学习目标:

学习内容:
1.继承的方式
继承的基本语法:class 子类:继承方式 父类
继承方式主要有:
- 公共继承(public);
- 保护继承(protected);
- 私有继承(private)
1.1 公共继承
//公共继承
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
class Base
{
public:
int m_A;
protected:
int m_B;
private:
int m_C;
};
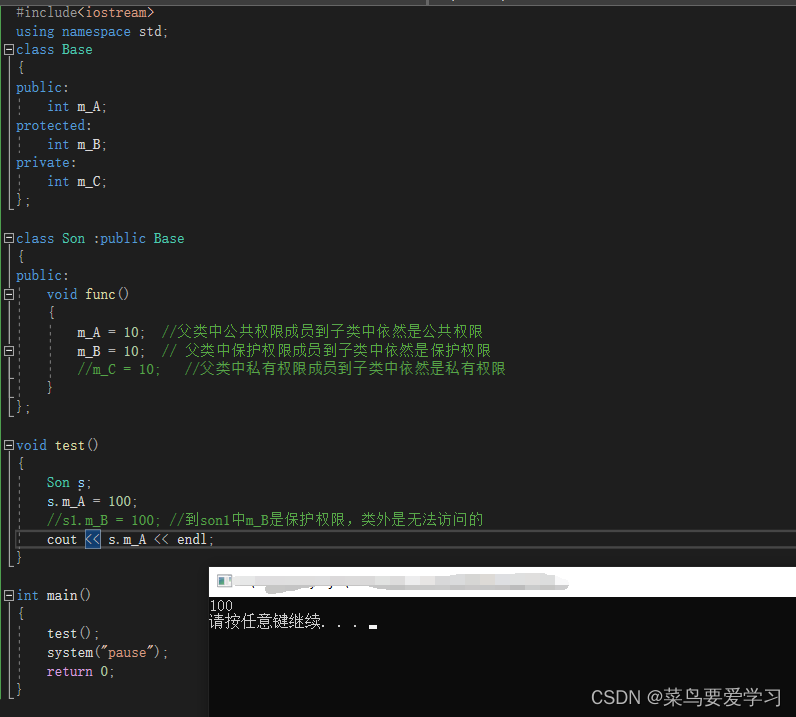
class Son :public Base
{
public:
void func()
{
m_A = 10; //父类中公共权限成员到子类中依然是公共权限
m_B = 10; // 父类中保护权限成员到子类中依然是保护权限
//m_C = 10; //父类中私有权限成员到子类中依然是私有权限
}
};
void test()
{
Son s;
s.m_A = 100;
//s1.m_B = 100; //到son1中m_B是保护权限,类外是无法访问的
cout << s.m_A << endl;
}
int main()
{
test();
system("pause");
return 0;
}

1.2 保护继承
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
class Base
{
public:
int m_A;
protected:
int m_B;
private:
int m_C;
};
class Son :protected Base
{
public:
void func()
{
m_A = 10; //父类中公共权限成员到子类中依然是保护权限
m_B = 10; // 父类中保护权限成员到子类中依然是保护权限
//m_C = 10; //父类中私有权限成员到子类中依然是私有权限,无法访问
}
};
void test()
{
Son s;
//s.m_A = 100; //继承的是保护权限,在类外无法访问
//s.m_B = 100;//继承的是保护权限,在类外无法访问
//s1.m_B = 100; //到son1中m_B是保护权限,类外是无法访问的
}
int main()
