每天进步一点点,坚持带来大改变!!!

前言:
?在C语言的学习过程中会遇到许多的关键字,我们是否真的详细了解这些关键字的使用方法和使用场景,下面我们来详解C语言中的32个关键字
1.C语言关键字概览:
关键字? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? 说明
auto? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? 声明自动变量
short? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?声明短整型变量或函数
int? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?声明整型变量或函数
long? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? 声明长整型变量或函数
float? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? 声明浮点型变量或函数
double? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? 声明双精度变量或函数
char? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? 声明字符型变量或函数
struct? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? 声明结构体变量或函数
union? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? 声明共用数据类型
enum? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?声明枚举类型
typedef? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? 用以给数据类型取别名
const? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?声明只读变量
unsigned? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?声明无符号类型变量或函数
signed? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?声明有符号类型变量或函数
extern? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? 声明变量是在其他文件正声明
register? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? 声明寄存器变量
static? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? 声明静态变量
volatile? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?说明变量在程序执行中可被隐含地改变
void? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?声明函数无返回值或无参数,声明无类型指针
if? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? 条件语句
else? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?条件语句否定分支(与 if 连用)
switch? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? 用于开关语句
case? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? 开关语句分支
for? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?一种循环语句
do? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?循环语句的循环体
while? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?循环语句的循环条件
goto? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? 无条件跳转语句
continue? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? 结束当前循环,开始下一轮循环
break? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? 跳出当前循环
default? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? 开关语句中的“其他”分支
sizeof? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?计算数据类型长度
return? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?子程序返回语句(可以带参数,也可不带参数)循环条件
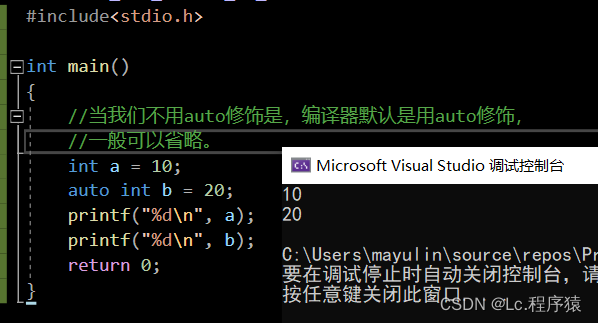
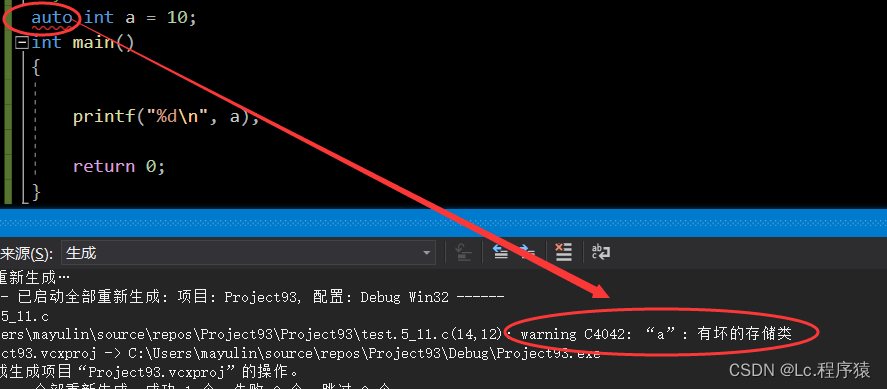
1. auto:
是用来修饰局部变量的
注:不能用来修饰全局变量
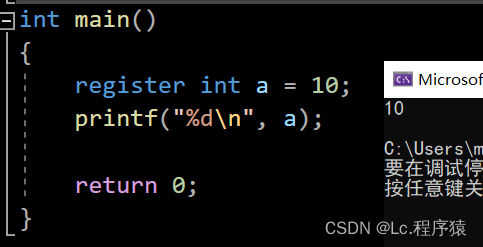
2.register:
计算机在进行数据的计算时是通过CPU来计算的,当计算的时候CPU就会访问数据。
数据的存储位置:
CPU访问数据的特点:
从上到下依次访问,访问速度越来越慢
定义变量:
是在内存中开辟一块空间用来存放,当我们需要高频率去使用一个变量的时候,可以通过register来修饰。
register修饰的特点:
将内存中的变量放到寄存器中,用来提高访问效率:
注:register修饰的变量不能用来&,因为&是相对于内存中的概念
3.extern和static?
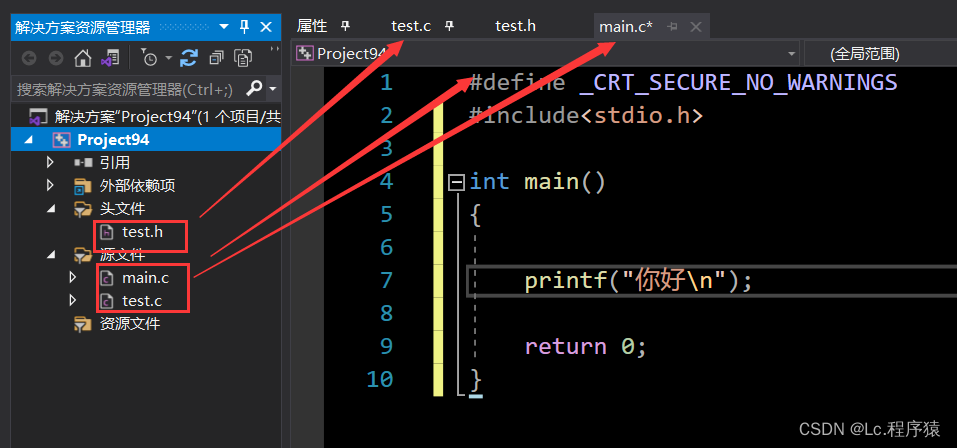
1.认识多文件
解释:
//.h:我们称之为头文件,一般包含函数声明,变量声明,宏定义,头文件等内容(header)
//.c: 我们称之为源文件,一般包含函数实现,变量定义等 (.c:c语言)?
