一、构造函数
? ? ? ? 在一个类中,用成员函数初始化成员变量的值,定义了一个类对象后忘记调用了这个成员函数,则该对象里面的成员变量的值变得不确定(未被初始化),如果不小心使用了这些成员变量的值,则会出现代码编写错误,如下:
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include<time.h>
using namespace std;
class calendar
{
public:
int year; //成员变量
int month;//成员变量
int day;
int hour;
int minute;
int second;
void calInitFunc(int calYear,int calMonth,int calDay,int calHour,int calMin,int calSec)//成员函数
{
this->year = calYear+ 1900;
this->month = calMonth+1;
this->day = calDay;
this->hour = calHour;
this->minute = calMin;
this->second = calSec;
}
};
int main()
{
calendar cal;
time_t timep;
tm* p;
//time函数会返回从公元1970年1月1日的UTC时间从0时0分0秒算起到现在所经过的秒数
time(&timep);
//struct tm *localtime(const time_t * timep)将参数timep所指的time_t结构中的信息转换成真实世界所使用的时间日期表示方法,然后将结果由结构 tm 返回
p = localtime(&timep);
//将时间结构数据转换成经过的秒数
timep = mktime(p);
这里calInitFunc的初始化很重要,如果没有初始化calInitFunc,则获取的日期和时间都时乱码
cal.calInitFunc(p->tm_year,p->tm_mon,p->tm_mday,p->tm_hour,p->tm_min,p->tm_sec);
//打印日期和时间
cout << cal.year << "年" << cal.month << "月" << cal.day << "日" << " " << cal.hour << "时" << cal.minute << "分" << cal.second << "秒" << endl;;
return 0;
}? ? ? ? 在类中有一种特殊的成员函数,它的名字与类名相同,在创建类对象的时候,这个特殊的成员函数会被系统自动调用,这个成员函数叫做“构造函数”。如果把一些成员变量的初始化放在构造函数中,就不需要手工调用成员函数来初始化成员变量了,因为构造函数会被系统自动调用。可以简单理解成:构造函数的目的就是为了初始化类对象的数据成员(成员变量)。
把上面calendar类中的成员函数改成构造函数,如下:
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include<time.h>
using namespace std;
class calendar
{
public:
int year; //成员变量
int month;//成员变量
int day;
int hour;
int minute;
int second;
calendar(int calYear,int calMonth,int calDay,int calHour,int calMin,int calSec)//构造函数
{
this->year = calYear+ 1900;
this->month = calMonth+1;
this->day = calDay;
this->hour = calHour;
this->minute = calMin;
this->second = calSec;
}
};
void delay_ms(int ms)//延时函数:单位是ms
{
clock_t start = clock();
while (clock() - start < ms);
}
int main()
{
time_t timep;
tm* p;
time(&timep);
p = localtime(&timep);
timep = mktime(p);
//构造函数初始化方式一
calendar cal1 = calendar(p->tm_year, p->tm_mon, p->tm_mday, p->tm_hour, p->tm_min, p->tm_sec);
cout << cal1.year << "年" << cal1.month << "月" << cal1.day << "日" << " " << cal1.hour << "时" << cal1.minute << "分" << cal1.second << "秒" << endl;;
delay_ms(1000);
time(&timep);
p = localtime(&timep);
timep = mktime(p);
//构造函数初始化方式二
calendar cal2(p->tm_year, p->tm_mon, p->tm_mday, p->tm_hour, p->tm_min, p->tm_sec);
cout << cal2.year << "年" << cal2.month << "月" << cal2.day << "日" << " " << cal2.hour << "时" << cal2.minute << "分" << cal2.second << "秒" << endl;;
delay_ms(1000);
time(&timep);
p = localtime(&timep);
timep = mktime(p);
//构造函数初始化方式三
calendar cal3 = calendar{ p->tm_year, p->tm_mon, p->tm_mday, p->tm_hour, p->tm_min, p->tm_sec };
cout << cal3.year << "年" << cal3.month << "月" << cal3.day << "日" << " " << cal3.hour << "时" << cal3.minute << "分" << cal3.second << "秒" << endl;;
