- Object Based:面对的是单一的class设计
- Object Oriented:面对的是多重classes的设计(classes和classes)之间的关系
一、两个基本的类
(1)不带指针的类
知识点:
(1)构造函数成员变量初始化->尽量在初始化列表中进行初始化(而不是在赋值)
(2)成员函数后面加 const 表示这个函数不能修改成员变量的值(否则当定义一个 const 对象时出现错误)
(3)传递参数和返回值的时候尽量使用 reference 传递,不修改值时要使用 const ,(返回值如果不是local object 就可以传递引用)
(4)friend 友元函数可以直接使用类中成员变量,相同 class 的各个 object 互为友元
(5)操作符重载 两种形式:成员函数 和 普通非成员函数
#pragma once
#include <iostream>
class complex
{
public:
//构造函数 使用初始化列表
complex(double r, double i) : re(r), im(i)
{
}
//成员函数
double real() const
{
return re;
}
double imag() const
{
return im;
}
//成员函数运算符重载
complex& operator += (const complex& o);
complex& operator -= (const complex& o);
complex& operator *= (const complex& o);
complex& operator /= (const complex& o);
private:
double re; //实部
double im; //虚部
//加减乘除 add , subtract , multiply and divide
//友元函数,方便直接操作private成员
friend complex& __add(complex* ths,const complex& o);
friend complex& __subtract(complex* ths,const complex& o);
friend complex& __multiply(complex* ths,const complex& o);
friend complex& __divide(complex* ths,const complex& o);
};
// complex.cpp : 此文件包含 "main" 函数。程序执行将在此处开始并结束。
//
#include "complex.h"
double real(const complex& o)
{
return o.real();
}
double imag(const complex& o)
{
return o.imag();
}