test.h
test.c,main.c
使用函数声明,头文件包含,宏定义等,只需要包含头文件include"test.h"?
2.多文件之间全局变量和函数的使用?
1.跨文件函数的使用:
main.c
#include"test.h" int main() { show(); return 0; }test.c
#include"test.h" void show() { printf("haha\n"); }
总结:跨文件函数使用的时候可以不用声明就可以直接使用(存在警告!)。
原因:函数具有外部链接属性
2.跨文件全局变量的使用:
test.c
int g_val = 100;main.c
printf("%d\n", g_val);
总结:跨文件全局变量不能直接使用,需要进行声明:
声明关键字:extern
注意:
extern int g_val = 100; //err?声明并没有开辟空间,不能进行初始化和赋值
总结:所有变量声明的时候,不能设置初始值!!!
3.潜在问题 :
当一个变量和函数需要在多个文件中使用的时候,如果逐一包含,会使得后期维护成本越来越高!
解决办法:使用.h文件,目的是为了组织项目结构的时候,减少大型项目的维护成本问题!
其它源文件如main.c只需包含
#include"test.h"
?4.问题优化:
在头文件进行函数的声明和全局变量声明
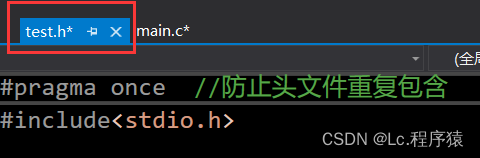
test.h
#pragma once //防止头文件重复包含 #include<stdio.h> extern int g_val; extern void show();
注意:
变量声明必须带上extern。
函数声明建议带上extern。
?3.static
通过上面的总结明确了函数和全局变量可以跨文件使用。
那有什么方法让函数和全局变量不能跨文件使用?
接下来就开始对satic这个关键字的功能逐一剖析:
1.static修饰全局变量
?
总结:static修饰全局变量的时候,全局变量只能在本文件中使用而不能跨文件使用。
原因:改变了全局变量的作用域
2.static修饰函数:
不能直接访问:
间接访问
?main.c
int main() { show_helper(); return 0; }test.h
extern void show_helper();test.c
static void show(int num) { printf("%d\n", num); } void show_helper() { show(20); }
总结:static修饰函数的时候,该函数只能在本文件内访问,不能再外部或其它文件中直接使用
?原因:改变了函数的作用域
实际项目中static的作用:项目维护,提供安全保证?
3.static修饰局部变量:
不用static修饰:
static void fun() { int i = 0; i++; printf("%d ", i); } int main() { int i = 0; for (i = 0; i < 10; i++) { fun(); } return 0; }
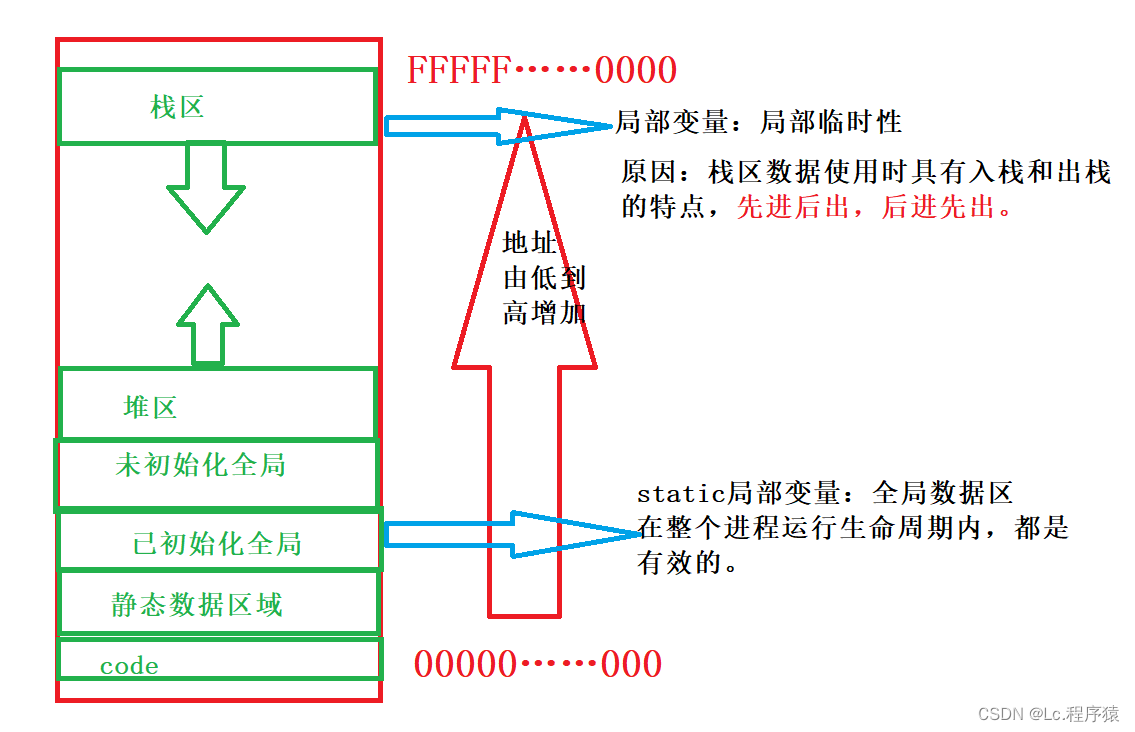
解释:局部变量具有临时性,函数调用开辟空间并初始化,函数结束释放空间
局部变量用static修饰:
static void fun() { static int i = 0; i++; printf("%d ", i); } int main() { int i = 0; for (i = 0; i < 10; i++) { fun(); } return 0; }?