delay_ms(1000);
time(&timep);
p = localtime(&timep);
timep = mktime(p);
//构造函数初始化方式四
calendar cal4{ p->tm_year, p->tm_mon, p->tm_mday, p->tm_hour, p->tm_min, p->tm_sec };
cout << cal4.year << "年" << cal4.month << "月" << cal4.day << "日" << " " << cal4.hour << "时" << cal4.minute << "分" << cal4.second << "秒" << endl;;
delay_ms(1000);
time(&timep);
p = localtime(&timep);
timep = mktime(p);
//构造函数初始化方式五
calendar cal5 = { p->tm_year, p->tm_mon, p->tm_mday, p->tm_hour, p->tm_min, p->tm_sec };
cout << cal5.year << "年" << cal5.month << "月" << cal5.day << "日" << " " << cal5.hour << "时" << cal5.minute << "分" << cal5.second << "秒" << endl;;
return 0;
}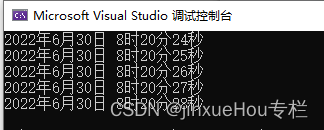
?上面的代码中提供了多种calendar?对象的初始化方式,可以发现,每次创建calendar?对象时,都会自动调用calendar?类的构造函数,程序是按每一秒重新获取系统时间(时间秒数应更新),并创建calendar类?对象,新创建的类对象调用构造函数。
如下几种复制对象写法并没有调用构造函数,调用的实际是“拷贝构造函数”,
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include<time.h>
using namespace std;
class calendar
{
public:
int year; //成员变量
int month;//成员变量
int day;
int hour;
int minute;
int second;
calendar(int calYear,int calMonth,int calDay,int calHour,int calMin,int calSec)//构造函数
{
this->year = calYear+ 1900;
this->month = calMonth+1;
this->day = calDay;
this->hour = calHour;
this->minute = calMin;
this->second = calSec;
}
};
void delay_ms(int ms)//延时函数:单位是ms
{
clock_t start = clock();
while (clock() - start < ms);
}
int main()
{
time_t timep;
tm* p;
time(&timep);
p = localtime(&timep);
timep = mktime(p);
//构造函数初始化方式一
calendar cal1 = calendar(p->tm_year, p->tm_mon, p->tm_mday, p->tm_hour, p->tm_min, p->tm_sec);
cout << cal1.year << "年" << cal1.month << "月" << cal1.day << "日" << " " << cal1.hour << "时" << cal1.minute << "分" << cal1.second << "秒" << endl;;
delay_ms(1000);
time(&timep);
p = localtime(&timep);
timep = mktime(p);
//构造函数初始化方式二
calendar cal2 = cal1;//执行时并不调用构造函数
cout << cal2.year << "年" << cal2.month << "月" << cal2.day << "日" << " " << cal2.hour << "时" << cal2.minute << "分" << cal2.second << "秒" << endl;;
delay_ms(1000);
time(&timep);
p = localtime(&timep);
timep = mktime(p);
//构造函数初始化方式三
calendar cal3 = (cal1);//执行时并不调用构造函数
cout << cal3.year << "年" << cal3.month << "月" << cal3.day << "日" << " " << cal3.hour << "时" << cal3.minute << "分" << cal3.second << "秒" << endl;;
delay_ms(1000);
time(&timep);
p = localtime(&timep);
timep = mktime(p);
//构造函数初始化方式四
calendar cal4{ cal1 };//执行时并不调用构造函数
cout << cal4.year << "年" << cal4.month << "月" << cal4.day << "日" << " " << cal4.hour << "时" << cal4.minute << "分" << cal4.second << "秒" << endl;;
delay_ms(1000);
time(&timep);
p = localtime(&timep);
timep = mktime(p);
//构造函数初始化方式五
calendar cal5 = { cal1 };//执行时并不调用构造函数
cout << cal5.year << "年" << cal5.month << "月" << cal5.day << "日" << " " << cal5.hour << "时" << cal5.minute << "分" << cal5.second << "秒" << endl;;