{
test();
system("pause");
return 0;
}

1.3 保护继承
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
class Base1
{
public:
int m_A;
protected:
int m_B;
private:
int m_C;
};
class Son :private Base1
{
public:
void func()
{
m_A = 10; //父类中公共权限成员到子类中依然是私有权限
m_B = 10; // 父类中保护权限成员到子类中依然是私有权限
//m_C = 10; //父类中私有权限成员到子类中依然是私有权限,无法访问
}
};
void test()
{
Son s;
//s.m_A = 100; //继承的是私有权限,在类外无法访问
//s.m_B = 100;//继承的是私有权限,在类外无法访问
//s1.m_B = 100; //到son1中m_B是保护权限,类外是无法访问的
}
int main()
{
test();
system("pause");
return 0;
}

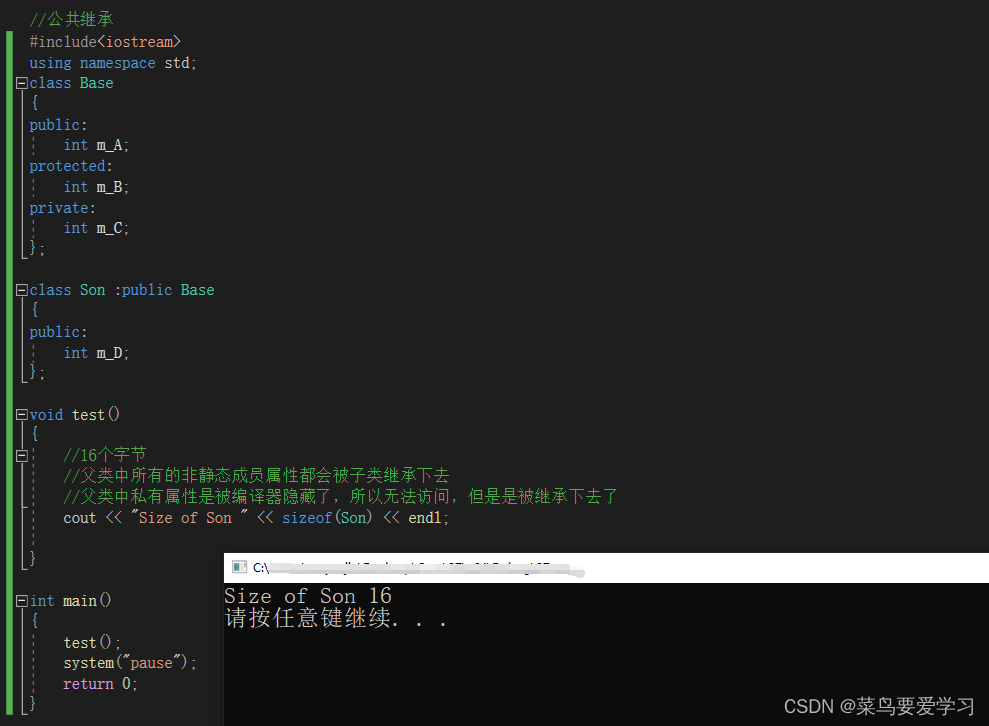
2.继承的对象模型
子类继承父类的相关属性之后,有哪些是属于子类上的对象。
//公共继承
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
class Base
{
public:
int m_A;
protected:
int m_B;
private:
int m_C;
};
class Son :public Base
{
public:
int m_D;
};
void test()
{
//16个字节
//父类中所有的非静态成员属性都会被子类继承下去
//父类中私有属性是被编译器隐藏了,所以无法访问,但是是被继承下去了
cout << "Size of Son " << sizeof(Son) << endl;
}
int main()
{
test();
system("pause");
return 0;
}
3.继承中构造和析构的顺序
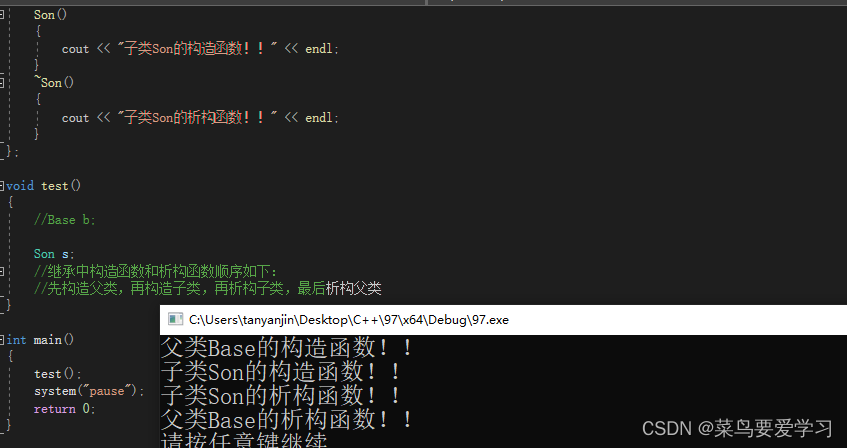
在继承中,构造函数和析构函数是如何调用的?