解释:当局部变量用static修饰时,局部变量从栈区保存改到静态区,局部变量声明周期延长,函数调用结束时,局部变量存放空间不销毁。
5.绝命三问:
为什么全局变量可以跨文件访问?
为什么函数可以跨文件访问?
解释:有一定规模的项目,一定是多文件的,多个文件之间,后续一定要进行数据交互,如果不能进行跨文件,交互成本高,所以C语言默认规定可以跨文件访问
为什么临时变量具有临时性,全局变量生命周期具有全局性?
?C程序地址空间:
注:C程序地址空间不是内存,而是在操作系统中的进程地址空间。
4.sizeof:
sizeof:计算变量和类型在内存中所占空间的大小,单位是字节。
注:使用%zu打印,sizeof的返回值是unsigned int(无符号整形)。
1.基本数据类型:
内置类型:
char? ? 字符型
short? ?短整型
int? ? ? ?整形
long? ? 长整型
long long? ?长长整形
float? ? ? 单精度浮点型
double? 双精度浮点型
#include<stdio.h> int main() { printf("%zu\n", sizeof(char)); printf("%zu\n", sizeof(short)); printf("%zu\n", sizeof(int)); printf("%zu\n", sizeof(long)); printf("%zu\n", sizeof(long long)); printf("%zu\n", sizeof(double)); printf("%zu\n", sizeof(float)); return 0; }
总结:不同的类型决定了变量在开辟空间所占空间的大小。
?为什么需要根据类型开辟空间?
解释:本质上是对内存进行合理划分,按需索取。
C语言中为何有多种类型?
解释:?因为在实际生活中针对不同的应用场景有不同的计算方式,所需空间大小不同。本质上是用最小的成本解决多样化的场景问题。
?注:sizeof是一个操作符,不是函数。
5.signed,unsigned与整形在内存中的存储:
1.原码,反码,补码
数据在内存中如何存储的?
数据在内存中是以二进制补码的形式存储的。
概念:
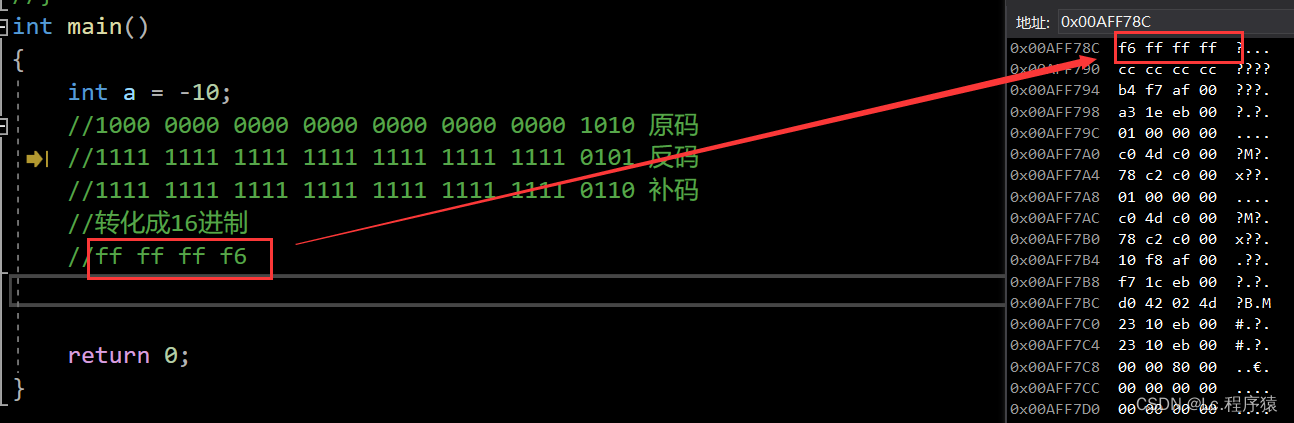
原码:直接按照二进制形式写出来。
反码:符号位不变,其它位按位取反。
补码:反码+1。
符号位:在二进制中,最高位表示符号位,1表示负数,0表示正数。?
2.有符号数:?