//必须为非类成员函数 << 要作用于 ostream
std::ostream& operator << (std::ostream& os,const complex& o)
{
return os << "(" << real(o) << "," << imag(o) << ")";
}
// + 非类成员函数 要考虑不是两个复数的情况
inline complex operator + (const complex& o1, const complex& o2)
{
return complex(o1.real() + o2.real(), o1.imag() + o2.imag());
}
inline complex operator + (double o1, const complex& o2)
{
return complex(o1+ o2.real(), o2.imag());
}
inline complex operator + (const complex& o1, double o2)
{
return complex(o1.real(), o1.imag() + o2);
}
inline bool operator == (const complex& o1, const complex& o2)
{
return o1.real() == o2.real() && o1.imag() == o2.imag();
}
//+ 正号
inline complex operator + (const complex& o)
{
return o;
}
//- 负号
inline complex operator - (const complex& o)
{
return complex(-o.real(), -o.imag());
}
//友元函数
complex& __add(complex* ths, const complex& o)
{
ths->re += o.re;
ths->im += o.im;
return *ths;
}
complex& __subtract(complex* ths, const complex& o)
{
ths->re -= o.re;
ths->im -= o.im;
return *ths;
}
complex& __multiply(complex* ths, const complex& o)
{
ths->re *= o.re;
ths->im *= o.im;
return *ths;
}
complex& __divide(complex* ths, const complex& o)
{
ths->re /= o.re;
ths->im /= o.im;
return *ths;
}
complex& complex::operator += (const complex& o)