//继承中构造和析构顺序
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
class Base
{
public:
Base()
{
cout << "父类Base的构造函数!!" << endl;
}
~Base()
{
cout << "父类Base的析构函数!!" << endl;
}
};
class Son:public Base
{
public:
Son()
{
cout << "子类Son的构造函数!!" << endl;
}
~Son()
{
cout << "子类Son的析构函数!!" << endl;
}
};
void test()
{
//Base b;
Son s;
//继承中构造函数和析构函数顺序如下:
//先构造父类,再构造子类,再析构子类,最后析构父类
}
int main()
{
test();
system("pause");
return 0;
}
4.继承中同名处理方式
当子类和父类出现同名的成员时,如何通过子类对象去访问子类或者父类中同名的数据?
访问子类同名成员,直接访问即可;访问父类同名成员,需要加上作用域;
4.1 继承中同名成员属性的处理
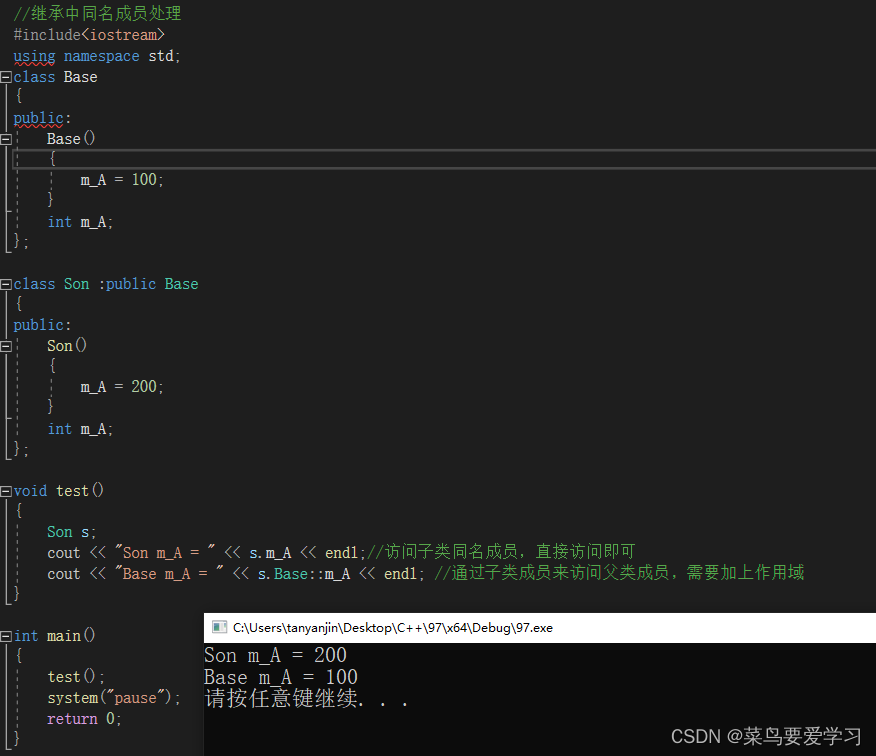
//继承中同名成员处理
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
class Base
{
public:
Base()
{
m_A = 100;
}
int m_A;
};
class Son :public Base
{
public:
Son()
{
m_A = 200;
}
int m_A;
};