存储:
有符号正数:
原码,反码,补码相同
?有符号负数:
反码:符号位不变,其它位按位取反;
补码:反码+1得到补码。
打印:
以原码的形式打印:
有符号正数:
有符号负数:
方法1:
?方法2:
3.无符号数:
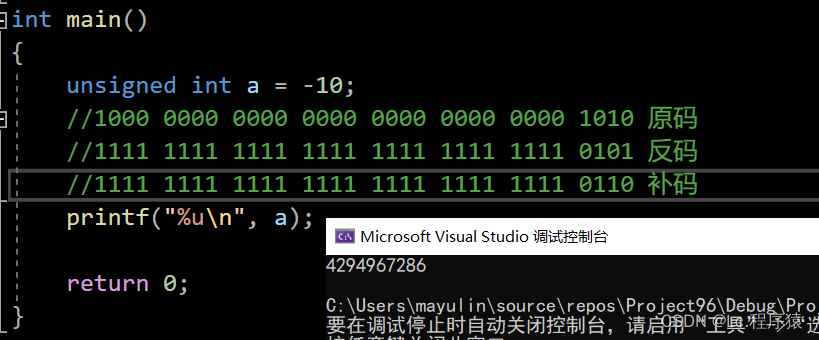
不区分正负数,原码,反码,补码相同
注:无符号数的打印用%u
正数无符号数;
?负数无符号数:
?解释:变量在定义的时候,开辟空间,当-10转化为补码存储到空间的时候,类型是无符号数,因此原反补相同。输出的时候原码就是补码。
4.十进制与二进制之间的互相转换:
口诀:1的后面跟n个0,就是2的n次方
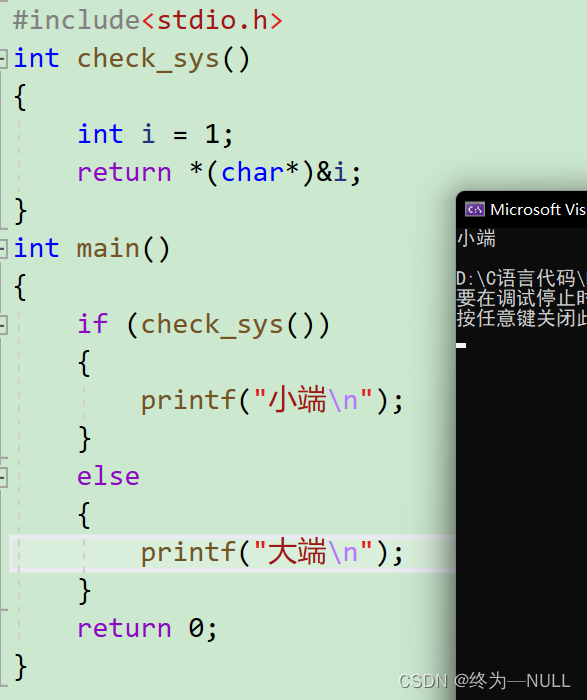
5.大小端:?
1.如何产生大小端:
当我们选择将高权值位或低权值位的数据存放到高地址或是低地址不同的选择则产生了大小端的问题。
2.如何定义大小端?
大端:将高字节序(高权值位)的数据存放到低地址,将低字节序(低权值位)的数据存放到高地址。
小端:将高字节序(高权值位)的数据存放到低地址,将低字节序(低权值位)的数据存放到高地址。
3.如何测试大小端??
6.if else语句
执行细则:
1.先执行()中的表达式or函数,得到真假结果
2.条件? 判定功能
3.进行? 分支功能
什么是bool类型:
在C99标准中引入_Bool类型,然后通过宏定义的方式写成了bool,目的是为了做到和C++中的bool类型做到兼容
#include<stdbool.h>//注意引头文件 int main() { //x表示一个bool变量 bool x = true; return 0; }
bool变量在内存中所占空间大小:
bool变量在内存中占一个字节的大小?
bool类型的应用:
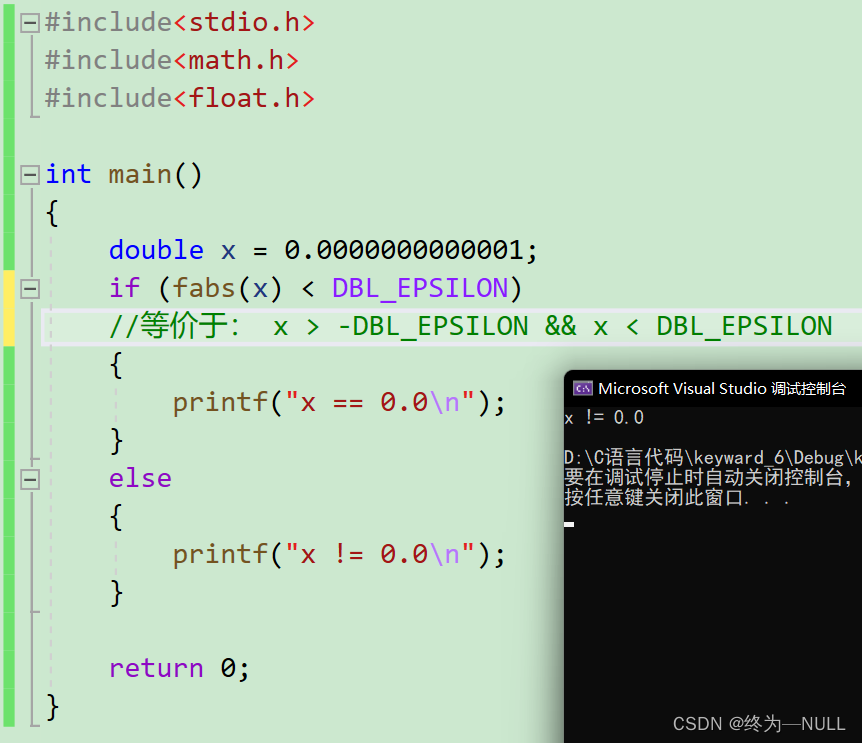
浮点数与0比较:
浮点数的精度损失:
?通过代码显示发现浮点数不能通过==比较,因此浮点数变量与0比较不能用==
那么浮点数之间如何比较呢?