return 0;
}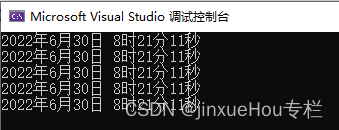
?可以看出,程序是按每一秒重新获取系统时间(时间秒数应更新),并创建对象,新创建的类对象调用的一直是cal1对象的构造函数,而不是属于自己的构造函数。
二、多个构造函数
一个类中可以有多个构造函数,只要规定每个构造函数的参数数量或者参数类型不同就可以。
我们在上面calendar?类中添加一个无参数的构造函数,如下:
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include<time.h>
using namespace std;
class calendar
{
public:
int year; //成员变量
int month;//成员变量
int day;
int hour;
int minute;
int second;
calendar(int calYear,int calMonth,int calDay,int calHour,int calMin,int calSec)//构造函数
{
this->year = calYear+ 1900;
this->month = calMonth+1;
this->day = calDay;
this->hour = calHour;
this->minute = calMin;
this->second = calSec;
}
calendar()//无参构造函數
{
cout << "调用无参构造函数" << endl;
}
};
void delay_ms(int ms)//延时函数:单位是ms
{
clock_t start = clock();
while (clock() - start < ms);
}
int main()
{
time_t timep;
tm* p;
time(&timep);
p = localtime(&timep);
timep = mktime(p);
calendar cal1 = calendar();//调用无参的构造函数
cout << cal1.year << "年" << cal1.month << "月" << cal1.day << "日" << " " << cal1.hour << "时" << cal1.minute << "分" << cal1.second << "秒" << endl;;
delay_ms(1000);
time(&timep);
p = localtime(&timep);
timep = mktime(p);
calendar cal2;//调用无参的构造函数
cout << cal2.year << "年" << cal2.month << "月" << cal2.day << "日" << " " << cal2.hour << "时" << cal2.minute << "分" << cal2.second << "秒" << endl;;
delay_ms(1000);
time(&timep);
p = localtime(&timep);
timep = mktime(p);
calendar cal3 = { calendar() };//调用无参的构造函数
cout << cal3.year << "年" << cal3.month << "月" << cal3.day << "日" << " " << cal3.hour << "时" << cal3.minute << "分" << cal3.second << "秒" << endl;;
delay_ms(1000);
time(&timep);
p = localtime(&timep);
timep = mktime(p);
calendar cal4{};//调用无参的构造函数
cout << cal4.year << "年" << cal4.month << "月" << cal4.day << "日" << " " << cal4.hour << "时" << cal4.minute << "分" << cal4.second << "秒" << endl;;
delay_ms(1000);
time(&timep);
p = localtime(&timep);
timep = mktime(p);
calendar cal5 = {};//调用无参的构造函数
cout << cal5.year << "年" << cal5.month << "月" << cal5.day << "日" << " " << cal5.hour << "时" << cal5.minute << "分" << cal5.second << "秒" << endl;;
return 0;
}程序执行后打印的信息如下:
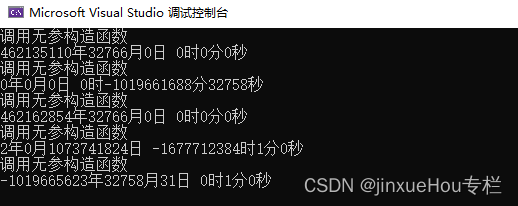
从上面的代码中可以发现,每次创建calendar?对象时,都会自动调用calendar?类的构造函数,但是调用的是无参的构造函数,无参数的函数没有对日期和时间初始化,打印出来的日期时间都是乱码。
三、函数的默认参数
我们对上面的带6个参数的构造函数修改一下,把最后一个参数这样修改:
calendar(int?stuYear,int?stuMonth,int?stuDay,int?stuHour,int?min,int?sec=45);//成员函数
此时sec参数就叫做函数的默认参数,也就说创建calendar?新对象时,如果不给这个参数传参,那么这个参数的值就是45。程序代码如下,
在main.h头文件声明calendar类:
#ifndef __MAIN_H__
#define __MAIN_H__
class calendar
{
public:
int year; //成员变量
int month;//成员变量
int day;
int hour;
int minute;
int second;
calendar(int calYear,int calMonth,int calDay,int calHour,int calMin,int calSec=45);//构造函数
};
#endif // !__MAIN_H__在main.cpp中定义calendar中的带6个参数的构造函数和调用如下:
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include<time.h>
#include"main.h"
using namespace std;
calendar::calendar(int calYear,int calMonth,int calDay,int calHour,int calMin,int calSec)//构造函数
{
this->year = calYear+ 1900;
this->month = calMonth+1;
this->day = calDay;
this->hour = calHour;
this->minute = calMin;
this->second = calSec;
}
void delay_ms(int ms)//延时函数:单位是ms
{
clock_t start = clock();
while (clock() - start < ms);
}
int main()
{
time_t timep;
tm* p;
time(&timep);
p = localtime(&timep);
timep = mktime(p);
//构造函数初始化方式一:缺省sec参数传参
calendar cal1 = calendar(p->tm_year, p->tm_mon, p->tm_mday, p->tm_hour, p->tm_min);
cout << cal1.year << "年" << cal1.month << "月" << cal1.day << "日" << " " << cal1.hour << "时" << cal1.minute << "分" << cal1.second << "秒" << endl;;
delay_ms(1000);
time(&timep);
p = localtime(&timep);
timep = mktime(p);
//构造函数初始化方式二:缺省sec参数传参
calendar cal2(p->tm_year, p->tm_mon, p->tm_mday, p->tm_hour, p->tm_min);
cout << cal2.year << "年" << cal2.month << "月" << cal2.day << "日" << " " << cal2.hour << "时" << cal2.minute << "分" << cal2.second << "秒" << endl;;
delay_ms(1000);
time(&timep);
p = localtime(&timep);
timep = mktime(p);
//构造函数初始化方式三:缺省sec参数传参
calendar cal3 = calendar{ p->tm_year, p->tm_mon, p->tm_mday, p->tm_hour, p->tm_min};
cout << cal3.year << "年" << cal3.month << "月" << cal3.day << "日" << " " << cal3.hour << "时" << cal3.minute << "分" << cal3.second << "秒" << endl;;
delay_ms(1000);
time(&timep);
p = localtime(&timep);
timep = mktime(p);
//构造函数初始化方式四:缺省sec参数传参
calendar cal4{ p->tm_year, p->tm_mon, p->tm_mday, p->tm_hour, p->tm_min};
cout << cal4.year << "年" << cal4.month << "月" << cal4.day << "日" << " " << cal4.hour << "时" << cal4.minute << "分" << cal4.second << "秒" << endl;;
delay_ms(1000);
time(&timep);
p = localtime(&timep);
timep = mktime(p);
//构造函数初始化方式五:缺省sec参数传参
calendar cal5 = { p->tm_year, p->tm_mon, p->tm_mday, p->tm_hour, p->tm_min};
cout << cal5.year << "年" << cal5.month << "月" << cal5.day << "日" << " " << cal5.hour << "时" << cal5.minute << "分" << cal5.second << "秒" << endl;;
return 0;
}
没有对秒传参,但是默认参数是45,也就是我们在对这个构造函数声明时赋的值。
任何函数都可以有默认参数,默认参数一般是放在函数声明中而不放在函数定义中,除非该函数没有声明只有定义。
对于类中的成员函数,默认参数写在类的成员函数声明中,而不是写在函数定义中,也就是写在.h头文件中。
函数默认参数的规定:
在具有多个参数的函数中,指定参数默认值时,默认参数都必须出现在非默认参数的右侧,一旦开始为某个参数指定默认值,则它右侧的所有参数都必须指定默认值。
calendar(int calYear,int calMonth,int calDay,int calHour,int calMin=20,int calSec=45);//可以
calendar(int calYear,int calMonth,int calDay,int calHour,int calMin=20,int calSec);//不可以
现在有一个问题,如果一个类中声明了只带5个参数的构造函数,即只有stuYear、stuMonth、stuDay、stuHour和min,在调用5个参数和6个参数构造函数(一个默认参数不传参)系统编译就会出错,系统不清楚这是带5个参数的、还是带6个参数的构造函数,所以只能把默认参数赋值删除。
四、隐式转换和explicit
这里讲一下单参数的构造函数带来的隐式转换,编译系统其实背着开发者在私下里还是做了很多事情。如下main函数中定义和初始化,会发现语法错误:
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include<time.h>
#include"main.h"