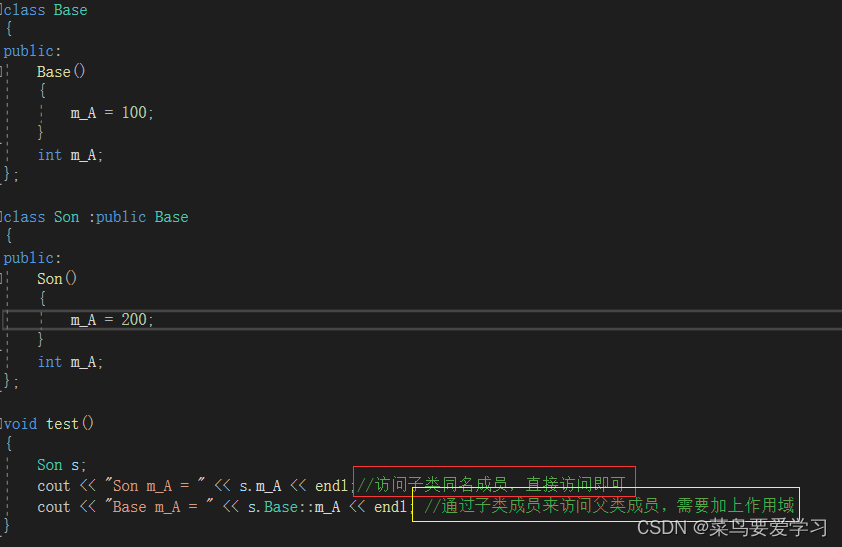
void test()
{
Son s;
cout << "Son m_A = " << s.m_A << endl;//访问子类同名成员,直接访问即可
cout << "Base m_A = " << s.Base::m_A << endl; //通过子类成员来访问父类成员,需要加上作用域
}
int main()
{
test();
system("pause");
return 0;
}
4.2 继承中同名成员函数的处理
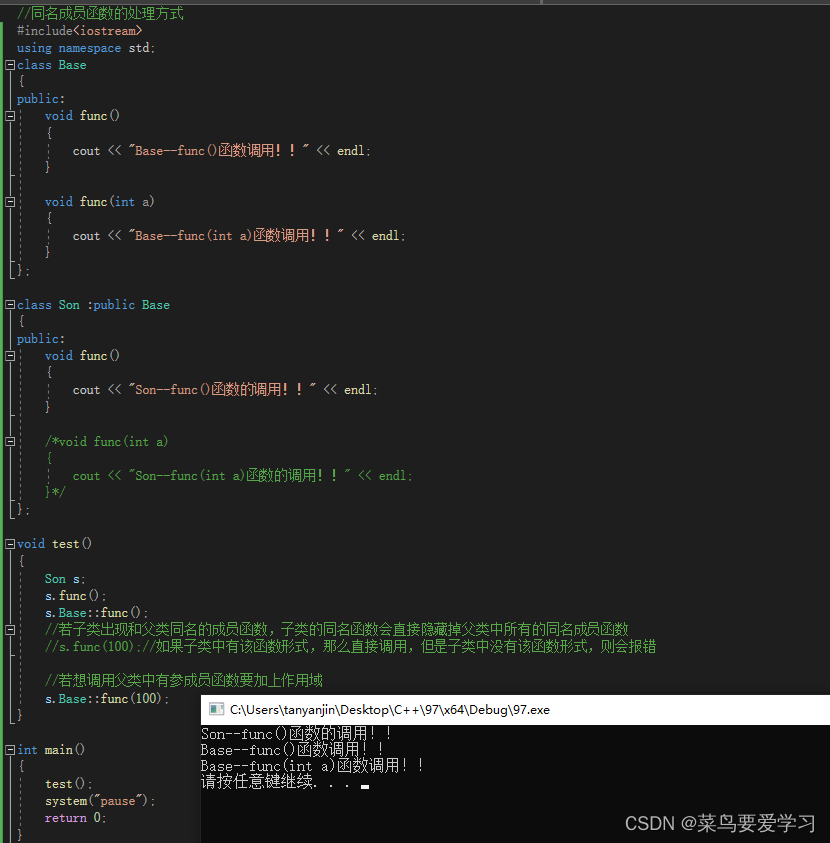
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
class Base
{
public:
void func()
{
cout << "Base--func()函数调用!!" << endl;
}
void func(int a)
{
cout << "Base--func(int a)函数调用!!" << endl;
}
};
class Son :public Base
{
public:
void func()
{
cout << "Son--func()函数的调用!!" << endl;
}
/*void func(int a)
{
cout << "Son--func(int a)函数的调用!!" << endl;
}*/
};
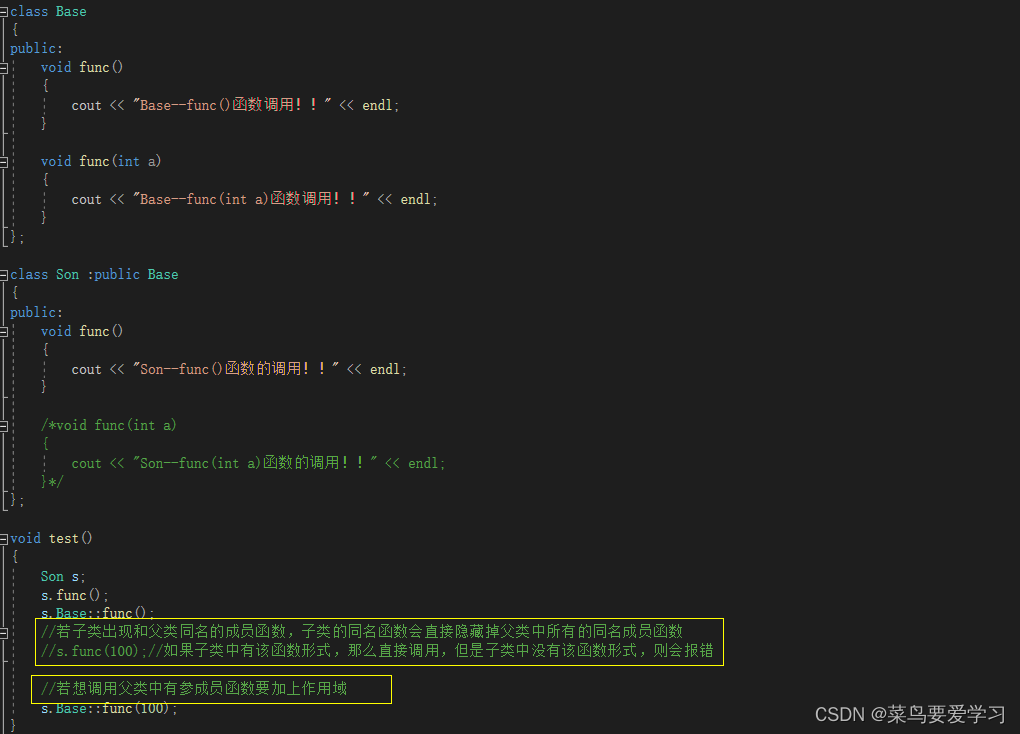
void test()
{
Son s;
s.func();
s.Base::func();