当浮点数之间通过相减符合一个范围之间,则条件为真:
系统范围值:
双精度浮点数最小值:2.2204460492503131e-016
单精度浮点数最小值:1.192092896e-07F
浮点数与0值进行比较:
指针变量与0值的比较:
if 与 else的匹配原则
else匹配采用就近原则?
7.switch case语句
switch(整型变量/常量/整型表达式)
{
?????case var1:
?????????break;
????case var2:
?????????break;
????case var3:
?????????break;
????default:
?????????break;
}case:判定功能
break:分支功能
default:用来提醒当用户输入的值有误的时候进行报错,可以放在switch case 语句中的任意位置
注:当case和break中定义变量的时候需要在中间加上{};
case:整形常量:
8.do while for 关键字:
//while
条件初始化
while(条件判定){
?//业务更新
?条件更新
}
//for
for(条件初始化; 条件判定; 条件更新){
?//业务代码
}
//do while
条件初始化
do{
????条件更新}while(条件判定);
注:
任何C程序在编译的时候都会默认打开三个输入输出流:
stdin:标准输入? FILE* stdin? ?键盘
stdout:标准输出 FILE*stdout? 显示器
stderr:标准错误 FILE*stderr? ? 显示器
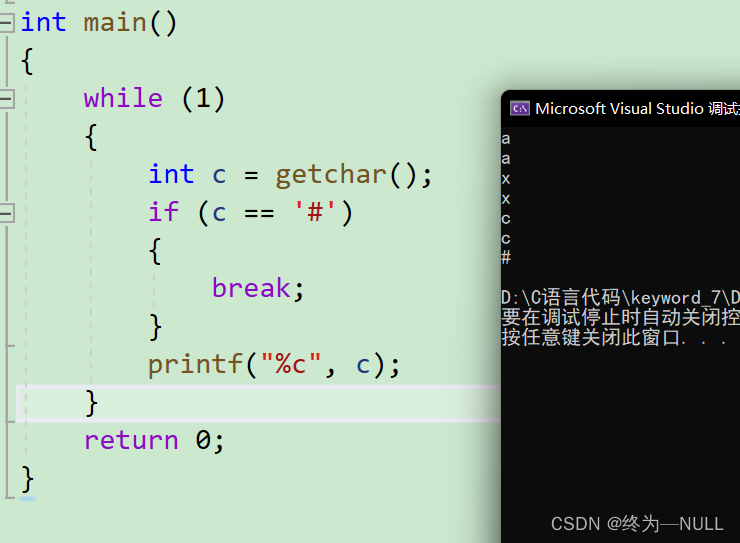
关于getchar函数:获取字符
注意1:getchar函数向输入流中读取字符,在输入的时候先输入一个字符,然后再按回车键,相当与输入两个字符,字符和‘\n’,因此会默认换行。
getchar函数的返回值:
虽然我们读取的是字符,但返回值是整形的原因是因为:
如果读取成功:返回字符ASCII值【0,255】,
但是读取失败:如果错误信息ASCCII值超过【0.255】的范围,无法正确的返回错误信息,因此将返回值设置为整形。?
当通过键盘输入或输出的时候,全部都是”字符“。
因此:
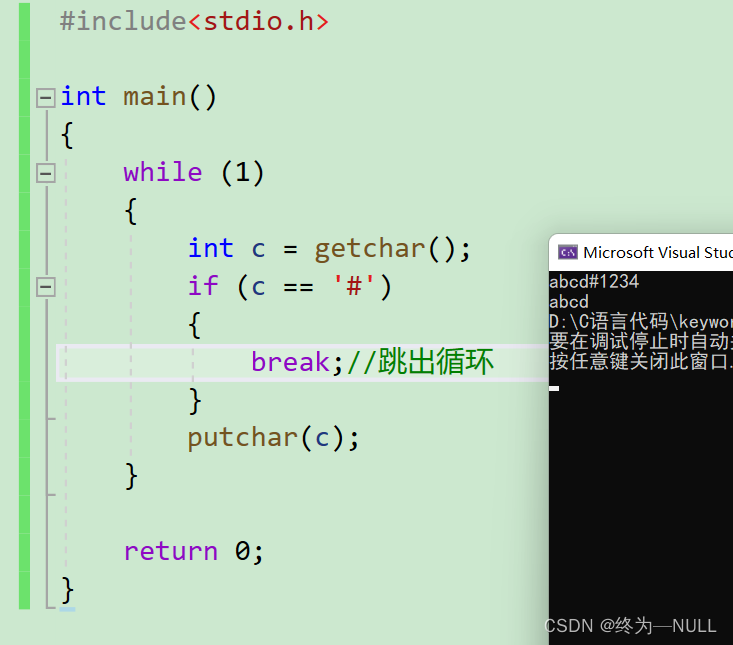
9.break关键字:
10.continue关键字:
在do while 循环和while循环中continue跳转到条件判断的部分,在for循环中continue跳转到条件更行处。?
