);
};
//main.cpp文件
int main()
{
person hututu{"hututu",18,88.99};//定义一个person对象为hututu
cout<<"/----------调用宏实现:to json-----------/"<<endl;
json j1 = hututu;
cout << j1<< endl;
cout << j1.dump() << endl;
cout<<"/----------调用宏实现:from json-----------/"<<endl;
j1["name"]="new name";
person hututu_new = j1;
hututu_new.display();
return 0;
}
输出结果:
/----------调用宏实现:to json-----------/
{“age”:18,“name”:“hututu”,“score”:88.99}
{“age”:18,“name”:“hututu”,“score”:88.99}
/----------调用宏实现:from json-----------/
person name = new name
person age = 18
person score = 88.99