//若子类出现和父类同名的成员函数,子类的同名函数会直接隐藏掉父类中所有的同名成员函数
//s.func(100);//如果子类中有该函数形式,那么直接调用,但是子类中没有该函数形式,则会报错
//若想调用父类中有参成员函数要加上作用域
s.Base::func(100);
}
int main()
{
test();
system("pause");
return 0;
}
5.继承同名静态成员处理方式
问题:继承中同名静态成员在子类对象上如何访问?
- 静态成员和非静态成员出现同名时,处理方式一致;
- 访问子类同名成员,直接访问即可;
- 访问父类同名成员,需要加作用域;
5.1 继承中同名静态成员属性处理方式
//继承中同名静态成员处理方式
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
class Base
{
public:
static int m_A;
};
int Base::m_A = 100;
class Son :public Base
{
public:
static int m_A;
};
int Son::m_A = 200;
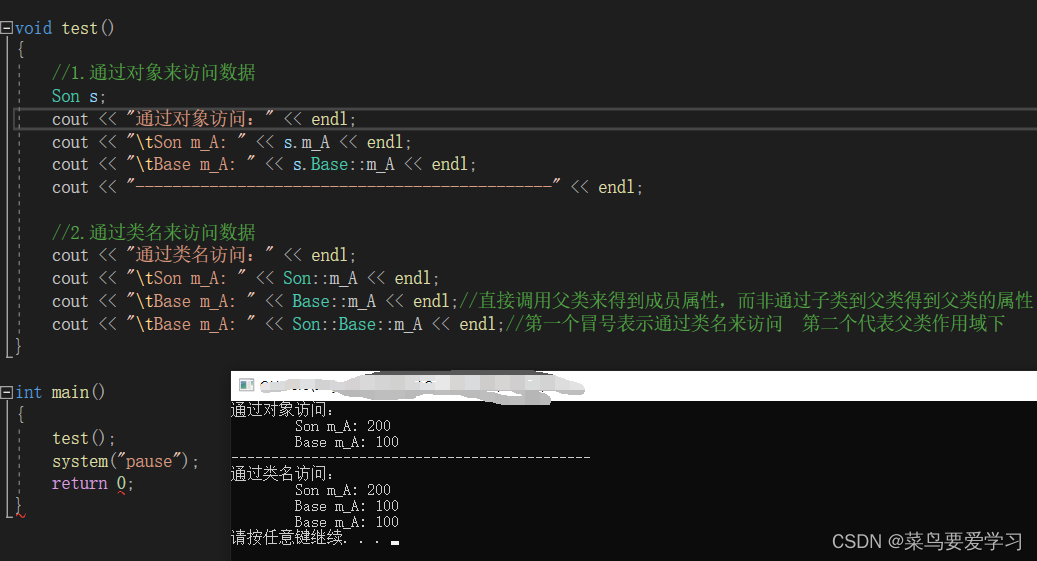
void test()
{
//1.通过对象来访问数据
Son s;
cout << "通过对象访问:" << endl;
cout << "\tSon m_A: " << s.m_A << endl;
cout << "\tBase m_A: " << s.Base::m_A << endl;
cout << "--------------------------------------------------------------------------" << endl;