11.goto 关键字
向上跳转:
向下跳转:
12.void关键字?
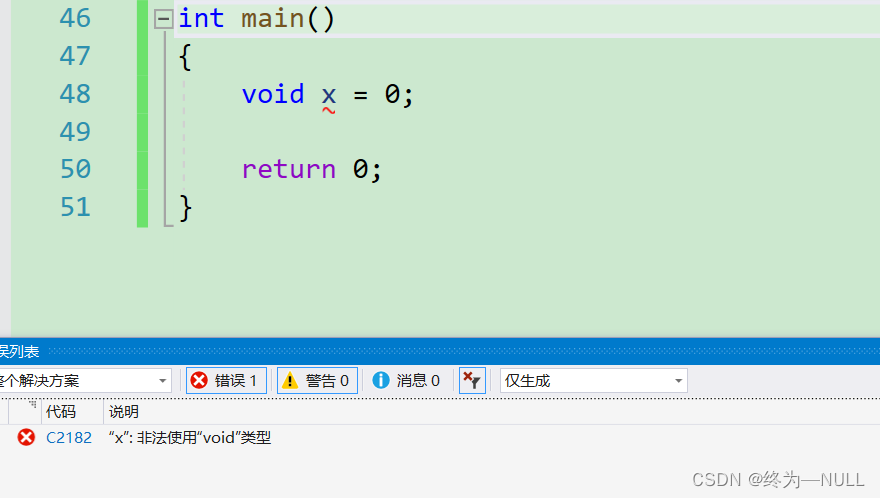
1.void 可以定义变量吗?
结论:void不能定义变量
原因:void本身被编译器解释为空类型,强制不允许定义变量
2.void 修饰函数的返回值:
1.充当一个占位符,让用户明确不需要返回值。
2.告知编译器这个返回值无法接受。?
void和指针:
void可以定义指针变量吗?
结论:可以定义指针变量。
原因:void*是一个指针变量,指针32位机器平台占4个字节,在64位机器平台占8个字节。
void*指针可以被任何一种指针接受,void*接受任意类型的指针。?
void*的指针不能加减操作:
void*的指针不能解引用操作:
13.return关键字
#include<stdio.h> char* show() { char str[] = "hello bit"; return str; } int main() { char* s = show(); printf("%s\n", s); return 0; }
?1.为什么会输出随机值:
解释:当main函数调用show函数时在栈区上开辟栈帧,str创建临时局部变量在show函数栈帧中,当show函数调用完之后,释放空间。
2.函数的细节:
当创建函数栈帧的时候,如何确定开辟空间大小?
答:编译器在编译的时候通过函数内部创建的临时变量来确定开辟空间的大小。
当函数调用完之后,释放空间的时候是否将全部数据清零?
答:当函数调用完之后,函数内部数据无效,并没有将数据全部清零,如上图,show函数调用完之后,str数据内容依然存在,并没有清零,而是调用printf函数的时候,创建栈帧覆盖了show 函数的栈帧。
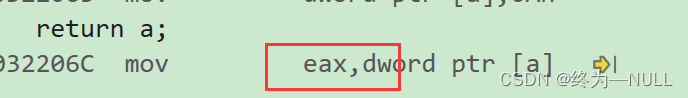
return返回局部变量:
函数在调用完之后会释放空间,函数内部的数据也会无效,那为什么会返回a的值?
从反汇编的角度理解:
?