{
return __add(this,o);
}
complex& complex::operator -= (const complex& o)
{
return __subtract(this, o);
}
complex& complex::operator *= (const complex& o)
{
return __multiply(this, o);
}
complex& complex::operator /= (const complex& o)
{
return __divide(this, o);
}
int main()
{
complex a(10, 20);
complex b(1,2);
std::cout << a << std::endl;
std::cout << b << std::endl;
std::cout << +a << std::endl;
std::cout << -a << std::endl;
std::cout << a + b << std::endl;
std::cout << (a == b) << std::endl;
std::cout << (a += b) << std::endl;
std::cout << (a -= b) << std::endl;
std::cout << (a *= b) << std::endl;
std::cout << (a /= b) << std::endl;
}
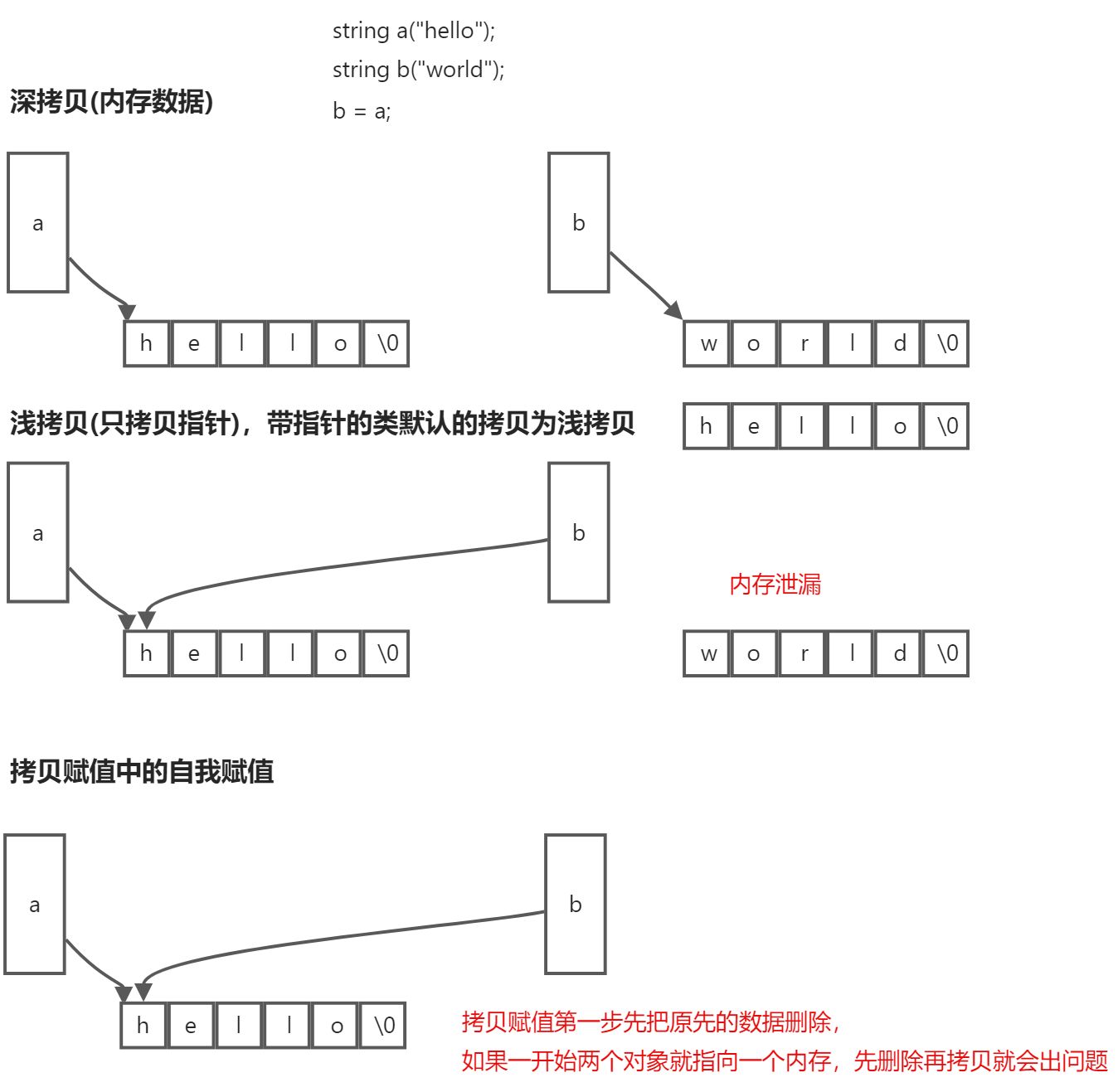
(2)带指针的类
知识点:
(1)带指针的类需要实现的三个函数(big three)拷贝构造、拷贝复制、析构,目的是要避免浅拷贝
(2)拷贝赋值需要注意处理是否是自我赋值
(3)拷贝赋值返回类类型,需要考虑 连续=赋值这种操作
#pragma once
class String
{
public:
//构造函数
String(const char* cstr = 0);
//拷贝构造
String(const String& str);
//拷贝赋值
String& operator= (const String& str);
//析构函数
~String();
inline char* get_cstr() const{ return m_data; }
private:
char* m_data = { nullptr };
};
// string.cpp : 此文件包含 "main" 函数。程序执行将在此处开始并结束。
//
#include <iostream>
#include "string.h"
using namespace std;
std::ostream& operator << (std::ostream& os, const String& o)
{