//2.通过类名来访问数据
cout << "通过类名访问:" << endl;
cout << "\tSon m_A: " << Son::m_A << endl;
cout << "\tBase m_A: " << Base::m_A << endl;//直接调用父类来得到成员属性,而非通过子类到父类得到父类的属性
cout << "\tBase m_A: " << Son::Base::m_A << endl;//第一个冒号表示通过类名来访问 第二个代表父类作用域下
}
int main()
{
test();
system("pause");
return 0;
}


5.2 继承中同名静态成员函数处理方式
//继承中同名静态成员函数处理方式
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
class Base
{
public:
static void func()
{
cout << "父类的调用!!!!!" << endl;
}
};
class Son :public Base
{
public:
static void func()
{
cout << "子类的调用!!!!" << endl;
}
};
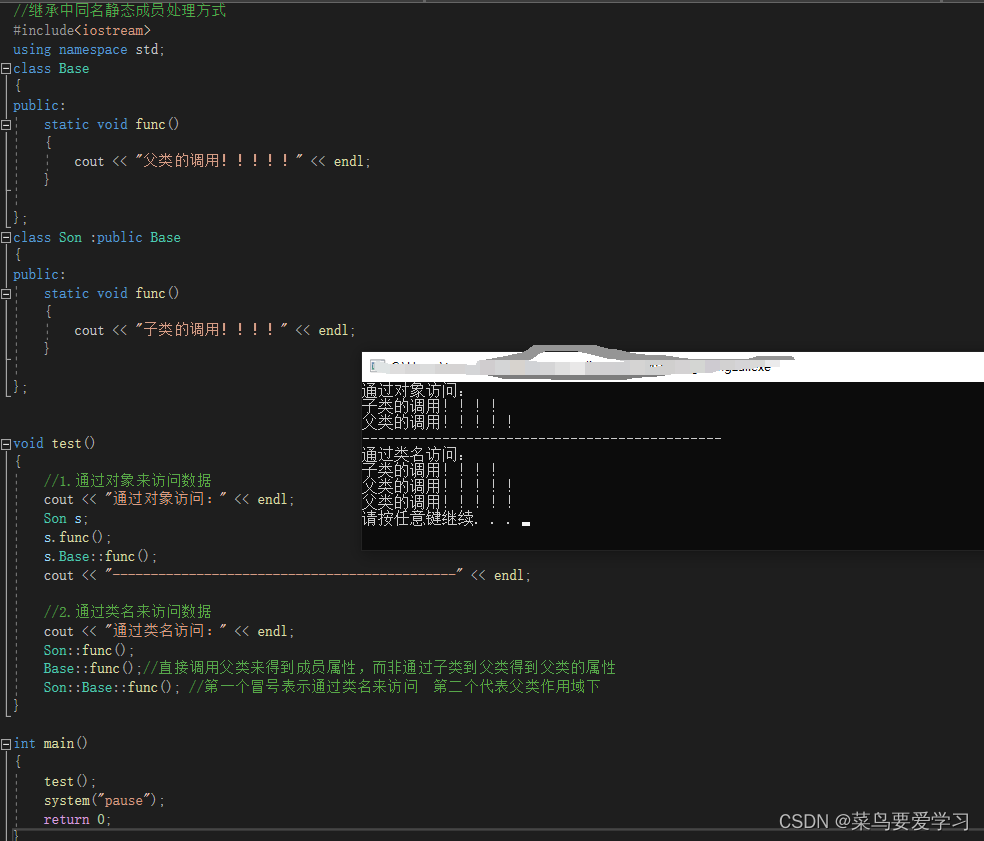
void test()
{
//1.通过对象来访问数据
cout << "通过对象访问:" << endl;
Son s;
s.func();
s.Base::func();
cout << "---------------------------------------------" << endl;