解释:当创建局部变量的时候,将局部变量的值保存在寄存器(eax)中,当返回的时候将保存在寄存器eax的值(a)赋给ret。
14.const关键字
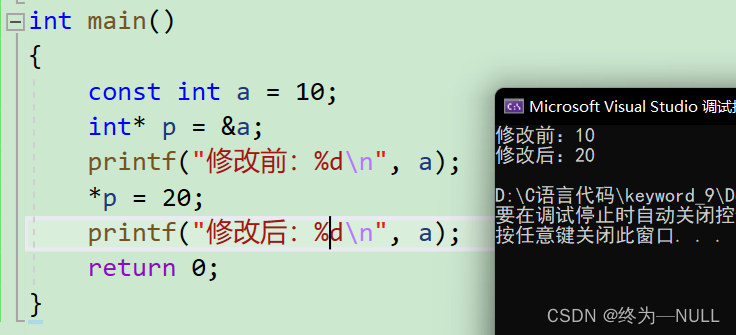
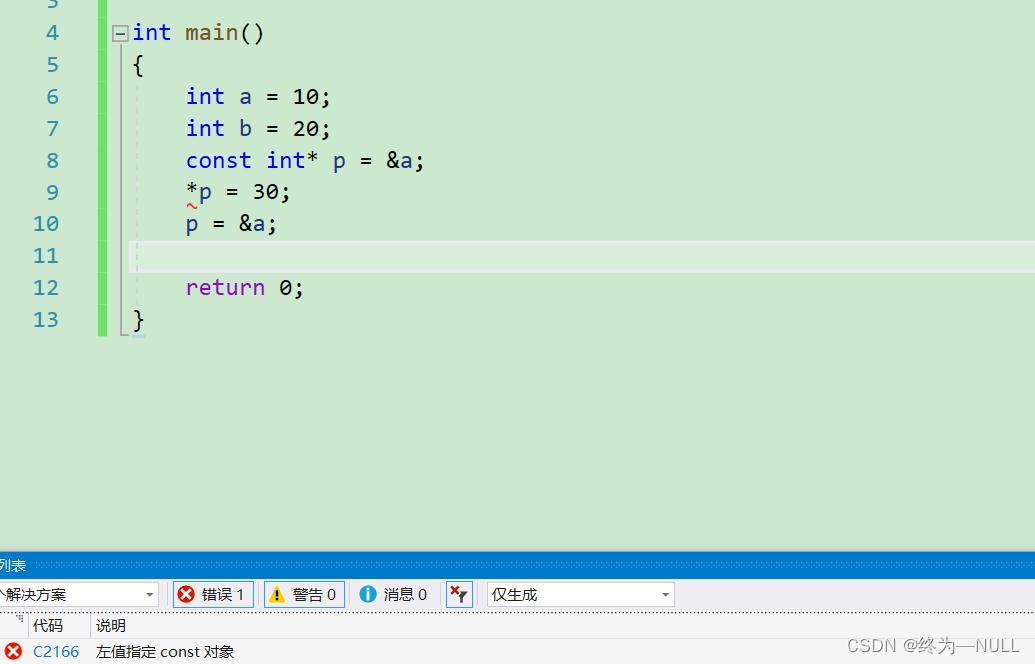
1.const修饰一般变量:
const修饰变量的时候使变量具有了常属性,不能被直接修改。
可以通过指针的方式进行修改:
注:const放在类型前面和放在类型后面是等价的
?
既然const修饰的变量可以通过指针的方式进行修改,那const的意义是什么呢?
答:1.为了编译器在编译的时候提前报错,提高代码的质量。
2.用const修饰的时候提醒程序员const修饰的变量不能被修改。
2.const修饰数组:
const修饰数组的时候,数组的每个元素都不可修改。?
3.const修饰指针变量:
1.const放在*的左边:
p指向的变量不可直接被修改,p的内容可以被修改。?
2.const放在*的右边
?p指向的变量可以被修改,p的内容不可以被修改。
3.const既放在*的左边又放在右边
?p指向的变量不可以被修改,p的内容也不能被修改。
4.const修饰函数
1.const修饰函数的参数:
函数的参数不可以被修改。?
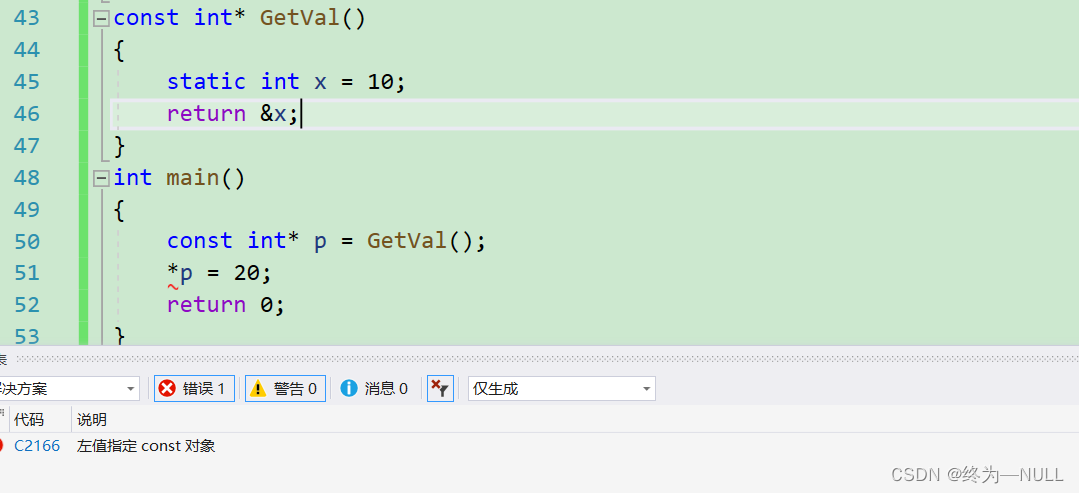
2.const修饰函数的返回值:
?const修饰函数的返回值的时候不能通过指针的形式,修改函数内部变量的值
15.易变关键字—volatile
volatile关键字可以用来提醒编译器,后面定义的变量随时可能被修改,因此CPU在访问数据的时候,都会直接从变量的地址中读取数据,如果没有volatile关键字修饰,则编译器可能会优化读取和存储,可能暂时使用寄存器中的值,如果这个变量又别的程序更新了的话,将会出现不一致的现象。
volatile int flag = 1; int main() { while (flag) { ; } return 0; }
9.结构体关键字——struct
结构体类型的意义:为了描述一个复杂的对象
定义一个学生类型:
结构体访问为什么会存在两种访问方式呢?