using namespace std;
class student
{
public:
int age;
int hight;
int num;
/*student(int stuAge);*/
student(int stuAge, int stuHight);
student(int stuAge, int stuHight, int stuNum);
};
/*student::student(int stuAge)
{
this->age = stuAge;
cout << "一个参数的构造函数!!!" << endl;
}*/
student::student(int stuAge, int stuHight)
{
this->age = stuAge;
this->hight = stuHight;
cout << "两个参数的构造函数!!!" << endl;
}
student::student(int stuAge, int stuHight, int stuNum)
{
this->age = stuAge;
this->hight = stuHight;
this->num = stuNum;
cout << "三个参数的构造函数!!!" << endl;
}
int main()
{
student myStu1 = 10;
student myStu2 = (10,11,12,13,14,15);
return 0;
}但是,当声明和定义了单参数的构造函数后,再次运行程序,程序不会再报错,而且myStu1 、myStu12两个类对象调用的都是单参数的构造函数(尤其时括号里面有很多数字的,系统只把最后一个数字作为参数传递到单参数构造函数中),调试和运行的现象如下所示:
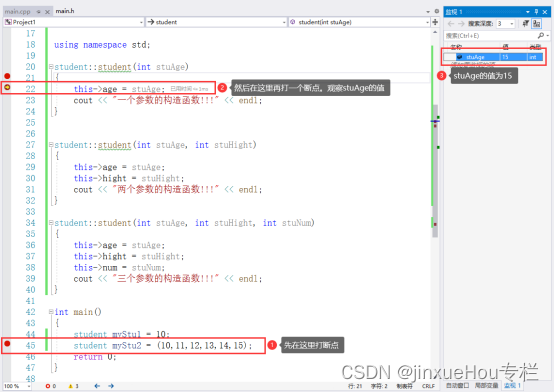
?
通过上面例子可以看到,系统把student myStu1 = 10;和student myStu2 = (10,11,12,13,14,15);
中的数字(上面的10和15)隐式转换成student 类类型。
再在上面的student类写一个普通函数:
void func(student stu)
{
return;
}调用func函数:
int main()
{
student myStu1 = 10;
student myStu2 = (10,11,12,13,14,15);
func(20);//这里还是调用到了student 类的单参数的构造函数
return 0;
}这说明系统进行了一个从数字20到student类对象(func函数的形参)的一个转换,产生了一个
student对象(临时对象),函数调用完毕后,student对象的什么周期结束,所占用的资源被系统回收。
上面几种隐式转换让人糊涂,是否可以强制让系统明确要求构造函数不能做隐式转换?是可以的。如果构造函数声明中带有explicit(显式),则这个构造函数只能用于初始化和显式类型转换。
上面我们讲到的calendar创建的5个对象都能够成功,此时把带有6个参数的calendar构造函数的声明前面加上explicit,如下:
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include<time.h>
using namespace std;
class calendar
{
public:
int year; //成员变量
int month;//成员变量
int day;
int hour;
int minute;
int second;
explicit calendar(int calYear,int calMonth,int calDay,int calHour,int calMin,int calSec);//构造函数
};
calendar::calendar(int calYear,int calMonth,int calDay,int calHour,int calMin,int calSec)//构造函数
{
this->year = calYear+ 1900;
this->month = calMonth+ 1;
this->day = calDay;
this->hour = calHour;
this->minute = calMin;
this->second = calSec;
}
void delay_ms(int ms)//延时函数:单位是ms
{
clock_t start = clock();
while (clock() - start < ms);
}
int main()
{
time_t timep;
tm* p;
time(&timep);
p = localtime(&timep);
timep = mktime(p);
//构造函数初始化方式一
calendar cal1 = calendar(p->tm_year, p->tm_mon, p->tm_mday, p->tm_hour, p->tm_min, p->tm_sec);
cout << cal1.year << "年" << cal1.month << "月" << cal1.day << "日" << " " << cal1.hour << "时" << cal1.minute << "分" << cal1.second << "秒" << endl;;
delay_ms(1000);
time(&timep);
p = localtime(&timep);
timep = mktime(p);
//构造函数初始化方式二
calendar cal2(p->tm_year, p->tm_mon, p->tm_mday, p->tm_hour, p->tm_min, p->tm_sec);
cout << cal2.year << "年" << cal2.month << "月" << cal2.day << "日" << " " << cal2.hour << "时" << cal2.minute << "分" << cal2.second << "秒" << endl;;
delay_ms(1000);
time(&timep);
p = localtime(&timep);
timep = mktime(p);
//构造函数初始化方式三
calendar cal3 = calendar{ p->tm_year, p->tm_mon, p->tm_mday, p->tm_hour, p->tm_min, p->tm_sec };