//2.通过类名来访问数据
cout << "通过类名访问:" << endl;
Son::func();
Base::func();//直接调用父类来得到成员属性,而非通过子类到父类得到父类的属性
Son::Base::func(); //第一个冒号表示通过类名来访问 第二个代表父类作用域下
}
int main()
{
test();
system("pause");
return 0;
}
6.多继承的语法
c++中允许一个类继承多个类
语法:class 子类: 继承方式 父类1,继承方式 父类, ……
多继承可能导致父类中有同名成员的出现,需要加上作用域;
在实际开发应用中,不建议用多继承!!!!!!!!!!
7.菱形继承问题和解决方案
概念:两个派生类继承同一个类,又有另一个类同时继承这两个派生类。
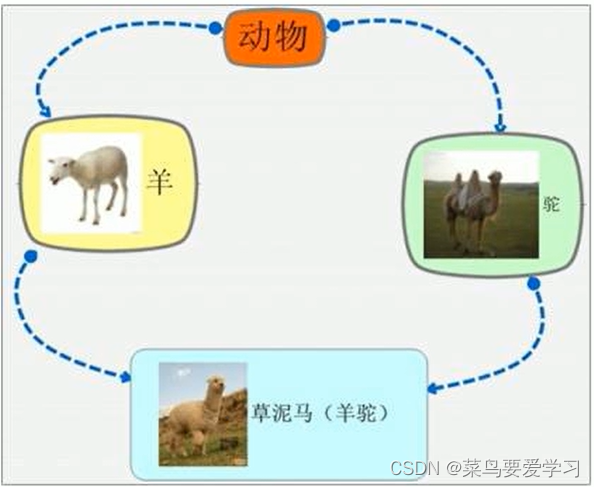
引发的问题:
- 羊和驼都继承了动物的属性,当羊驼使用数据时就会产生二义性;
- 羊驼继承了两份数据,造出来资源浪费。
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
class Animal
{
public:
int m_Age;
};
class sheep : public Animal {};
class camel : public Animal {};
class Alpaca :public sheep, public camel {};
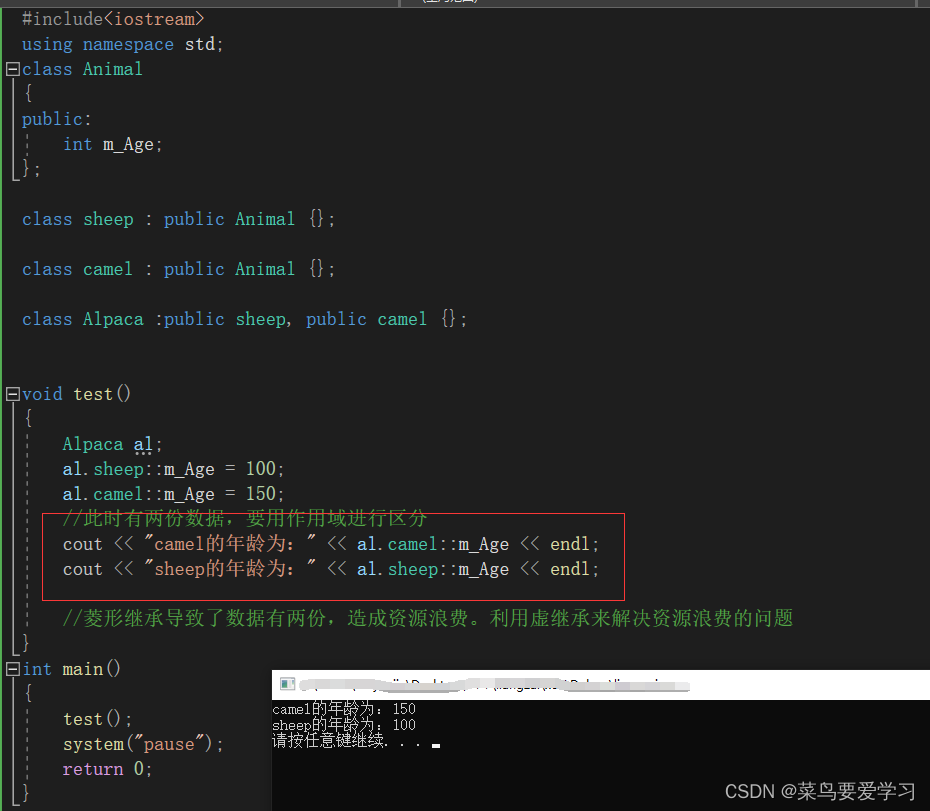
void test()
{
Alpaca al;
al.sheep::m_Age = 100;