当我们在函数传参的时候,参数为结构体类型,使用指针访问的时候可以节省内存。
16.联合体关键字——union
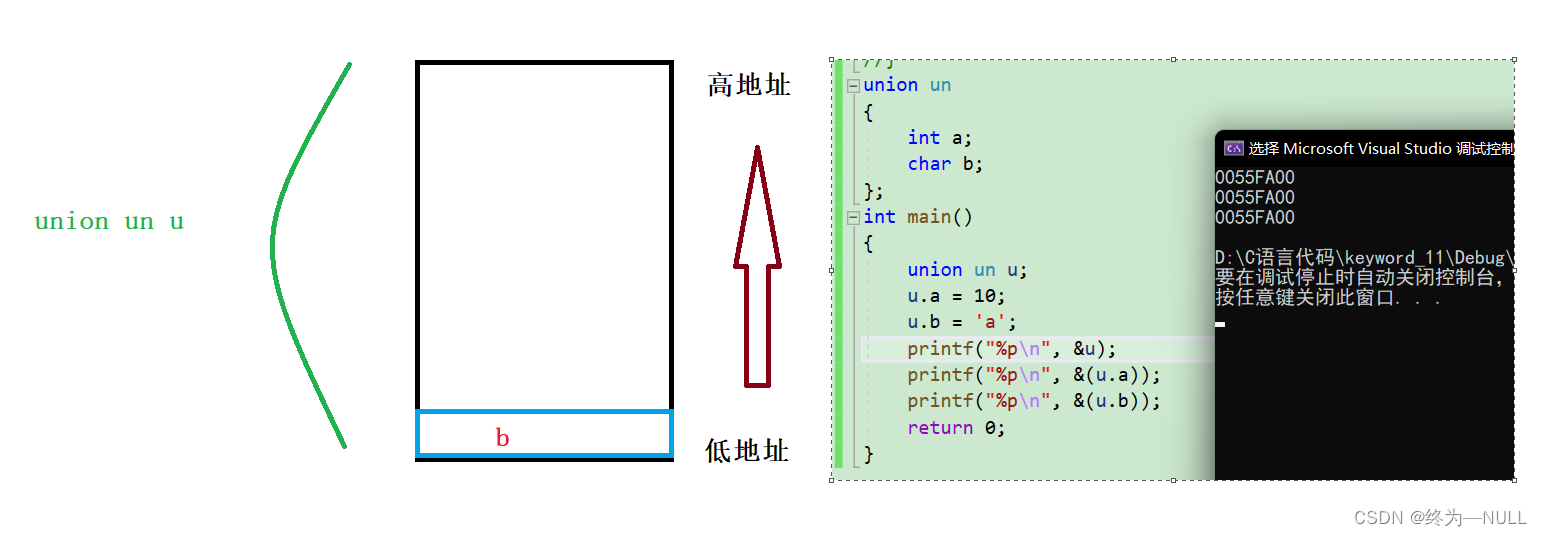
成员共用一块内存空间:空间开辟以最大成员为标准向内存申请空间
联合体成员在内存中的空间分布:
总结:任何一个联合体成员,起始地址都是相同的?
b永远在a的低地址处,每一个元素在使用这块空间的时候都认为自己是第一个元素。
实例:判断大小端:
?思路:
17.枚举关键字——enum
enum:是一组具有强相关性的一组常量,突显相关性。
?值如果不初始化默认从0开始,每次自增1,如果初始化则从初始化值自增1.
优点:
18.类型重命名——typedef
1.typedef对各种类型的重命名
2.typedef与#define的区别:
?#define只是对文本进行简单的替换,typedef是对类型进行重命名,相当于定义一种新的类型
19.关键字类型的总结:
1.数据类型关键字:
char :声明字符型变量或函数
short :声明短整型变量或函数
int : 声明整型变量或函数
long :声明长整型变量或函数
signed :声明有符号类型变量或函数
unsigned :声明无符号类型变量或函数
float :声明浮点型变量或函数
double :声明双精度变量或函数
struct :声明结构体变量或函数
union :声明共用体(联合)数据类型
enum :声明枚举类型
void :声明函数无返回值或无参数,声明无类型指针
2.控制语句关键字:
1. 循环控制(5个)
????????????????for :一种循环语句
????????????????do :循环语句的循环体
????????????????while :循环语句的循环条件
????????????????break :跳出当前循环
????????????????continue :结束当前循环,开始下一轮循环
2. 条件语句(3个)
????????????????if : 条件语句
????????????????else :条件语句否定分支
????????????????goto :无条件跳转语句
3. 开关语句 (3个)
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?switch :用于开关语句
????????????????case :开关语句分支
????????????????default :开关语句中的“其他”分支4. 返回语句(1个)
????????????????return :函数返回语句(可以带参数,也看不带参数)
3.存储类型关键字:
存储类型关键字(5个)
????????????????????????auto :声明自动变量,一般不使用
????????????????????????extern :声明变量是在其他文件中声明
????????????????????????register :声明寄存器变量
????????????????????????static :声明静态变量
????????????????????????typedef :用以给数据类型取别名(但是该关键字被分到存储关键字分类中,虽然看起来没什么相关性
注:存储类型关键字不能同时出现,也就是说定义变量只能出现一个
4.其它关键字:
const :声明只读变量
sizeof :计算数据类型长度
volatile :说明变量在程序执行中可被隐含地改变
以上就是对C语言所有关键字的详解,希望能够在学习C语言的过程中对你有所帮助。