cout << cal3.year << "年" << cal3.month << "月" << cal3.day << "日" << " " << cal3.hour << "时" << cal3.minute << "分" << cal3.second << "秒" << endl;;
delay_ms(1000);
time(&timep);
p = localtime(&timep);
timep = mktime(p);
//构造函数初始化方式四
calendar cal4{ p->tm_year, p->tm_mon, p->tm_mday, p->tm_hour, p->tm_min, p->tm_sec };
cout << cal4.year << "年" << cal4.month << "月" << cal4.day << "日" << " " << cal4.hour << "时" << cal4.minute << "分" << cal4.second << "秒" << endl;;
delay_ms(1000);
time(&timep);
p = localtime(&timep);
timep = mktime(p);
//构造函数初始化方式五
calendar cal5 = { p->tm_year, p->tm_mon, p->tm_mday, p->tm_hour, p->tm_min, p->tm_sec };
cout << cal5.year << "年" << cal5.month << "月" << cal5.day << "日" << " " << cal5.hour << "时" << cal5.minute << "分" << cal5.second << "秒" << endl;;
return 0;
}编译项目程序,发现如下这行代码出现语法错误:
calendar?cal5 = { p->tm_year, p->tm_mon, p->tm_mday, p->tm_hour, p->tm_min, p->tm_sec };
报错信息为:
"calendar" 的复制列表初始化不能使用显式构造函数。
可以看到calendar?cal4和calendar?cal5的定义之间就之差一个“=”等号,说明有了这个等号,就变成隐式初始化,没有这个等号,就变成和显式初始化。
在看以下程序,在构造函数student(int stuAge);前面加explicit ,再运行程序:
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include<time.h>
#include"main.h"
using namespace std;
class student
{
public:
int age;
int hight;
int num;
explicit student(int stuAge);
student(int stuAge, int stuHight);
student(int stuAge, int stuHight, int stuNum);
};
student::student(int stuAge)
{
this->age = stuAge;
cout << "一个参数的构造函数!!!" << endl;
}
student::student(int stuAge, int stuHight)
{
this->age = stuAge;
this->hight = stuHight;
cout << "两个参数的构造函数!!!" << endl;
}
student::student(int stuAge, int stuHight, int stuNum)
{
this->age = stuAge;
this->hight = stuHight;
this->num = stuNum;
cout << "三个参数的构造函数!!!" << endl;
}
void func(student stu)
{
return;
}
int main()
{
student myStu1 = 10;
student myStu2 = (10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15);
func(20);//这里还是调用到了student 类的单参数的构造函数
return 0;
}发现main函数中student新创建的三个对象都报错了,报错如下所示:

?建议:单参数的构造函数都声明为explicit,除非有特别的原因。
五、构造函数初始化列表
在调用构造函数的同时,可以初始化成员变量的值,注意这种写法:
作者称之为冒号括号逗号式写法,要在构造函数的定义.cpp文件中实现。注意:这种写法只能用在构造函数中。
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include<time.h>
#include"main.h"
using namespace std;
class student
{
public:
int age;
int hight;
int num;
student(int stuAge, int stuHight, int stuNum);
};
//方式二:赋值方式
/*student::student(int stuAge, int stuHight, int stuNum)
{
this->age = stuAge;
this->hight = stuHight;
this->num = stuNum;
cout << this->age<< " " << this->hight << " " << this->num << endl;
}*/
//方式二:推荐以后使用这种方式,效率高
student::student(int stuAge, int stuHight, int stuNum):age(stuAge), hight(stuHight), num(stuNum)
{
cout << this->age << " " << this->hight << " " << this->num << endl;
}
int main()
{
student stu = student(12,34,56);
return 0;
}2022.06.30结。