?c++中list不是随机访问迭代器,所以需要自定义sort的比较规则。
demo中分别以fStep排序和fPer的排序如下:
#include <cmath>
#include <list>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
#define DEF_STAND 0.0001
class DataVal {
public:
float fStep;
float fPer;
DataVal(float f1, float f2)
{
fStep = f1;
fPer = f2;
}
};
bool compareStep(DataVal cst1, DataVal cst2)
{
if (cst1.fStep - cst2.fStep <= DEF_STAND)
{
return true;
}
else
{
return false;
}
}
bool compareFer(DataVal cst1, DataVal cst2)
{
if (cst1.fPer - cst2.fPer <= DEF_STAND)
{
return true;
}
else
{
return false;
}
}
void printList(list<DataVal>& lst) //打印输出list容器中数据
{
for (list<DataVal>::iterator it = lst.begin(); it != lst.end(); it++)
{
cout << "first:" << (*it).fStep << " second:" << (*it).fPer << endl;
}
}
void FindVal(list<DataVal> &lstData,list<DataVal>& dstData)
{
auto it = lstData.begin();
float nDst = it->fStep * 1.5;
for (;it != lstData.end(); it++)
{
if (it->fStep - nDst <= DEF_STAND)
{
dstData.push_back(*it);
}
else
{
break;
}
}
return;
}
void main()
{
list<DataVal> lstData;
DataVal p1(1.234, 13.3);
DataVal p2(2.233, 14.5);
DataVal p3(3.235, 1.6);
DataVal p4(10.23,18);
DataVal p5(11.1,15.1);
DataVal p6(18.1,23.1);
lstData.push_back(p1);
lstData.push_back(p2);
lstData.push_back(p3);
lstData.push_back(p4);
lstData.push_back(p5);
lstData.push_back(p6);
//1.排序
lstData.sort(compareStep);
printList(lstData);
//2.查找值,找最小
list<DataVal> DstData;
FindVal(lstData, DstData);
DstData.sort(compareFer);
cout << DstData.begin()->fPer << endl;
}附加知识:
1、list的介绍:C++ list容器详解_&不逝的博客-CSDN博客_c++list容器
2、迭代器分类:
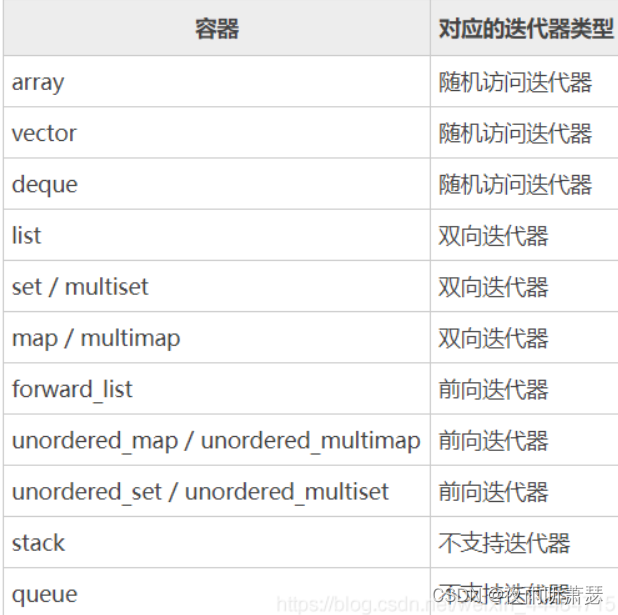
?上述迭代器知识参考于:
2 STL迭代器介绍【前向迭代器、双向迭代器、随机访问迭代器】【迭代器遍历容器】_温酒煮青梅的博客-CSDN博客_双向迭代器
3、迭代器sort函数介绍如下:
stl的sort函数需要提供一个比较函数comp(有默认版本),而该比较函数需要满足严格弱序的条件,何谓严格弱序?根据标准库手册的描述,comp需要满足如下属性:
对于任一变量a,comp(a,a)为false
如果comp(a,b) 为true,那么comp(b,a)为false
如果comp(a,b)为true且comp(b,c)true,则comp(a,c)为true