al.camel::m_Age = 150;
//此时有两份数据,要用作用域进行区分
cout << "camel的年龄为:" << al.camel::m_Age << endl;
cout << "sheep的年龄为:" << al.sheep::m_Age << endl;
//菱形继承导致了数据有两份,造成资源浪费。利用虚继承来解决资源浪费的问题
}
int main()
{
test();
system("pause");
return 0;
}
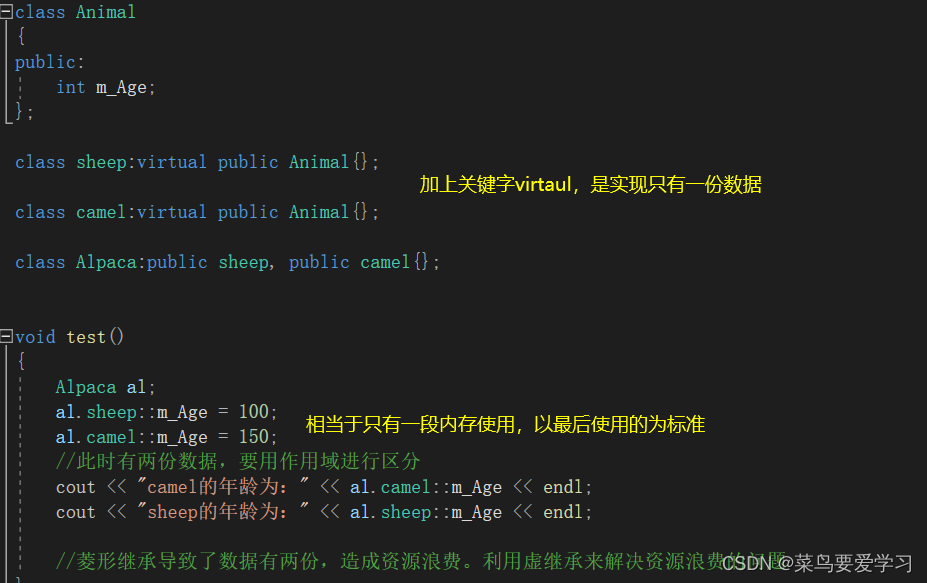
7.1.虚继承解决菱形继承
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
class Animal
{
public:
int m_Age;
};
class sheep:virtual public Animal{};
class camel:virtual public Animal{};
class Alpaca:public sheep, public camel{};
void test()
{
Alpaca al;
al.sheep::m_Age = 100;
al.camel::m_Age = 150;
//此时有两份数据,要用作用域进行区分
cout << "camel的年龄为:" << al.camel::m_Age << endl;
cout << "sheep的年龄为:" << al.sheep::m_Age << endl;
//菱形继承导致了数据有两份,造成资源浪费。利用虚继承来解决资源浪费的问题
}
int main()
{
test();
system("pause");
return 0;
}