return os << o.get_cstr();
}
String::String(const char* cstr)
{
if (cstr)
{
//注意字符串后面的结束符
int strLen = strlen(cstr) + 1;
m_data = new char[strLen];
strcpy_s(m_data, strLen ,cstr);
}
else
{
m_data = new char[1];
*m_data = '\n';
}
}
String::String(const String& str)
{
//str.m_data 直接取另一个对象的私有成员,相同 class 的各个 object 互为友元
int strLen = strlen(str.m_data) + 1;
m_data = new char[strLen];
strcpy_s(m_data, strLen, str.m_data);
}
String& String::operator= (const String& str)
{
//检查是否是自我复制,非常重要,否则自己给自己赋值时会报错
if (this == &str)
{
return *this;
}
delete[] m_data; //删除原来的
int strLen = strlen(str.m_data) + 1;
m_data = new char[strLen];
strcpy_s(m_data, strLen, str.m_data);
//注意返回值 不是local 可以返回引用
return *this;
}
String::~String()
{
delete[] m_data;
m_data = nullptr;
}
int main()
{
String a("hello");
String b(a);
String c;
c = a;
a = a; //自我赋值,拷贝赋值函数中不进行自我赋值检查,此处会报错
cout << "a:" << a << endl;
cout << "b:" << b << endl;
cout << "c:" << c << endl;
}
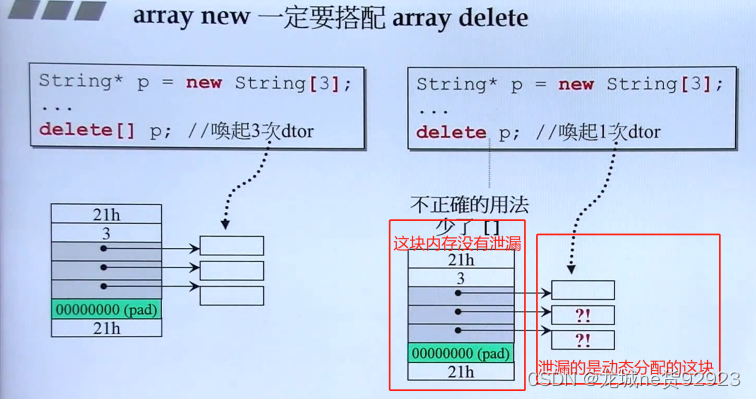
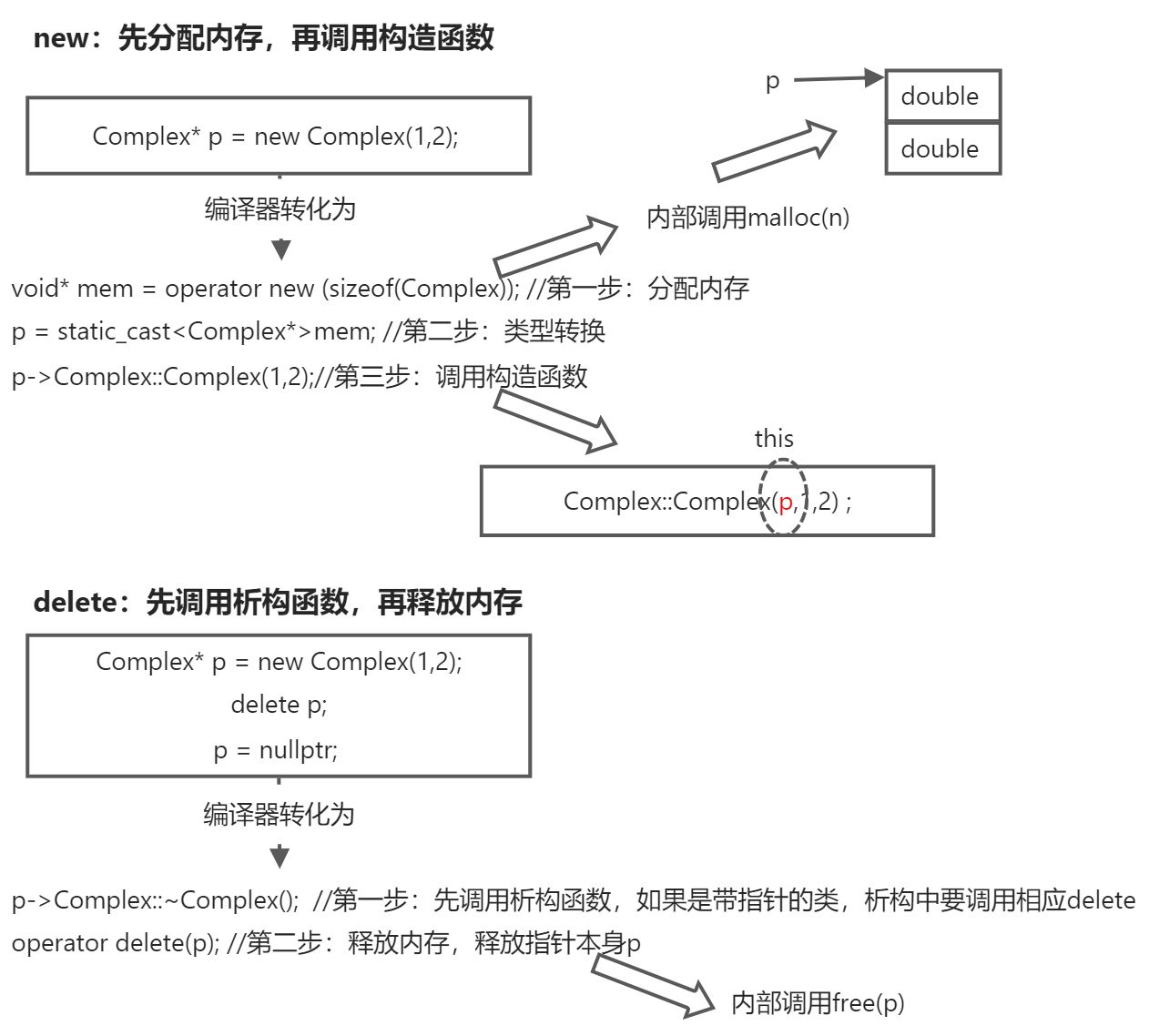
(3)new/delete 对象
(4)动态分配内存实际大小
- 红砖色:cookie 保存分配内存大小,例如:
0000004140表示64的十六进制,1标记申请内存 - 灰色:dubug模式信息
- 绿色:数据
- 深绿色:为了满足16倍数填补
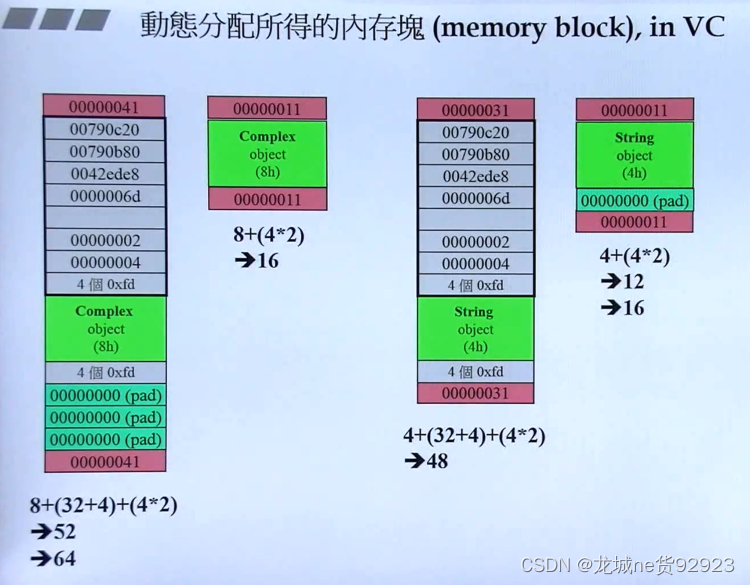
- 白色:数组的元素个数
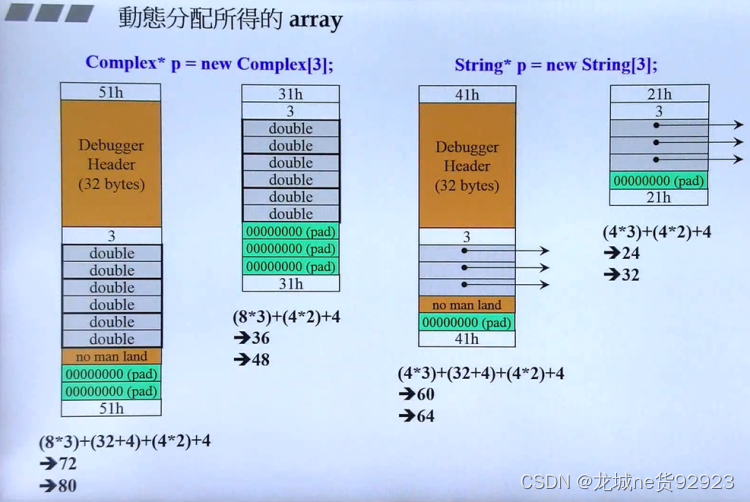
(5)动态分配数组delete时的正确写法